Abstract
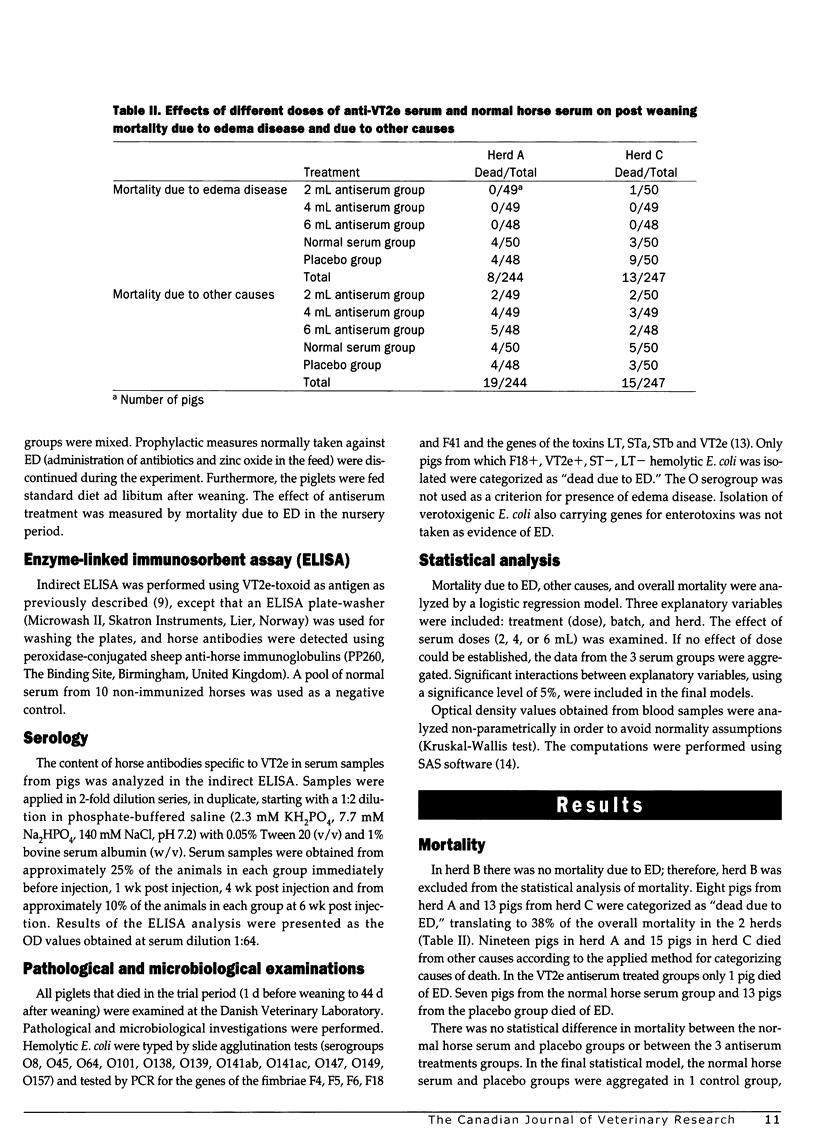
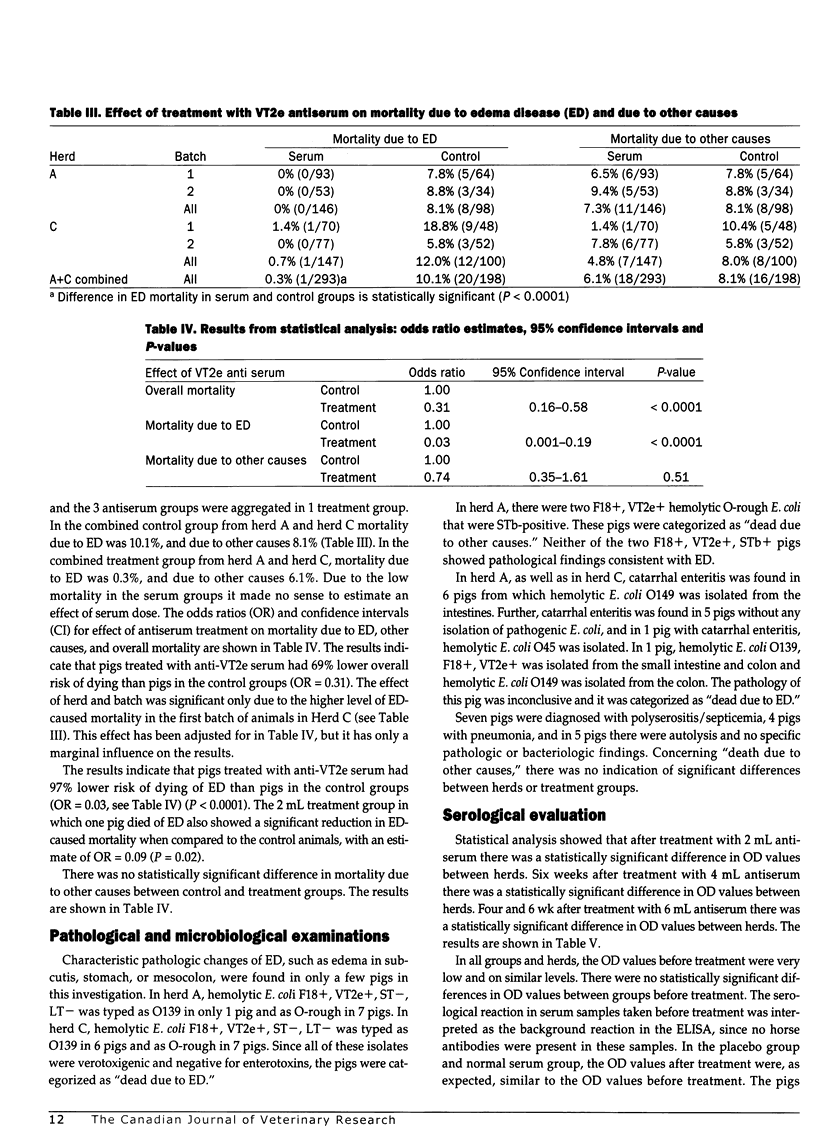
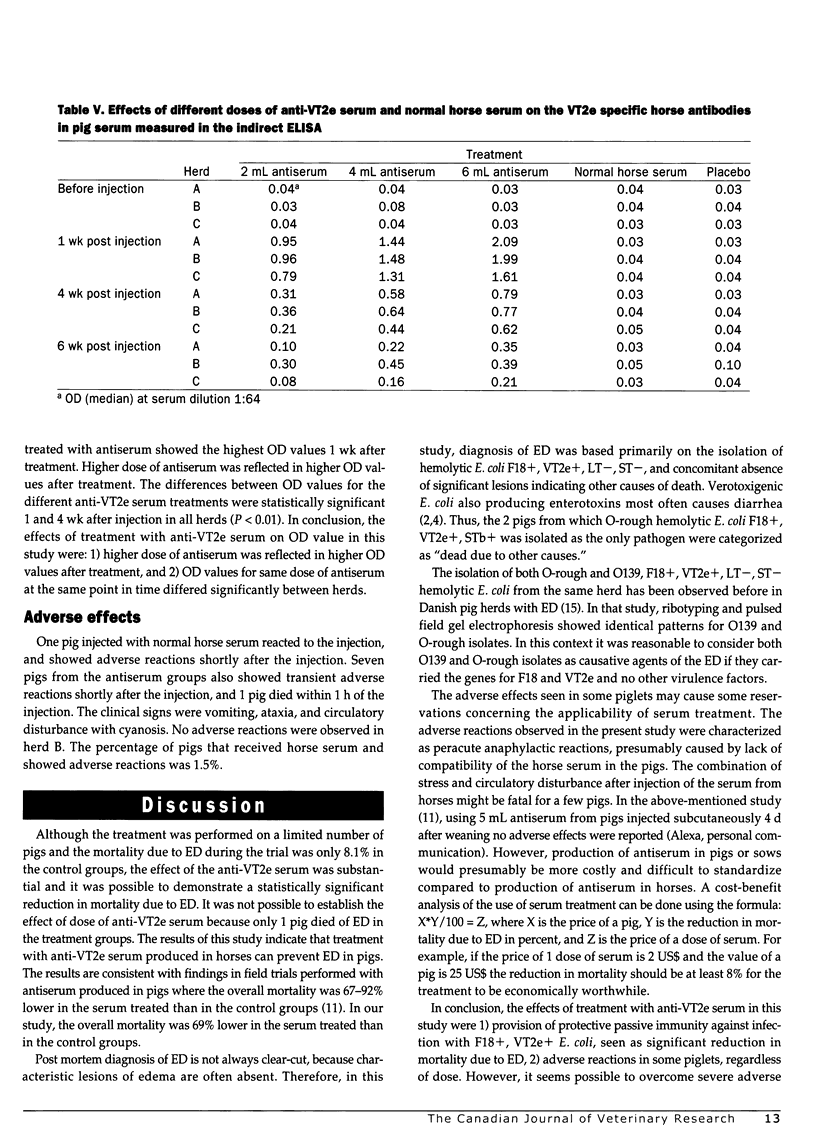
The effect of treatment with verotoxin 2e (VT2e) specific antiserum was evaluated in 3 Danish pig herds with edema disease (ED). The antiserum was prepared by immunizing horses with a VT2e toxoid. The study was performed as a randomized blind field trial with parallel treatment and control groups. There were approximately 50 piglets in each group in each of the 3 herds and 741 piglets were included in the study (244 from herd A, 249 from herd B, and 247 from herd C). Treatment groups received 2, 4, or 6 mL anti-VT2e serum intramuscularly the day before weaning. Control groups were treated with 6 mL normal horse serum or 6 mL RPMI 1640 medium as placebo. All pigs that died in the trial period (1 d before weaning to 44 d after weaning) were examined pathologically and microbiologically. Mortality due to ED, mortality due to other causes, and adverse effects due to treatment were recorded. As there was no mortality due to ED, herd B was excluded from statistical calculations on mortality. The content of horse antibodies specific to VT2e in serum from pigs was analyzed in an indirect ELISA. A higher dose of anti-VT2e serum was reflected in higher optical density values in the indirect ELISA. Transient adverse reactions, seen as vomiting, ataxia, and cyanosis, occurred shortly after the injection of horse serum in 1.5% of the pigs, and one pig died. There were no statistically significant differences in mortality due to other causes among the 3 treatment groups in herds A and C. Only pigs from which F18+, VT2e+, ST-, LT- hemolytic E. coli (0139 or O-rough) was isolated were diagnosed as dead due to ED. Deaths due to ED in the control groups were 8.1% and 12.0% in herds A and C, respectively, compared with 0% and 0.7% in the corresponding serum groups. The difference between treatment and control groups was statistically significant (P<0.0001). It was not possible to establish an effect of dose (2, 4, or 6 mL) of anti-VT2e serum, because only one pig died of ED in the treatment groups. It was concluded that passive immunization by intramuscular injection of a VT2e-specific antiserum can be used for protecting piglets against ED.
Full text
PDF


Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Aarestrup F. M., Jorsal S. E., Ahrens P., Wiuff C., Scheutz F. Oedema disease caused by O-rough Escherichia coli. Vet Rec. 1996 Oct 12;139(15):373–373. doi: 10.1136/vr.139.15.373. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bosworth B. T., Samuel J. E., Moon H. W., O'Brien A. D., Gordon V. M., Whipp S. C. Vaccination with genetically modified Shiga-like toxin IIe prevents edema disease in swine. Infect Immun. 1996 Jan;64(1):55–60. doi: 10.1128/iai.64.1.55-60.1996. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Imberechts H., Bertschinger H. U., Stamm M., Sydler T., Pohl P., De Greve H., Hernalsteens J. P., Van Montagu M., Lintermans P. Prevalence of F107 fimbriae on Escherichia coli isolated from pigs with oedema disease or postweaning diarrhoea. Vet Microbiol. 1994 Jun;40(3-4):219–230. doi: 10.1016/0378-1135(94)90111-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Imberechts H., De Greve H., Lintermans P. The pathogenesis of edema disease in pigs. A review. Vet Microbiol. 1992 Jun 1;31(2-3):221–233. doi: 10.1016/0378-1135(92)90080-d. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Johansen M., Andresen L. O., Jorsal S. E., Thomsen L. K., Waddell T. E., Gyles C. L. Prevention of edema disease in pigs by vaccination with verotoxin 2e toxoid. Can J Vet Res. 1997 Oct;61(4):280–285. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- MacLeod D. L., Gyles C. L. Immunization of pigs with a purified Shiga-like toxin II variant toxoid. Vet Microbiol. 1991 Nov;29(3-4):309–318. doi: 10.1016/0378-1135(91)90138-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- MacLeod D. L., Gyles C. L., Wilcock B. P. Reproduction of edema disease of swine with purified Shiga-like toxin-II variant. Vet Pathol. 1991 Jan;28(1):66–73. doi: 10.1177/030098589102800109. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ojeniyi B., Ahrens P., Meyling A. Detection of fimbrial and toxin genes in Escherichia coli and their prevalence in piglets with diarrhoea. The application of colony hybridization assay, polymerase chain reaction and phenotypic assays. Zentralbl Veterinarmed B. 1994 Mar;41(1):49–59. doi: 10.1111/j.1439-0450.1994.tb00205.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Waddell T. E., Lingwood C. A., Gyles C. L. Interaction of verotoxin 2e with pig intestine. Infect Immun. 1996 May;64(5):1714–1719. doi: 10.1128/iai.64.5.1714-1719.1996. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


