Abstract
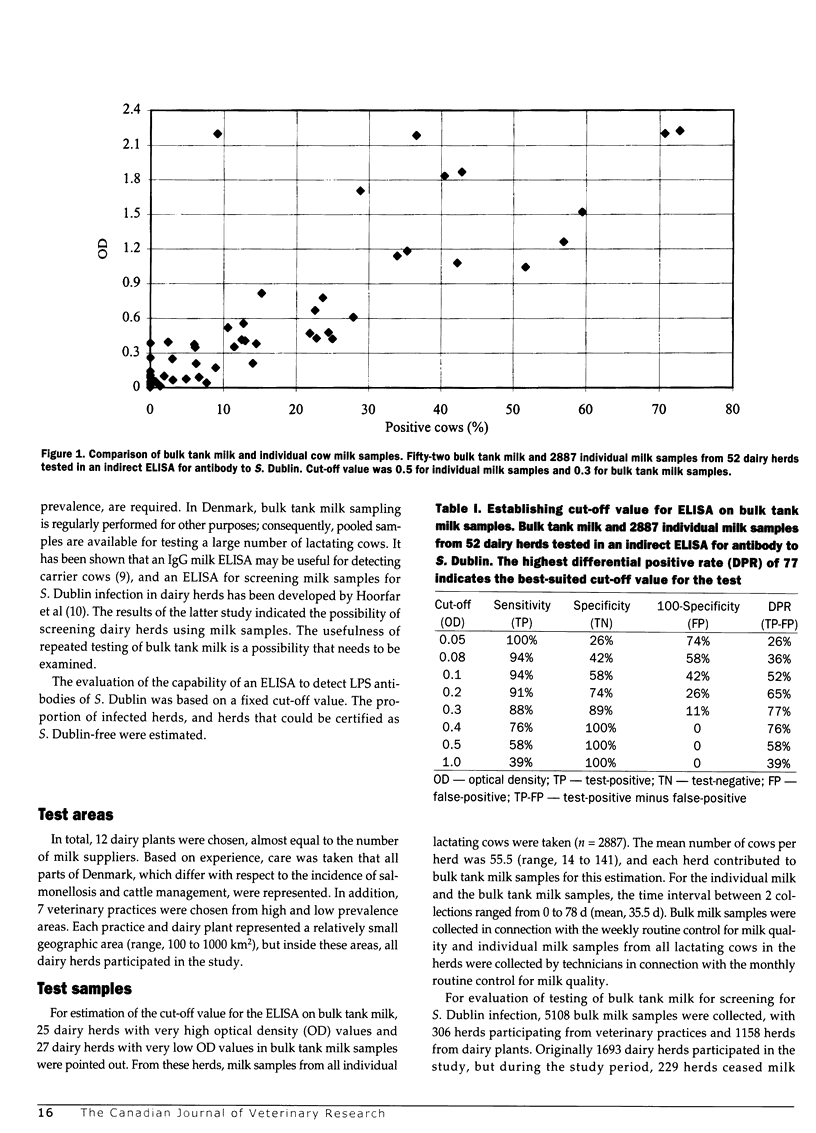
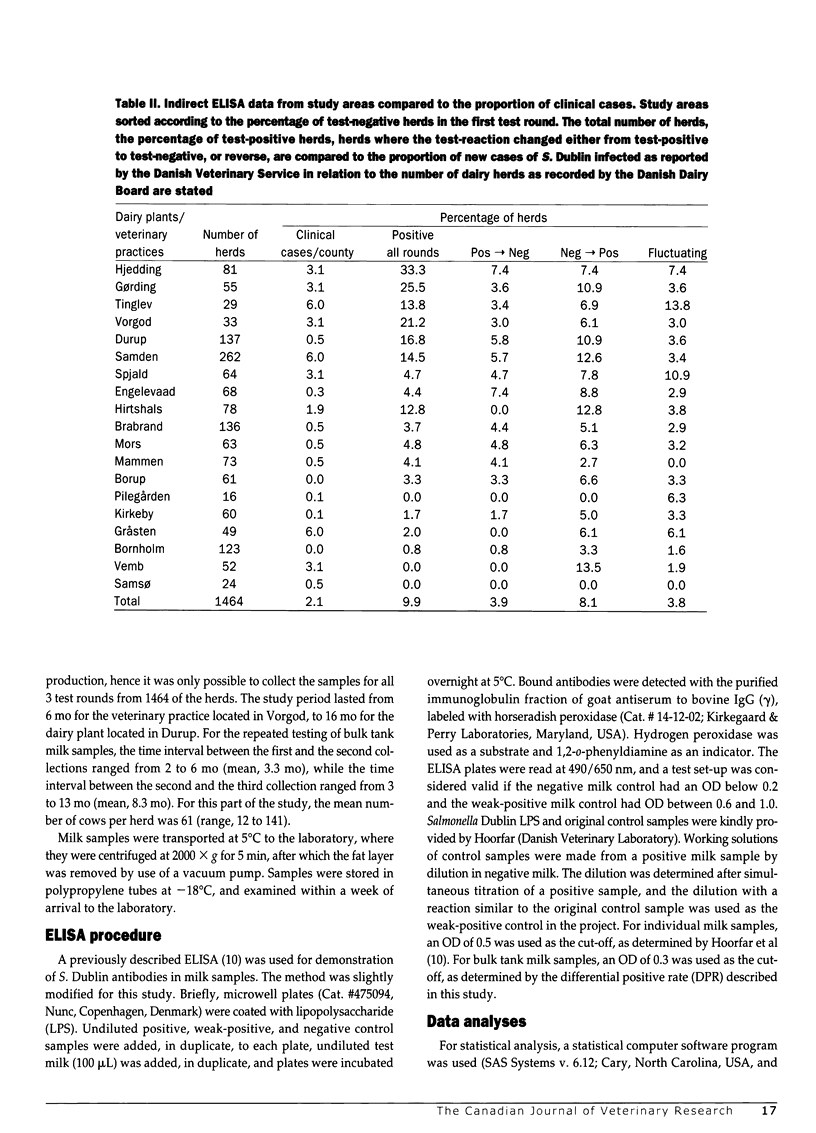
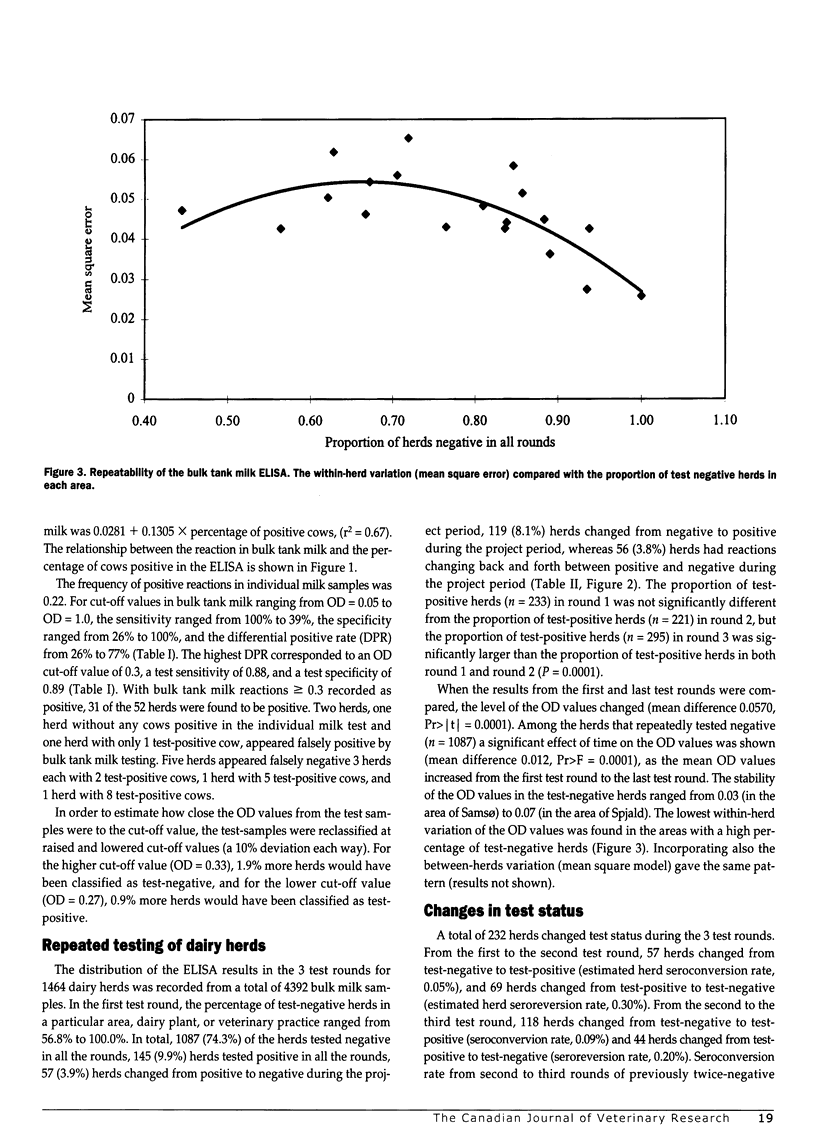
The usefulness of enzyme-linked immunosorbent assay (ELISA) was investigated as a simple method to screen for Salmonella Dublin infection in dairy herds, examining bulk tank milk samples for lipopolysaccharide (O:1,9,12) antibodies. The cut-off value for the ELISA on bulk tank milk was established based on individual milk samples (n = 2887) and bulk tank milk from 52 herds. Bulk tank milk samples (n = 5108) were collected from 1464 dairy herds located in 19 different areas. About 10% of the dairy herds in Denmark participated in the study. The percentage of herds changing from test-negative to test-positive in each area was correlated with the incidence of S. Dublin outbreaks in the corresponding county (r = 0.48, n = 19; P < 0.025). The mean level of the OD values obtained in the first and third test rounds was not constant (Pr /t/ = 0.0001). The study demonstrated that the probability of being test-negative in the third test round was 0.926 for a herd with 2 previous test-negative results. It was concluded that the investigated ELISA method was in general accordance with the cases of clinical S. Dublin infection recorded, and that the method has a potential for national screening purposes.
Full text
PDF



Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Bulgin M. S. Salmonella dublin: what veterinarians should know. J Am Vet Med Assoc. 1983 Jan 15;182(2):116–118. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Butler J. E. Bovine immunoglobulins: an augmented review. Vet Immunol Immunopathol. 1983 Mar;4(1-2):43–152. doi: 10.1016/0165-2427(83)90056-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hinton M. The diagnosis of salmonella abortion in cattle with particular reference to Salmonella dublin. A review. J Hyg (Lond) 1977 Aug;79(1):25–38. doi: 10.1017/s0022172400052815. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hoorfar J., Lind P., Bitsch V. Evaluation of an O antigen enzyme-linked immunosorbent assay for screening of milk samples for Salmonella dublin infection in dairy herds. Can J Vet Res. 1995 Apr;59(2):142–148. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jensen A. L., Poulsen J. S. Evaluation of diagnostic tests using relative operating characteristic (ROC) curves and the differential positive rate. An example using the total serum bile acid concentration and the alanine aminotransferase activity in the diagnosis of canine hepatobiliary diseases. Zentralbl Veterinarmed A. 1992 Nov;39(9):656–668. doi: 10.1111/j.1439-0442.1992.tb00231.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lawson G. H., McPherson E. A., Laing A. H., Wooding P. The epidemiology of Salmonella dublin infection in a dairy herd. I. Excretion and persistence of the organism. J Hyg (Lond) 1974 Jun;72(3):311–328. doi: 10.1017/s0022172400023548. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Richardson A. Salmonellosis in cattle. Vet Rec. 1975 Apr 12;96(15):329–331. doi: 10.1136/vr.96.15.329. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Richardson A. The transmission of Salmonella dublin to calves from adult carrier cows. Vet Rec. 1973 Feb 3;92(5):112–115. doi: 10.1136/vr.92.5.112. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Smith B. P., Oliver D. G., Singh P., Dilling G., Martin P. A., Ram B. P., Jang L. S., Sharkov N., Orsborn J. S., Marvin P. A. Detection of Salmonella dublin mammary gland infection in carrier cows, using an enzyme-linked immunosorbent assay for antibody in milk or serum. Am J Vet Res. 1989 Aug;50(8):1352–1360. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wray C., Wadsworth Q. C., Richards D. W., Morgan J. H. A three-year study of Salmonella dublin infection in a closed dairy herd. Vet Rec. 1989 May 20;124(20):532–537. doi: 10.1136/vr.124.20.532. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


