Abstract
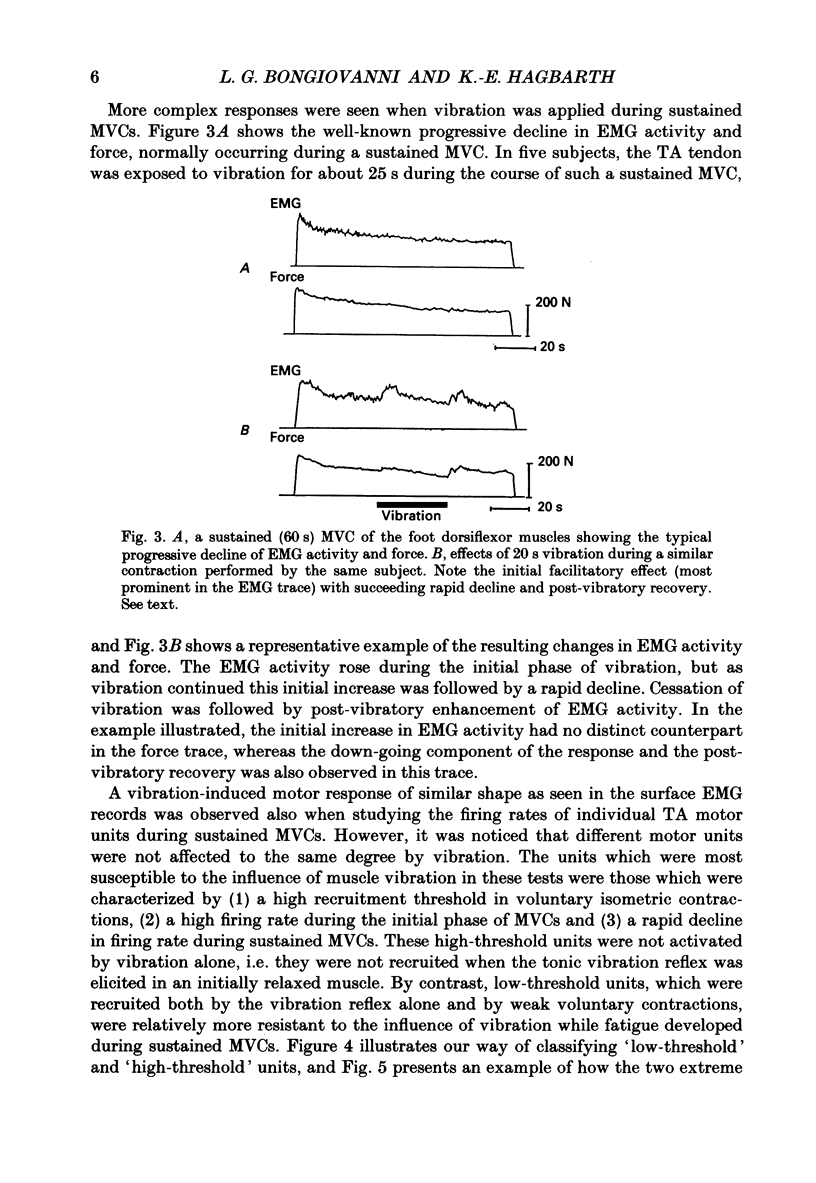
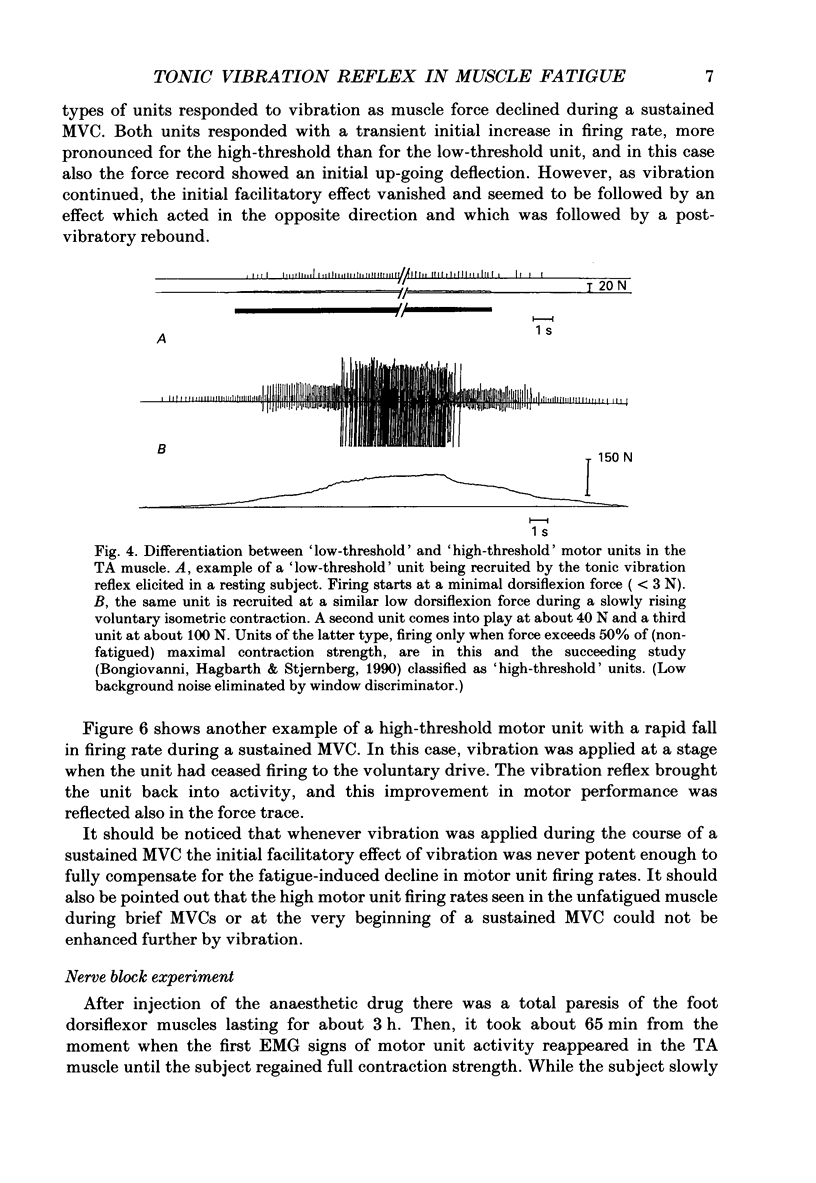
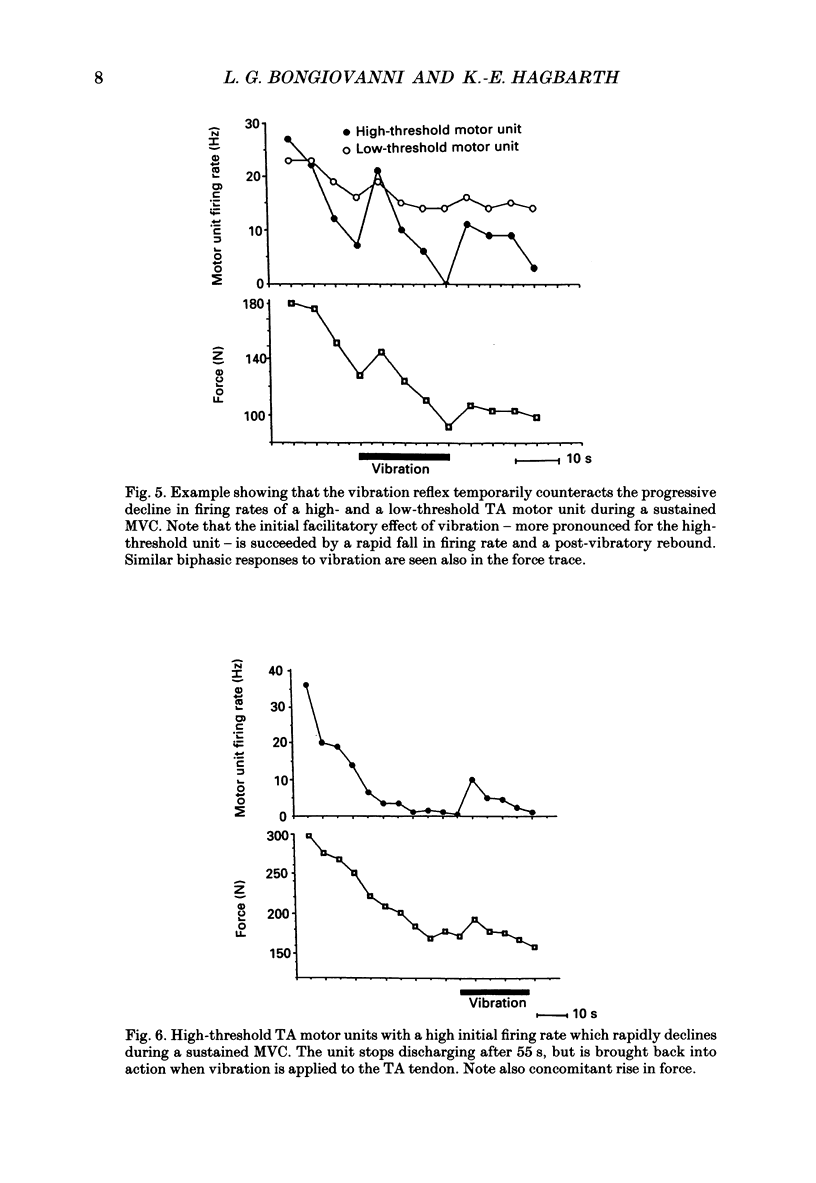
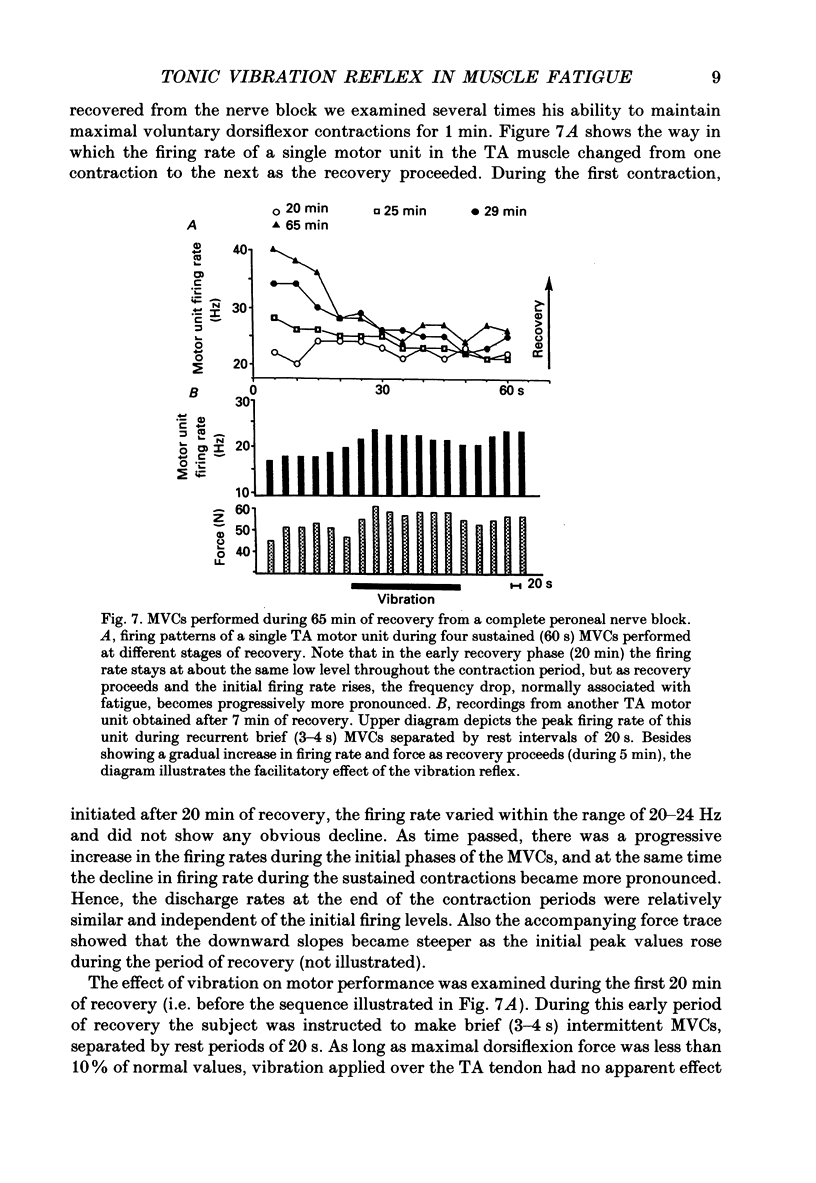
1. In the present study on human foot dorsiflexor muscles we have examined the effects of high-frequency (150 Hz) muscle vibration on weak or moderate voluntary contractions (maintained by constant effort) and on maximal voluntary contractions (MCVs) of (i) non-fatigued muscles, (ii) muscles fatigued by sustained MVCs and (iii) muscles deprived of gamma-fibre innervation by partial anaesthetic nerve block. The motor outcome of the voluntary dorsiflexion efforts was assessed by measuring the firing rates of single motor units in the anterior tibial (TA) muscle, the mean voltage EMG activity from the pretibial muscles and foot dorsiflexion force. 2. With the subject instructed to exert constant effort in maintaining a weak or moderate contraction, superimposed vibration caused an enhancement of EMG activity and contraction force. 3. Previous claims that muscle vibration has no facilitatory effect on motor output in MVCs were found to hold true for non-fatigued but not for fatigued muscles. Thus, the fatigue-induced decline in EMG activity and motor unit firing rates was counteracted by short periods (less than 10-20 s) of superimposed vibration. However, with longer vibration periods it seemed as if the initial facilitation converted into an opposite effect which accentuated the fatigue-induced decline in motor output and contraction force. 4. Like muscle fatigue, a partial anesthetic block of the deep peroneal nerve, supposedly interrupting transmission in gamma-motor fibres, caused a reduction of MVC motor unit firing rates which could be counteracted by muscle vibration. In prolonged MVCs performed during the block, motor unit firing rates did not show the normal progressive decline from an initially high level, but stayed at a relatively constant low level throughout the contraction period. 5. Even though alternative interpretations are possible, the results agree with the hypotheses (i) that in sustained MVCs, fatigue processes occur not only in extrafusal but also in intrafusal muscle fibres, (ii) that the intrafusal fatigue leads to a reduction of the voluntary drive conveyed to the alpha-motoneurones via the gamma-loop and (iii) that vibration-induced activity in group Ia afferents can act as a substitute for the diminished fusimotor drive.
Full text
PDF









Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Barker D., Emonet-Dénand F., Harker D. W., Jami L., Laporte Y. Distribution of fusimotor axons to intrafusal muscle fibres in cat tenuissimus spindles as determined by the glycogen-depletion method. J Physiol. 1976 Sep;261(1):49–69. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1976.sp011548. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bigland-Ritchie B. R., Dawson N. J., Johansson R. S., Lippold O. C. Reflex origin for the slowing of motoneurone firing rates in fatigue of human voluntary contractions. J Physiol. 1986 Oct;379:451–459. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1986.sp016263. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bigland-Ritchie B., Johansson R., Lippold O. C., Smith S., Woods J. J. Changes in motoneurone firing rates during sustained maximal voluntary contractions. J Physiol. 1983 Jul;340:335–346. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1983.sp014765. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bigland-Ritchie B., Jones D. A., Woods J. J. Excitation frequency and muscle fatigue: electrical responses during human voluntary and stimulated contractions. Exp Neurol. 1979 May;64(2):414–427. doi: 10.1016/0014-4886(79)90280-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bigland-Ritchie B., Kukulka C. G., Lippold O. C., Woods J. J. The absence of neuromuscular transmission failure in sustained maximal voluntary contractions. J Physiol. 1982 Sep;330:265–278. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1982.sp014340. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bigland-Ritchie B., Woods J. J. Changes in muscle contractile properties and neural control during human muscular fatigue. Muscle Nerve. 1984 Nov-Dec;7(9):691–699. doi: 10.1002/mus.880070902. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bongiovanni L. G., Hagbarth K. E., Stjernberg L. Prolonged muscle vibration reducing motor output in maximal voluntary contractions in man. J Physiol. 1990 Apr;423:15–26. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1990.sp018008. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Burke D., Hagbarth K. E., Löfstedt L., Wallin B. G. The responses of human muscle spindle endings to vibration during isometric contraction. J Physiol. 1976 Oct;261(3):695–711. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1976.sp011581. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Burke D., Hagbarth K. E., Löfstedt L., Wallin B. G. The responses of human muscle spindle endings to vibration of non-contracting muscles. J Physiol. 1976 Oct;261(3):673–693. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1976.sp011580. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Burke D., Hagbarth K. E., Skuse N. F. Recruitment order of human spindle endings in isometric voluntary contractions. J Physiol. 1978 Dec;285:101–112. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1978.sp012560. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- De Gail P., Lance J. W., Neilson P. D. Differential effects on tonic and phasic reflex mechanisms produced by vibration of muscles in man. J Neurol Neurosurg Psychiatry. 1966 Feb;29(1):1–11. doi: 10.1136/jnnp.29.1.1. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Decorte L., Emonet-Dénand F., Harker D. W., Jami L., Laporte Y. Glycogen depletion elicited in tenuissimus intrafusal muscle fibres by stimulation of static gamma-axons in the cat. J Physiol. 1984 Jan;346:341–352. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1984.sp015026. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Desmedt J. E., Godaux E. Mechanism of the vibration paradox: excitatory and inhibitory effects of tendon vibration on single soleus muscle motor units in man. J Physiol. 1978 Dec;285:197–207. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1978.sp012567. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Eklund G., Hagbarth K. E. Normal variability of tonic vibration reflexes in man. Exp Neurol. 1966 Sep;16(1):80–92. doi: 10.1016/0014-4886(66)90088-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Emonet-Dénand F., Laporte Y. Effects of prolonged stimulation at high frequency of static and dynamic gamma axons on spindle primary endings. Brain Res. 1978 Aug 11;151(3):593–598. doi: 10.1016/0006-8993(78)91092-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Garland S. J., Garner S. H., McComas A. J. Reduced voluntary electromyographic activity after fatiguing stimulation of human muscle. J Physiol. 1988 Jul;401:547–556. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1988.sp017178. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Grimby L., Hannerz J., Hedman B. The fatigue and voluntary discharge properties of single motor units in man. J Physiol. 1981 Jul;316:545–554. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1981.sp013805. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hagbarth K. E., Eklund G. The muscle vibrator--a useful tool in neurological therapeutic work. Scand J Rehabil Med. 1969;1(1):26–34. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hagbarth K. E., Kunesch E. J., Nordin M., Schmidt R., Wallin E. U. Gamma loop contributing to maximal voluntary contractions in man. J Physiol. 1986 Nov;380:575–591. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1986.sp016303. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hultborn H., Meunier S., Morin C., Pierrot-Deseilligny E. Assessing changes in presynaptic inhibition of I a fibres: a study in man and the cat. J Physiol. 1987 Aug;389:729–756. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1987.sp016680. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hultborn H., Meunier S., Pierrot-Deseilligny E., Shindo M. Changes in presynaptic inhibition of Ia fibres at the onset of voluntary contraction in man. J Physiol. 1987 Aug;389:757–772. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1987.sp016681. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kernell D., Monster A. W. Motoneurone properties and motor fatigue. An intracellular study of gastrocnemius motoneurones of the cat. Exp Brain Res. 1982;46(2):197–204. doi: 10.1007/BF00237177. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kernell D., Monster A. W. Time course and properties of late adaptation in spinal motoneurones of the cat. Exp Brain Res. 1982;46(2):191–196. doi: 10.1007/BF00237176. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- MERTON P. A. Voluntary strength and fatigue. J Physiol. 1954 Mar 29;123(3):553–564. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1954.sp005070. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Marsden C. D., Meadows J. C., Merton P. A. Isolated single motor units in human muscle and their rate of discharge during maximal voluntary effort. J Physiol. 1971;217 (Suppl):12P–13P. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- McCloskey D. I., Ebeling P., Goodwin G. M. Estimation of weights and tensions and apparent involvement of a "sense of effort". Exp Neurol. 1974 Jan;42(1):220–232. doi: 10.1016/0014-4886(74)90019-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Vallbo A. B., Hagbarth K. E., Torebjörk H. E., Wallin B. G. Somatosensory, proprioceptive, and sympathetic activity in human peripheral nerves. Physiol Rev. 1979 Oct;59(4):919–957. doi: 10.1152/physrev.1979.59.4.919. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Vallbo A. B. Human muscle spindle discharge during isometric voluntary contractions. Amplitude relations between spindle frequency and torque. Acta Physiol Scand. 1974 Feb;90(2):319–336. doi: 10.1111/j.1748-1716.1974.tb05594.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Woods J. J., Furbush F., Bigland-Ritchie B. Evidence for a fatigue-induced reflex inhibition of motoneuron firing rates. J Neurophysiol. 1987 Jul;58(1):125–137. doi: 10.1152/jn.1987.58.1.125. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


