Abstract
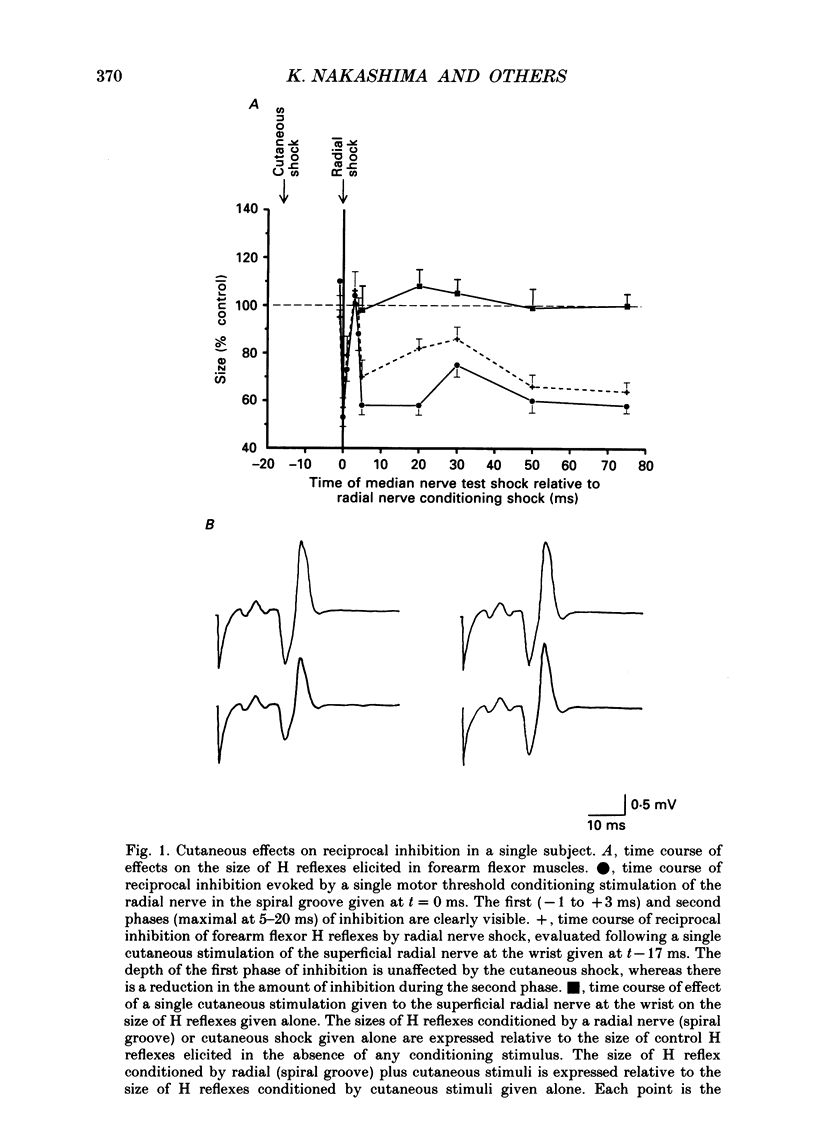
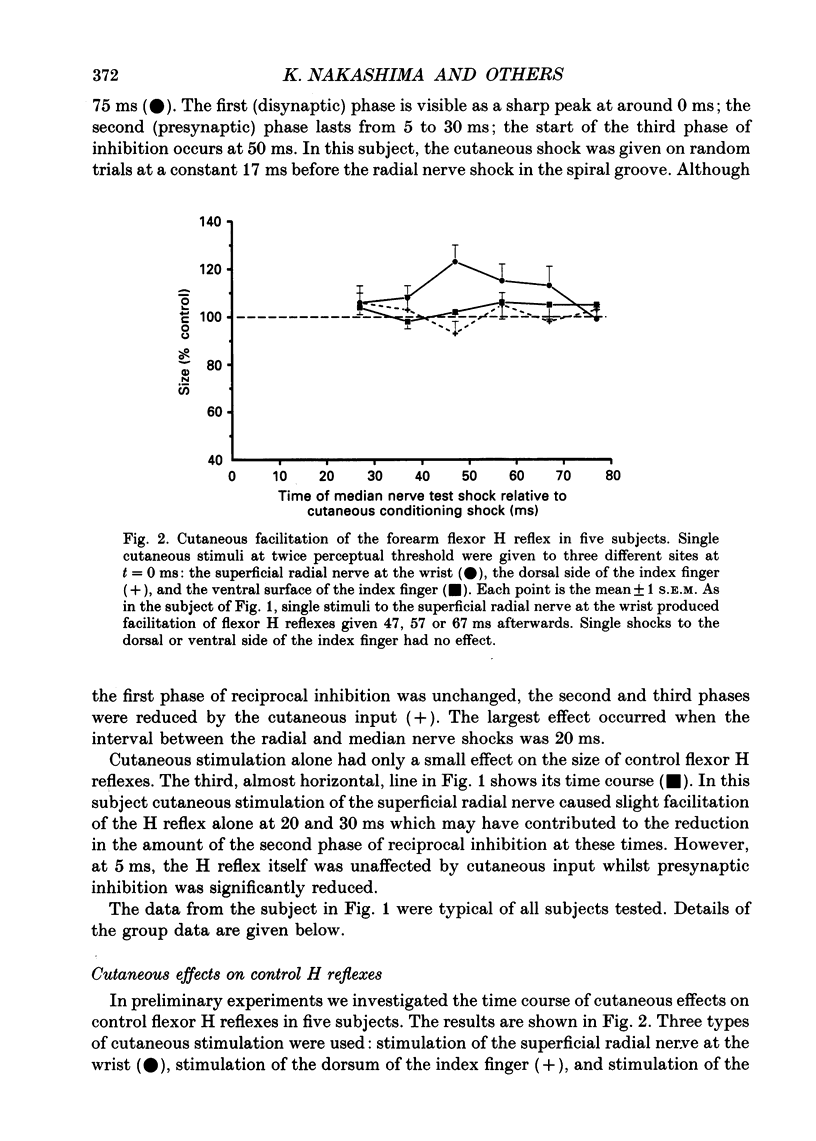
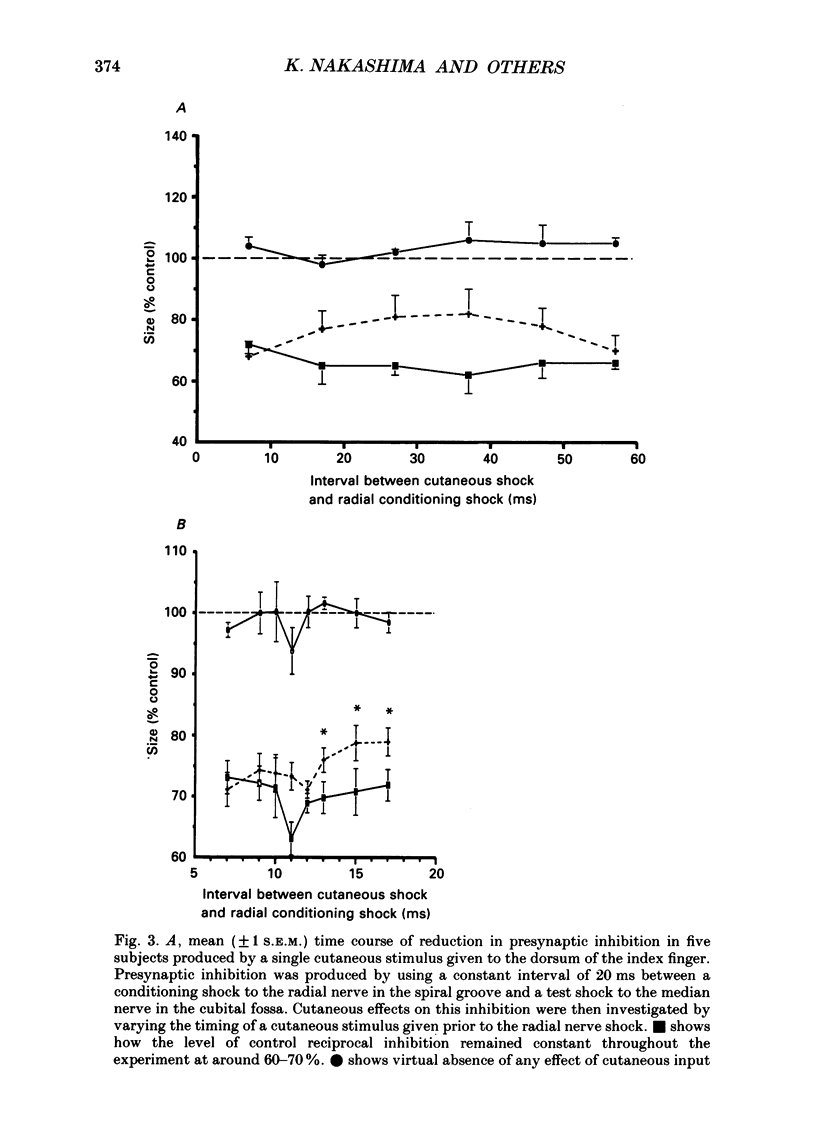
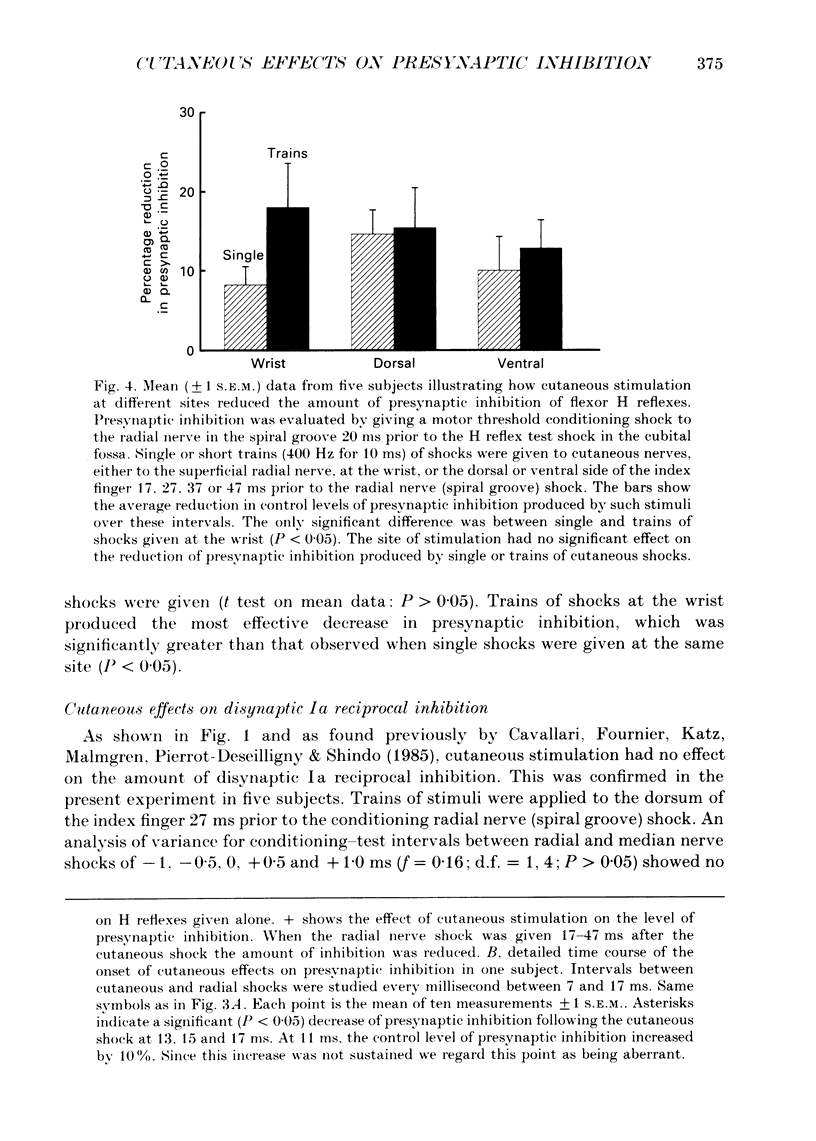
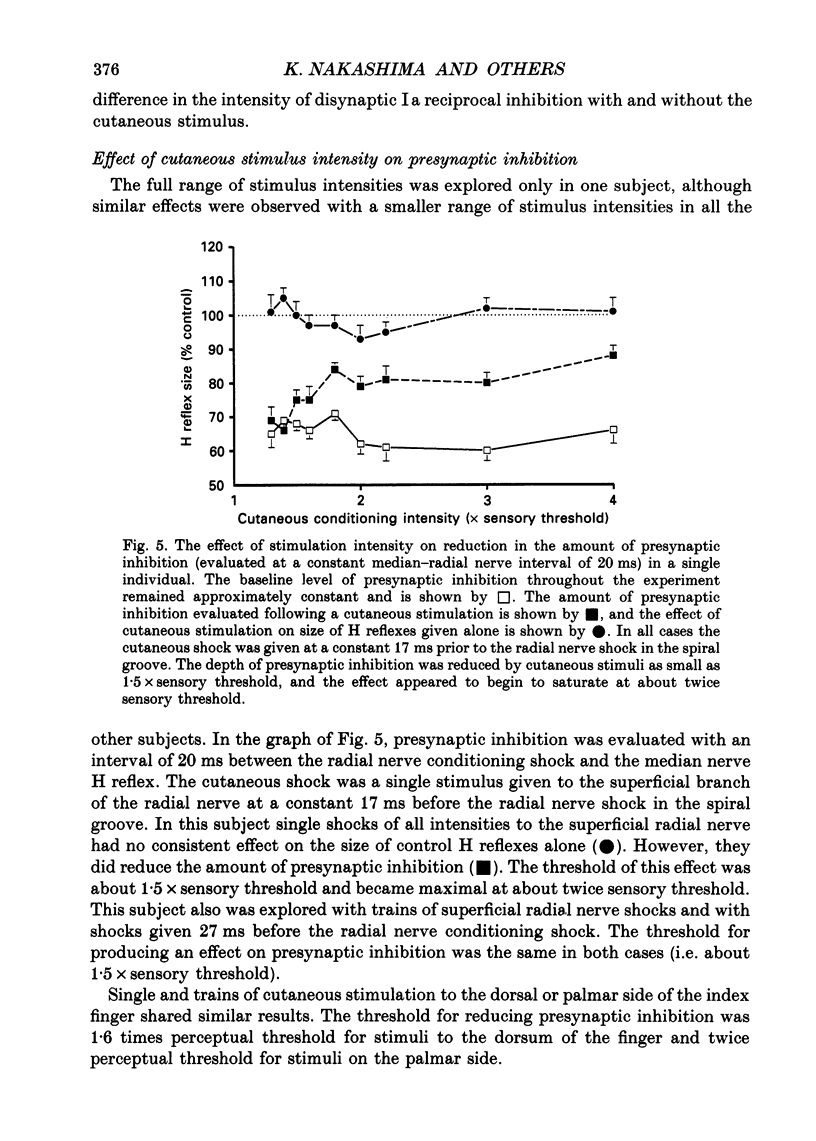
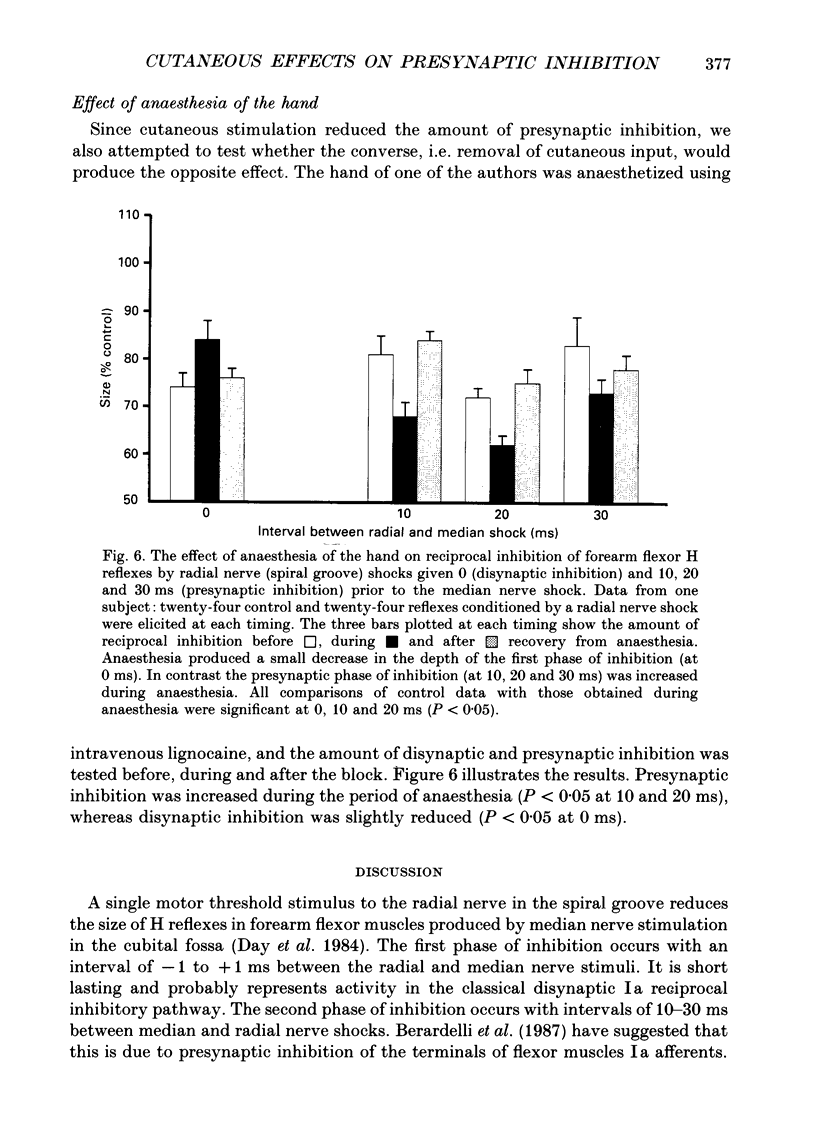
1. In six subjects, H reflexes obtained in the flexor muscles in the forearm were inhibited by single motor threshold shocks to the radial nerve in the spiral groove. The first two phases of the inhibitory time course were studied: with intervals between the radial and median nerve shocks of -1 to +1 ms, and +5 to +30 ms. These two phases are thought to be due respectively to disynaptic inhibition between radial Ia afferents and flexor alpha-motoneurones, and to presynaptic inhibition of flexor Ia afferents. 2. Single or short trains (10 ms, 400 Hz) of cutaneous stimuli to the dorsal or palmar aspect of the proximal phalanx of the index finger or to the superficial radial nerve at the wrist, reduced the amount of presynaptic inhibition by 10-20%, but had no effect on the earlier disynaptic inhibition. Single stimuli to either side of the index finger or trains of stimuli to the ventral side, had no effect on the size of control H reflexes elicited alone. 3. Effects of cutaneous nerve shocks on presynaptic inhibition could be seen with stimuli as small as 1.5 x perceptual threshold. 4. Anaesthesia of the hand in one subject reversibly increased the amount of presynaptic inhibition and decreased the amount of disynaptic inhibition. 5. We conclude that, as in the cat, cutaneous input can modulate transmission in presynaptic inhibitory pathways in man.
Full text
PDF





Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Berardelli A., Day B. L., Marsden C. D., Rothwell J. C. Evidence favouring presynaptic inhibition between antagonist muscle afferents in the human forearm. J Physiol. 1987 Oct;391:71–83. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1987.sp016726. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Caccia M. R., McComas A. J., Upton A. R., Blogg T. Cutaneous reflexes in small muscles of the hand. J Neurol Neurosurg Psychiatry. 1973 Dec;36(6):960–977. doi: 10.1136/jnnp.36.6.960. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cavallari P., Fournier E., Katz R., Malmgren K., Pierrot-Deseilligny E., Shindo M. Cutaneous facilitation of transmission in Ib reflex pathways in the human upper limb. Exp Brain Res. 1985;60(1):197–199. doi: 10.1007/BF00237033. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Day B. L., Marsden C. D., Obeso J. A., Rothwell J. C. Reciprocal inhibition between the muscles of the human forearm. J Physiol. 1984 Apr;349:519–534. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1984.sp015171. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Iles J. F., Roberts R. C. Inhibition of monosynaptic reflexes in the human lower limb. J Physiol. 1987 Apr;385:69–87. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1987.sp016484. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jenner J. R., Stephens J. A. Cutaneous reflex responses and their central nervous pathways studied in man. J Physiol. 1982 Dec;333:405–419. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1982.sp014461. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lund S., Lundberg A., Vyklický L. Inhibitory action from the flexor reflex afferents on transmission to Ia afferents. Acta Physiol Scand. 1965 Aug;64(4):345–355. doi: 10.1111/j.1748-1716.1965.tb04189.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nakashima K., Rothwell J. C., Day B. L., Thompson P. D., Shannon K., Marsden C. D. Reciprocal inhibition between forearm muscles in patients with writer's cramp and other occupational cramps, symptomatic hemidystonia and hemiparesis due to stroke. Brain. 1989 Jun;112(Pt 3):681–697. doi: 10.1093/brain/112.3.681. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rudomin P., Solodkin M., Jiménez I. PAD and PAH response patterns of group Ia- and Ib-fibers to cutaneous and descending inputs in the cat spinal cord. J Neurophysiol. 1986 Oct;56(4):987–1006. doi: 10.1152/jn.1986.56.4.987. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rudomín P., Jiménez I., Solodkin M., Dueñas S. Sites of action of segmental and descending control of transmission on pathways mediating PAD of Ia- and Ib-afferent fibers in cat spinal cord. J Neurophysiol. 1983 Oct;50(4):743–769. doi: 10.1152/jn.1983.50.4.743. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sheehy M. P., Rothwell J. C., Marsden C. D. Writer's cramp. Adv Neurol. 1988;50:457–472. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wallace W. A., Guardini R., Ellis S. J. Standard intravenous regional analgesia. Br Med J (Clin Res Ed) 1982 Aug 21;285(6341):554–556. doi: 10.1136/bmj.285.6341.554. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


