Abstract
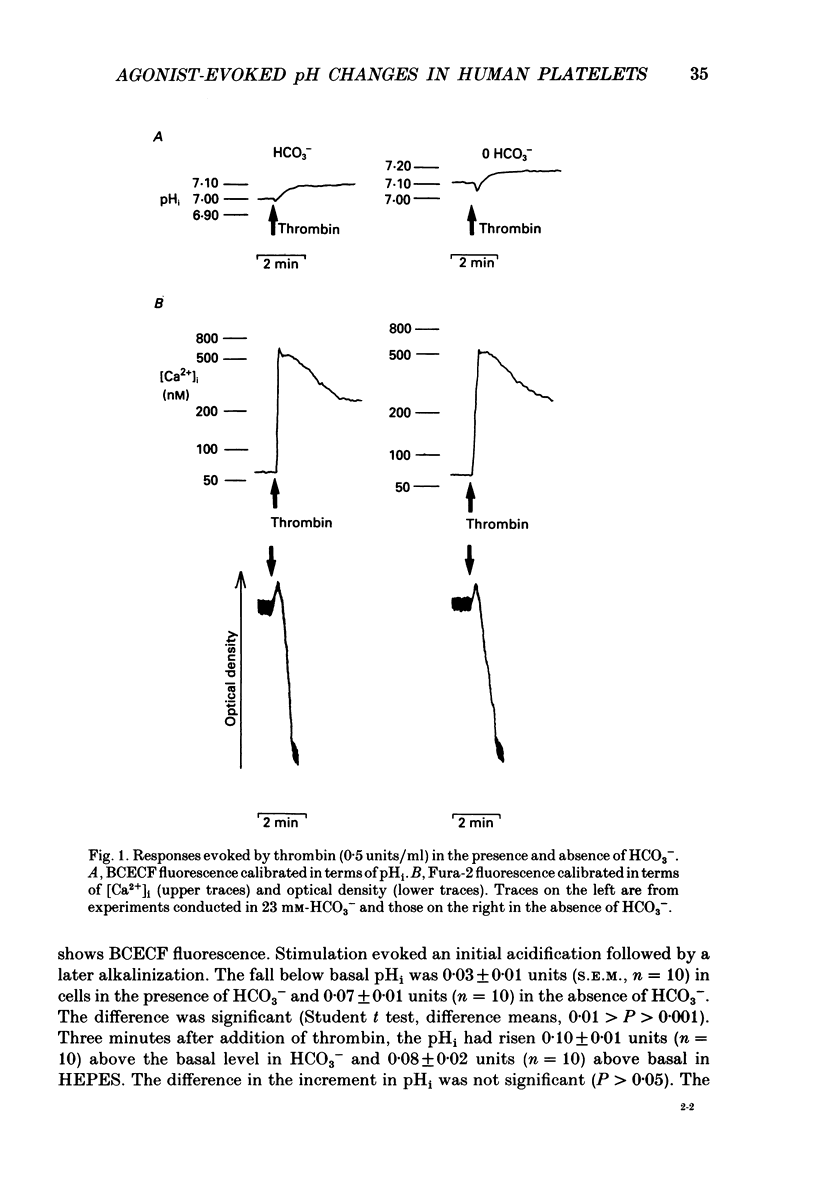
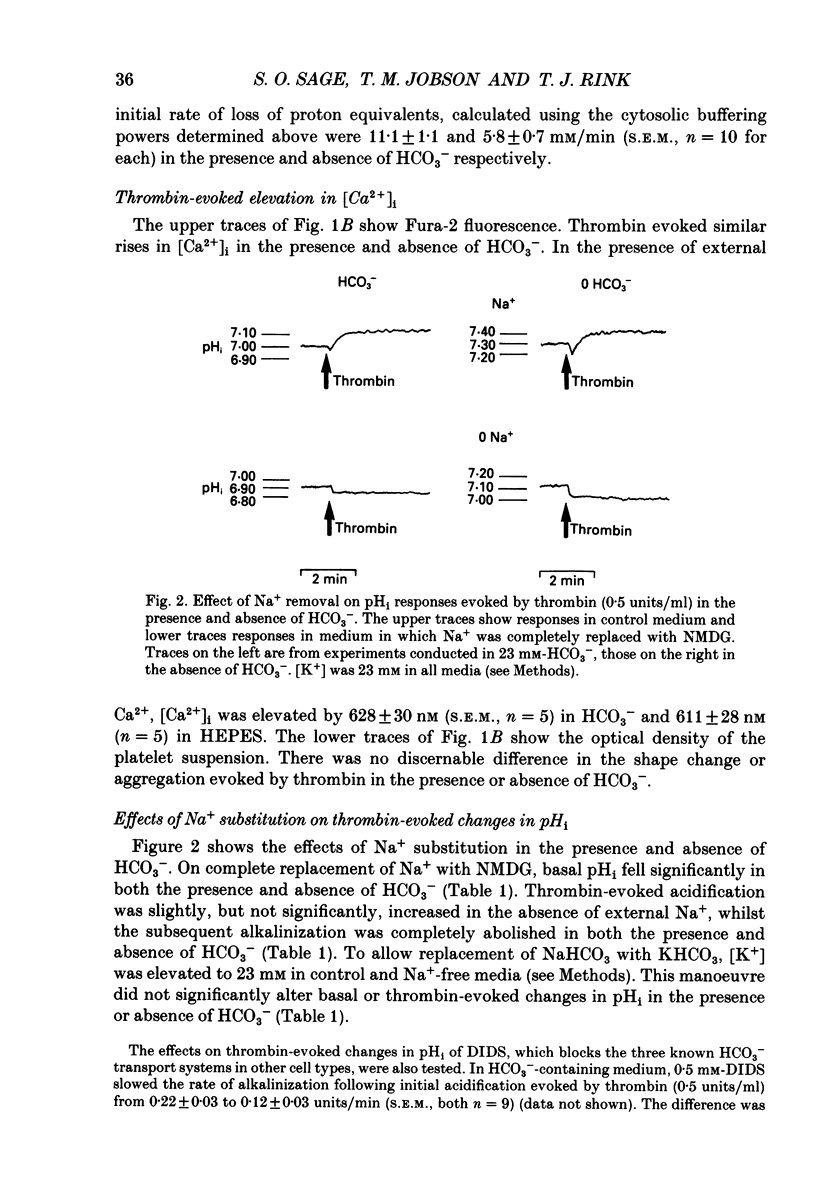
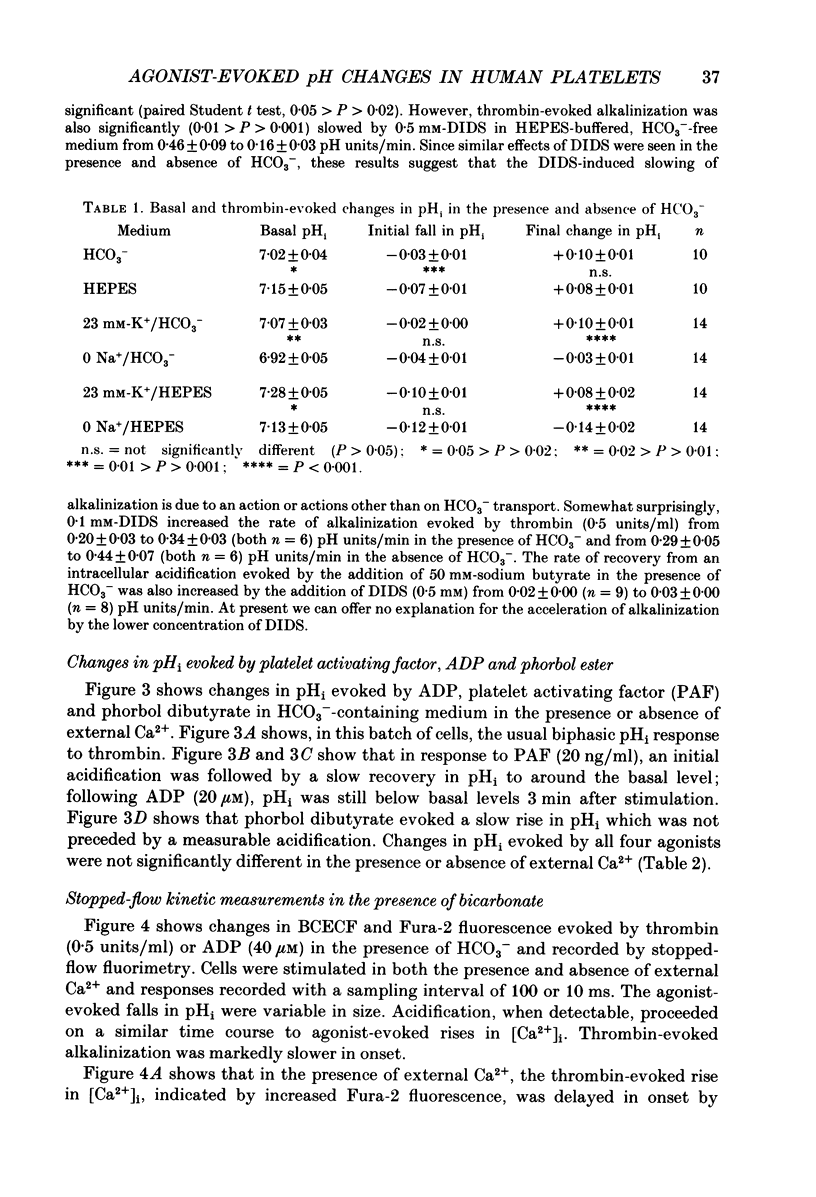
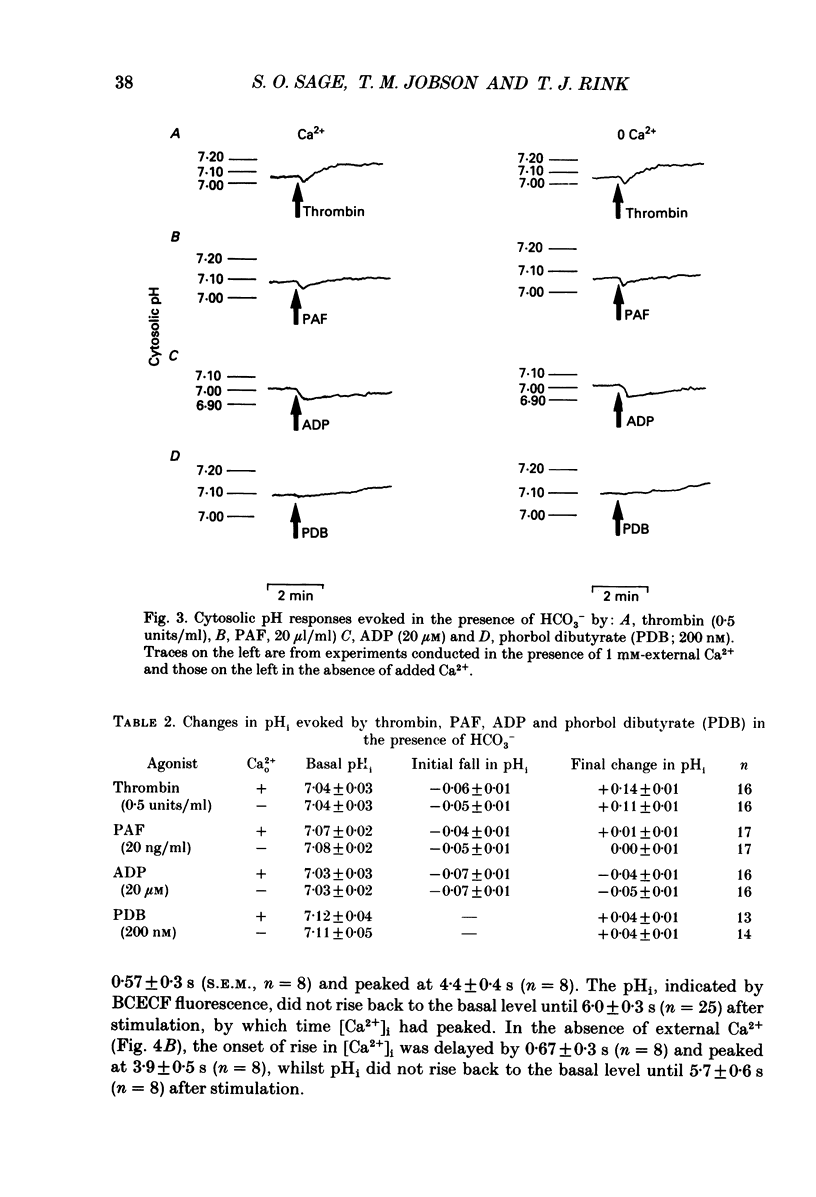
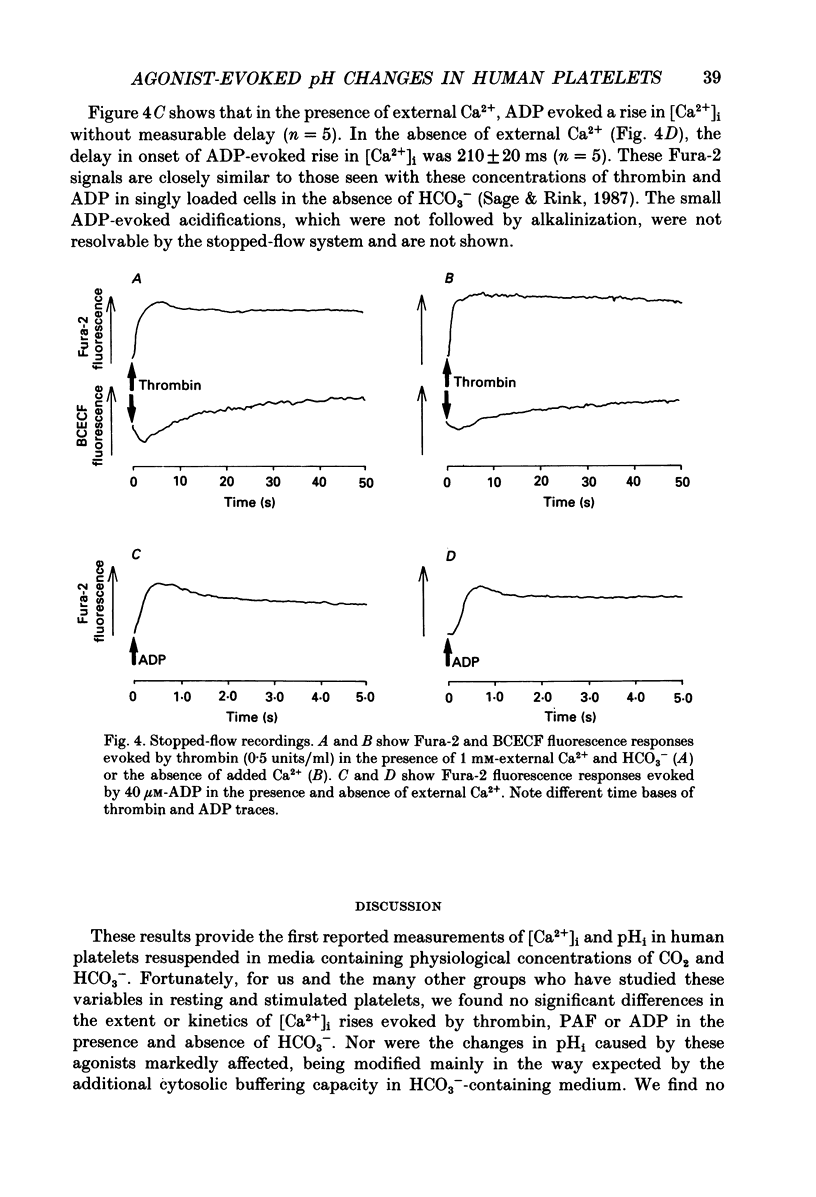
1. Cytosolic pH (pHi) and calcium concentration ([Ca2+]i) have been investigated in the presence and absence of physiological HCO3- in human platelets co-loaded with the fluorescent indicators BCECF and Fura-2. Basal pHi and changes evoked by butyrate, thrombin, platelet activating factor (PAF), ADP and phorbol ester were investigated, as were the effects of removing external Na+. 2. In the presence of physiological HCO3- and CO2, basal pHi was 7.02 +/- 0.04 compared with 7.15 +/- 0.05 in the absence of HCO3-. Estimated cytosolic buffering power was reduced from 35.6 +/- 3.0 to 14.5 +/- 0.4 mM/pH unit by the omission of HCO3-. 3. Thrombin evoked an immediate acidification of 0.03 +/- 0.01 pH units in the presence of HCO3- and 0.07 +/- 0.01 pH units in its absence. The acidifications were followed by a slow alkalinization. The final pHi was 0.10 +/- 0.01 units above basal in the presence of HCO3- and 0.08 +/- 0.02 units above basal in the absence of HCO3-. The initial acidification was significantly greater in the absence of HCO3-. The subsequent increase in pHi was similar in the presence and absence of this ion, but the calculated loss of proton equivalents was greater in the presence of HCO3-. 4. Replacement of extracellular Na+ with N-methyl-D-glucamine resulted in a fall in basal pHi and abolished recovery from thrombin-evoked acidification in both the presence and absence of HCO3-. 5. In the presence of HCO3-, PAF and ADP evoked an intracellular acidification similar to that caused by thrombin. However, with PAF and ADP, the subsequent recovery in pHi was slow and did not rise above basal levels. Phorbol dibutyrate, an activator of protein kinase C, evoked a similar elevation in pHi of 0.04 +/- 0.01 units over 3 min in the presence and absence of HCO3-. 6. Stopped-flow fluorimetric measurements were made of both BCECF and Fura-2 fluorescence in the presence of HCO3-. In the presence and absence of external Ca2+, thrombin-evoked rises in [Ca2+]i peaked before any cytoplasmic alkalinization occurred. ADP evoked rapid elevations in [Ca2+]i, but caused no alkalinization.(ABSTRACT TRUNCATED AT 400 WORDS)
Full text
PDF









Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Born G. V. Observations on the change in shape of blood platelets brought about by adenosine diphosphate. J Physiol. 1970 Aug;209(2):487–511. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1970.sp009176. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Boron W. F. Intracellular pH regulation in epithelial cells. Annu Rev Physiol. 1986;48:377–388. doi: 10.1146/annurev.ph.48.030186.002113. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Brass L. F., Joseph S. K. A role for inositol triphosphate in intracellular Ca2+ mobilization and granule secretion in platelets. J Biol Chem. 1985 Dec 5;260(28):15172–15179. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Connolly T. M., Limbird L. E. Removal of extraplatelet Na+ eliminates indomethacin-sensitive secretion from human platelets stimulated by epinephrine, ADP, and thrombin. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1983 Sep;80(17):5320–5324. doi: 10.1073/pnas.80.17.5320. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Daniel J. L., Dangelmaier C. A., Selak M., Smith J. B. ADP stimulates IP3 formation in human platelets. FEBS Lett. 1986 Oct 6;206(2):299–303. doi: 10.1016/0014-5793(86)81000-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fisher G. J., Bakshian S., Baldassare J. J. Activation of human platelets by ADP causes a rapid rise in cytosolic free calcium without hydrolysis of phosphatidylinositol-4,5-bisphosphate. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1985 Jun 28;129(3):958–964. doi: 10.1016/0006-291x(85)91984-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ganz M. B., Boyarsky G., Sterzel R. B., Boron W. F. Arginine vasopressin enhances pHi regulation in the presence of HCO3- by stimulating three acid-base transport systems. Nature. 1989 Feb 16;337(6208):648–651. doi: 10.1038/337648a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gillespie J. I., Greenwell J. R. Changes in intracellular pH and pH regulating mechanisms in somitic cells of the early chick embryo: a study using fluorescent pH-sensitive dye. J Physiol. 1988 Nov;405:385–395. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1988.sp017338. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Grinstein S., Rotin D., Mason M. J. Na+/H+ exchange and growth factor-induced cytosolic pH changes. Role in cellular proliferation. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1989 Jan 18;988(1):73–97. doi: 10.1016/0304-4157(89)90004-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hallam T. J., Rink T. J. Responses to adenosine diphosphate in human platelets loaded with the fluorescent calcium indicator quin2. J Physiol. 1985 Nov;368:131–146. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1985.sp015850. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hallam T. J., Sanchez A., Rink T. J. Stimulus-response coupling in human platelets. Changes evoked by platelet-activating factor in cytoplasmic free calcium monitored with the fluorescent calcium indicator quin2. Biochem J. 1984 Mar 15;218(3):819–827. doi: 10.1042/bj2180819. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Horne W. C., Norman N. E., Schwartz D. B., Simons E. R. Changes in cytoplasmic pH and in membrane potential in thrombin-stimulated human platelets. Eur J Biochem. 1981 Nov;120(2):295–302. doi: 10.1111/j.1432-1033.1981.tb05703.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kettenmann H., Schlue W. R. Intracellular pH regulation in cultured mouse oligodendrocytes. J Physiol. 1988 Dec;406:147–162. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1988.sp017373. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ozaki Y., Yatomi Y., Kariya T., Kume S. Anion channels contribute to the regulation of intracellular pH in human platelets. Thromb Res. 1989 Feb 1;53(3):221–230. doi: 10.1016/0049-3848(89)90097-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pollock W. K., Rink T. J., Irvine R. F. Liberation of [3H]arachidonic acid and changes in cytosolic free calcium in fura-2-loaded human platelets stimulated by ionomycin and collagen. Biochem J. 1986 May 1;235(3):869–877. doi: 10.1042/bj2350869. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rink T. J. Intracellular pH and cytoplasmic free Ca2+. Nature. 1987 Jun 4;327(6121):375–376. doi: 10.1038/327375b0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rink T. J., Pozzan T. Using quin2 in cell suspensions. Cell Calcium. 1985 Apr;6(1-2):133–144. doi: 10.1016/0143-4160(85)90040-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rink T. J., Sage S. O. Stimulated calcium efflux from fura-2-loaded human platelets. J Physiol. 1987 Dec;393:513–524. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1987.sp016837. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rink T. J., Sanchez A., Hallam T. J. Diacylglycerol and phorbol ester stimulate secretion without raising cytoplasmic free calcium in human platelets. Nature. 1983 Sep 22;305(5932):317–319. doi: 10.1038/305317a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rink T. J., Smith S. W., Tsien R. Y. Cytoplasmic free Ca2+ in human platelets: Ca2+ thresholds and Ca-independent activation for shape-change and secretion. FEBS Lett. 1982 Nov 1;148(1):21–26. doi: 10.1016/0014-5793(82)81234-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rink T. J., Tsien R. Y., Pozzan T. Cytoplasmic pH and free Mg2+ in lymphocytes. J Cell Biol. 1982 Oct;95(1):189–196. doi: 10.1083/jcb.95.1.189. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sage S. O., Rink T. J. Effects of ionic substitution on [Ca2+]i rises evoked by thrombin and PAF in human platelets. Eur J Pharmacol. 1986 Aug 22;128(1-2):99–107. doi: 10.1016/0014-2999(86)90563-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sage S. O., Rink T. J. The kinetics of changes in intracellular calcium concentration in fura-2-loaded human platelets. J Biol Chem. 1987 Dec 5;262(34):16364–16369. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Siess W., Siegel F. L., Lapetina E. G. Arachidonic acid stimulates the formation of 1,2-diacylglycerol and phosphatidic acid in human platelets. Degree of phospholipase C activation correlates with protein phosphorylation, platelet shape change, serotonin release, and aggregation. J Biol Chem. 1983 Sep 25;258(18):11236–11242. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Siffert W., Akkerman J. W. Activation of sodium-proton exchange is a prerequisite for Ca2+ mobilization in human platelets. 1987 Jan 29-Feb 4Nature. 325(6103):456–458. doi: 10.1038/325456a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Siffert W., Fox G., Mückenhoff K., Scheid P. Thrombin stimulates Na+-H+ exchange across the human platelet plasma membrane. FEBS Lett. 1984 Jul 9;172(2):272–274. doi: 10.1016/0014-5793(84)81139-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Siffert W., Siffert G., Scheid P. Activation of Na+/H+ exchange in human platelets stimulated by thrombin and a phorbol ester. Biochem J. 1987 Jan 1;241(1):301–303. doi: 10.1042/bj2410301. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Siffert W., Siffert G., Scheid P., Akkerman J. W. Activation of Na+/H+ exchange and Ca2+ mobilization start simultaneously in thrombin-stimulated platelets. Evidence that platelet shape change disturbs early rises of BCECF fluorescence which causes an underestimation of actual cytosolic alkalinization. Biochem J. 1989 Mar 1;258(2):521–527. doi: 10.1042/bj2580521. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Simpson A. W., Rink T. J. Elevation of pHi is not an essential step in calcium mobilisation in fura-2-loaded human platelets. FEBS Lett. 1987 Sep 28;222(1):144–148. doi: 10.1016/0014-5793(87)80208-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sweatt J. D., Blair I. A., Cragoe E. J., Limbird L. E. Inhibitors of Na+/H+ exchange block epinephrine- and ADP-induced stimulation of human platelet phospholipase C by blockade of arachidonic acid release at a prior step. J Biol Chem. 1986 Jul 5;261(19):8660–8666. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sweatt J. D., Connolly T. M., Cragoe E. J., Limbird L. E. Evidence that Na+/H+ exchange regulates receptor-mediated phospholipase A2 activation in human platelets. J Biol Chem. 1986 Jul 5;261(19):8667–8673. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Szatkowski M. S., Thomas R. C. New method for calculating pHi from accurately measured changes in pHi induced by a weak acid and base. Pflugers Arch. 1986 Jul;407(1):59–63. doi: 10.1007/BF00580721. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Thomas J. A., Buchsbaum R. N., Zimniak A., Racker E. Intracellular pH measurements in Ehrlich ascites tumor cells utilizing spectroscopic probes generated in situ. Biochemistry. 1979 May 29;18(11):2210–2218. doi: 10.1021/bi00578a012. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Thomas R. C. Cell growth factors. Bicarbonate and pHi response. Nature. 1989 Feb 16;337(6208):601–601. doi: 10.1038/337601a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Thomas R. C. Experimental displacement of intracellular pH and the mechanism of its subsequent recovery. J Physiol. 1984 Sep;354:3P–22P. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1984.sp015397. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Watson S. P., Reep B., McConnell R. T., Lapetina E. G. Collagen stimulates [3H]inositol trisphosphate formation in indomethacin-treated human platelets. Biochem J. 1985 Mar 15;226(3):831–837. doi: 10.1042/bj2260831. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zavoico G. B., Cragoe E. J., Jr Ca2+ mobilization can occur independent of acceleration of Na+/H+ exchange in thrombin-stimulated human platelets. J Biol Chem. 1988 Jul 15;263(20):9635–9639. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zavoico G. B., Cragoe E. J., Jr, Feinstein M. B. Regulation of intracellular pH in human platelets. Effects of thrombin, A23187, and ionomycin and evidence for activation of Na+/H+ exchange and its inhibition by amiloride analogs. J Biol Chem. 1986 Oct 5;261(28):13160–13167. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


