Abstract
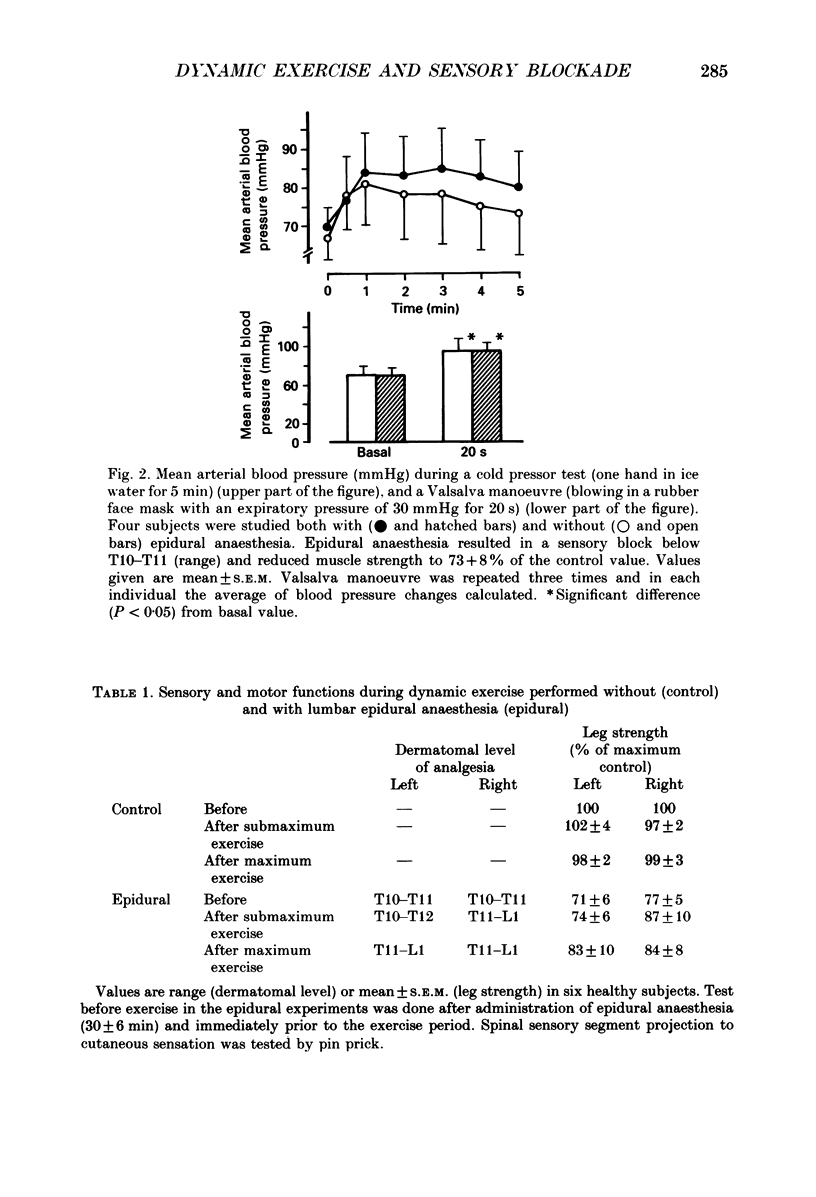
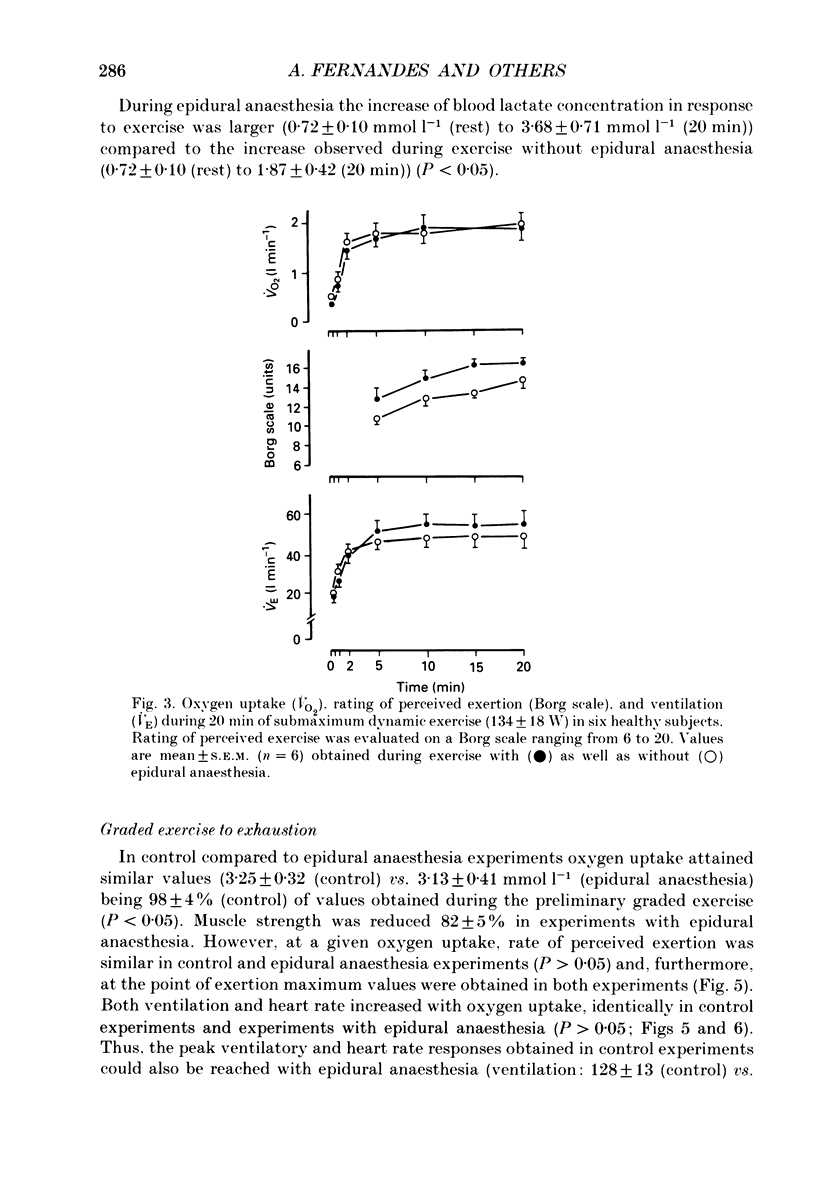
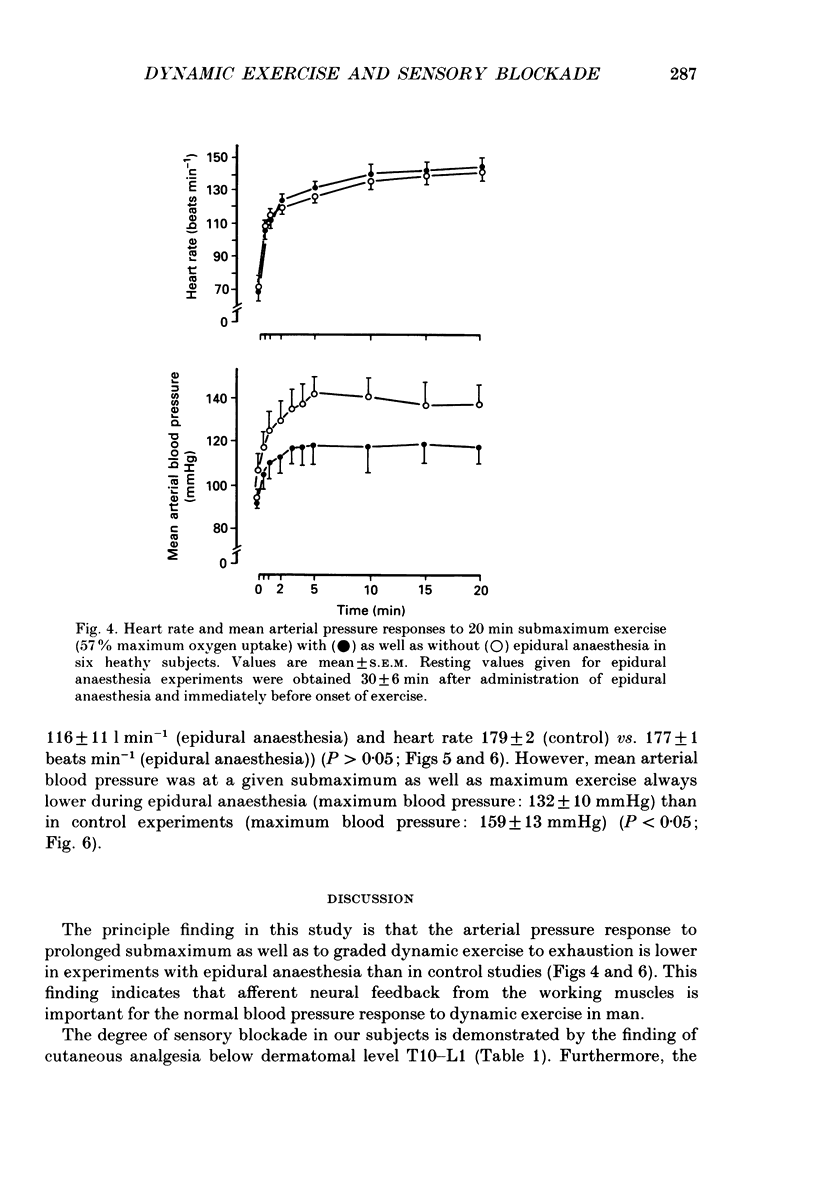
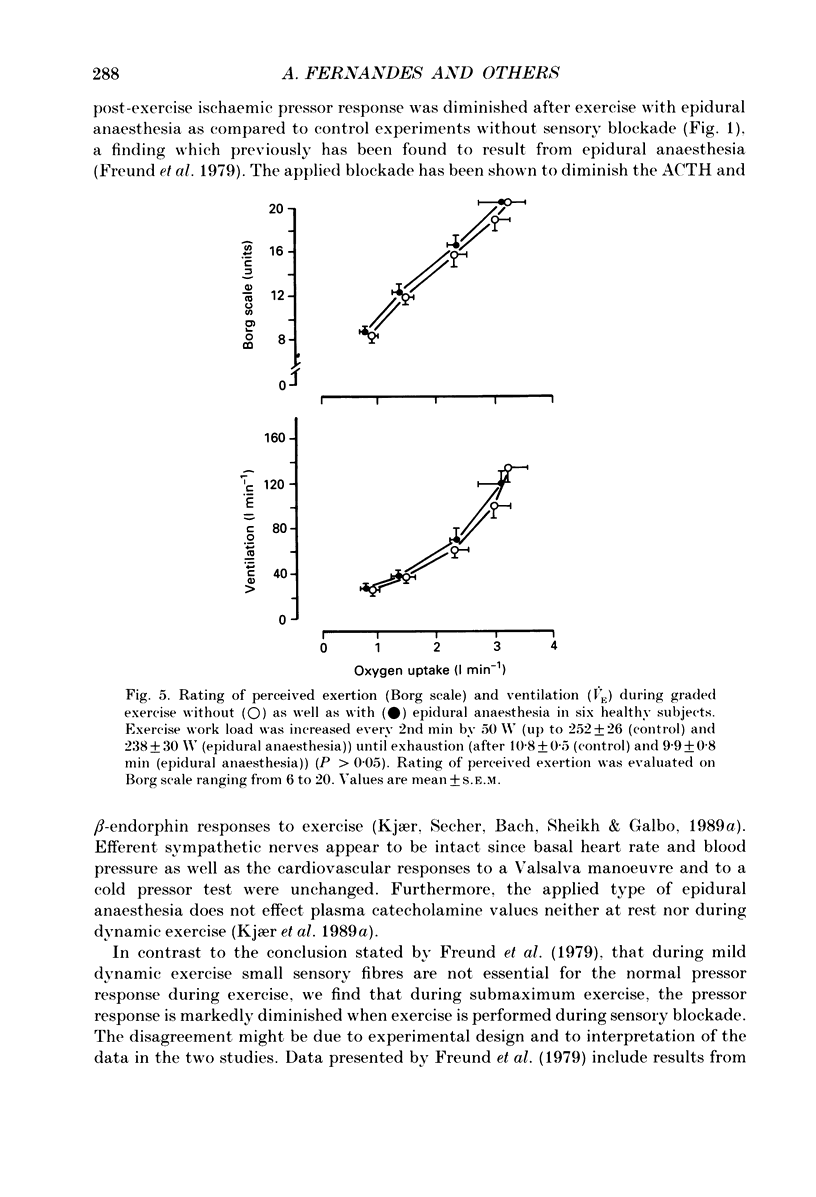
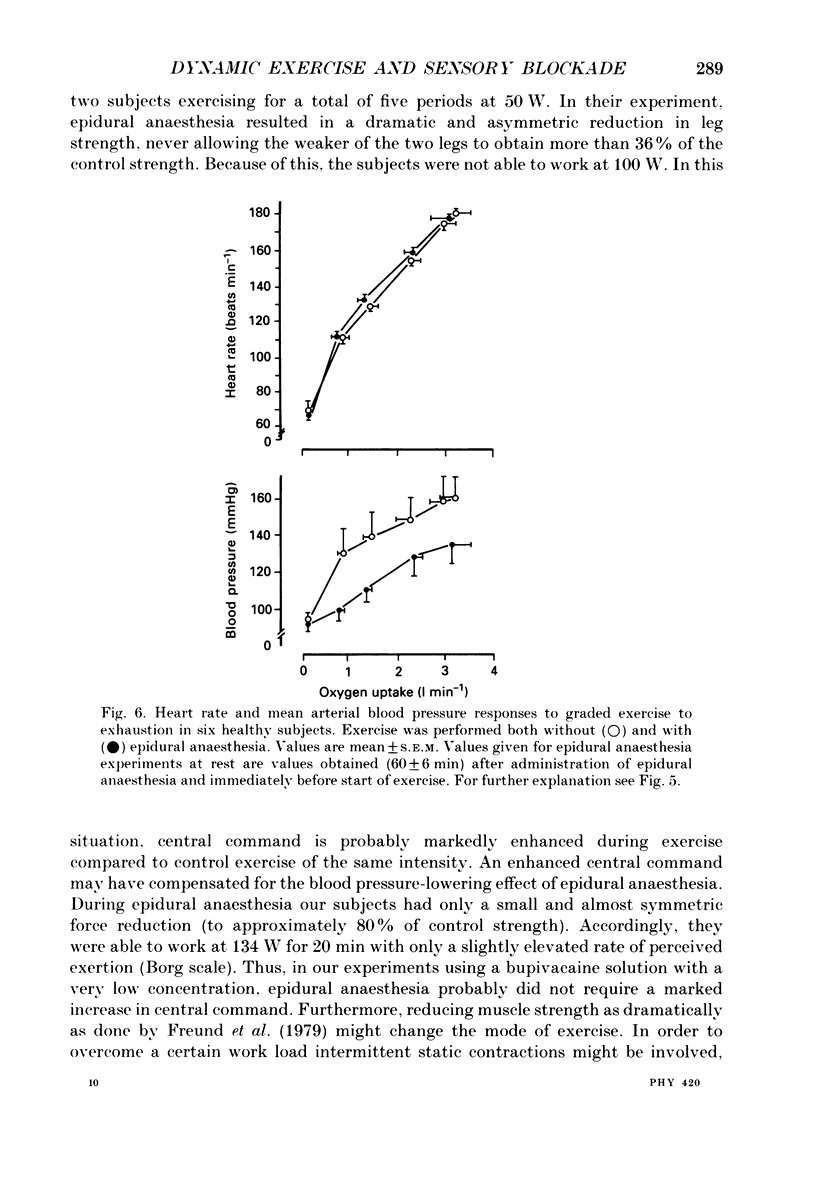
1. In order to evaluate the importance of afferent neural feedback from the working muscles for cardiovascular and ventilatory responses to dynamic exercise, epidural anaesthesia was induced at L3-L4. Six healthy males cycled for 20 min at 57% of maximum oxygen uptake and for 8-12 min at increasing work intensities until exhaustion at 238 +/- 30 W without as well as with epidural anaesthesia. 2. Presence of afferent neural blockade was verified by cutaneous sensory analgesia below T10-T11 and attenuated post-exercise ischaemic pressor response (45 +/- 8-24 +/- 6 mmHg). Efferent sympathetic nerves appear to be intact since basal heart rate and blood pressure as well as the cardiovascular responses to a Valsalva manoeuvre and to a cold pressor test were unchanged. 3. During dynamic exercise with epidural anaesthesia, blood pressure was lower than in control experiments; however, ventilation and heart rate were not affected. 4. The results indicate that afferent neural activity from the working muscles is important for blood pressure regulation during dynamic exercise in man but may not be necessary for eliciting the ventilatory and heart rate responses.
Full text
PDF






Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- ASMUSSEN E., JOHANSEN S. H., JORGENSEN M., NIELSEN M. ON THE NERVOUS FACTORS CONTROLLING RESPIRATION AND CIRCULATION DURING EXERCISE. EXPERIMENTS WITH CURARIZATION. Acta Physiol Scand. 1965 Mar;63:343–350. doi: 10.1111/j.1748-1716.1965.tb04073.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Adams L., Garlick J., Guz A., Murphy K., Semple S. J. Is the voluntary control of exercise in man necessary for the ventilatory response? J Physiol. 1984 Oct;355:71–83. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1984.sp015407. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Alam M., Smirk F. H. Observations in man on a pulse-accelerating reflex from the voluntary muscles of the legs. J Physiol. 1938 Mar 14;92(2):167–177. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1938.sp003592. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Alam M., Smirk F. H. Observations in man upon a blood pressure raising reflex arising from the voluntary muscles. J Physiol. 1937 Jun 3;89(4):372–383. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1937.sp003485. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Borg G. Perceived exertion as an indicator of somatic stress. Scand J Rehabil Med. 1970;2(2):92–98. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Clausen J. P. Effect of physical training on cardiovascular adjustments to exercise in man. Physiol Rev. 1977 Oct;57(4):779–815. doi: 10.1152/physrev.1977.57.4.779. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Duncan G., Johnson R. H., Lambie D. G. Role of sensory nerves in the cardiovascular and respiratory changes with isometric forearm exercise in man. Clin Sci (Lond) 1981 Feb;60(2):145–155. doi: 10.1042/cs0600145. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
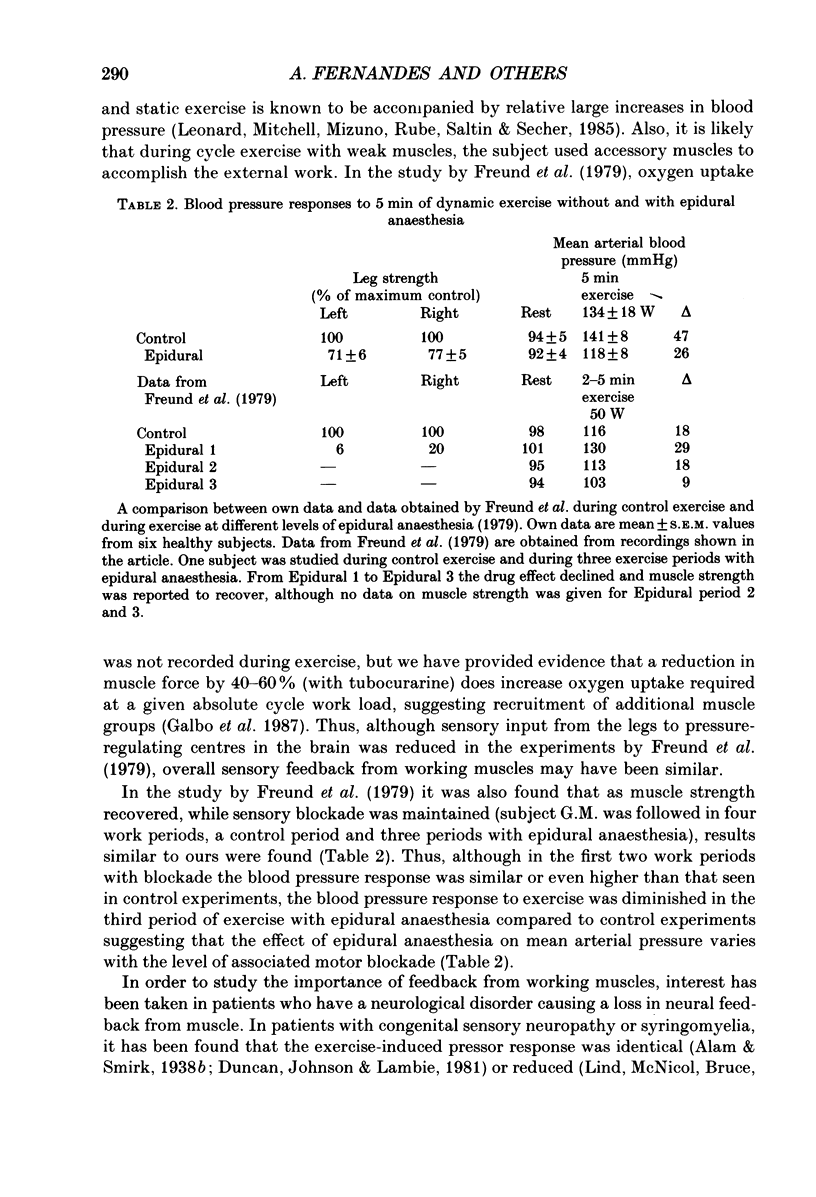
- Freund P. R., Rowell L. B., Murphy T. M., Hobbs S. F., Butler S. H. Blockade of the pressor response to muscle ischemia by sensory nerve block in man. Am J Physiol. 1979 Oct;237(4):H433–H439. doi: 10.1152/ajpheart.1979.237.4.H433. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Galbo H., Kjaer M., Secher N. H. Cardiovascular, ventilatory and catecholamine responses to maximal dynamic exercise in partially curarized man. J Physiol. 1987 Aug;389:557–568. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1987.sp016672. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kjaer M., Secher N. H., Bach F. W., Galbo H. Role of motor center activity for hormonal changes and substrate mobilization in humans. Am J Physiol. 1987 Nov;253(5 Pt 2):R687–R695. doi: 10.1152/ajpregu.1987.253.5.R687. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kjaer M., Secher N. H., Bach F. W., Sheikh S., Galbo H. Hormonal and metabolic responses to exercise in humans: effect of sensory nervous blockade. Am J Physiol. 1989 Jul;257(1 Pt 1):E95–101. doi: 10.1152/ajpendo.1989.257.1.E95. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Krogh A., Lindhard J. A comparison between voluntary and electrically induced muscular work in man. J Physiol. 1917 Jul 3;51(3):182–201. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1917.sp001795. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Leonard B., Mitchell J. H., Mizuno M., Rube N., Saltin B., Secher N. H. Partial neuromuscular blockade and cardiovascular responses to static exercise in man. J Physiol. 1985 Feb;359:365–379. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1985.sp015590. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lind A. R., McNicol G. W., Bruce R. A., Macdonald H. R., Donald K. W. The cardiovascular responses to sustained contractions of a patient with unilateral syringomyelia. Clin Sci. 1968 Aug;35(1):45–53. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- McCloskey D. I., Mitchell J. H. Reflex cardiovascular and respiratory responses originating in exercising muscle. J Physiol. 1972 Jul;224(1):173–186. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1972.sp009887. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mitchell J. H., Reardon W. C., McCloskey D. I. Reflex effects on circulation and respiration from contracting skeletal muscle. Am J Physiol. 1977 Sep;233(3):H374–H378. doi: 10.1152/ajpheart.1977.233.3.H374. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mitchell J. H., Reeves D. R., Jr, Rogers H. B., Secher N. H. Epidural anaesthesia and cardiovascular responses to static exercise in man. J Physiol. 1989 Oct;417:13–24. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1989.sp017787. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rowell L. B., Hermansen L., Blackmon J. R. Human cardiovascular and respiratory responses to graded muscle ischemia. J Appl Physiol. 1976 Nov;41(5 Pt 1):693–701. doi: 10.1152/jappl.1976.41.5.693. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Secher N. H., Ruberg-Larsen N., Binkhorst R. A., Bonde-Petersen F. Maximal oxygen uptake during arm cranking and combined arm plus leg exercise. J Appl Physiol. 1974 May;36(5):515–518. doi: 10.1152/jappl.1974.36.5.515. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


