Abstract
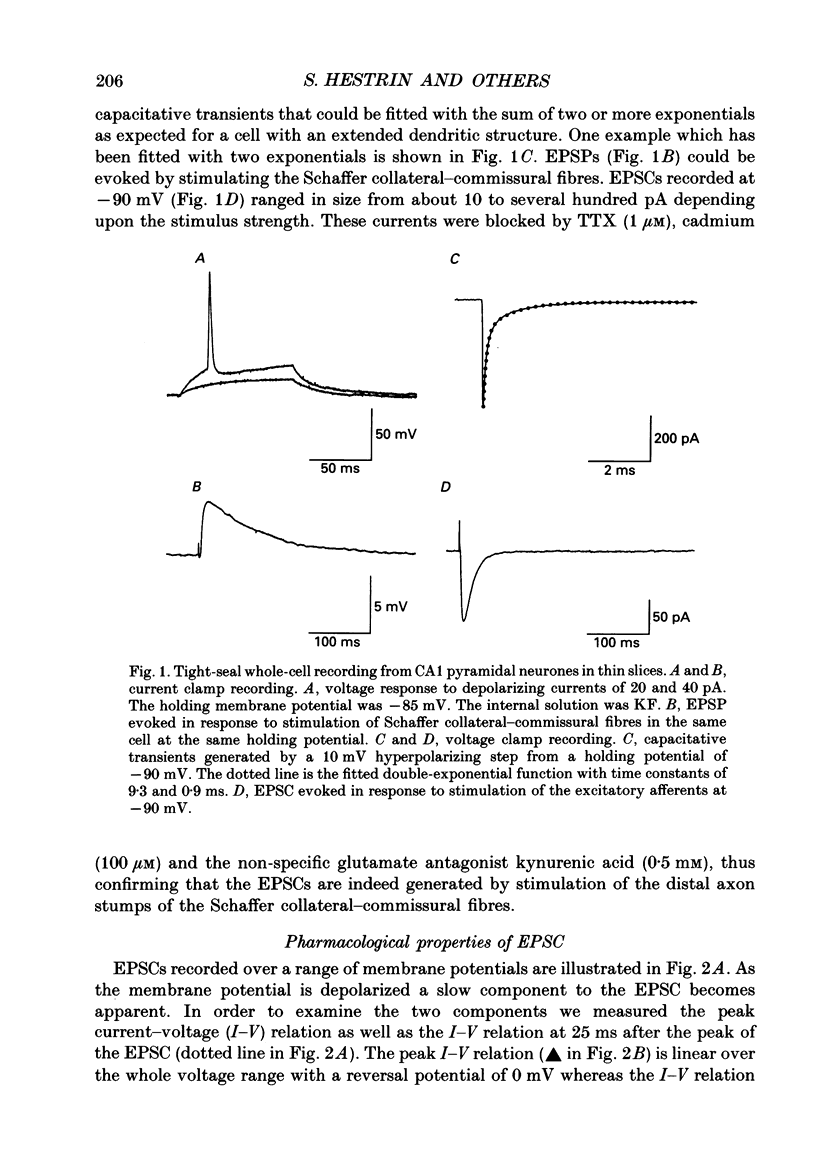
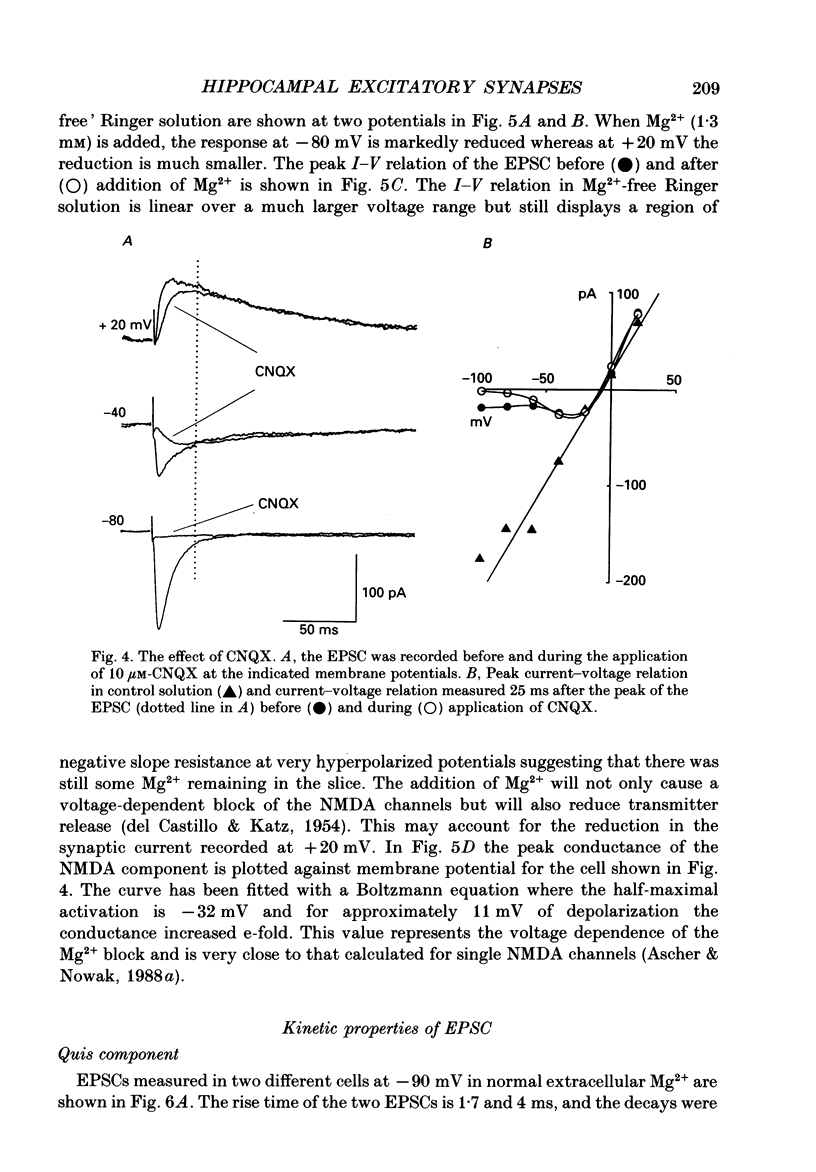
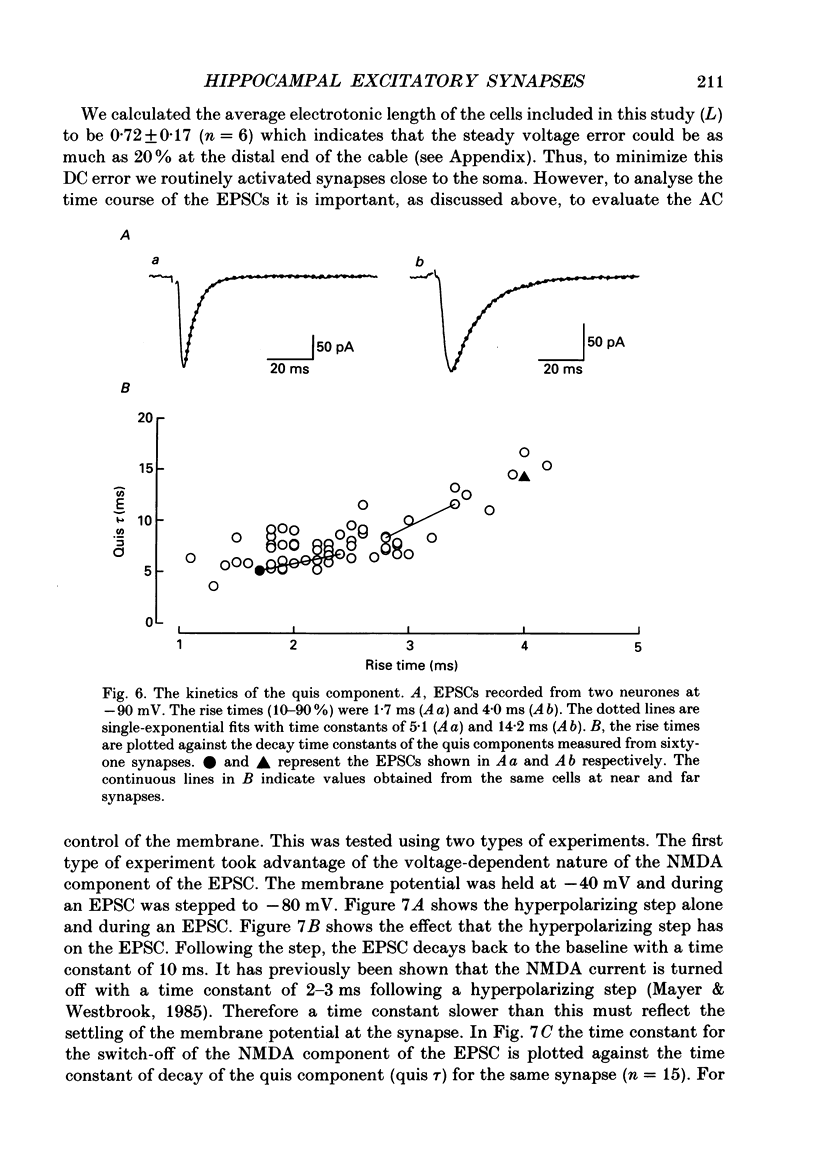
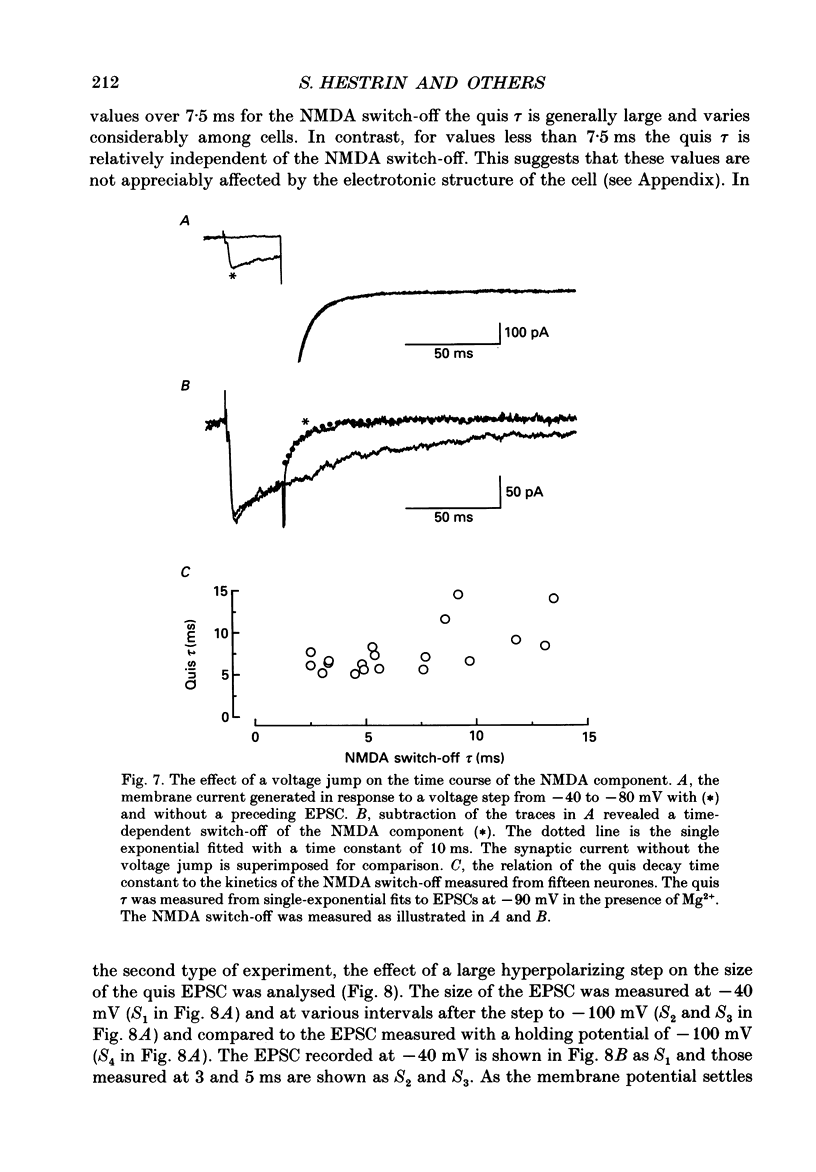
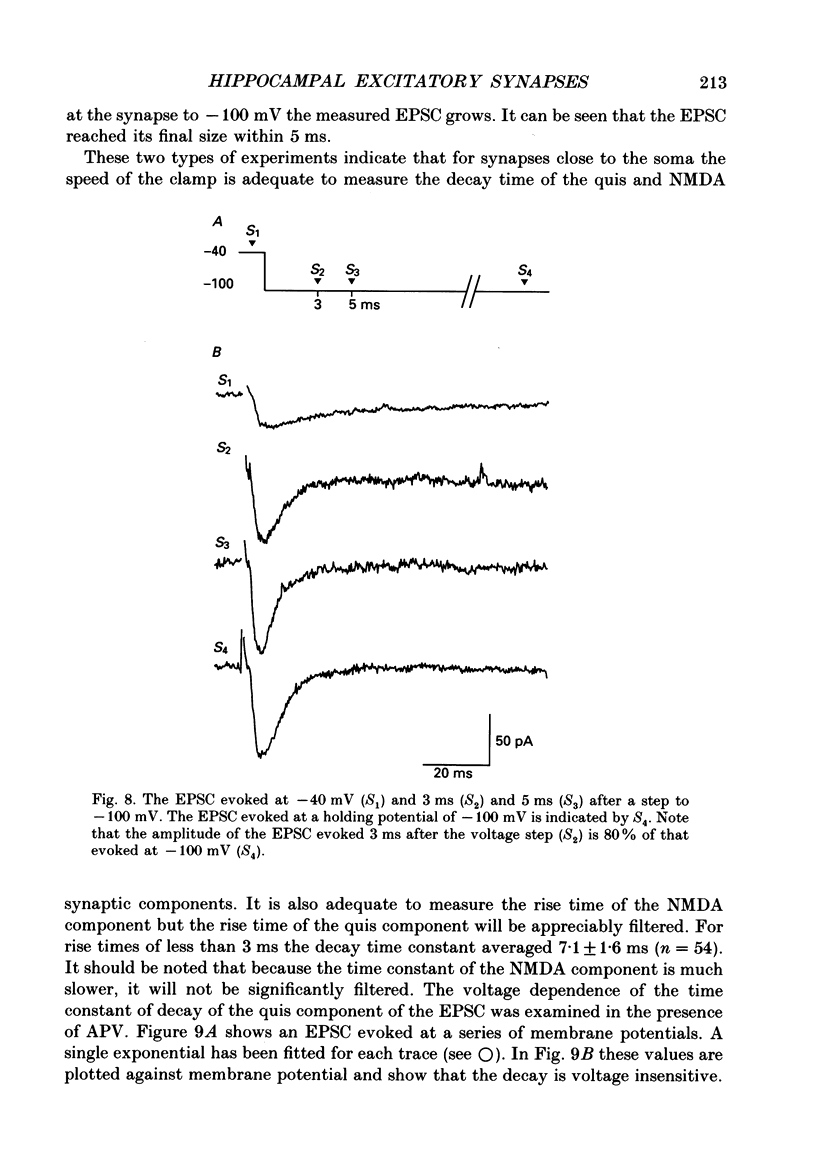
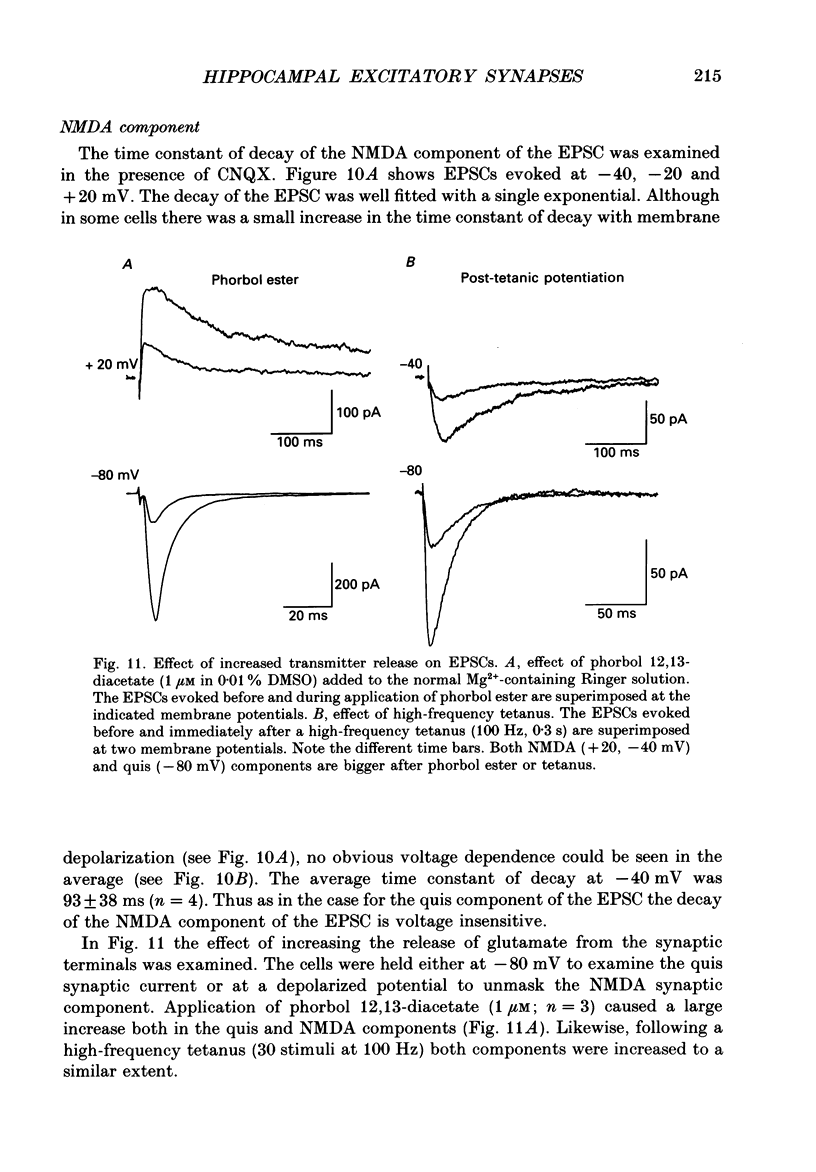
1. The pharmacological and biophysical properties of excitatory synapses in the CA1 region of the hippocampus were studied using patch electrodes and whole-cell recording from thin slices. 2. Excitatory postsynaptic currents (EPSCs) had a fast component whose amplitude was voltage insensitive and a slow component whose amplitude was voltage dependent with a region of negative slope resistance in the range of -70 to -30 mV. 3. The voltage-dependent component was abolished by the N-methyl-D-aspartate (NMDA) receptor antagonist DL-2-amino-5-phosphonovalerate (APV; 50 microM), which had no effect on the fast component. Conversely, the fast voltage-insensitive component was abolished by the non-NMDA receptor antagonist 6-cyano-7-nitroquinoxaline-2,3-dione (CNQX; 10 microM) which had no effect on the slow component. 4. In Ringer solution with no added Mg2+ the current-voltage relation of the NMDA component was linear over a much larger voltage range than in the presence of 1.3 mM-Mg2+. 5. The NMDA component of the EPSC could be switched off with a hyperpolarizing voltage step at the soma. The kinetics of this switch-off was used to estimate the speed of clamp control of the subsynaptic membrane as well as the electrotonic distance from the soma. The kinetic analysis of the EPSC was restricted to synapses which were judged to be under adequate voltage control. 6. For those synapses that were close to the soma the time constant for decay for the non-NMDA component, which was voltage insensitive, ranged from 4-8 ms. 7. The rise time for the NMDA component was 8-20 ms and the time constant for decay ranged from 60-150 ms. 8. During increased transmitter release with post-tetanic potentiation or application or phorbol esters, both components of the EPSC increased to a similar extent. 9. These experiments provide a detailed description of the dual receptor mechanism operating at hippocampal excitatory synapses. In addition, the experiments provide an electrophysiological method for estimating the electrotonic distance of synaptic inputs.
Full text
PDF
















Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Andreasen M., Lambert J. D., Jensen M. S. Effects of new non-N-methyl-D-aspartate antagonists on synaptic transmission in the in vitro rat hippocampus. J Physiol. 1989 Jul;414:317–336. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1989.sp017690. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ascher P., Bregestovski P., Nowak L. N-methyl-D-aspartate-activated channels of mouse central neurones in magnesium-free solutions. J Physiol. 1988 May;399:207–226. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1988.sp017076. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ascher P., Nowak L. Quisqualate- and kainate-activated channels in mouse central neurones in culture. J Physiol. 1988 May;399:227–245. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1988.sp017077. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ascher P., Nowak L. The role of divalent cations in the N-methyl-D-aspartate responses of mouse central neurones in culture. J Physiol. 1988 May;399:247–266. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1988.sp017078. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Blake J. F., Brown M. W., Collingridge G. L. CNQX blocks acidic amino acid induced depolarizations and synaptic components mediated by non-NMDA receptors in rat hippocampal slices. Neurosci Lett. 1988 Jun 29;89(2):182–186. doi: 10.1016/0304-3940(88)90378-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Brown T. H., Johnston D. Voltage-clamp analysis of mossy fiber synaptic input to hippocampal neurons. J Neurophysiol. 1983 Aug;50(2):487–507. doi: 10.1152/jn.1983.50.2.487. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Collingridge G. L., Herron C. E., Lester R. A. Frequency-dependent N-methyl-D-aspartate receptor-mediated synaptic transmission in rat hippocampus. J Physiol. 1988 May;399:301–312. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1988.sp017081. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Collingridge G. L., Herron C. E., Lester R. A. Synaptic activation of N-methyl-D-aspartate receptors in the Schaffer collateral-commissural pathway of rat hippocampus. J Physiol. 1988 May;399:283–300. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1988.sp017080. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Collingridge G. L., Kehl S. J., McLennan H. Excitatory amino acids in synaptic transmission in the Schaffer collateral-commissural pathway of the rat hippocampus. J Physiol. 1983 Jan;334:33–46. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1983.sp014478. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cull-Candy S. G., Howe J. R., Ogden D. C. Noise and single channels activated by excitatory amino acids in rat cerebellar granule neurones. J Physiol. 1988 Jun;400:189–222. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1988.sp017117. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cull-Candy S. G., Usowicz M. M. Multiple-conductance channels activated by excitatory amino acids in cerebellar neurons. Nature. 1987 Feb 5;325(6104):525–528. doi: 10.1038/325525a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- DEL CASTILLO J., KATZ B. The effect of magnesium on the activity of motor nerve endings. J Physiol. 1954 Jun 28;124(3):553–559. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1954.sp005128. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dale N., Roberts A. Dual-component amino-acid-mediated synaptic potentials: excitatory drive for swimming in Xenopus embryos. J Physiol. 1985 Jun;363:35–59. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1985.sp015694. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dingledine R., Hynes M. A., King G. L. Involvement of N-methyl-D-aspartate receptors in epileptiform bursting in the rat hippocampal slice. J Physiol. 1986 Nov;380:175–189. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1986.sp016279. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Edwards F. A., Konnerth A., Sakmann B., Takahashi T. A thin slice preparation for patch clamp recordings from neurones of the mammalian central nervous system. Pflugers Arch. 1989 Sep;414(5):600–612. doi: 10.1007/BF00580998. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Finkel A. S., Redman S. J. The synaptic current evoked in cat spinal motoneurones by impulses in single group 1a axons. J Physiol. 1983 Sep;342:615–632. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1983.sp014872. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Forsythe I. D., Westbrook G. L. Slow excitatory postsynaptic currents mediated by N-methyl-D-aspartate receptors on cultured mouse central neurones. J Physiol. 1988 Feb;396:515–533. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1988.sp016975. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hablitz J. J., Langmoen I. A. Excitation of hippocampal pyramidal cells by glutamate in the guinea-pig and rat. J Physiol. 1982 Apr;325:317–331. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1982.sp014152. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Honoré T., Davies S. N., Drejer J., Fletcher E. J., Jacobsen P., Lodge D., Nielsen F. E. Quinoxalinediones: potent competitive non-NMDA glutamate receptor antagonists. Science. 1988 Aug 5;241(4866):701–703. doi: 10.1126/science.2899909. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Howe J. R., Colquhoun D., Cull-Candy S. G. On the kinetics of large-conductance glutamate-receptor ion channels in rat cerebellar granule neurons. Proc R Soc Lond B Biol Sci. 1988 May 23;233(1273):407–422. doi: 10.1098/rspb.1988.0030. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jahr C. E., Stevens C. F. Glutamate activates multiple single channel conductances in hippocampal neurons. Nature. 1987 Feb 5;325(6104):522–525. doi: 10.1038/325522a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Johnston D., Brown T. H. Interpretation of voltage-clamp measurements in hippocampal neurons. J Neurophysiol. 1983 Aug;50(2):464–486. doi: 10.1152/jn.1983.50.2.464. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kauer J. A., Malenka R. C., Nicoll R. A. A persistent postsynaptic modification mediates long-term potentiation in the hippocampus. Neuron. 1988 Dec;1(10):911–917. doi: 10.1016/0896-6273(88)90148-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kay A. R., Miles R., Wong R. K. Intracellular fluoride alters the kinetic properties of calcium currents facilitating the investigation of synaptic events in hippocampal neurons. J Neurosci. 1986 Oct;6(10):2915–2920. doi: 10.1523/JNEUROSCI.06-10-02915.1986. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kiskin N. I., Krishtal O. A., Tsyndrenko AYa Excitatory amino acid receptors in hippocampal neurons: kainate fails to desensitize them. Neurosci Lett. 1986 Jan 30;63(3):225–230. doi: 10.1016/0304-3940(86)90360-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kostyuk P. G., Krishtal O. A., Pidoplichko V. I. Effect of internal fluoride and phosphate on membrane currents during intracellular dialysis of nerve cells. Nature. 1975 Oct 23;257(5528):691–693. doi: 10.1038/257691a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lester R. A., Quarum M. L., Parker J. D., Weber E., Jahr C. E. Interaction of 6-cyano-7-nitroquinoxaline-2,3-dione with the N-methyl-D-aspartate receptor-associated glycine binding site. Mol Pharmacol. 1989 May;35(5):565–570. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Magleby K. L., Stevens C. F. A quantitative description of end-plate currents. J Physiol. 1972 May;223(1):173–197. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1972.sp009840. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Malenka R. C., Ayoub G. S., Nicoll R. A. Phorbol esters enhance transmitter release in rat hippocampal slices. Brain Res. 1987 Feb 10;403(1):198–203. doi: 10.1016/0006-8993(87)90145-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mayer M. L., Vyklicky L., Jr Concanavalin A selectively reduces desensitization of mammalian neuronal quisqualate receptors. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1989 Feb;86(4):1411–1415. doi: 10.1073/pnas.86.4.1411. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mayer M. L., Westbrook G. L., Guthrie P. B. Voltage-dependent block by Mg2+ of NMDA responses in spinal cord neurones. Nature. 1984 May 17;309(5965):261–263. doi: 10.1038/309261a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mayer M. L., Westbrook G. L. Mixed-agonist action of excitatory amino acids on mouse spinal cord neurones under voltage clamp. J Physiol. 1984 Sep;354:29–53. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1984.sp015360. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mayer M. L., Westbrook G. L. The action of N-methyl-D-aspartic acid on mouse spinal neurones in culture. J Physiol. 1985 Apr;361:65–90. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1985.sp015633. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mayer M. L., Westbrook G. L. The physiology of excitatory amino acids in the vertebrate central nervous system. Prog Neurobiol. 1987;28(3):197–276. doi: 10.1016/0301-0082(87)90011-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- McCarren M., Alger B. E. Use-dependent depression of IPSPs in rat hippocampal pyramidal cells in vitro. J Neurophysiol. 1985 Feb;53(2):557–571. doi: 10.1152/jn.1985.53.2.557. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Monaghan D. T., Nguyen L., Cotman C. W. The distribution of [3H]kainate binding sites in primate hippocampus is similar to the distribution of both Ca2+-sensitive and Ca2+-insensitive [3H]kainate binding sites in rat hippocampus. Neurochem Res. 1986 Jul;11(7):1073–1082. doi: 10.1007/BF00965595. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Muller D., Joly M., Lynch G. Contributions of quisqualate and NMDA receptors to the induction and expression of LTP. Science. 1988 Dec 23;242(4886):1694–1697. doi: 10.1126/science.2904701. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nelson P. G., Pun R. Y., Westbrook G. L. Synaptic excitation in cultures of mouse spinal cord neurones: receptor pharmacology and behaviour of synaptic currents. J Physiol. 1986 Mar;372:169–190. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1986.sp016003. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nowak L., Bregestovski P., Ascher P., Herbet A., Prochiantz A. Magnesium gates glutamate-activated channels in mouse central neurones. Nature. 1984 Feb 2;307(5950):462–465. doi: 10.1038/307462a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Perkel D. H., Perkel D. J. Dendritic spines: role of active membrane in modulating synaptic efficacy. Brain Res. 1985 Jan 28;325(1-2):331–335. doi: 10.1016/0006-8993(85)90334-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Peterfreund R. A., Vale W. W. Phorbol diesters stimulate somatostatin secretion from cultured brain cells. Endocrinology. 1983 Jul;113(1):200–208. doi: 10.1210/endo-113-1-200. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pozzan T., Gatti G., Dozio N., Vicentini L. M., Meldolesi J. Ca2+-dependent and -independent release of neurotransmitters from PC12 cells: a role for protein kinase C activation? J Cell Biol. 1984 Aug;99(2):628–638. doi: 10.1083/jcb.99.2.628. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rink T. J., Sanchez A., Hallam T. J. Diacylglycerol and phorbol ester stimulate secretion without raising cytoplasmic free calcium in human platelets. Nature. 1983 Sep 22;305(5932):317–319. doi: 10.1038/305317a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shapira R., Silberberg S. D., Ginsburg S., Rahamimoff R. Activation of protein kinase C augments evoked transmitter release. Nature. 1987 Jan 1;325(6099):58–60. doi: 10.1038/325058a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tang C. M., Dichter M., Morad M. Quisqualate activates a rapidly inactivating high conductance ionic channel in hippocampal neurons. Science. 1989 Mar 17;243(4897):1474–1477. doi: 10.1126/science.2467378. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Trussell L. O., Fischbach G. D. Glutamate receptor desensitization and its role in synaptic transmission. Neuron. 1989 Aug;3(2):209–218. doi: 10.1016/0896-6273(89)90034-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Trussell L. O., Thio L. L., Zorumski C. F., Fischbach G. D. Rapid desensitization of glutamate receptors in vertebrate central neurons. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1988 Jun;85(12):4562–4566. doi: 10.1073/pnas.85.12.4562-a. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wakade A. R., Malhotra R. K., Wakade T. D. Phorbol ester, an activator of protein kinase C, enhances calcium-dependent release of sympathetic neurotransmitter. Naunyn Schmiedebergs Arch Pharmacol. 1985 Oct;331(1):122–124. doi: 10.1007/BF00498863. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Watkins J. C., Evans R. H. Excitatory amino acid transmitters. Annu Rev Pharmacol Toxicol. 1981;21:165–204. doi: 10.1146/annurev.pa.21.040181.001121. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Westerberg E., Monaghan D. T., Kalimo H., Cotman C. W., Wieloch T. W. Dynamic changes of excitatory amino acid receptors in the rat hippocampus following transient cerebral ischemia. J Neurosci. 1989 Mar;9(3):798–805. doi: 10.1523/JNEUROSCI.09-03-00798.1989. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wigström H., Gustafsson B. Facilitation of hippocampal long-lasting potentiation by GABA antagonists. Acta Physiol Scand. 1985 Sep;125(1):159–172. doi: 10.1111/j.1748-1716.1985.tb07703.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zucker R. S. Short-term synaptic plasticity. Annu Rev Neurosci. 1989;12:13–31. doi: 10.1146/annurev.ne.12.030189.000305. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zurgil N., Zisapel N. Phorbol ester and calcium act synergistically to enhance neurotransmitter release by brain neurons in culture. FEBS Lett. 1985 Jun 17;185(2):257–261. doi: 10.1016/0014-5793(85)80918-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


