Abstract
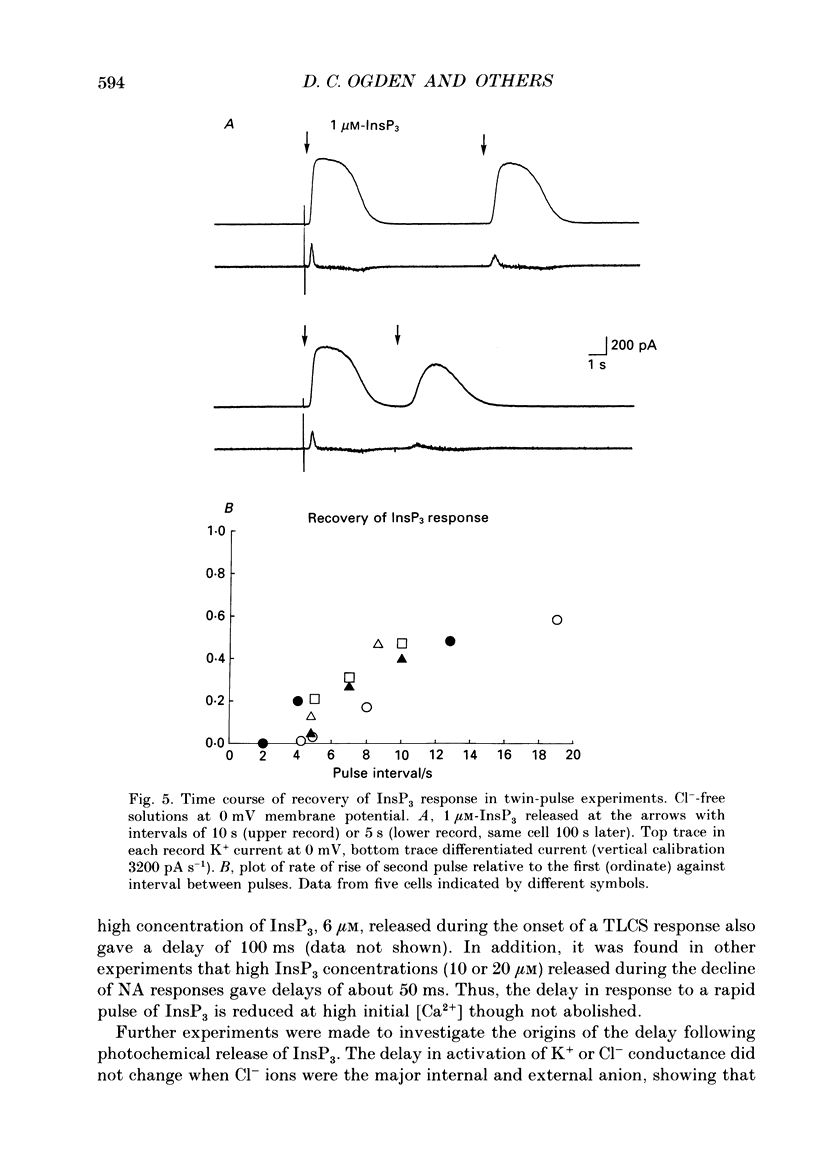
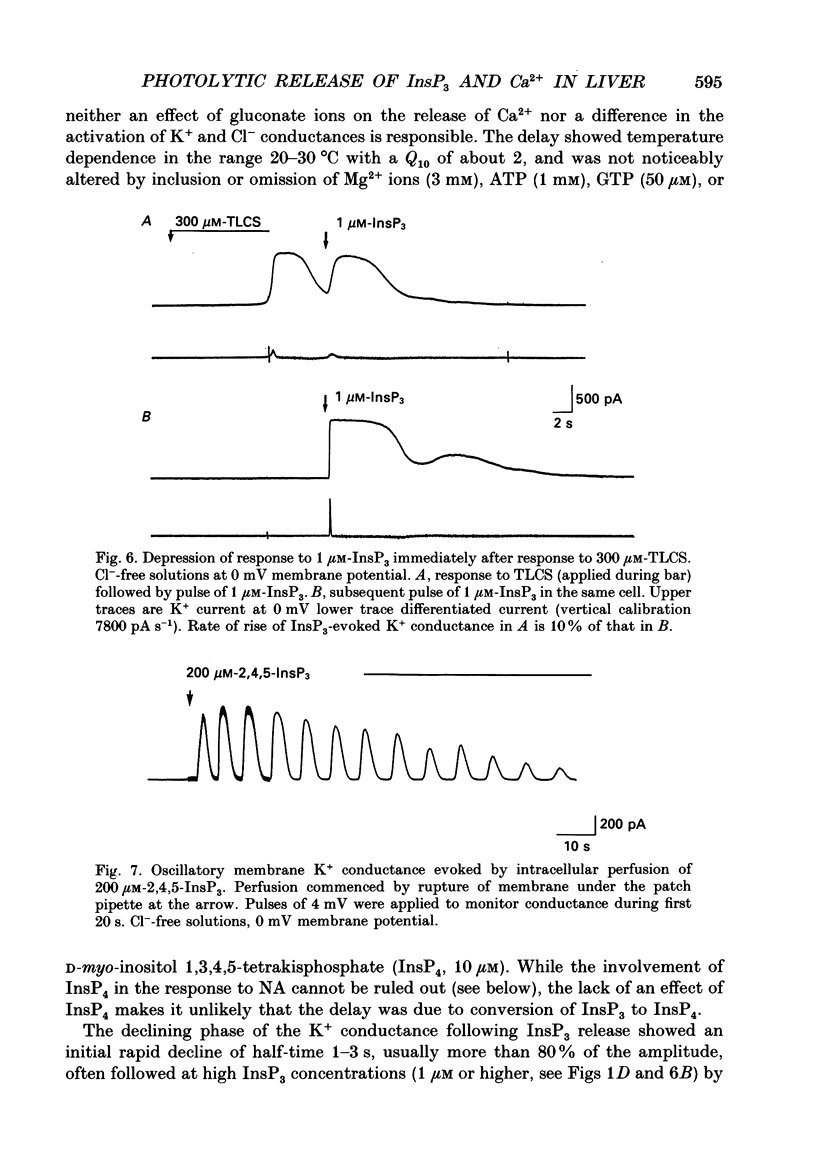
1. Guinea-pig hepatocytes respond to noradrenaline (NA, 5-10 microM) with a large membrane conductance increase to K+ and Cl-. The response has a long initial delay (range 2-30 s). Following the delay, the K+ conductance (studied in Cl(-)-free solutions) rises quickly to a peak in 1-2 s and is maintained in the continued presence of NA, though often with superimposed oscillations of conductance. The roles of intracellular Ca2+ and D-myo-inositol 1,4,5-trisphosphate (InsP3) in this complex response have been investigated by rapid photolytic release of intracellular Ca2+ (from Nitr5-Ca2+ buffers) or InsP3 from 'caged' InsP3. 2. A rapid increase of intracellular [Ca2+] produced an immediate membrane conductance increase which rose approximately exponentially to a new steady level, consistent with a direct activation of Ca2(+)-dependent ion channels. 3. Following a pulse of InsP3, conductance rose after a brief delay (range 70-1500 ms) which was shortest at high [InsP3] or if the initial cytosolic [Ca2+] had been raised above normal levels. The maximum conductance produced by InsP3 was similar in each cell to the peak recorded with NA and could be evoked by InsP3 concentrations of 0.5-1 microM. 4. The rates of rise of conductance increased with InsP3 concentration in the range 0.25-12.5 microM (range 10-90%, rise times 90-1000 ms), indicating that InsP3-evoked Ca2(+)-efflux from stores increases with InsP3 concentration in this range. 5. Photochemically released InsP3 and Ca2+ activate at physiological concentrations the same membrane conductances as NA. The results indicate that the long initial delay in NA action occurs prior to or during generation of InsP3. The mechanism of the delay and the subsequent apparently all-or-none conductance increase during NA action are discussed in terms of the high co-operativity in InsP3 and Ca2+ actions and an additional positive feedback step. 6. Evidence was found of a negative interaction between [Ca2+] and InsP3-evoked Ca2+ release. The time course of the recovery of InsP3-evoked Ca2+ release following a rise of cytosolic [Ca2+] suggests that this interaction may be important in regulating oscillatory responses of [Ca2+] during hormonal stimulation of guinea-pig hepatocytes.
Full text
PDF















Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Banks B. E., Brown C., Burgess G. M., Burnstock G., Claret M., Cocks T. M., Jenkinson D. H. Apamin blocks certain neurotransmitter-induced increases in potassium permeability. Nature. 1979 Nov 22;282(5737):415–417. doi: 10.1038/282415a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Berridge M. J., Galione A. Cytosolic calcium oscillators. FASEB J. 1988 Dec;2(15):3074–3082. doi: 10.1096/fasebj.2.15.2847949. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Berridge M. J. Inositol trisphosphate-induced membrane potential oscillations in Xenopus oocytes. J Physiol. 1988 Sep;403:589–599. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1988.sp017266. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Berthon B., Binet A., Mauger J. P., Claret M. Cytosolic free Ca2+ in isolated rat hepatocytes as measured by quin2. Effects of noradrenaline and vasopressin. FEBS Lett. 1984 Feb 13;167(1):19–24. doi: 10.1016/0014-5793(84)80824-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Burgess G. M., Claret M., Jenkinson D. H. Effects of quinine and apamin on the calcium-dependent potassium permeability of mammalian hepatocytes and red cells. J Physiol. 1981 Aug;317:67–90. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1981.sp013814. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Burgess G. M., Godfrey P. P., McKinney J. S., Berridge M. J., Irvine R. F., Putney J. W., Jr The second messenger linking receptor activation to internal Ca release in liver. Nature. 1984 May 3;309(5963):63–66. doi: 10.1038/309063a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Burgess G. M., Irvine R. F., Berridge M. J., McKinney J. S., Putney J. W., Jr Actions of inositol phosphates on Ca2+ pools in guinea-pig hepatocytes. Biochem J. 1984 Dec 15;224(3):741–746. doi: 10.1042/bj2240741. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Burgess G. M., McKinney J. S., Fabiato A., Leslie B. A., Putney J. W., Jr Calcium pools in saponin-permeabilized guinea pig hepatocytes. J Biol Chem. 1983 Dec 25;258(24):15336–15345. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Capiod T., Combettes L., Claret M. Natural bile acids mimic hormonal action on K+ conductance in guinea-pig liver cells. Pflugers Arch. 1989;414 (Suppl 1):S162–S163. doi: 10.1007/BF00582283. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Capiod T., Field A. C., Ogden D. C., Sandford C. A. Internal perfusion of guinea-pig hepatocytes with buffered Ca2+ or inositol 1,4,5-trisphosphate mimics noradrenaline activation of K+ and Cl- conductances. FEBS Lett. 1987 Jun 15;217(2):247–252. doi: 10.1016/0014-5793(87)80672-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Capiod T., Ogden D. C. Properties of membrane ion conductances evoked by hormonal stimulation of guinea-pig and rabbit isolated hepatocytes. Proc R Soc Lond B Biol Sci. 1989 Mar 22;236(1283):187–201. doi: 10.1098/rspb.1989.0020. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Capiod T., Ogden D. C. The properties of calcium-activated potassium ion channels in guinea-pig isolated hepatocytes. J Physiol. 1989 Feb;409:285–295. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1989.sp017497. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Champeil P., Combettes L., Berthon B., Doucet E., Orlowski S., Claret M. Fast kinetics of calcium release induced by myo-inositol trisphosphate in permeabilized rat hepatocytes. J Biol Chem. 1989 Oct 25;264(30):17665–17673. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Combettes L., Berthon B., Doucet E., Erlinger S., Claret M. Characteristics of bile acid-mediated Ca2+ release from permeabilized liver cells and liver microsomes. J Biol Chem. 1989 Jan 5;264(1):157–167. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Combettes L., Dumont M., Berthon B., Erlinger S., Claret M. Release of calcium from the endoplasmic reticulum by bile acids in rat liver cells. J Biol Chem. 1988 Feb 15;263(5):2299–2303. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cook N. S., Haylett D. G. Effects of apamin, quinine and neuromuscular blockers on calcium-activated potassium channels in guinea-pig hepatocytes. J Physiol. 1985 Jan;358:373–394. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1985.sp015556. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dolphin A. C., Wootton J. F., Scott R. H., Trentham D. R. Photoactivation of intracellular guanosine triphosphate analogues reduces the amplitude and slows the kinetics of voltage-activated calcium channel currents in sensory neurones. Pflugers Arch. 1988 Jun;411(6):628–636. doi: 10.1007/BF00580858. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Egashira K. Biphasic response to noradrenaline in the guinea pig liver cells. Jpn J Physiol. 1980;30(1):81–91. doi: 10.2170/jjphysiol.30.81. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Exton J. H. Role of phosphoinositides in the regulation of liver function. Hepatology. 1988 Jan-Feb;8(1):152–166. doi: 10.1002/hep.1840080129. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Field A. C., Jenkinson D. H. The effect of noradrenaline on the ion permeability of isolated mammalian hepatocytes, studied by intracellular recording. J Physiol. 1987 Nov;392:493–512. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1987.sp016793. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gray P. T. Oscillations of free cytosolic calcium evoked by cholinergic and catecholaminergic agonists in rat parotid acinar cells. J Physiol. 1988 Dec;406:35–53. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1988.sp017367. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gurney A. M., Tsien R. Y., Lester H. A. Activation of a potassium current by rapid photochemically generated step increases of intracellular calcium in rat sympathetic neurons. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1987 May;84(10):3496–3500. doi: 10.1073/pnas.84.10.3496. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hamill O. P., Marty A., Neher E., Sakmann B., Sigworth F. J. Improved patch-clamp techniques for high-resolution current recording from cells and cell-free membrane patches. Pflugers Arch. 1981 Aug;391(2):85–100. doi: 10.1007/BF00656997. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Harootunian A. T., Kao J. P., Tsien R. Y. Agonist-induced calcium oscillations in depolarized fibroblasts and their manipulation by photoreleased Ins(1,4,5)P3, Ca++, and Ca++ buffer. Cold Spring Harb Symp Quant Biol. 1988;53(Pt 2):935–943. doi: 10.1101/sqb.1988.053.01.108. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Haylett D. G. Effects of sympathomimetic amines on 45Ca efflux from liver slices. Br J Pharmacol. 1976 May;57(1):158–160. doi: 10.1111/j.1476-5381.1976.tb07668.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Haylett D. G., Jenkinson D. H. Effects of noradrenaline on potassium reflux, membrane potential and electrolyte levels in tissue slices prepared from guinea-pig liver. J Physiol. 1972 Sep;225(3):721–750. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1972.sp009966. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Irvine R. F., Moor R. M. Micro-injection of inositol 1,3,4,5-tetrakisphosphate activates sea urchin eggs by a mechanism dependent on external Ca2+. Biochem J. 1986 Dec 15;240(3):917–920. doi: 10.1042/bj2400917. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Joseph S. K., Thomas A. P., Williams R. J., Irvine R. F., Williamson J. R. myo-Inositol 1,4,5-trisphosphate. A second messenger for the hormonal mobilization of intracellular Ca2+ in liver. J Biol Chem. 1984 Mar 10;259(5):3077–3081. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kaplan J. H., Forbush B., 3rd, Hoffman J. F. Rapid photolytic release of adenosine 5'-triphosphate from a protected analogue: utilization by the Na:K pump of human red blood cell ghosts. Biochemistry. 1978 May 16;17(10):1929–1935. doi: 10.1021/bi00603a020. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Meyer T., Holowka D., Stryer L. Highly cooperative opening of calcium channels by inositol 1,4,5-trisphosphate. Science. 1988 Apr 29;240(4852):653–656. doi: 10.1126/science.2452482. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Meyer T., Stryer L. Molecular model for receptor-stimulated calcium spiking. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1988 Jul;85(14):5051–5055. doi: 10.1073/pnas.85.14.5051. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Payne R., Walz B., Levy S., Fein A. The localization of calcium release by inositol trisphosphate in Limulus photoreceptors and its control by negative feedback. Philos Trans R Soc Lond B Biol Sci. 1988 Jul 26;320(1199):359–379. doi: 10.1098/rstb.1988.0082. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pusch M., Neher E. Rates of diffusional exchange between small cells and a measuring patch pipette. Pflugers Arch. 1988 Feb;411(2):204–211. doi: 10.1007/BF00582316. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rapp G., Güth K. A low cost high intensity flash device for photolysis experiments. Pflugers Arch. 1988 Feb;411(2):200–203. doi: 10.1007/BF00582315. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rink T. J., Jacob R. Calcium oscillations in non-excitable cells. Trends Neurosci. 1989 Feb;12(2):43–46. doi: 10.1016/0166-2236(89)90133-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rodbell M., Lin M. C., Salomon Y. Evidence for interdependent action of glucagon and nucleotides on the hepatic adenylate cyclase system. J Biol Chem. 1974 Jan 10;249(1):59–65. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Storey D. J., Shears S. B., Kirk C. J., Michell R. H. Stepwise enzymatic dephosphorylation of inositol 1,4,5-trisphosphate to inositol in liver. Nature. 1984 Nov 22;312(5992):374–376. doi: 10.1038/312374a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wakui M., Potter B. V., Petersen O. H. Pulsatile intracellular calcium release does not depend on fluctuations in inositol trisphosphate concentration. Nature. 1989 May 25;339(6222):317–320. doi: 10.1038/339317a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Walker J. W., Feeney J., Trentham D. R. Photolabile precursors of inositol phosphates. Preparation and properties of 1-(2-nitrophenyl)ethyl esters of myo-inositol 1,4,5-trisphosphate. Biochemistry. 1989 Apr 18;28(8):3272–3280. doi: 10.1021/bi00434a023. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Walker J. W., Somlyo A. V., Goldman Y. E., Somlyo A. P., Trentham D. R. Kinetics of smooth and skeletal muscle activation by laser pulse photolysis of caged inositol 1,4,5-trisphosphate. Nature. 1987 May 21;327(6119):249–252. doi: 10.1038/327249a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Woods N. M., Cuthbertson K. S., Cobbold P. H. Agonist-induced oscillations in cytoplasmic free calcium concentration in single rat hepatocytes. Cell Calcium. 1987 Feb;8(1):79–100. doi: 10.1016/0143-4160(87)90038-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Worley P. F., Baraban J. M., Supattapone S., Wilson V. S., Snyder S. H. Characterization of inositol trisphosphate receptor binding in brain. Regulation by pH and calcium. J Biol Chem. 1987 Sep 5;262(25):12132–12136. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


