Abstract
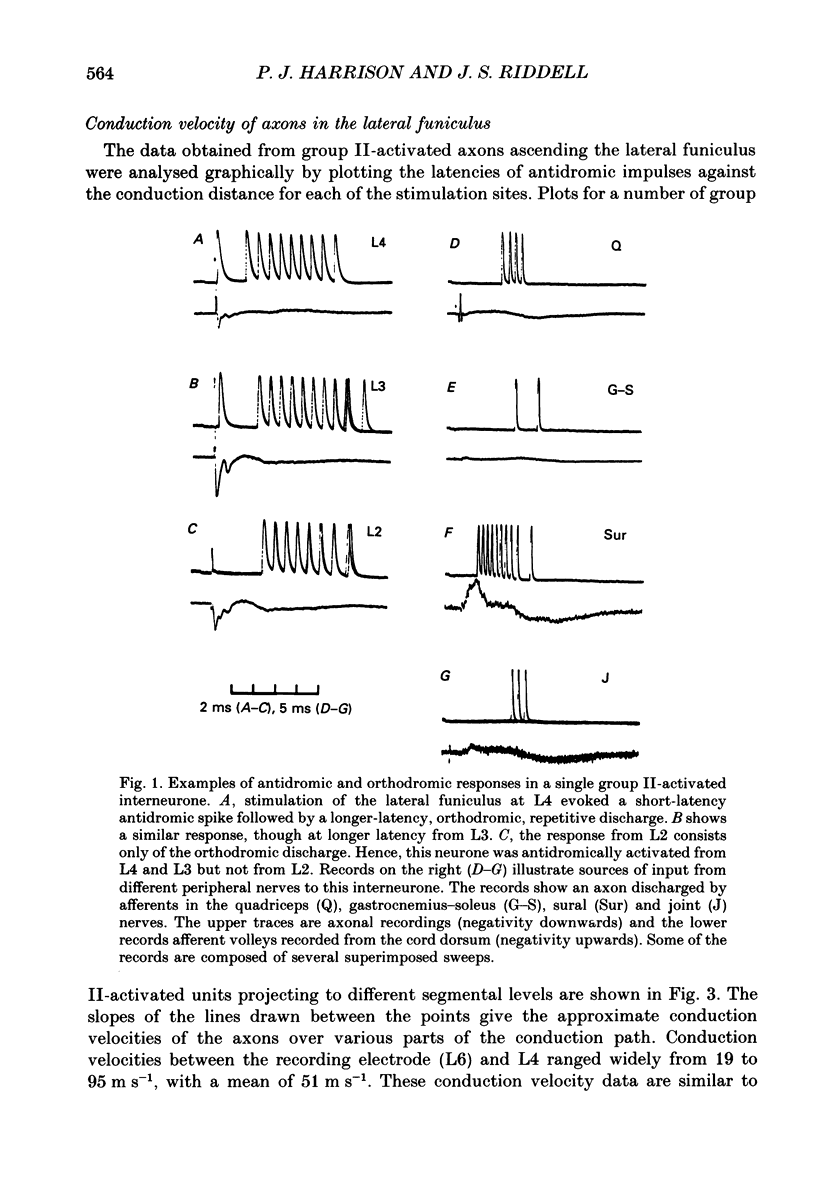
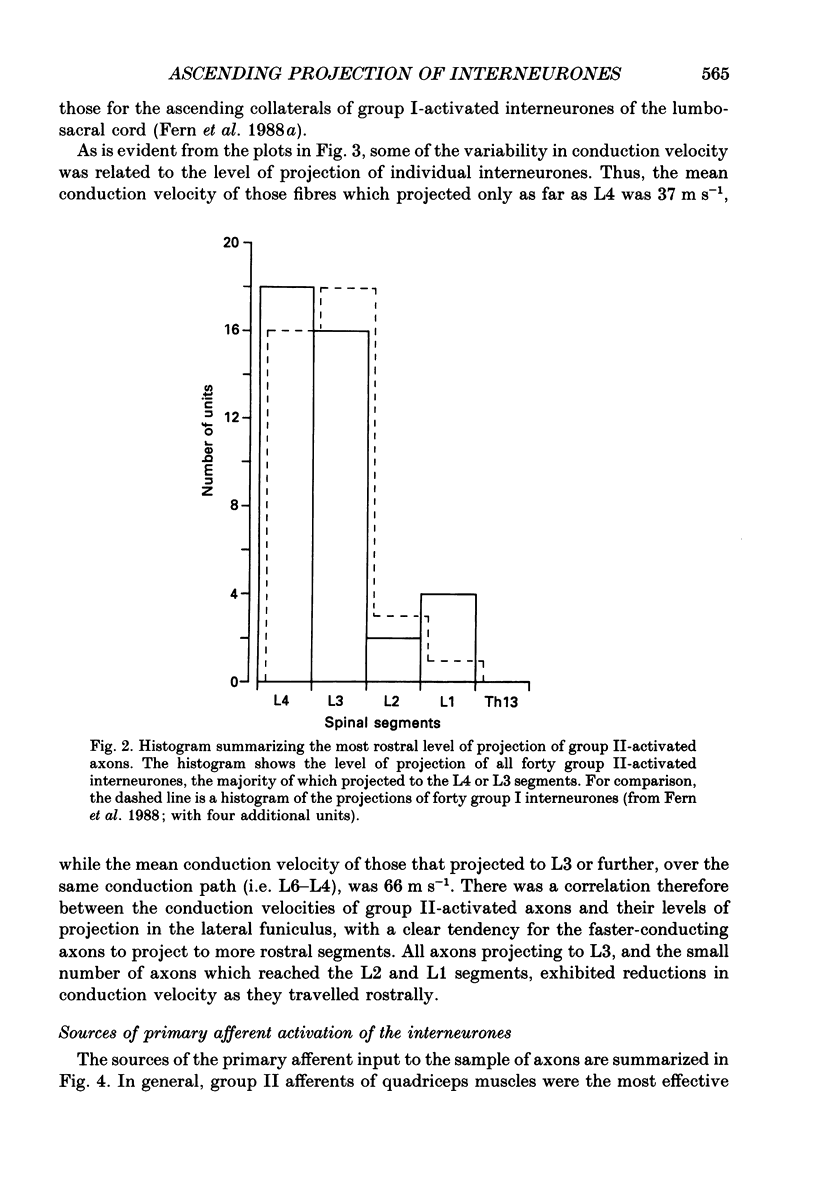
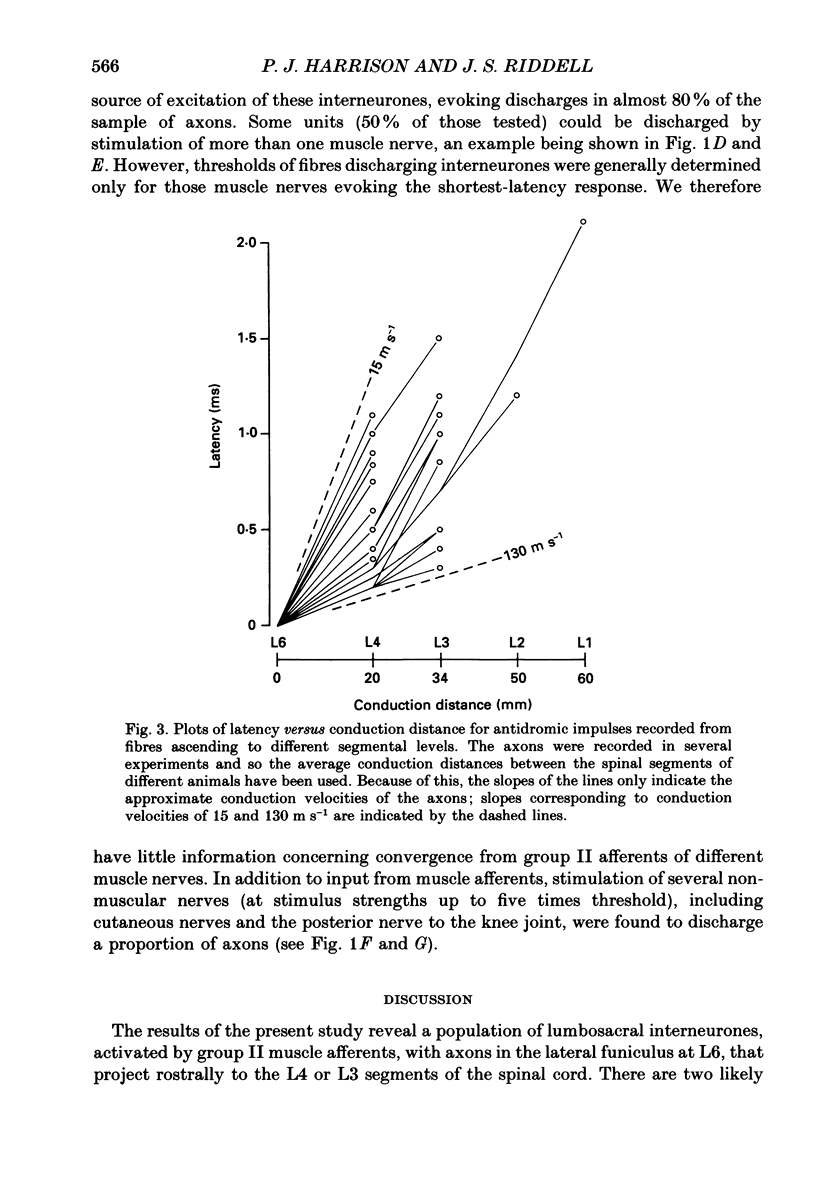
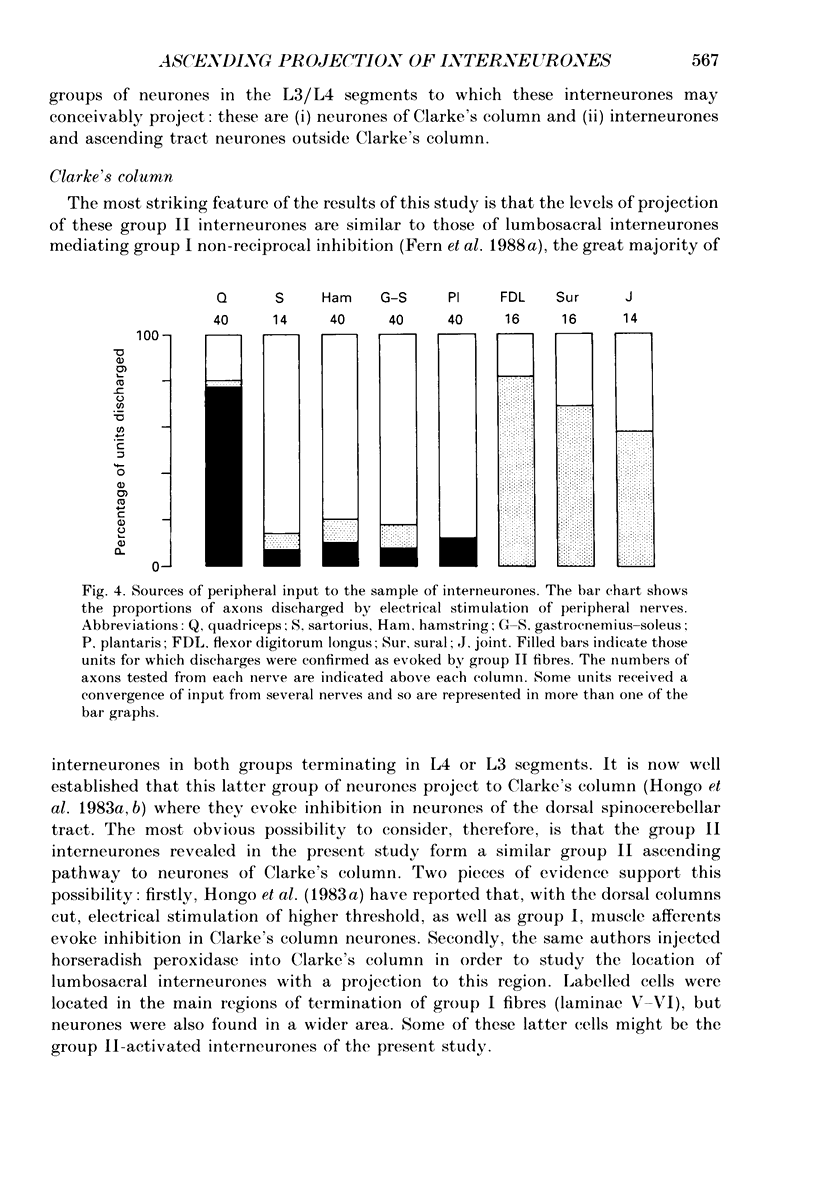
1. In anaesthetized cats, single-unit microelectrode recordings were made in the lateral funiculus at L6, from the axons of lumbosacral interneurones discharged by hindlimb group II muscle afferents. 2. The level of the ascending projection of these interneurones was investigated by antidromic activation of their axons in the lateral funiculus from different spinal levels. The majority of units encountered were found to have an ascending projection to at least the L4 level and, of these, most (85%) did not project beyond the L4 or L3 segments of the cord. 3. The axons studied were discharged by group II afferents primarily from knee extensor muscles. Some units were discharged in addition by cutaneous and/or joint afferents. 4. The implications of this ascending projection are discussed.
Full text
PDF





Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Brink E., Harrison P. J., Jankowska E., McCrea D. A., Skoog B. Post-synaptic potentials in a population of motoneurones following activity of single interneurones in the cat. J Physiol. 1983 Oct;343:341–359. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1983.sp014896. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Brink E., Jankowska E., McCrea D. A., Skoog B. Inhibitory interactions between interneurones in reflex pathways from group Ia and group Ib afferents in the cat. J Physiol. 1983 Oct;343:361–373. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1983.sp014897. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cavallari P., Edgley S. A., Jankowska E. Post-synaptic actions of midlumbar interneurones on motoneurones of hind-limb muscles in the cat. J Physiol. 1987 Aug;389:675–689. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1987.sp016677. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Edgley S. A., Gallimore C. M. The morphology and projections of dorsal horn spinocerebellar tract neurones in the cat. J Physiol. 1988 Mar;397:99–111. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1988.sp016990. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Edgley S. A., Jankowska E. An interneuronal relay for group I and II muscle afferents in the midlumbar segments of the cat spinal cord. J Physiol. 1987 Aug;389:647–674. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1987.sp016676. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Edgley S. A., Jankowska E. Field potentials generated by group II muscle afferents in the middle lumbar segments of the cat spinal cord. J Physiol. 1987 Apr;385:393–413. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1987.sp016498. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Edgley S. A., Jankowska E. Information processed by dorsal horn spinocerebellar tract neurones in the cat. J Physiol. 1988 Mar;397:81–97. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1988.sp016989. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ellaway P. H., Murphy P. R., Tripathi A. Closely coupled excitation of gamma-motoneurones by group III Muscle afferents with low mechanical threshold in the cat. J Physiol. 1982 Oct;331:481–498. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1982.sp014385. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fern R., Harrison P. J., Riddell J. S. The ascending projection of interneurones activated by group I muscle afferent fibres of the cat hindlimb. J Physiol. 1988 Nov;405:275–288. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1988.sp017333. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fukushima K., Kato M. Spinal interneurons responding to group II muscle afferent fibers in the cat. Brain Res. 1975 Jun 13;90(2):307–312. doi: 10.1016/0006-8993(75)90311-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Harrison P. J., Jami L., Jankowska E. Further evidence for synaptic actions of muscle spindle secondaries in the middle lumbar segments of the cat spinal cord. J Physiol. 1988 Aug;402:671–686. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1988.sp017228. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Harrison P. J., Jankowska E. Organization of input to the interneurones mediating group I non-reciprocal inhibition of motoneurones in the cat. J Physiol. 1985 Apr;361:403–418. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1985.sp015652. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Harrison P. J., Jankowska E. Sources of input to interneurones mediating group I non-reciprocal inhibition of motoneurones in the cat. J Physiol. 1985 Apr;361:379–401. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1985.sp015651. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hongo T., Jankowska E., Ohno T., Sasaki S., Yamashita M., Yoshida K. Inhibition of dorsal spinocerebellar tract cells by interneurones in upper and lower lumbar segments in the cat. J Physiol. 1983 Sep;342:145–159. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1983.sp014844. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hongo T., Jankowska E., Ohno T., Sasaki S., Yamashita M., Yoshida K. The same interneurones mediate inhibition of dorsal spinocerebellar tract cells and lumbar motoneurones in the cat. J Physiol. 1983 Sep;342:161–180. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1983.sp014845. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lundberg A., Malmgren K., Schomburg E. D. Reflex pathways from group II muscle afferents. 1. Distribution and linkage of reflex actions to alpha-motoneurones. Exp Brain Res. 1987;65(2):271–281. doi: 10.1007/BF00236299. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lundberg A., Malmgren K., Schomburg E. D. Reflex pathways from group II muscle afferents. 2. Functional characteristics of reflex pathways to alpha-motoneurones. Exp Brain Res. 1987;65(2):282–293. doi: 10.1007/BF00236300. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


