Abstract
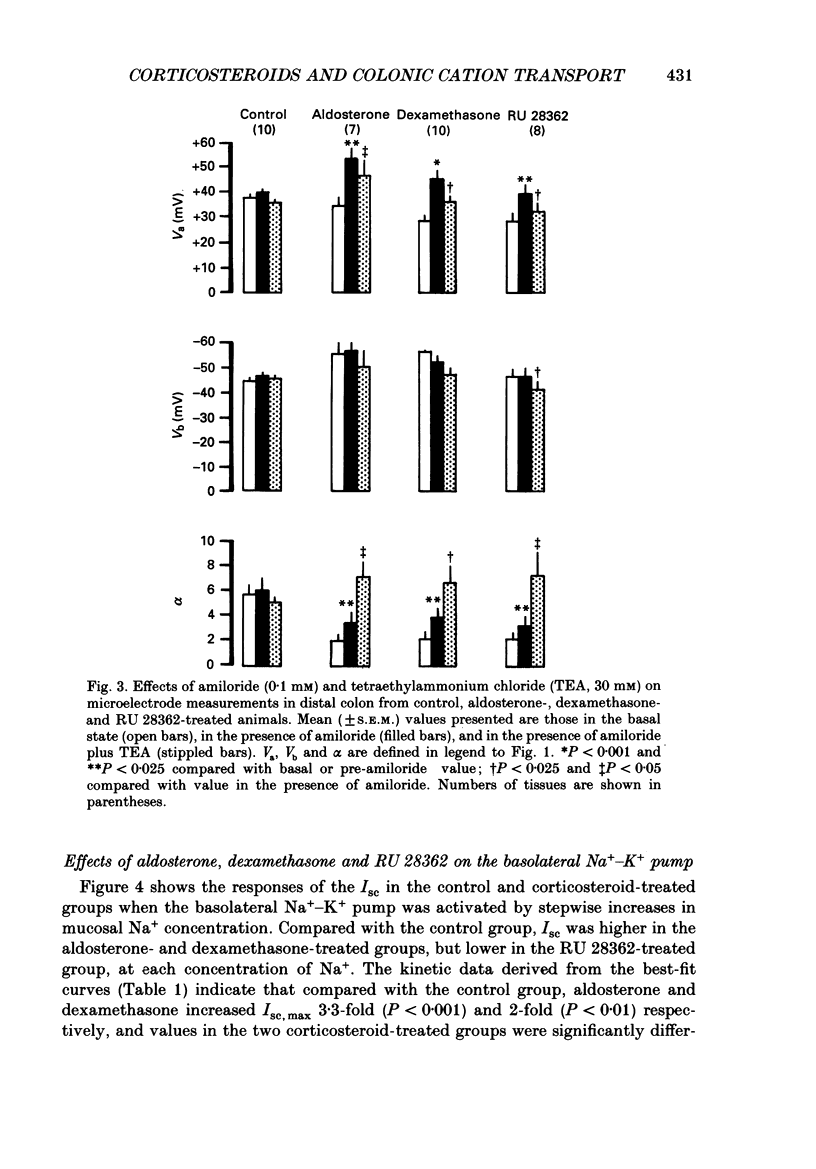
1. Conventional microelectrodes, the Na+ channel blocker amiloride (0.1 mM), and the K+ channel blocker tetraethylammonium chloride (TEA, 30 mM) were used to examine the effects of corticosteroid hormones administered in vivo on the Na+ and K+ transport properties of isolated rat distal colon. The cell membrane changes induced by aldosterone (a specific mineralocorticoid), RU 28362 (a synthetic glucocorticoid with negligible affinity for mineralocorticoid receptors), and dexamethasone (an activator of both mineralocorticoid and glucocorticoid receptors) were compared. 2. In control animals, there was no amiloride-sensitive apical Na+ conductance, and only a relatively small TEA-sensitive apical K+ conductance. 3. Hyperaldosteronism secondary to dietary Na+ depletion for 10-14 days, dexamethasone (600 micrograms 100 g-1 day-1 for 3 days), and RU 28362 (600 micrograms 100 g-1 day-1 for 3 days) induced amiloride-sensitive electrogenic Na+ transport, with the potency of aldosterone greater than dexamethasone greater than RU 28362. 4. With each corticosteroid, increased electrogenic Na+ transport reflected enhanced apical Na+ conductance, and in the case of aldosterone and dexamethasone, 3.3-fold and 2-fold increases respectively in the maximum activity of the basolateral Na+-K+ pump. In contrast, RU 28362 suppressed the maximum activity of the basolateral Na+-K+ pump by 45%. 5. All three corticosteroids enhanced the K+ conductance of the apical membrane, with the potency of aldosterone greater than dexamethasone greater than RU 28362. 6. Co-administration of spironolactone (5 mg 100 g-1 day-1) inhibited the effects of aldosterone on Na+ and K+ transport, but in dexamethasone-treated animals spironolactone resulted in a pattern of response similar to that found in RU 28362-treated animals. 7. The results support the view that mineralocorticoid receptors mediate changes in colonic Na+ and K+ transport which differ quantitatively and qualitatively from those mediated by glucocorticoid receptors. Dexamethasone and similar 'glucocorticoids' activate both types of receptor, with an overall epithelial response which mimics that induced by aldosterone.
Full text
PDF


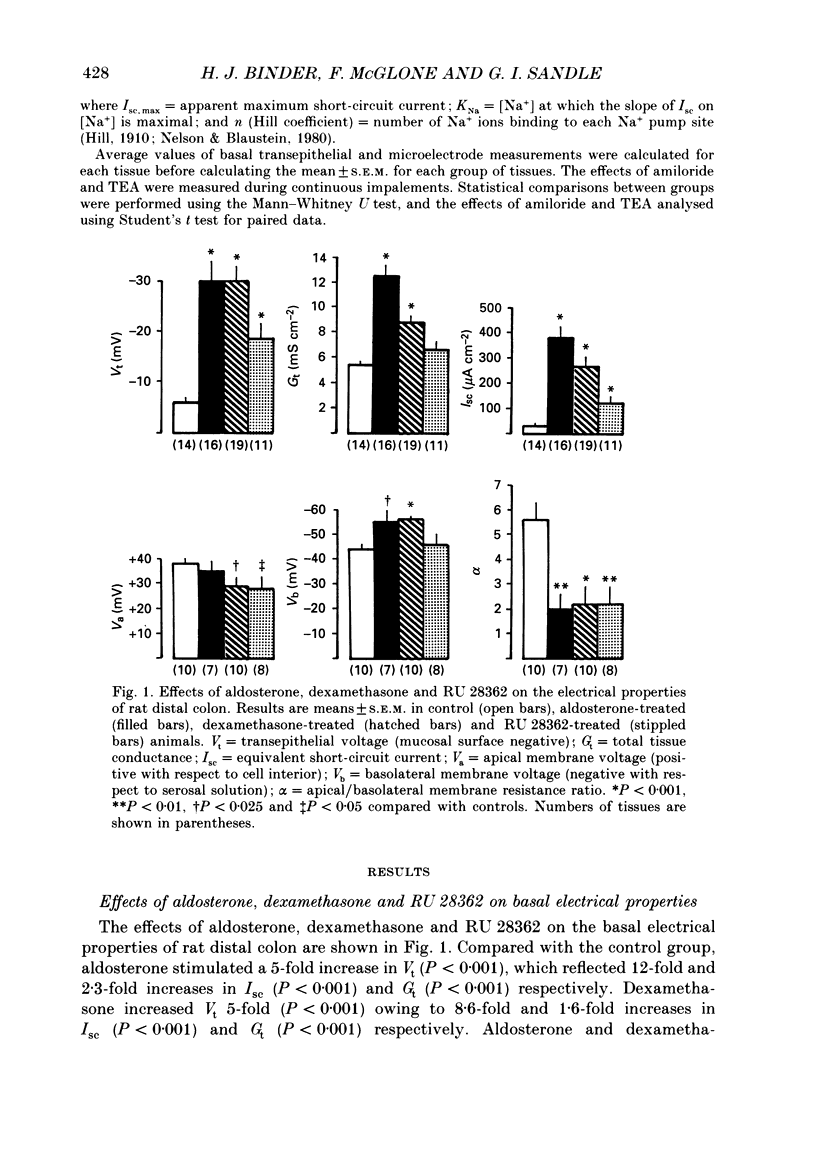

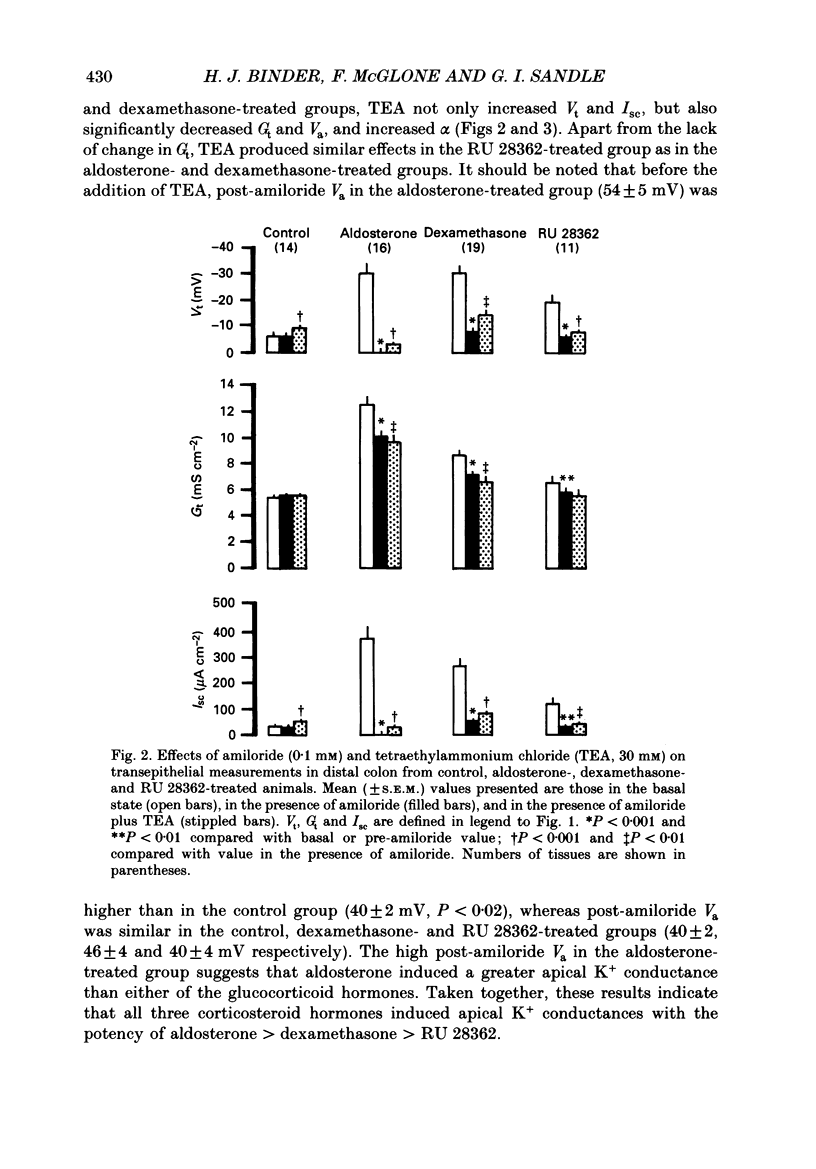
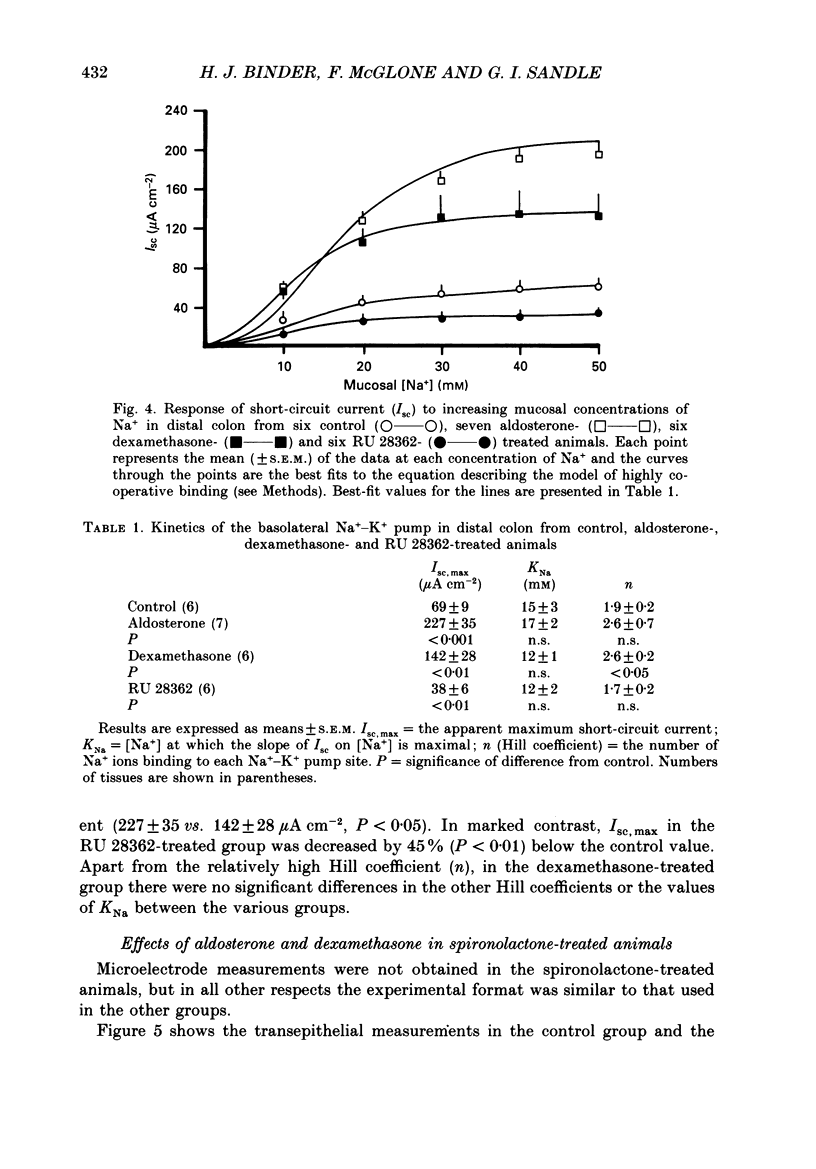
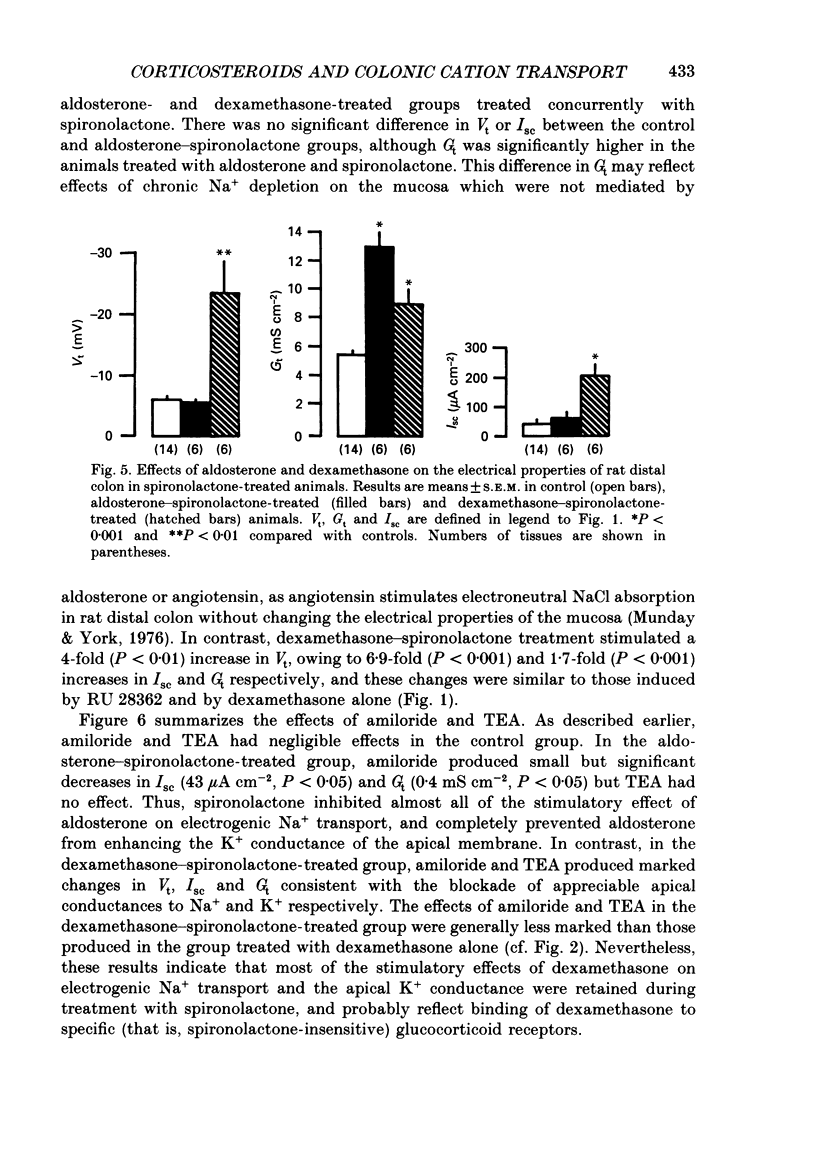






Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
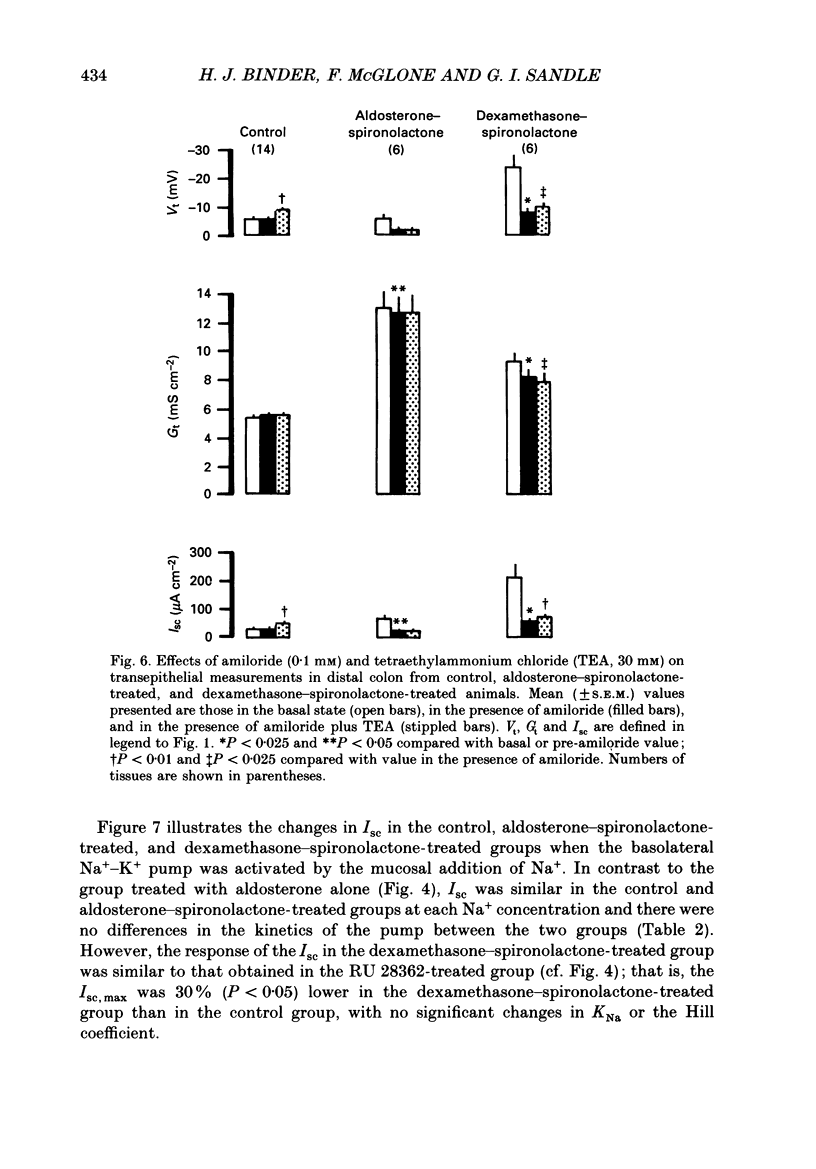
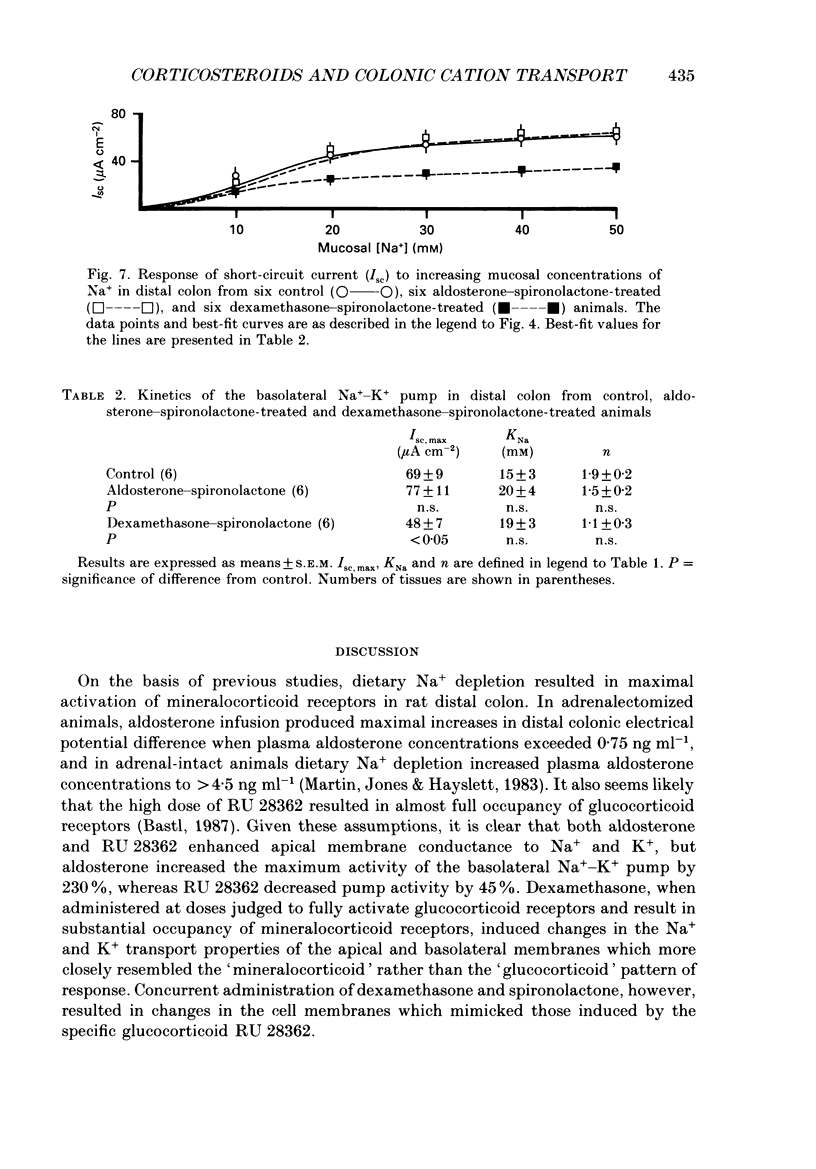
- Bastl C. P., Barnett C. A., Schmidt T. J., Litwack G. Glucocorticoid stimulation of sodium absorption in colon epithelia is mediated by corticosteroid IB receptor. J Biol Chem. 1984 Jan 25;259(2):1186–1195. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bastl C. P. Regulation of cation transport by low doses of glucocorticoids in in vivo adrenalectomized rat colon. J Clin Invest. 1987 Aug;80(2):348–356. doi: 10.1172/JCI113079. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Beaumont K., Fanestil D. D. Characterization of rat brain aldosterone receptors reveals high affinity for corticosterone. Endocrinology. 1983 Dec;113(6):2043–2051. doi: 10.1210/endo-113-6-2043. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Binder H. J. Effect of dexamethasone on electrolyte transport in the large intestine of the rat. Gastroenterology. 1978 Aug;75(2):212–217. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Binder H. J., White A., Whiting D., Hayslett J. Demonstration of specific high affinity receptors for aldosterone in cytosol of rat colon. Endocrinology. 1986 Feb;118(2):628–631. doi: 10.1210/endo-118-2-628. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bridges R. J., Rummel W., Schreiner J. In vitro effects of dexamethasone on sodium transport across rat colon. J Physiol. 1987 Feb;383:69–77. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1987.sp016396. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Charney A. N., Kinsey M. D., Myers L., Gainnella R. A., Gots R. E. Na+-K+-activated adenosine triphosphatase and intestinal electrolyte transport. Effect of adrenal steroids. J Clin Invest. 1975 Sep;56(3):653–660. doi: 10.1172/JCI108135. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Charney A. N., Wallach J., Ceccarelli S., Donowitz M., Costenbader C. L. Effects of spironolactone and amiloride on corticosteroid-induced changes in colonic function. Am J Physiol. 1981 Oct;241(4):G300–G305. doi: 10.1152/ajpgi.1981.241.4.G300. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Edelman I. S. Receptors and effectors in hormone action on the kidney. Am J Physiol. 1981 Oct;241(4):F333–F339. doi: 10.1152/ajprenal.1981.241.4.F333. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Edmonds C. J. Amiloride sensitivity of the transepithelial electrical potential and of sodium and potassium transport in rat distal colon in vivo. J Physiol. 1981;313:547–559. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1981.sp013681. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Foster E. S., Hayslett J. P., Binder H. J. Mechanism of active potassium absorption and secretion in the rat colon. Am J Physiol. 1984 May;246(5 Pt 1):G611–G617. doi: 10.1152/ajpgi.1984.246.5.G611. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Frizzell R. A., Schultz S. G. Effect of aldosterone on ion transport by rabbit colon in vitro. J Membr Biol. 1978 Feb 6;39(1):1–26. doi: 10.1007/BF01872752. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Halevy J., Budinger M. E., Hayslett J. P., Binder H. J. Role of aldosterone in the regulation of sodium and chloride transport in the distal colon of sodium-depleted rats. Gastroenterology. 1986 Nov;91(5):1227–1233. doi: 10.1016/s0016-5085(86)80021-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Halm D. R., Dawson D. C. Aldosterone does not stimulate the Na:K pump in isolated turtle colon. Pflugers Arch. 1985 Mar;403(3):236–239. doi: 10.1007/BF00583593. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jorkasky D., Cox M., Feldman G. M. Differential effects of corticosteroids on Na+ transport in rat distal colon in vitro. Am J Physiol. 1985 Apr;248(4 Pt 1):G424–G431. doi: 10.1152/ajpgi.1985.248.4.G424. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kashgarian M., Taylor C. R., Binder H. J., Hayslett J. P. Amplification of cell membrane surface in potassium adaptation. Lab Invest. 1980 Jun;42(6):581–588. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lan N. C., Graham B., Bartter F. C., Baxter J. D. Binding of steroids to mineralocorticoid receptors: implications for in vivo occupancy by glucocorticoids. J Clin Endocrinol Metab. 1982 Feb;54(2):332–342. doi: 10.1210/jcem-54-2-332. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Martin R. S., Jones W. J., Hayslett J. P. Animal model to study the effect of adrenal hormones on epithelial function. Kidney Int. 1983 Sep;24(3):386–391. doi: 10.1038/ki.1983.171. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Marusic E. T., Hayslett J. P., Binder H. J. Corticosteroid-binding studies in cytosol of colonic mucosa of the rat. Am J Physiol. 1981 Jun;240(6):G417–G423. doi: 10.1152/ajpgi.1981.240.6.G417. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nelson M. T., Blaustein M. P. Properties of sodium pumps in internally perfused barnacle muscle fibers. J Gen Physiol. 1980 Feb;75(2):183–206. doi: 10.1085/jgp.75.2.183. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sandle G. I., Foster E. S., Lewis S. A., Binder H. J., Hayslett J. P. The electrical basis for enhanced potassium secretion in rat distal colon during dietary potassium loading. Pflugers Arch. 1985 Apr;403(4):433–439. doi: 10.1007/BF00589258. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sandle G. I., Hayslett J. P., Binder H. J. Effect of chronic hyperaldosteronism on the electrophysiology of rat distal colon. Pflugers Arch. 1984 May;401(1):22–26. doi: 10.1007/BF00581528. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sandle G. I., Hayslett J. P., Binder H. J. Effect of glucocorticoids on rectal transport in normal subjects and patients with ulcerative colitis. Gut. 1986 Mar;27(3):309–316. doi: 10.1136/gut.27.3.309. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sandle G. I., McGlone F. Acute effects of dexamethasone on cation transport in colonic epithelium. Gut. 1987 Jun;28(6):701–706. doi: 10.1136/gut.28.6.701. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sandle G. I., McGlone F., Davies R. J. Electrophysiology of rat distal colon after partial nephrectomy. Implications for K transport. Pflugers Arch. 1988 Jul;412(1-2):172–182. doi: 10.1007/BF00583747. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sandle G. I., McGlone F. Segmental variability of membrane conductances in rat and human colonic epithelia. Implications for Na, K and Cl transport. Pflugers Arch. 1987 Sep;410(1-2):173–180. doi: 10.1007/BF00581912. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schmidt T. J., Litwack G. Activation of the glucocorticoid-receptor complex. Physiol Rev. 1982 Oct;62(4 Pt 1):1131–1192. doi: 10.1152/physrev.1982.62.4.1131. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schon D. A., Silva P., Hayslett J. P. Mechanism of potassium excretion in renal insufficiency. Am J Physiol. 1974 Dec;227(6):1323–1330. doi: 10.1152/ajplegacy.1974.227.6.1323. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Teutsch G., Costerousse G., Deraedt R., Benzoni J., Fortin M., Philibert D. 17 alpha-alkynyl-11 beta, 17-dihydroxyandrostane derivatives : a new class of potent glucocorticoids. Steroids. 1981 Dec;38(6):651–665. doi: 10.1016/0039-128x(81)90084-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Will P. C., DeLisle R. C., Cortright R. N., Hopfer U. Induction of amiloride-sensitive sodium transport in the intestines by adrenal steroids. Ann N Y Acad Sci. 1981;372:64–78. doi: 10.1111/j.1749-6632.1981.tb15458.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wills N. K., Lewis S. A., Eaton D. C. Active and passive properties of rabbit descending colon: a microelectrode and nystatin study. J Membr Biol. 1979 Mar 28;45(1-2):81–108. doi: 10.1007/BF01869296. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


