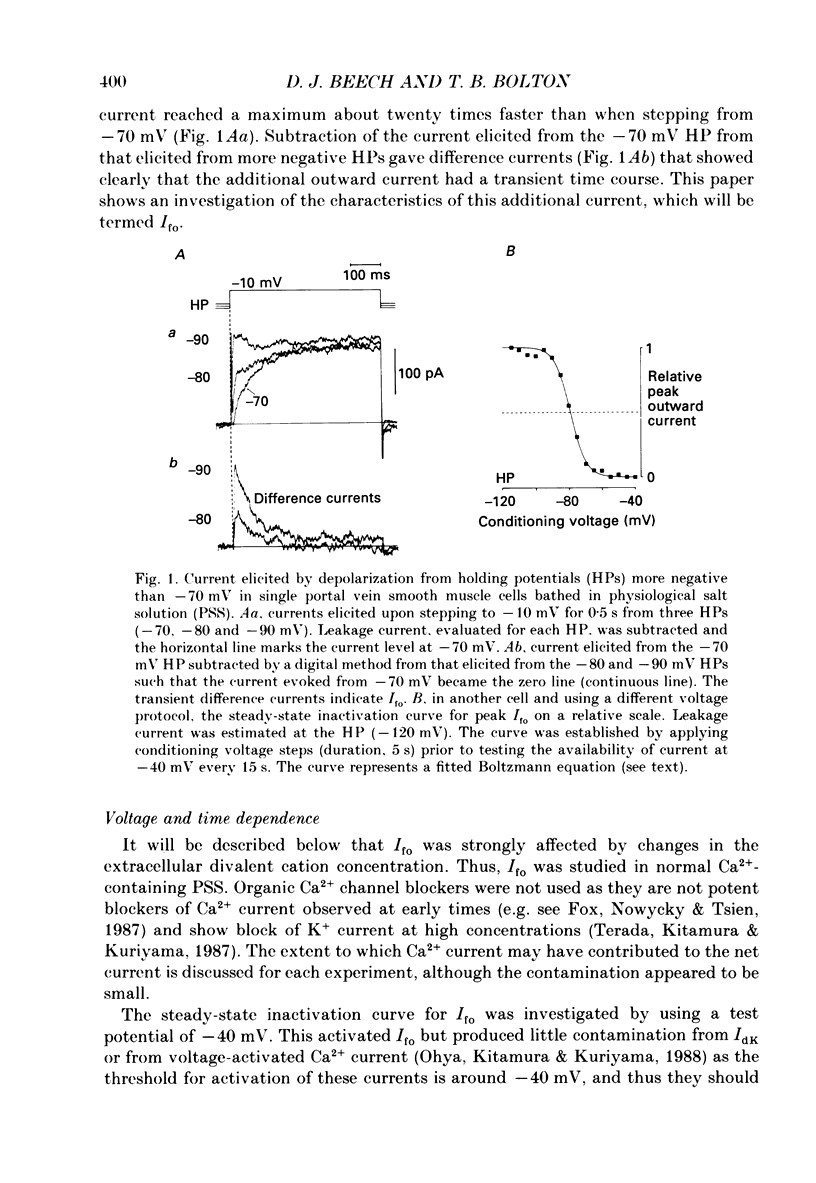
Abstract
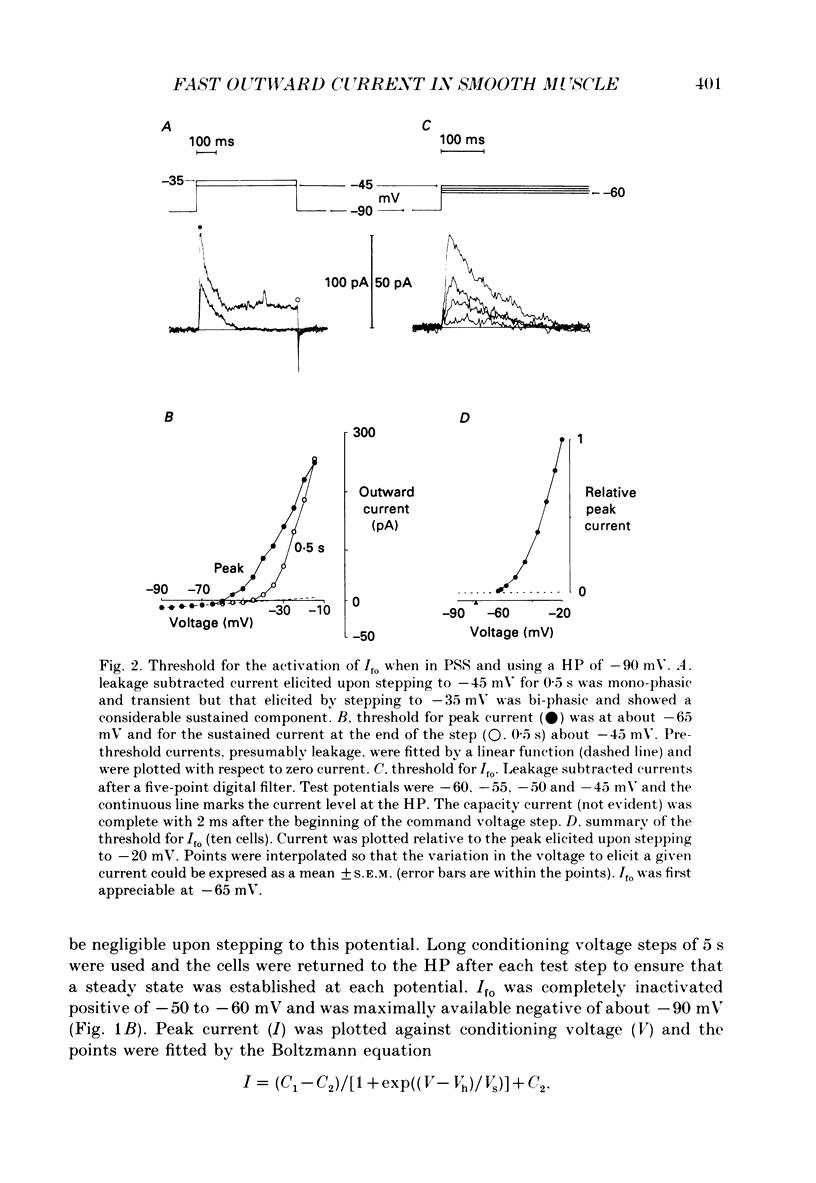
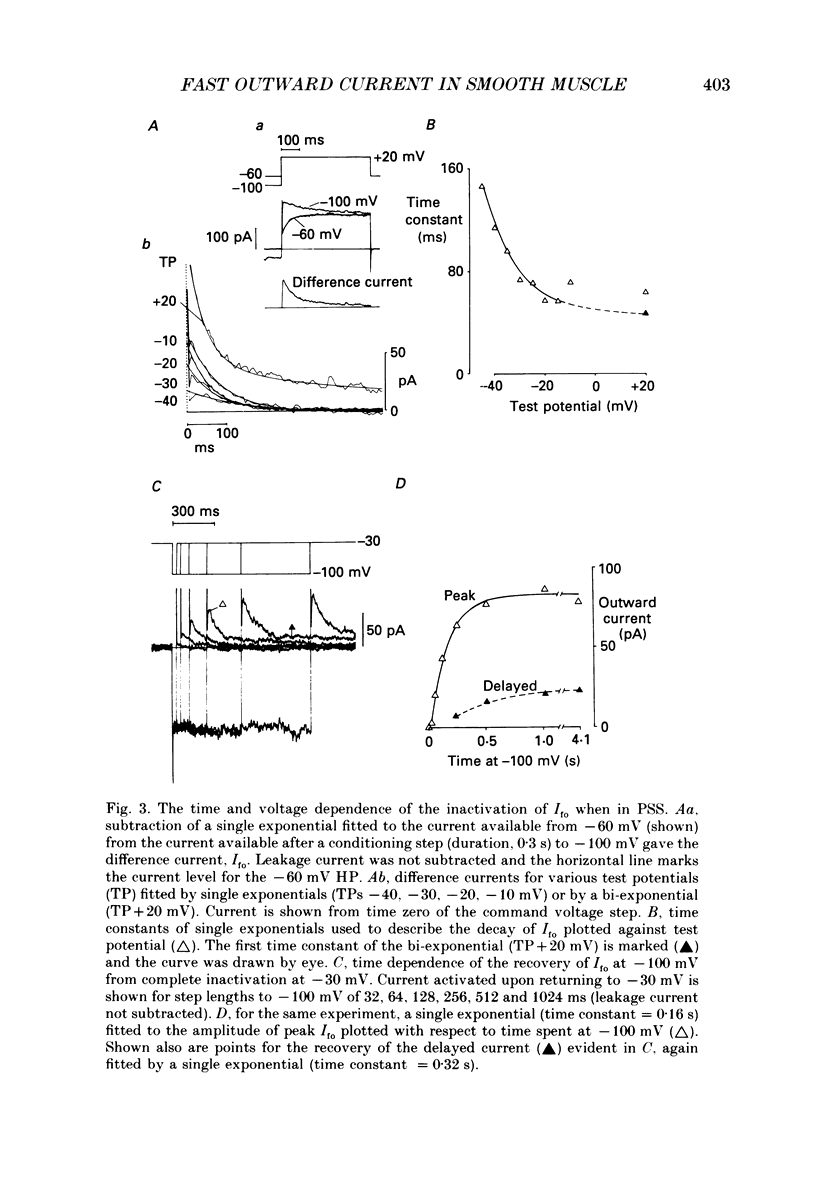
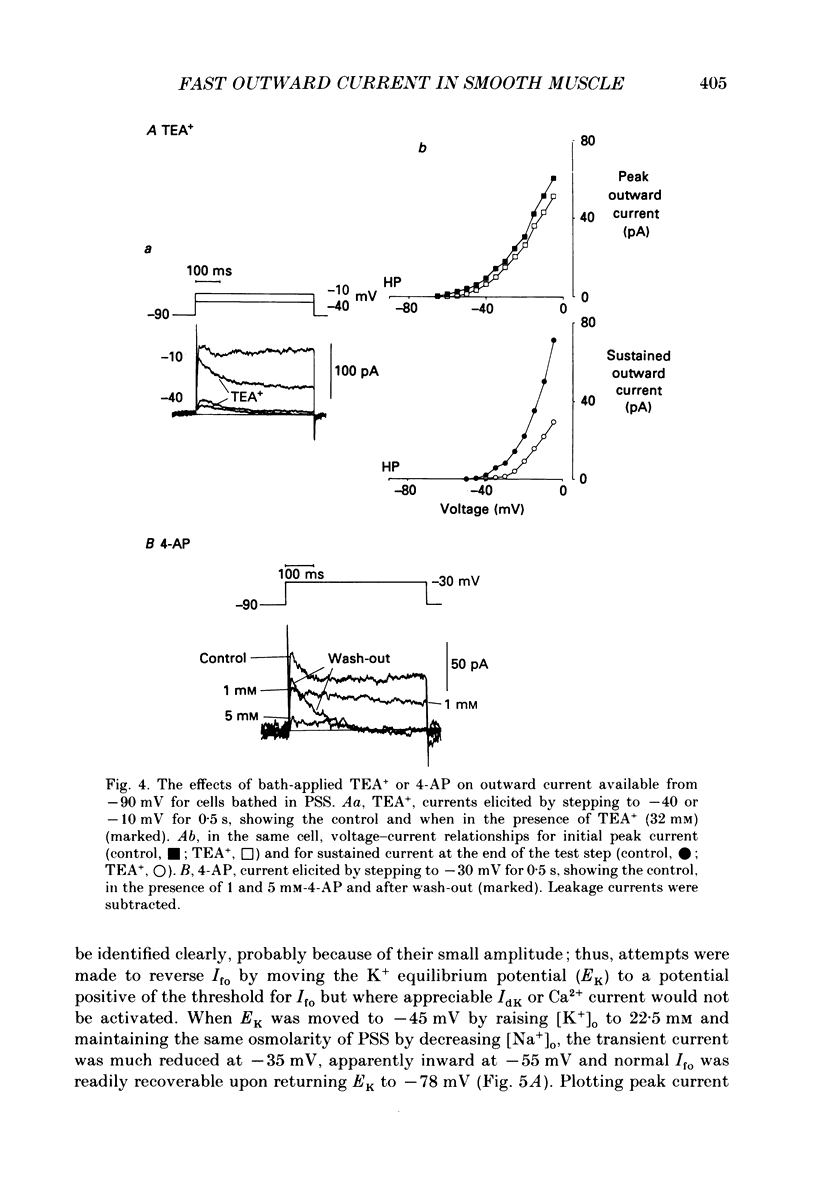
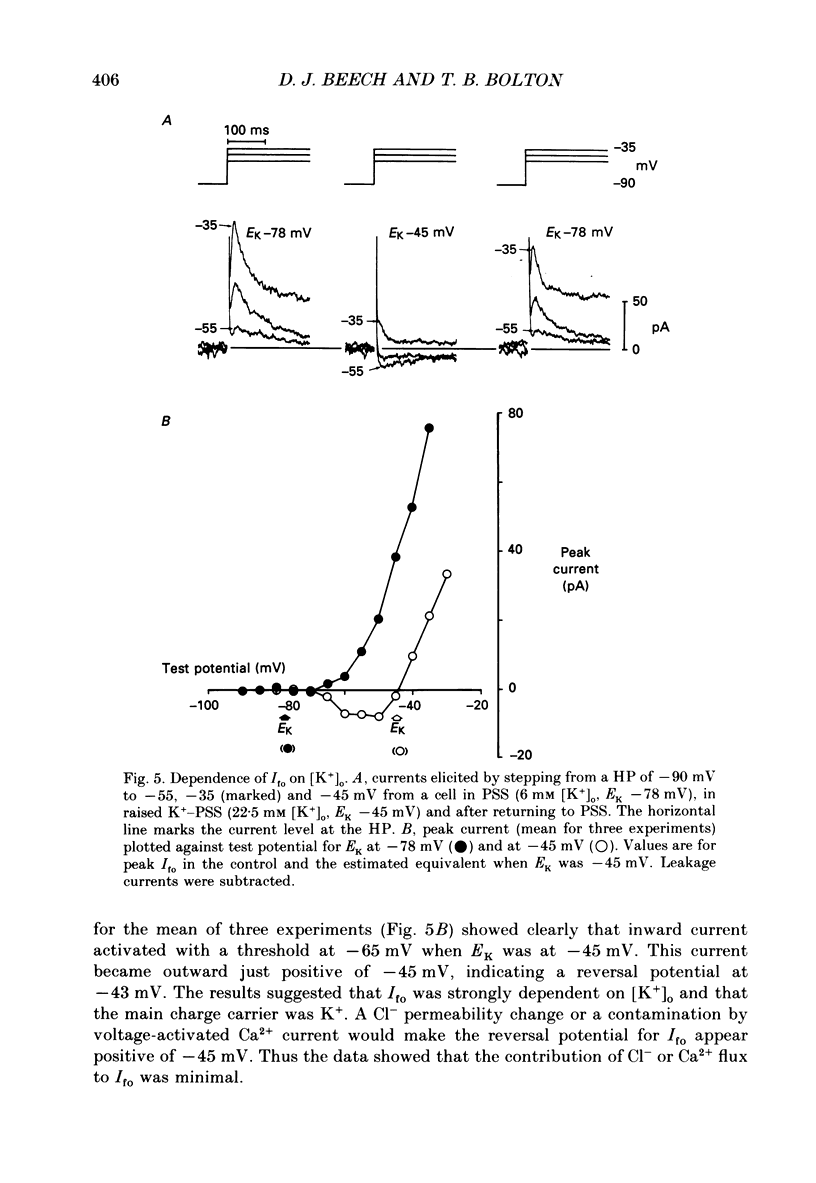
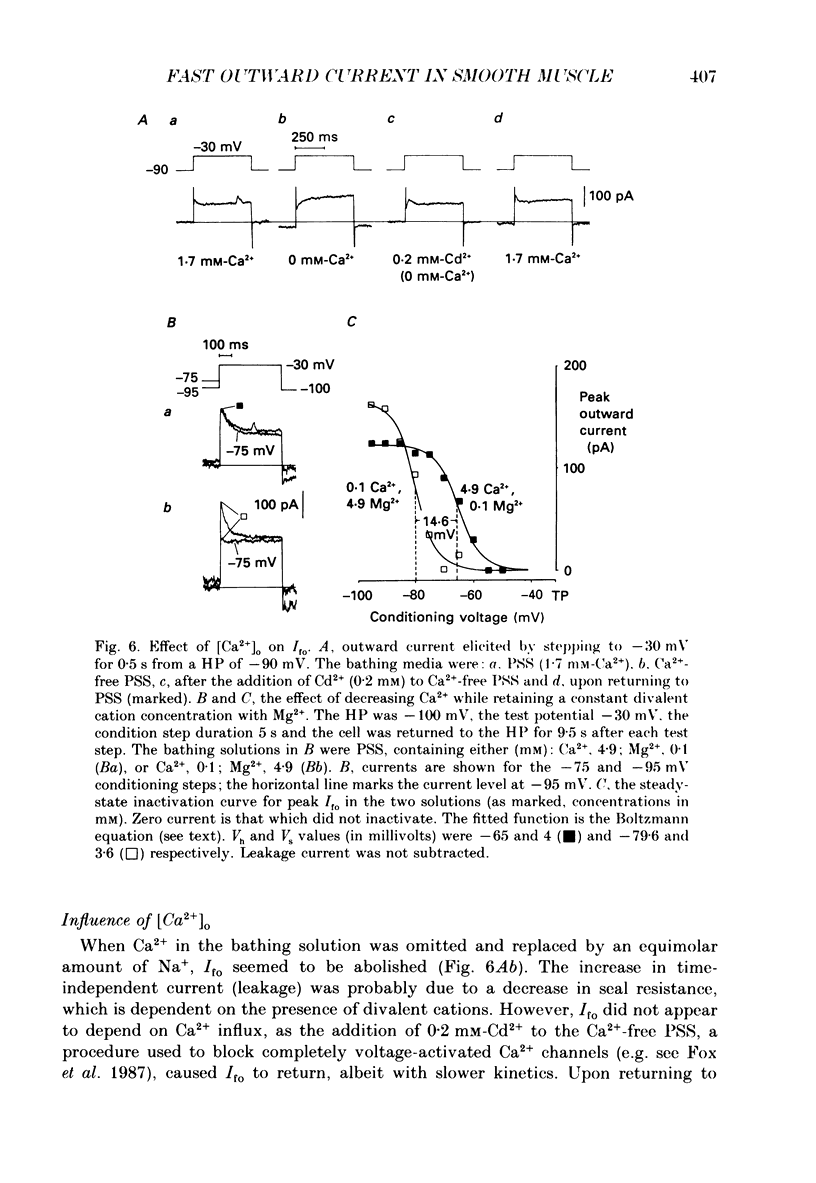
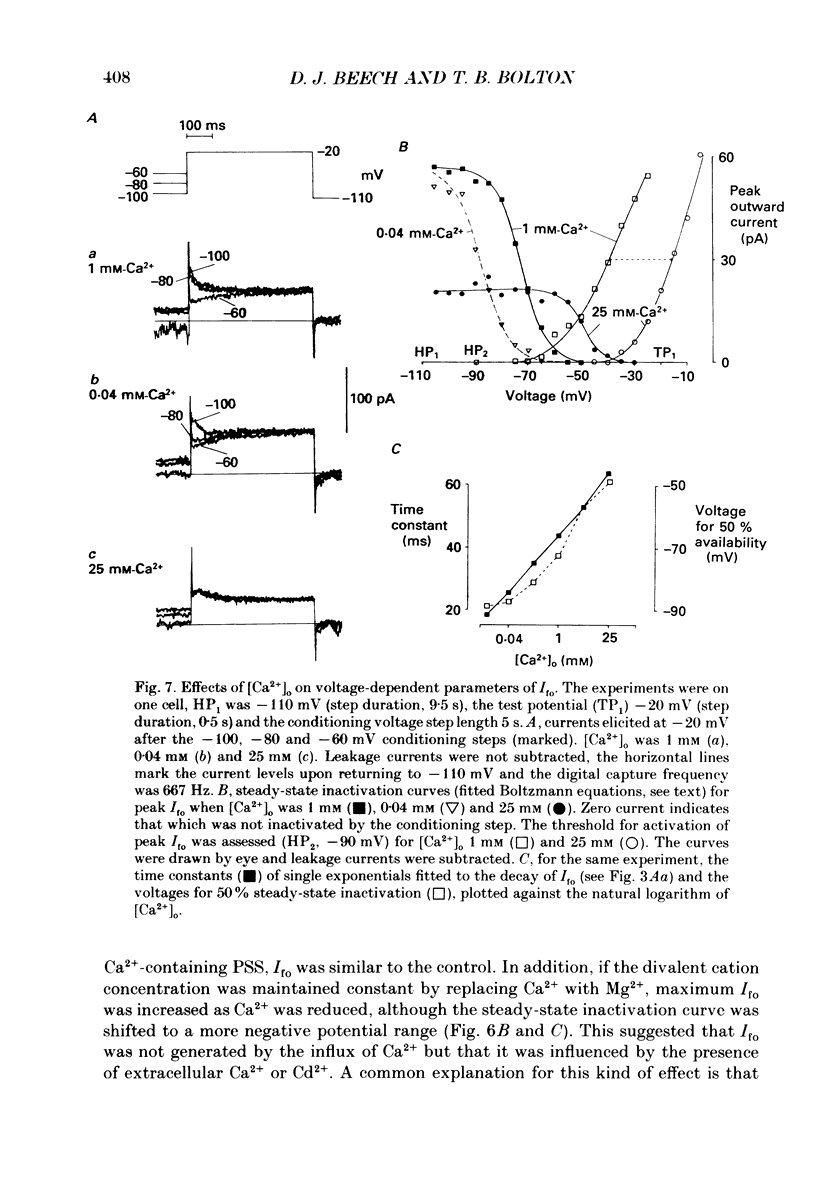
1. Single smooth muscle cells were isolated enzymatically from the rabbit portal vein. They were voltage-clamped at room temperature using the whole-cell configuration of the patch-clamp technique. 2. When cells were bathed in physiological salt solution, depolarization from a holding potential of -70 mV elicited a time-dependent outward current which reached a maximum within 0.2-0.5 s, but when a more negative holding potential was used, an additional outward current could be activated. The current (Ifo) developed rapidly, was transient and seemed to be carried by potassium ions (K+). 3. The steady-state inactivation plot for Ifo was steeply voltage-dependent between -90 and -60 mV, current being 50% inactivated at -78 mV. The activation threshold was around -65 mV. The activation and inactivation kinetics were fast and voltage-dependent. When the test potential was -35 mV, peak current occurred after about 15 ms and the decay was complete within 250 ms. Recovery from inactivation was maximal after 1 s at -100 mV but was about five times slower at -70 mV. 4. The outward current Ifo was blocked completely by 4-aminopyridine (5 mM) or phencyclidine (0.1 mM), but was insensitive to tetraethylammonium ions (32 mM), apamin (0.1 microM), charybdotoxin from the venom of Leiurus quinquestriatus (0.1 microM), toxin-I from the venom of Dendroaspis polylepis (1 microM) or the putative K+ channel opener, cromakalim (10 microM). 5. The steady-state inactivation range and activation threshold, kinetics of activation and inactivation all showed a marked dependence on the concentration of divalent cations in the bathing solution. This effect was consistent with the hypothesis that Ifo was affected by membrane surface potential. The current did not seem to be Ca2+-activated. 6. Ifo closely resembled the A-current which has been described previously in neurones but not in smooth muscle.
Full text
PDF










Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Adams D. J., Smith S. J., Thompson S. H. Ionic currents in molluscan soma. Annu Rev Neurosci. 1980;3:141–167. doi: 10.1146/annurev.ne.03.030180.001041. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Adams P. R., Brown D. A., Constanti A. M-currents and other potassium currents in bullfrog sympathetic neurones. J Physiol. 1982 Sep;330:537–572. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1982.sp014357. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- BULBRING E. Correlation between membrane potential, spike discharge and tension in smooth muscle. J Physiol. 1955 Apr 28;128(1):200–221. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1955.sp005299. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- BULBRING E., KURIYAMA H. Effects of changes in the external sodium and calcium concentrations on spontaneous electrical activity in smooth muscle of guinea-pig taenia coli. J Physiol. 1963 Apr;166:29–58. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1963.sp007089. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Beech D. J., Bolton T. B. The effects of tetraethylammonium ions, 4-aminopyridine or quinidine on K+-currents in single smooth muscle cells of the rabbit portal vein. Biomed Biochim Acta. 1987;46(8-9):S673–S676. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Belluzzi O., Sacchi O., Wanke E. A fast transient outward current in the rat sympathetic neurone studied under voltage-clamp conditions. J Physiol. 1985 Jan;358:91–108. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1985.sp015542. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Brown D. A., Constanti A., Adams P. R. Ca-activated potassium current in vertebrate sympathetic neurons. Cell Calcium. 1983 Dec;4(5-6):407–420. doi: 10.1016/0143-4160(83)90017-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Castle N. A., Strong P. N. Identification of two toxins from scorpion (Leiurus quinquestriatus) venom which block distinct classes of calcium-activated potassium channel. FEBS Lett. 1986 Dec 1;209(1):117–121. doi: 10.1016/0014-5793(86)81095-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Connor J. A. Slow repetitive activity from fast conductance changes in neurons. Fed Proc. 1978 Jun;37(8):2139–2145. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Connor J. A., Stevens C. F. Voltage clamp studies of a transient outward membrane current in gastropod neural somata. J Physiol. 1971 Feb;213(1):21–30. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1971.sp009365. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- FRANKENHAEUSER B., HODGKIN A. L. The action of calcium on the electrical properties of squid axons. J Physiol. 1957 Jul 11;137(2):218–244. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1957.sp005808. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fox A. P., Nowycky M. C., Tsien R. W. Kinetic and pharmacological properties distinguishing three types of calcium currents in chick sensory neurones. J Physiol. 1987 Dec;394:149–172. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1987.sp016864. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Galvan M., Sedlmeir C. Outward currents in voltage-clamped rat sympathetic neurones. J Physiol. 1984 Nov;356:115–133. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1984.sp015456. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gustafsson B., Galvan M., Grafe P., Wigström H. A transient outward current in a mammalian central neurone blocked by 4-aminopyridine. Nature. 1982 Sep 16;299(5880):252–254. doi: 10.1038/299252a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- HAGIWARA S., KUSANO K., SAITO N. Membrane changes of Onchidium nerve cell in potassium-rich media. J Physiol. 1961 Mar;155:470–489. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1961.sp006640. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Halliwell J. V., Othman I. B., Pelchen-Matthews A., Dolly J. O. Central action of dendrotoxin: selective reduction of a transient K conductance in hippocampus and binding to localized acceptors. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1986 Jan;83(2):493–497. doi: 10.1073/pnas.83.2.493. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hamill O. P., Marty A., Neher E., Sakmann B., Sigworth F. J. Improved patch-clamp techniques for high-resolution current recording from cells and cell-free membrane patches. Pflugers Arch. 1981 Aug;391(2):85–100. doi: 10.1007/BF00656997. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hamilton T. C., Weir S. W., Weston A. H. Comparison of the effects of BRL 34915 and verapamil on electrical and mechanical activity in rat portal vein. Br J Pharmacol. 1986 May;88(1):103–111. doi: 10.1111/j.1476-5381.1986.tb09476.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Holman M. E., Kasby C. B., Suthers M. B., Wilson J. A. Some properties of the smooth muscle of rabbit portal vein. J Physiol. 1968 May;196(1):111–132. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1968.sp008498. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Josephson I. R., Sanchez-Chapula J., Brown A. M. Early outward current in rat single ventricular cells. Circ Res. 1984 Feb;54(2):157–162. doi: 10.1161/01.res.54.2.157. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kuriyama H., Oshima K., Sakamoto Y. The membrane properties of the smooth muscle of the guinea-pig portal vein in isotonic and hypertonic solutions. J Physiol. 1971 Aug;217(1):179–199. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1971.sp009565. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mayer M. L., Sugiyama K. A modulatory action of divalent cations on transient outward current in cultured rat sensory neurones. J Physiol. 1988 Feb;396:417–433. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1988.sp016970. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nakao K., Inoue R., Yamanaka K., Kitamura K. Actions of quinidine and apamin on after-hyperpolarization of the spike in circular smooth muscle cells of the guinea-pig ileum. Naunyn Schmiedebergs Arch Pharmacol. 1986 Dec;334(4):508–513. doi: 10.1007/BF00569394. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Neher E. Two fast transient current components during voltage clamp on snail neurons. J Gen Physiol. 1971 Jul;58(1):36–53. doi: 10.1085/jgp.58.1.36. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Numann R. E., Wadman W. J., Wong R. K. Outward currents of single hippocampal cells obtained from the adult guinea-pig. J Physiol. 1987 Dec;393:331–353. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1987.sp016826. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ohya Y., Kitamura K., Kuriyama H. Cellular calcium regulates outward currents in rabbit intestinal smooth muscle cell. Am J Physiol. 1987 Apr;252(4 Pt 1):C401–C410. doi: 10.1152/ajpcell.1987.252.4.C401. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ohya Y., Kitamura K., Kuriyama H. Regulation of calcium current by intracellular calcium in smooth muscle cells of rabbit portal vein. Circ Res. 1988 Feb;62(2):375–383. doi: 10.1161/01.res.62.2.375. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Salkoff L. Drosophila mutants reveal two components of fast outward current. Nature. 1983 Mar 17;302(5905):249–251. doi: 10.1038/302249a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Siegelbaum S. A., Tsien R. W. Calcium-activated transient outward current in calf cardiac Purkinje fibres. J Physiol. 1980 Feb;299:485–506. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1980.sp013138. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stanfield P. R. Tetraethylammonium ions and the potassium permeability of excitable cells. Rev Physiol Biochem Pharmacol. 1983;97:1–67. doi: 10.1007/BFb0035345. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stansfeld C. E., Marsh S. J., Halliwell J. V., Brown D. A. 4-Aminopyridine and dendrotoxin induce repetitive firing in rat visceral sensory neurones by blocking a slowly inactivating outward current. Neurosci Lett. 1986 Mar 14;64(3):299–304. doi: 10.1016/0304-3940(86)90345-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Taylor P. S. Selectivity and patch measurements of A-current channels in Helix aspersa neurones. J Physiol. 1987 Jul;388:437–447. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1987.sp016623. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Thompson S. H. Three pharmacologically distinct potassium channels in molluscan neurones. J Physiol. 1977 Feb;265(2):465–488. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1977.sp011725. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Timpe L. C., Schwarz T. L., Tempel B. L., Papazian D. M., Jan Y. N., Jan L. Y. Expression of functional potassium channels from Shaker cDNA in Xenopus oocytes. Nature. 1988 Jan 14;331(6152):143–145. doi: 10.1038/331143a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


