Abstract
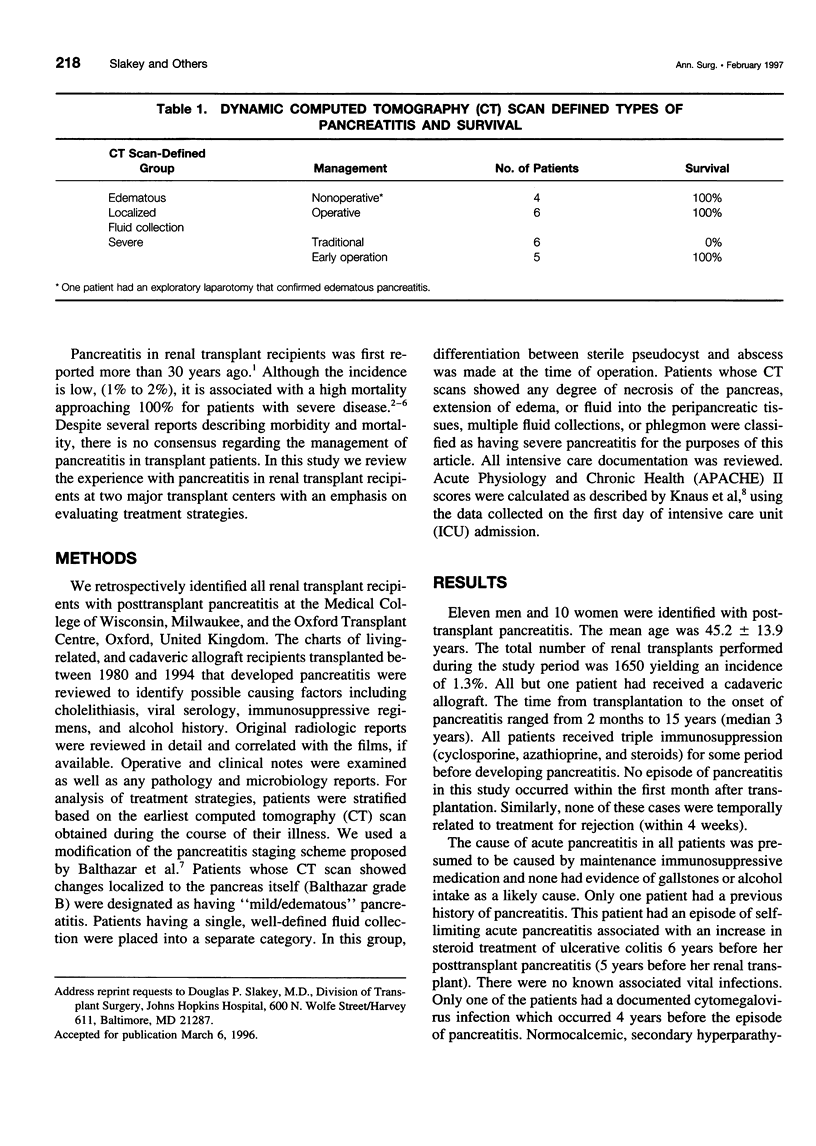
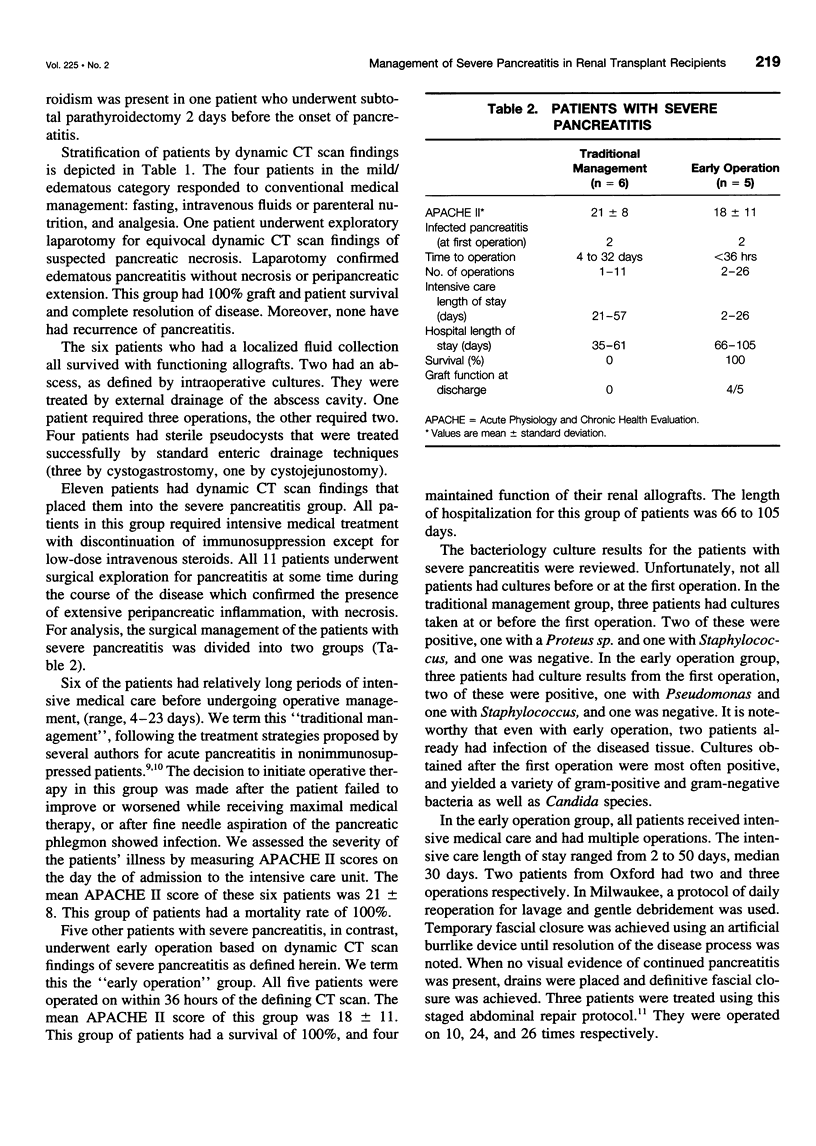
OBJECTIVE: The authors determine if any aspects of the treatment of renal transplant patients with pancreatitis were of particular benefit with regard to graft and patient survival. BACKGROUND: The incidence of pancreatitis in renal transplant patients is low (1%-2%), but the mortality of the disease approaches 100%. Although several descriptive reports have been published, there is no consensus-regarding management. METHODS: The authors conduct a retrospective chart review. RESULTS: Twenty-one patients were identified with posttransplant pancreatitis (1.3% incidence). The cause of pancreatitis was presumed to be maintenance immunosuppression in all cases. Patients were classified by dynamic computed tomography (CT) scans having 1) mild/edematous disease (4 patients), 2) localized abscess or pseudocyst (6 patients), or 3) severe disease (11 patients). Patients with mild/edematous pancreatitis did well with medical management. The six patients with localized abscess or pseudocyst were successfully treated with standard operative intervention. Of the 11 patients with severe disease, 6 had several days of intensive medical management before operation, and all died. The other five patients underwent early operative intervention based principally on CT scan findings, and all survived. The latter group had multiple operations and four of five had functioning renal allografts at discharge. CONCLUSION: The severity of pancreatitis in the posttranplant patients may be difficult to assess by clinical criteria. Dynamic CT scanning is, therefore, essential in defining the extent of disease. Early, and perhaps repeated, operations may be lifesaving in those patients having CT scan findings of severe pancreatitis.
Full text
PDF



Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Balthazar E. J., Ranson J. H., Naidich D. P., Megibow A. J., Caccavale R., Cooper M. M. Acute pancreatitis: prognostic value of CT. Radiology. 1985 Sep;156(3):767–772. doi: 10.1148/radiology.156.3.4023241. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Beger H. G. Surgical management of necrotizing pancreatitis. Surg Clin North Am. 1989 Jun;69(3):529–549. doi: 10.1016/s0039-6109(16)44834-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Burnstein M., Salter D., Cardella C., Himal H. S. Necrotizing pancreatitis in renal transplant patients. Can J Surg. 1982 Sep;25(5):547-9, 563. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Corrodi P., Knoblauch M., Binswanger U., Schölzel E., Largiader F. Pancreatitis after renal transplantation. Gut. 1975 Apr;16(4):285–289. doi: 10.1136/gut.16.4.285. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Echigo Y., Inoue K., Kogire M., Doi R., Higashide S., Sumi S., Kaji H., Imamura M. Effects of cyclosporine and tacrolimus (FK 506) on acute pancreatitis in mice. Arch Surg. 1995 Jan;130(1):64–68. doi: 10.1001/archsurg.1995.01430010066013. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Edwards C. M., Morgan J. D., Tilsed J. V., Donnelly P. K. Impaired acute phase response: a risk factor for life-threatening posttransplant pancreatitis? Transplant Proc. 1992 Dec;24(6):2769–2769. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fernández-Cruz L., Targarona E. M., Cugat E., Alcaraz A., Oppenheimer F. Acute pancreatitis after renal transplantation. Br J Surg. 1989 Nov;76(11):1132–1135. doi: 10.1002/bjs.1800761108. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Frick T. W., Fryd D. S., Goodale R. L., Simmons R. L., Sutherland D. E., Najarian J. S. Lack of association between azathioprine and acute pancreatitis in renal transplantation patients. Lancet. 1991 Jan 26;337(8735):251–252. doi: 10.1016/0140-6736(91)92229-u. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kenmochi T., Asano T., Shimada H., Ochiai T., Isono K. Clinical and experimental studies of acute pancreatitis after renal transplantation. Transplant Proc. 1992 Aug;24(4):1578–1580. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Knaus W. A., Draper E. A., Wagner D. P., Zimmerman J. E. APACHE II: a severity of disease classification system. Crit Care Med. 1985 Oct;13(10):818–829. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- London N. J., Leese T., Lavelle J. M., Miles K., West K. P., Watkin D. F., Fossard D. P. Rapid-bolus contrast-enhanced dynamic computed tomography in acute pancreatitis: a prospective study. Br J Surg. 1991 Dec;78(12):1452–1456. doi: 10.1002/bjs.1800781216. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Penn I., Durst A. L., Machado M., Halgrimson C. G., Booth A. S., Jr, Putman C. W., Groth C. G., Starzl T. E. Acute pancreatitis and hyperamylasemia in renal homograft recipients. Arch Surg. 1972 Aug;105(2):167–172. doi: 10.1001/archsurg.1972.04180080021004. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sitges-Serra A., Gores P., Hesse U., Fryd D. S., Najarian J. S., Sutherland D. E. Serum calcium as an early indicator for surgical treatment of hyperparathyroidism after renal transplantation. World J Surg. 1986 Aug;10(4):661–667. doi: 10.1007/BF01655550. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stanten R., Frey C. F. Comprehensive management of acute necrotizing pancreatitis and pancreatic abscess. Arch Surg. 1990 Oct;125(10):1269–1275. doi: 10.1001/archsurg.1990.01410220053008. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tran D. D., Cuesta M. A. Evaluation of severity in patients with acute pancreatitis. Am J Gastroenterol. 1992 May;87(5):604–608. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Underwood T. W., Frye C. B. Drug-induced pancreatitis. Clin Pharm. 1993 Jun;12(6):440–448. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wittmann D. H., Aprahamian C., Bergstein J. M., Edmiston C. E., Frantzides C. T., Quebbeman E. J., Condon R. E. A burr-like device to facilitate temporary abdominal closure in planned multiple laparotomies. Eur J Surg. 1993 Feb;159(2):75–79. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


