Abstract
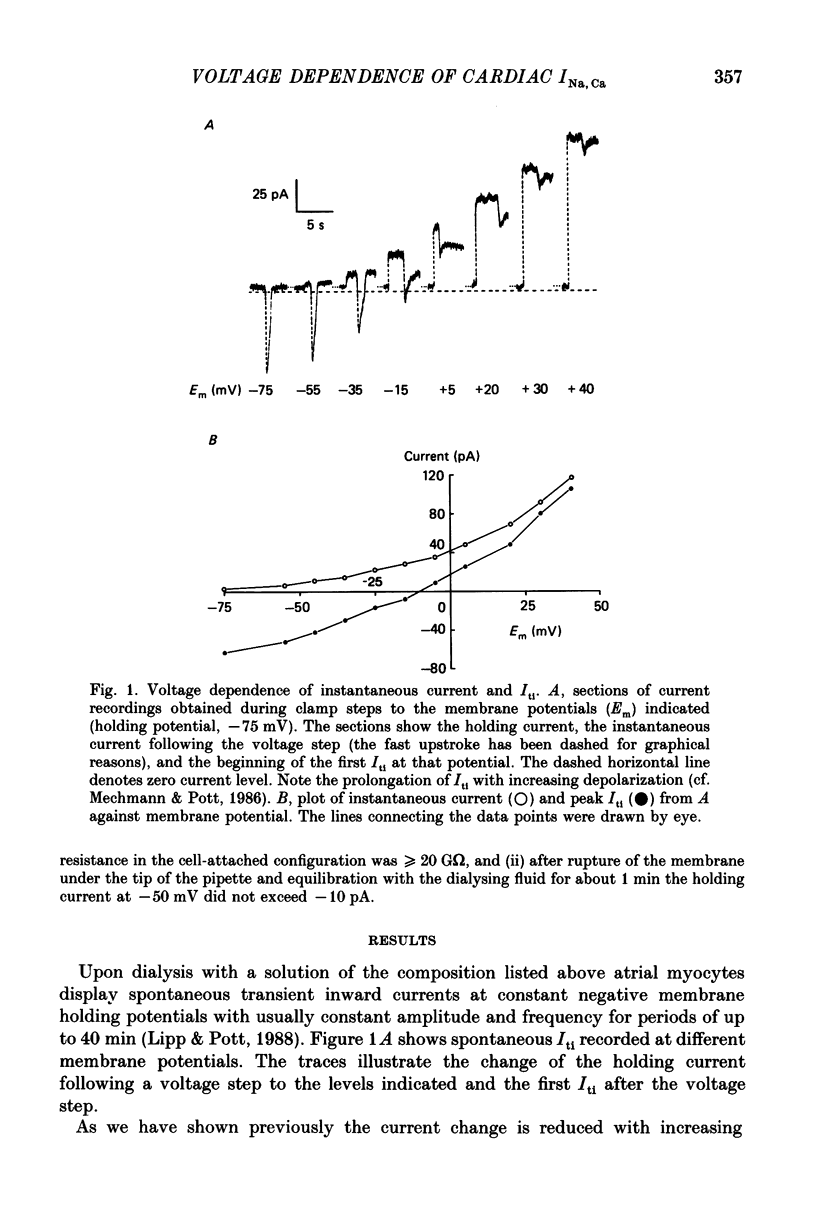
1. Spontaneous transient inward currents (Iti) caused by cyclic release of Ca2+ ions from the sarcoplasmic reticulum were studied in cultured atrial myocytes from hearts of adult guinea-pigs. K+ channel currents were blocked by replacing K+ on both sides of the membrane by Cs+; the L-type Ca2+ current was inhibited by D600. 2. The voltage dependence of peak Iti and the background current displayed distinct outward-going rectification. The I-V curves for both currents approach each other at strongly positive membrane potentials but do not intersect. 3. 3'-4'Dichlorobenzamil (DCB) causes a concentration-dependent inhibition of peak Iti and a shift of the holding current (at -60 to -40 mV) in the inward direction. Inhibition of Iti is half-maximal at a concentration of 30 microM. 4. DCB reduces the outward-rectifying component of both peak Iti and the background current. The I-V curves of the control and DCB-inhibited currents intersect at ca. +10 mV (peak Iti) and negative to -75 mV (background current), suggesting the reversal potential of the DCB-inhibited current to be shifted by ca. 85 mV in the positive direction if Cai2+ rises following Ca2+ release. 5. The voltage dependence of the DCB-inhibited currents is highly compatible with the concept of Na+-Ca2+ exchange being the charge-carrying mechanism of the outward-rectifying background current. Ca2+ release from the SR alters the I-V curve of this current according to the shift of the thermodynamic driving force.
Full text
PDF

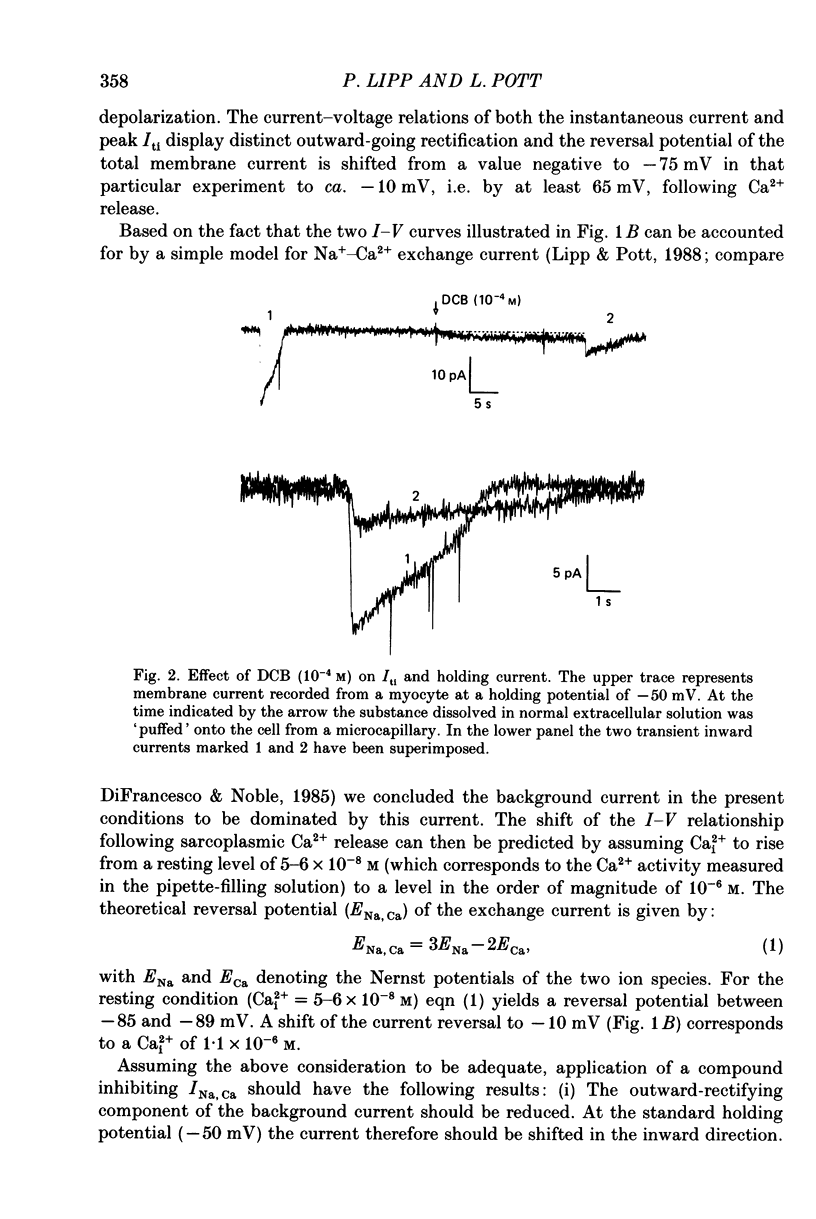

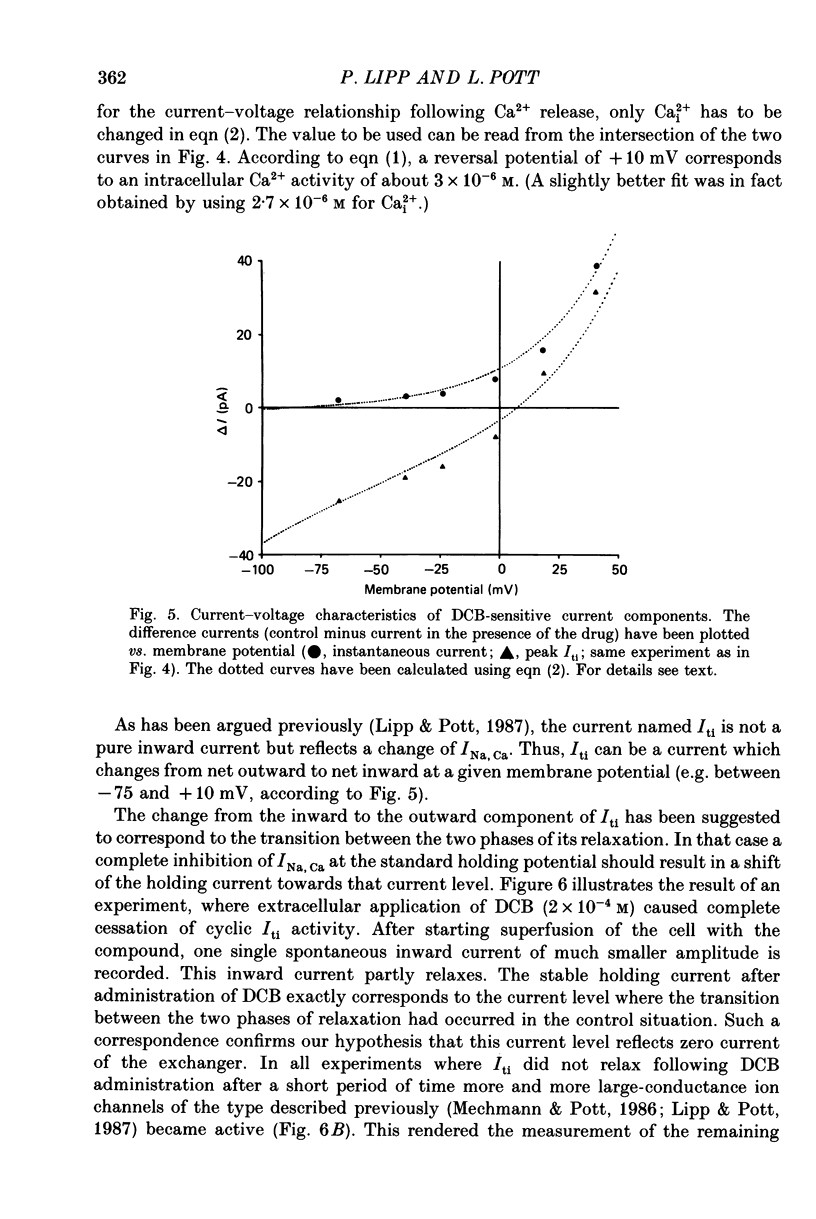
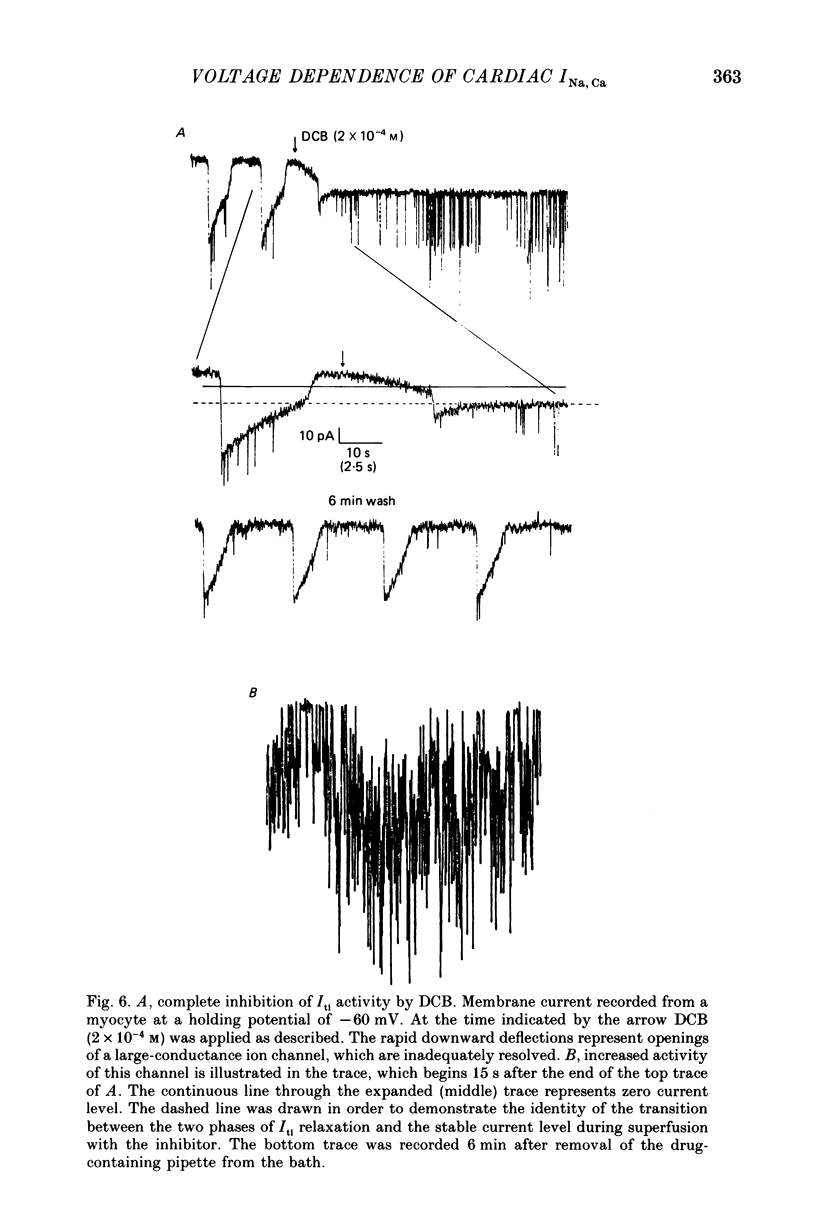



Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
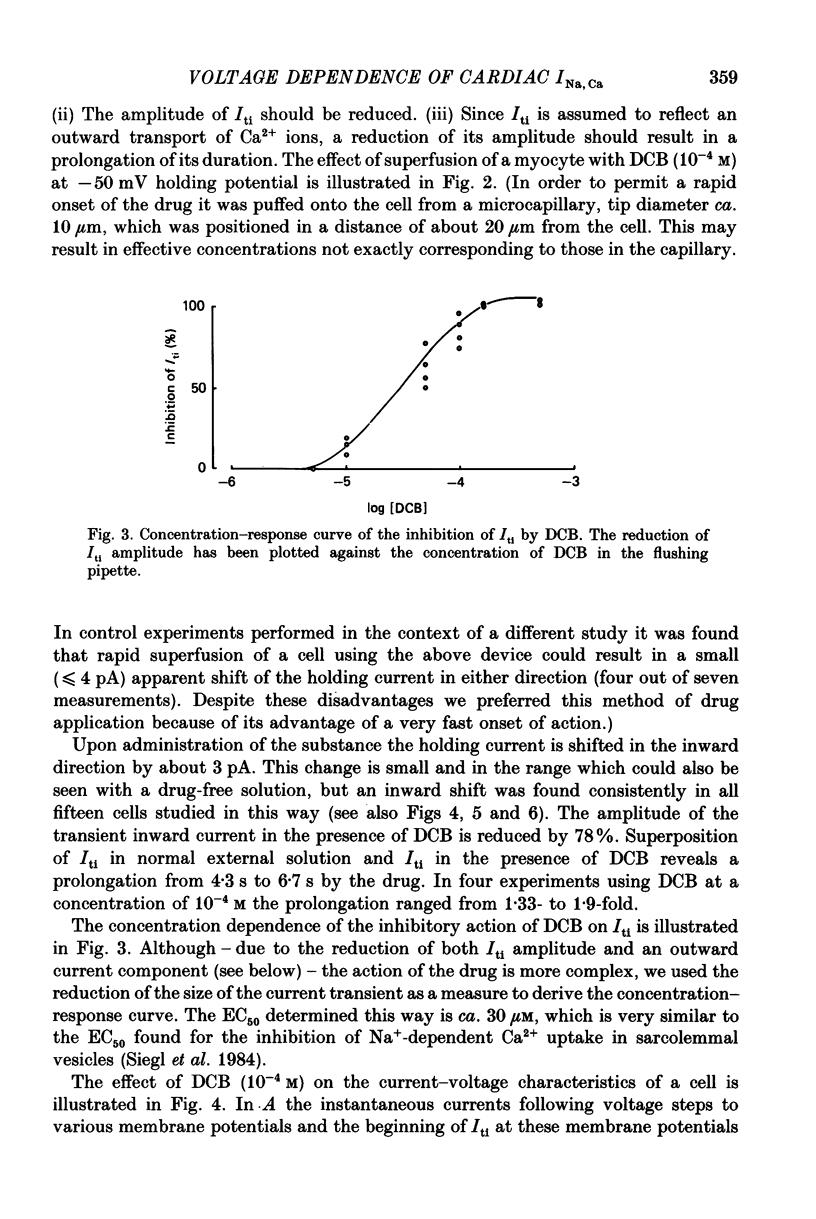
- Bechem M., Pott L. Removal of Ca current inactivation in dialysed guinea-pig atrial cardioballs by Ca chelators. Pflugers Arch. 1985 May;404(1):10–20. doi: 10.1007/BF00581485. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
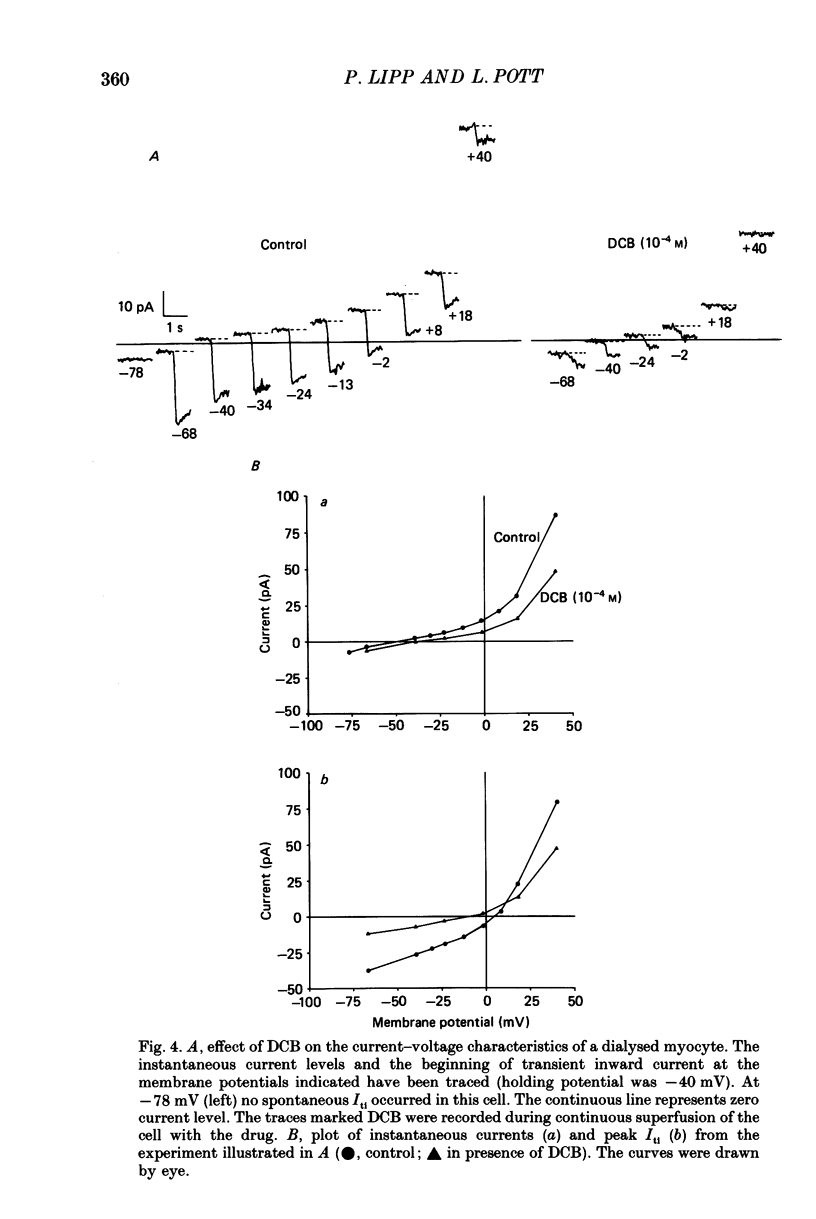
- Bechem M., Pott L., Rennebaum H. Atrial muscle cells from hearts of adult guinea-pigs in culture: a new preparation for cardiac cellular electrophysiology. Eur J Cell Biol. 1983 Sep;31(2):366–369. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bielefeld D. R., Hadley R. W., Vassilev P. M., Hume J. R. Membrane electrical properties of vesicular Na-Ca exchange inhibitors in single atrial myocytes. Circ Res. 1986 Oct;59(4):381–389. doi: 10.1161/01.res.59.4.381. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Carafoli E. Intracellular calcium homeostasis. Annu Rev Biochem. 1987;56:395–433. doi: 10.1146/annurev.bi.56.070187.002143. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Caroni P., Carafoli E. The regulation of the Na+ -Ca2+ exchanger of heart sarcolemma. Eur J Biochem. 1983 May 16;132(3):451–460. doi: 10.1111/j.1432-1033.1983.tb07383.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Deitmer J. W., Ellis D. Interactions between the regulation of the intracellular pH and sodium activity of sheep cardiac Purkinje fibres. J Physiol. 1980 Jul;304:471–488. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1980.sp013337. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- DiFrancesco D., Noble D. A model of cardiac electrical activity incorporating ionic pumps and concentration changes. Philos Trans R Soc Lond B Biol Sci. 1985 Jan 10;307(1133):353–398. doi: 10.1098/rstb.1985.0001. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Eisner D. A., Lederer W. J. Na-Ca exchange: stoichiometry and electrogenicity. Am J Physiol. 1985 Mar;248(3 Pt 1):C189–C202. doi: 10.1152/ajpcell.1985.248.3.C189. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hamill O. P., Marty A., Neher E., Sakmann B., Sigworth F. J. Improved patch-clamp techniques for high-resolution current recording from cells and cell-free membrane patches. Pflugers Arch. 1981 Aug;391(2):85–100. doi: 10.1007/BF00656997. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hilgemann D. W., Noble D. Excitation-contraction coupling and extracellular calcium transients in rabbit atrium: reconstruction of basic cellular mechanisms. Proc R Soc Lond B Biol Sci. 1987 Mar 23;230(1259):163–205. doi: 10.1098/rspb.1987.0015. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hume J. R., Uehara A. "Creep currents" in single frog atrial cells may be generated by electrogenic Na/Ca exchange. J Gen Physiol. 1986 Jun;87(6):857–884. doi: 10.1085/jgp.87.6.857. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kaila K., Vaughan-Jones R. D. Influence of sodium-hydrogen exchange on intracellular pH, sodium and tension in sheep cardiac Purkinje fibres. J Physiol. 1987 Sep;390:93–118. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1987.sp016688. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kimura J., Miyamae S., Noma A. Identification of sodium-calcium exchange current in single ventricular cells of guinea-pig. J Physiol. 1987 Mar;384:199–222. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1987.sp016450. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kimura J., Noma A., Irisawa H. Na-Ca exchange current in mammalian heart cells. Nature. 1986 Feb 13;319(6054):596–597. doi: 10.1038/319596a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lipp P., Pott L. Transient inward current in guinea-pig atrial myocytes reflects a change of sodium-calcium exchange current. J Physiol. 1988 Mar;397:601–630. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1988.sp017021. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mechmann S., Pott L. Identification of Na-Ca exchange current in single cardiac myocytes. Nature. 1986 Feb 13;319(6054):597–599. doi: 10.1038/319597a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mullins L. J. The generation of electric currents in cardiac fibers by Na/Ca exchange. Am J Physiol. 1979 Mar;236(3):C103–C110. doi: 10.1152/ajpcell.1979.236.3.C103. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Noble D. The surprising heart: a review of recent progress in cardiac electrophysiology. J Physiol. 1984 Aug;353:1–50. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1984.sp015320. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Philipson K. D. Sodium-calcium exchange in plasma membrane vesicles. Annu Rev Physiol. 1985;47:561–571. doi: 10.1146/annurev.ph.47.030185.003021. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Reeves J. P., Hale C. C. The stoichiometry of the cardiac sodium-calcium exchange system. J Biol Chem. 1984 Jun 25;259(12):7733–7739. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Reuter H., Seitz N. The dependence of calcium efflux from cardiac muscle on temperature and external ion composition. J Physiol. 1968 Mar;195(2):451–470. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1968.sp008467. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Siegl P. K., Cragoe E. J., Jr, Trumble M. J., Kaczorowski G. J. Inhibition of Na+/Ca2+ exchange in membrane vesicle and papillary muscle preparations from guinea pig heart by analogs of amiloride. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1984 May;81(10):3238–3242. doi: 10.1073/pnas.81.10.3238. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


