Abstract
1. The membrane current was recorded from retinal rods isolated from Ambystoma tigrinum using the suction pipette and whole-cell patch pipette techniques, while the concentration of calcium bathing the outer segment was rapidly reduced. 2. The increase in outer segment current induced by lowered external calcium in darkness could be resolved into two components, one as rapid as the time course of the solution change (as judged by the junction current) and the other somewhat slower. 3. Introduction of the calcium buffer BAPTA (1,2-bis(o-aminophenoxy)ethane-N ,N ,N' ,N'-tetraacetic acid) into the cell from a patch pipette led to a progressive slowing of the second component of current increase. 4. When several minutes had elapsed following rupture of the patch, to allow a substantial amount of BAPTA into the cell (ca. 10 mM in the patch pipette), the second component was slowed by a factor of about 20-fold, while the first component continued to have the same rapid time course as the solution change. 5. The rapid component is attributed to a direct effect of external calcium, Ca2+o, and the delayed component to an indirect effect mediated by a reduction in internal calcium, Ca2+i. 6. These results confirm that, in previous experiments in which BAPTA was introduced into photoreceptors, the internal calcium concentration was very significantly buffered. 7. When Ca2+o drops from 1 mM to less than 10(-8) M, the rapid external component corresponds to an increase in circulating current of 3- to 4-fold, and the internal component corresponds to an increase of at least 4- to 5-fold. However, the total current at late times is limited by electrical factors, so that the size of the internal effect is bound to be considerably greater.
Full text
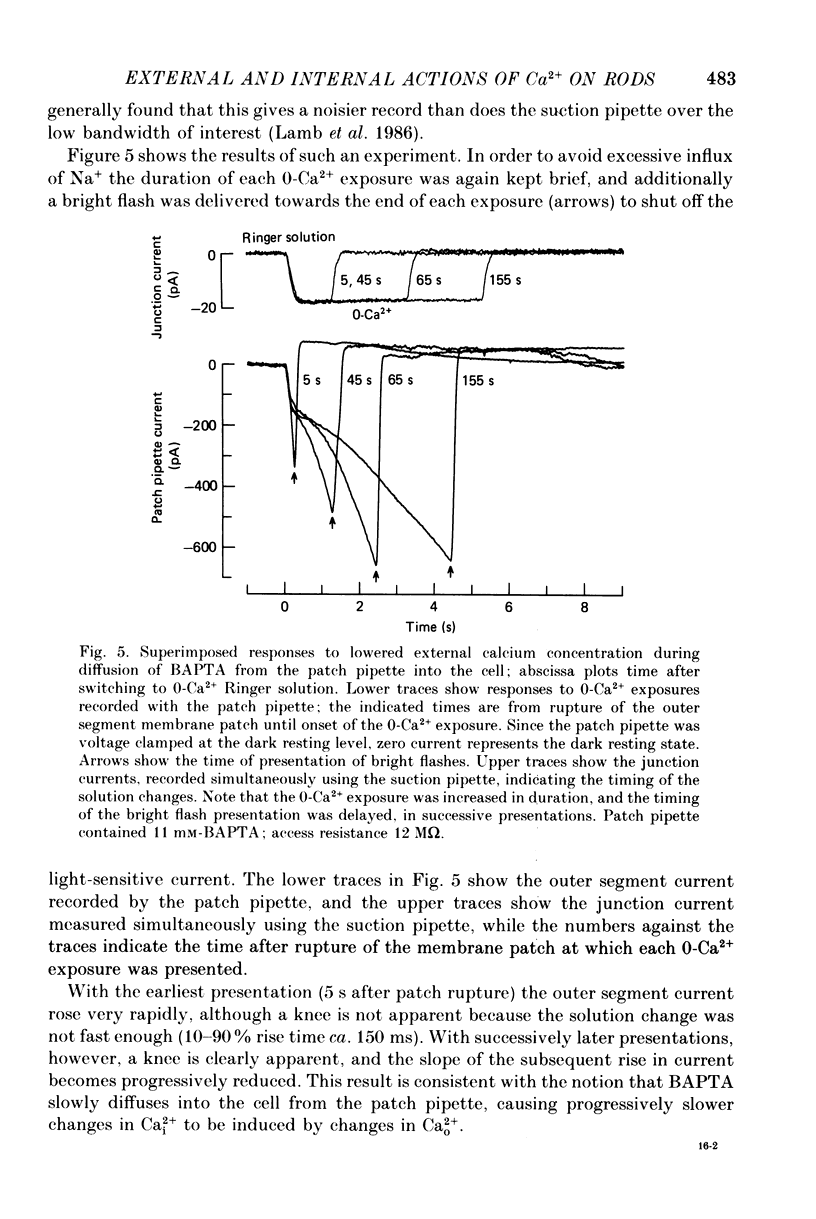
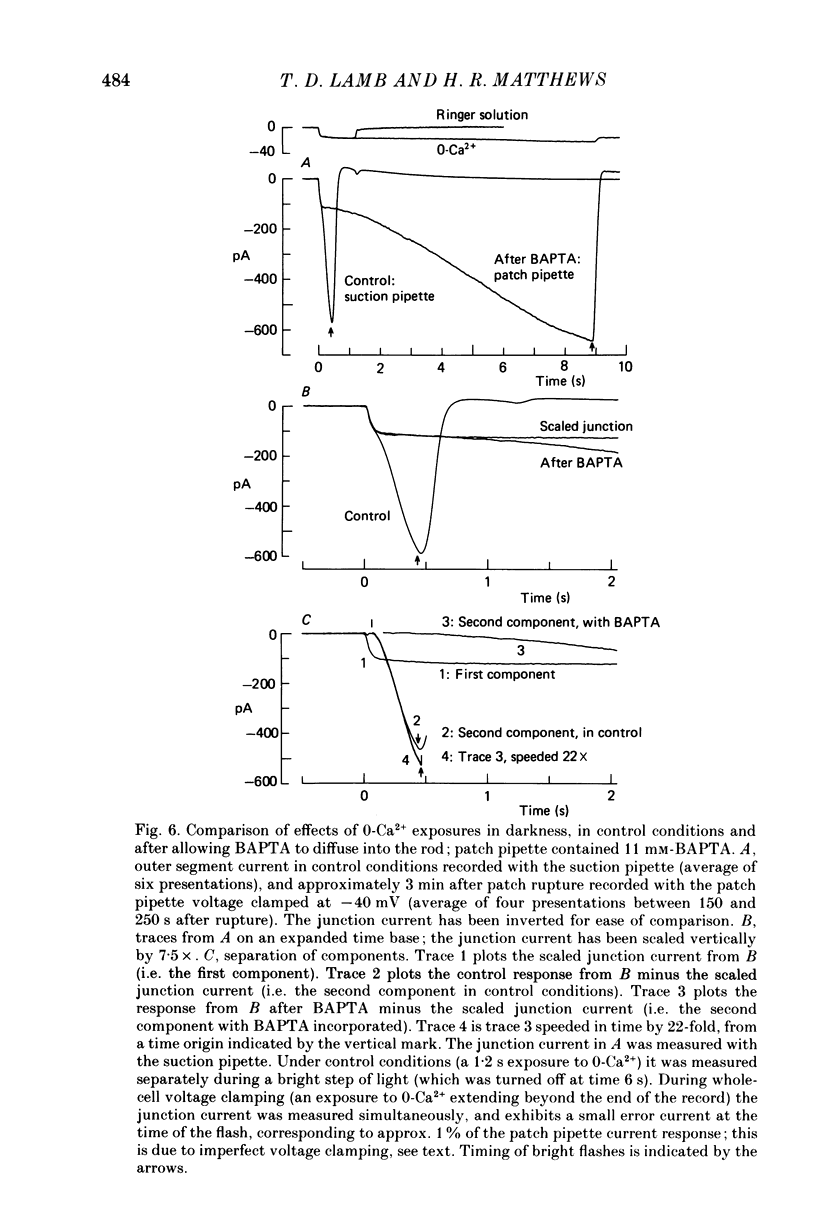
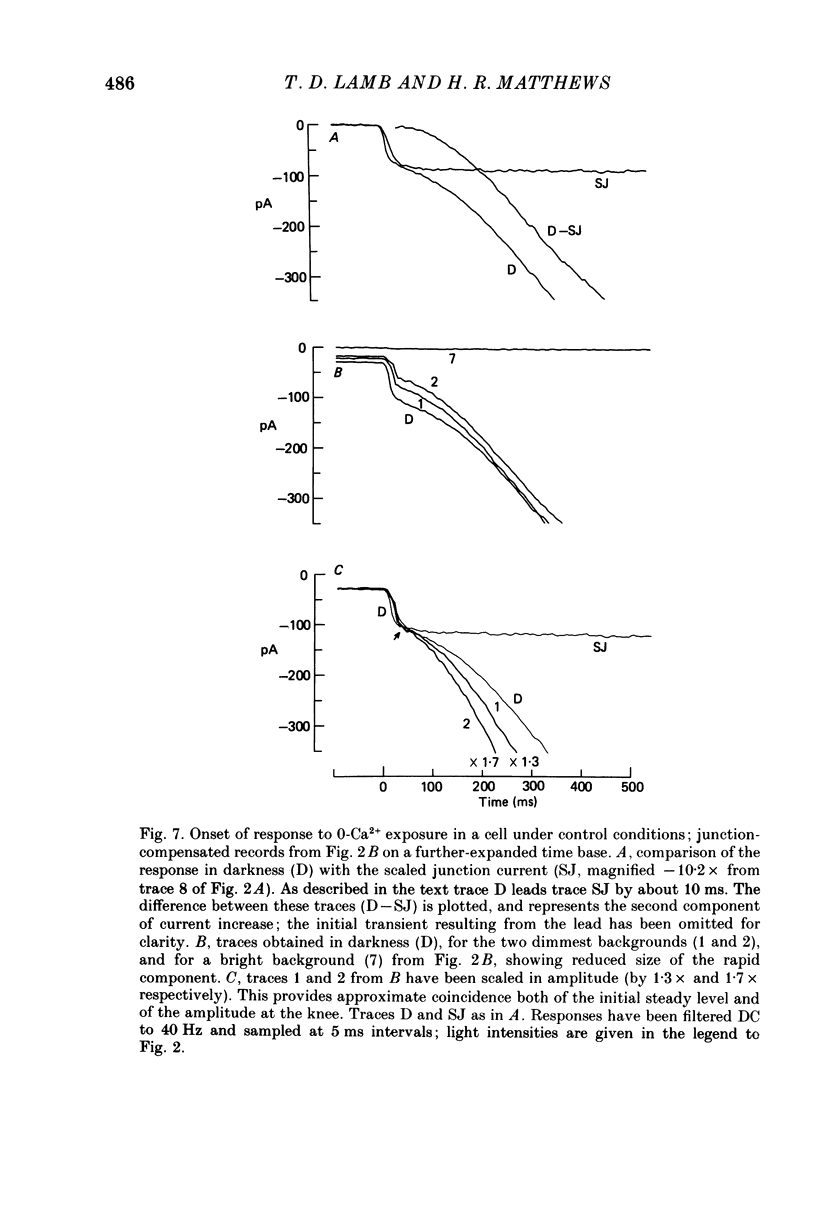
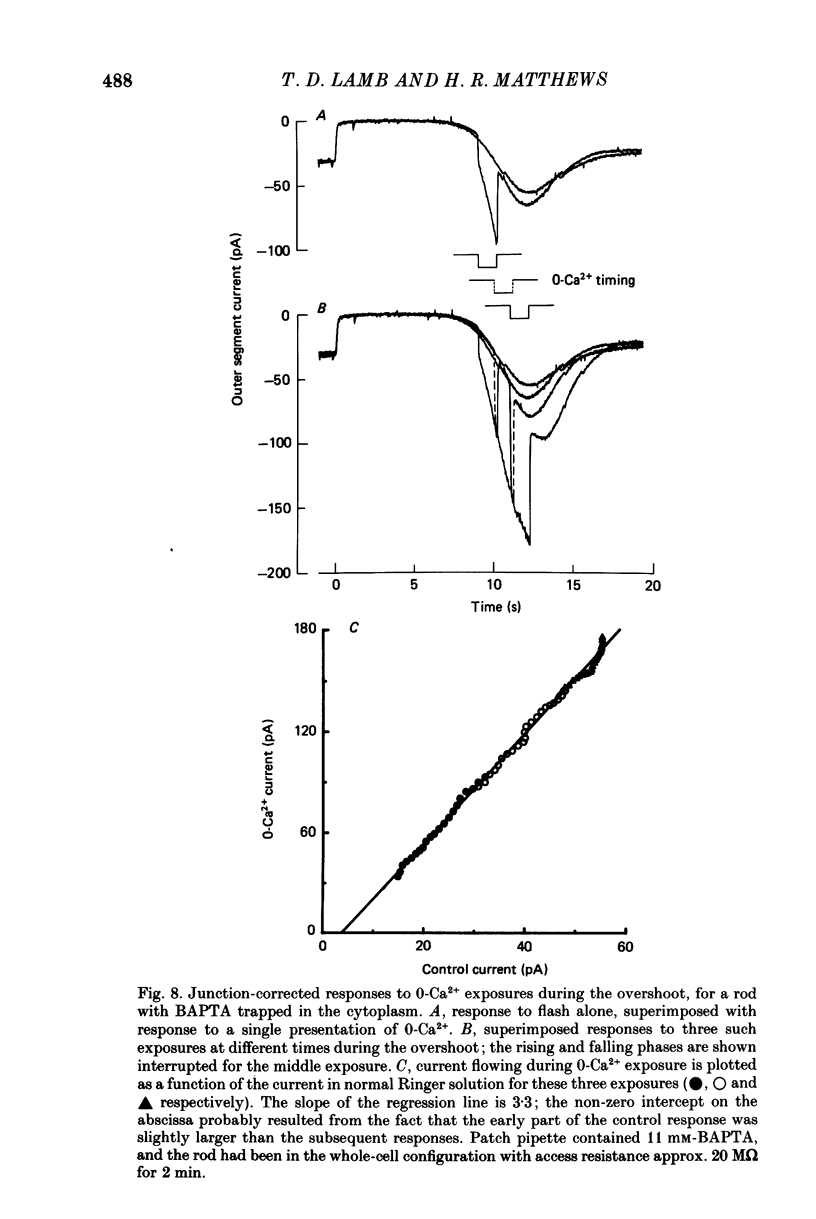
PDF


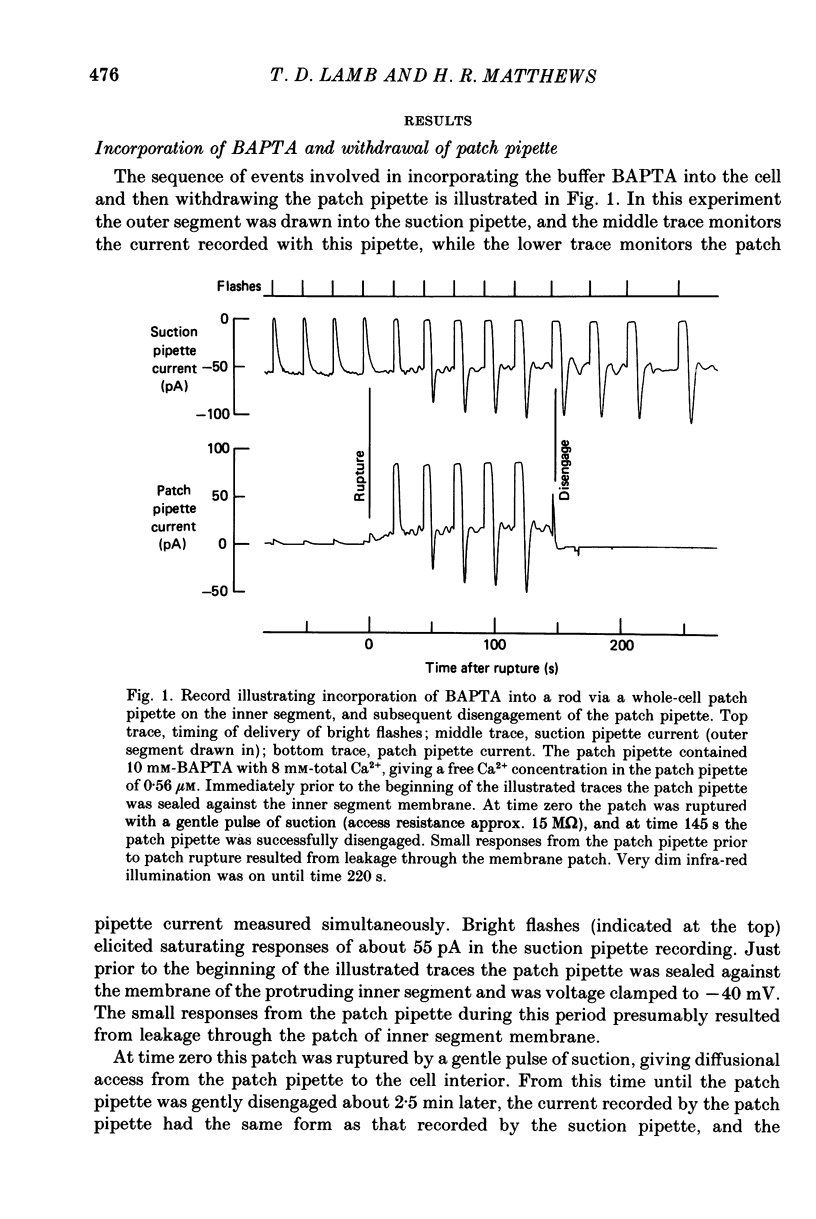

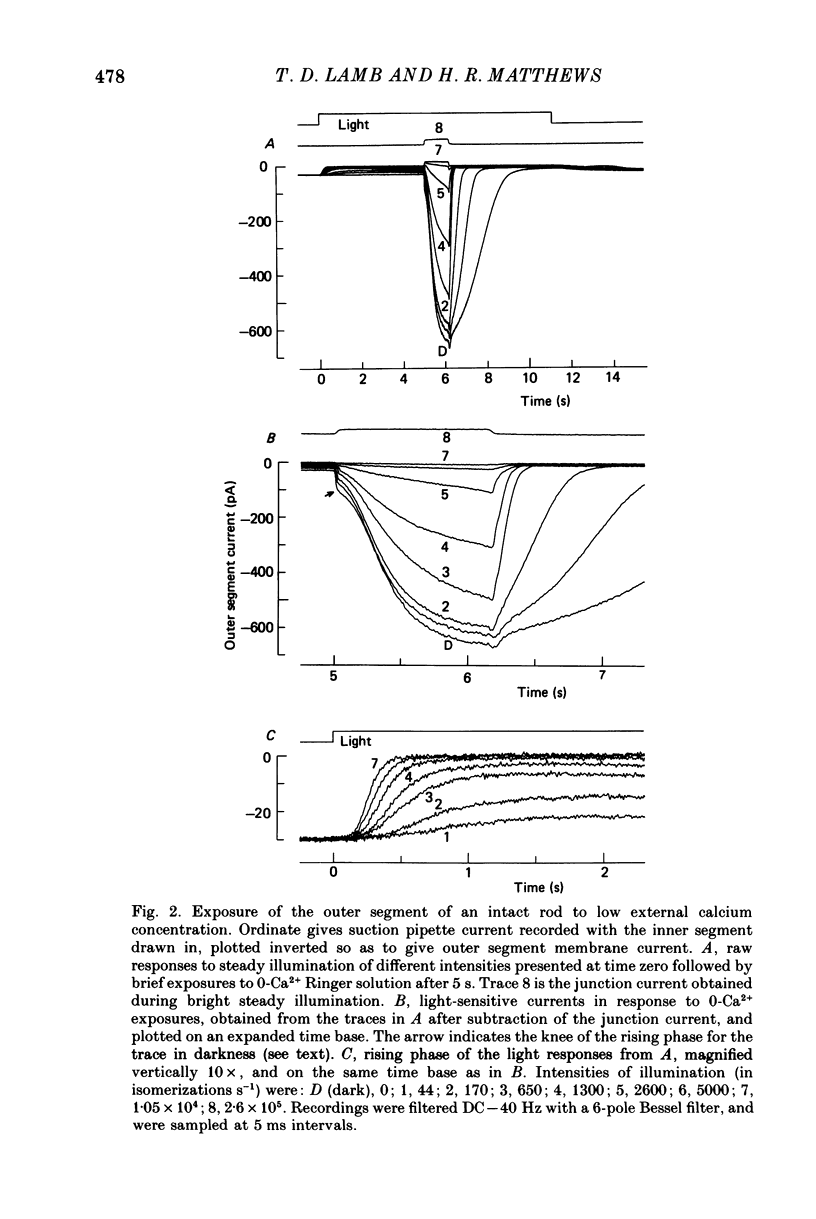

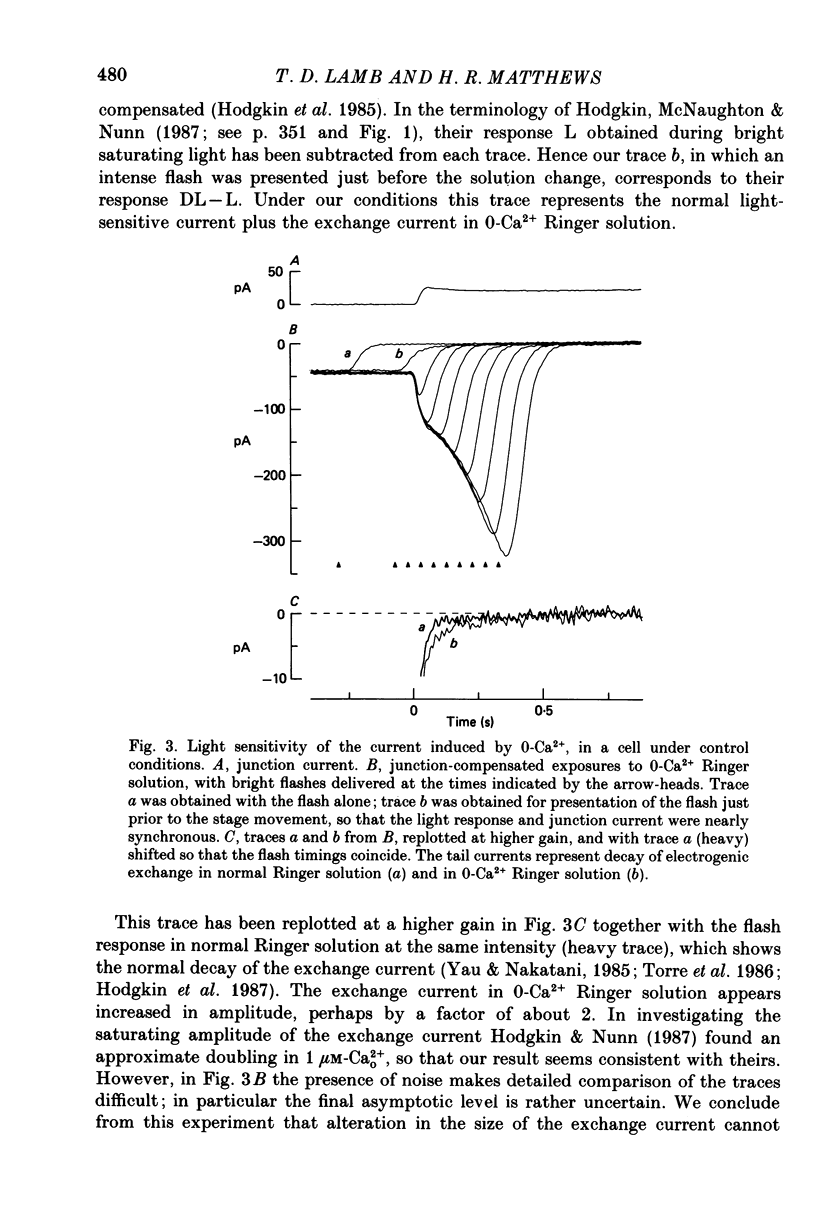

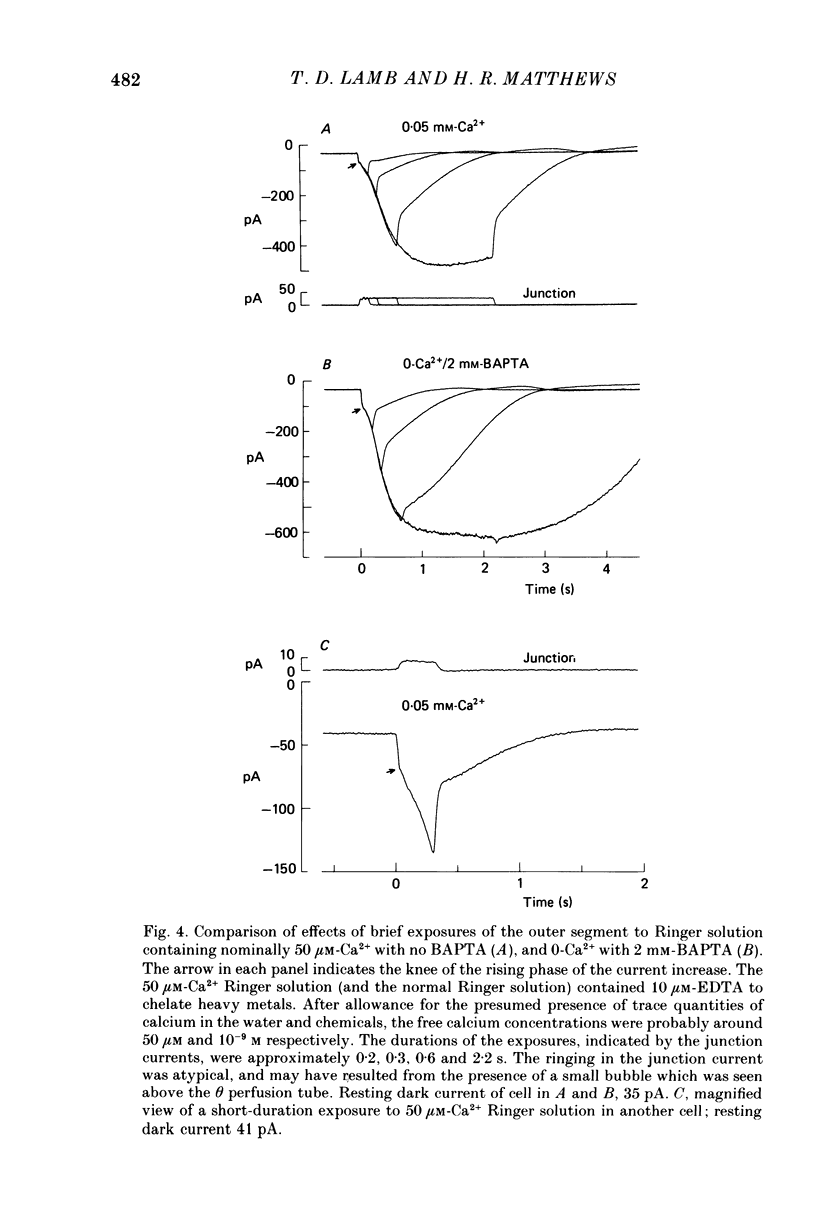








Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Bastian B. L., Fain G. L. Light adaptation in toad rods: requirement for an internal messenger which is not calcium. J Physiol. 1979 Dec;297(0):493–520. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1979.sp013053. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bertrand D., Fuortes M. G., Pochobradsky J. Actions of EGTA and high calcium on the cones in the turtle retina. J Physiol. 1978 Feb;275:419–437. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1978.sp012198. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bodoia R. D., Detwiler P. B. Patch-clamp recordings of the light-sensitive dark noise in retinal rods from the lizard and frog. J Physiol. 1985 Oct;367:183–216. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1985.sp015820. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Brown J. E., Pinto L. H. Ionic mechanism for the photoreceptor potential of the retina of Bufo marinus. J Physiol. 1974 Feb;236(3):575–591. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1974.sp010453. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gold G. H. Plasma membrane calcium fluxes in intact rods are inconsistent with the "calcium hypothesis". Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1986 Feb;83(4):1150–1154. doi: 10.1073/pnas.83.4.1150. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hagins W. A. The visual process: Excitatory mechanisms in the primary receptor cells. Annu Rev Biophys Bioeng. 1972;1:131–158. doi: 10.1146/annurev.bb.01.060172.001023. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hagins W. A., Yoshikami S. Proceedings: A role for Ca2+ in excitation of retinal rods and cones. Exp Eye Res. 1974 Mar;18(3):299–305. doi: 10.1016/0014-4835(74)90157-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hamill O. P., Marty A., Neher E., Sakmann B., Sigworth F. J. Improved patch-clamp techniques for high-resolution current recording from cells and cell-free membrane patches. Pflugers Arch. 1981 Aug;391(2):85–100. doi: 10.1007/BF00656997. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Haynes L. W., Kay A. R., Yau K. W. Single cyclic GMP-activated channel activity in excised patches of rod outer segment membrane. Nature. 1986 May 1;321(6065):66–70. doi: 10.1038/321066a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hodgkin A. L., McNaughton P. A., Nunn B. J. Measurement of sodium-calcium exchange in salamander rods. J Physiol. 1987 Oct;391:347–370. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1987.sp016742. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hodgkin A. L., McNaughton P. A., Nunn B. J. The ionic selectivity and calcium dependence of the light-sensitive pathway in toad rods. J Physiol. 1985 Jan;358:447–468. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1985.sp015561. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hodgkin A. L., McNaughton P. A., Nunn B. J., Yau K. W. Effect of ions on retinal rods from Bufo marinus. J Physiol. 1984 May;350:649–680. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1984.sp015223. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hodgkin A. L., Nunn B. J. The effect of ions on sodium-calcium exchange in salamander rods. J Physiol. 1987 Oct;391:371–398. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1987.sp016743. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lamb T. D., Matthews H. R., Torre V. Incorporation of calcium buffers into salamander retinal rods: a rejection of the calcium hypothesis of phototransduction. J Physiol. 1986 Mar;372:315–349. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1986.sp016011. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lamb T. D., McNaughton P. A., Yau K. W. Spatial spread of activation and background desensitization in toad rod outer segments. J Physiol. 1981;319:463–496. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1981.sp013921. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lipton S. A., Ostroy S. E., Dowling J. E. Electrical and adaptive properties of rod photoreceptors in Bufo marinus. I. Effects of altered extracellular Ca2+ levels. J Gen Physiol. 1977 Dec;70(6):747–770. doi: 10.1085/jgp.70.6.747. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Matthews H. R., Torre V., Lamb T. D. Effects on the photoresponse of calcium buffers and cyclic GMP incorporated into the cytoplasm of retinal rods. Nature. 1985 Feb 14;313(6003):582–585. doi: 10.1038/313582a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Menini A., Rispoli G., Torre V. The ionic selectivity of the light-sensitive current in isolated rods of the tiger salamander. J Physiol. 1988 Aug;402:279–300. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1988.sp017204. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nakatani K., Yau K. W. Calcium and magnesium fluxes across the plasma membrane of the toad rod outer segment. J Physiol. 1988 Jan;395:695–729. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1988.sp016942. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pugh E. N., Jr, Cobbs W. H. Visual transduction in vertebrate rods and cones: a tale of two transmitters, calcium and cyclic GMP. Vision Res. 1986;26(10):1613–1643. doi: 10.1016/0042-6989(86)90051-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stryer L. Cyclic GMP cascade of vision. Annu Rev Neurosci. 1986;9:87–119. doi: 10.1146/annurev.ne.09.030186.000511. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Torre V., Matthews H. R., Lamb T. D. Role of calcium in regulating the cyclic GMP cascade of phototransduction in retinal rods. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1986 Sep;83(18):7109–7113. doi: 10.1073/pnas.83.18.7109. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tsien R. Y. New calcium indicators and buffers with high selectivity against magnesium and protons: design, synthesis, and properties of prototype structures. Biochemistry. 1980 May 27;19(11):2396–2404. doi: 10.1021/bi00552a018. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yau K. W., McNaughton P. A., Hodgkin A. L. Effect of ions on the light-sensitive current in retinal rods. Nature. 1981 Aug 6;292(5823):502–505. doi: 10.1038/292502a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yau K. W., Nakatani K. Electrogenic Na-Ca exchange in retinal rod outer segment. Nature. 1984 Oct 18;311(5987):661–663. doi: 10.1038/311661a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yau K. W., Nakatani K. Light-induced reduction of cytoplasmic free calcium in retinal rod outer segment. Nature. 1985 Feb 14;313(6003):579–582. doi: 10.1038/313579a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zimmerman A. L., Baylor D. A. Cyclic GMP-sensitive conductance of retinal rods consists of aqueous pores. Nature. 1986 May 1;321(6065):70–72. doi: 10.1038/321070a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


