Abstract
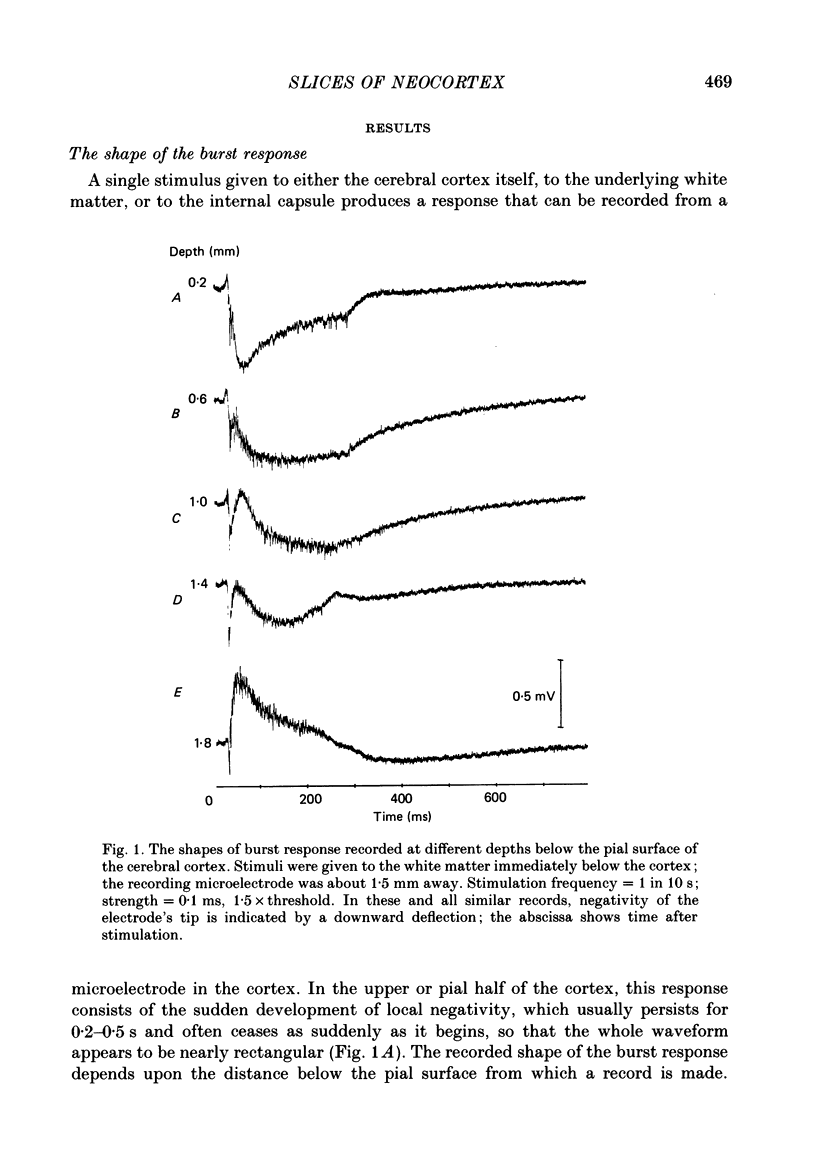
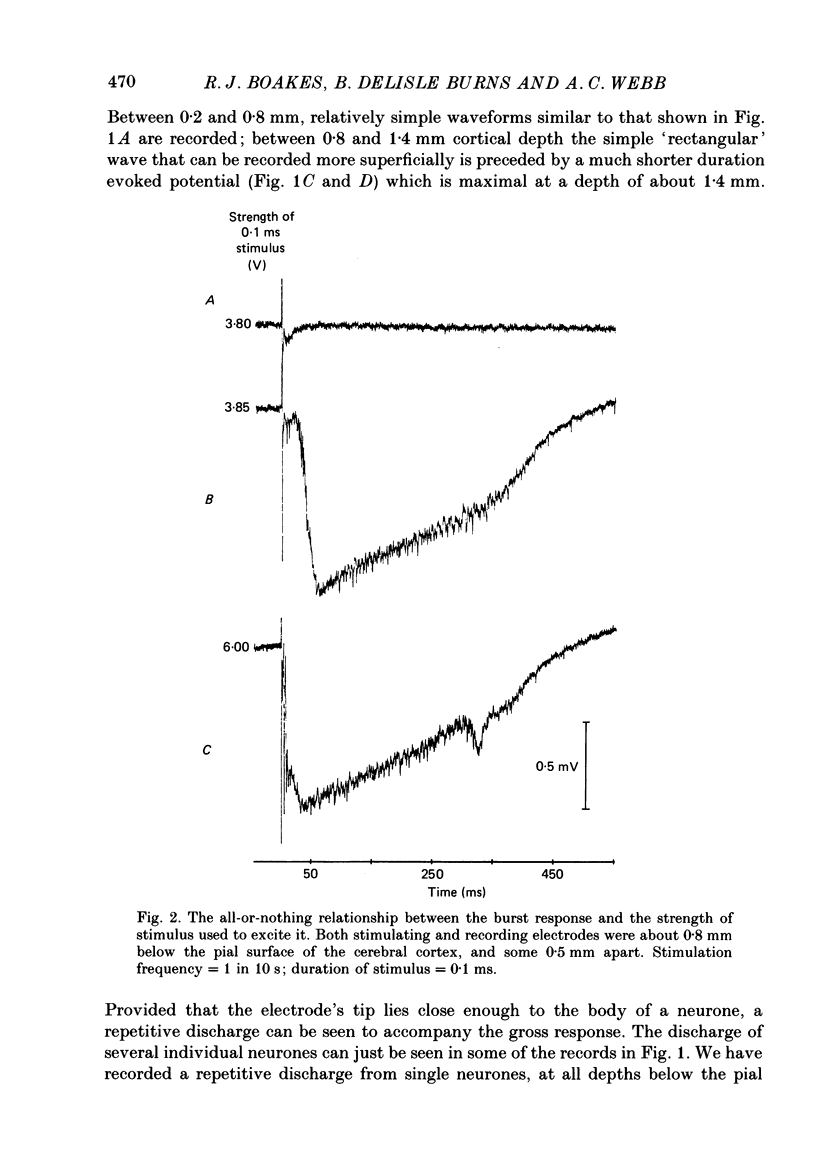
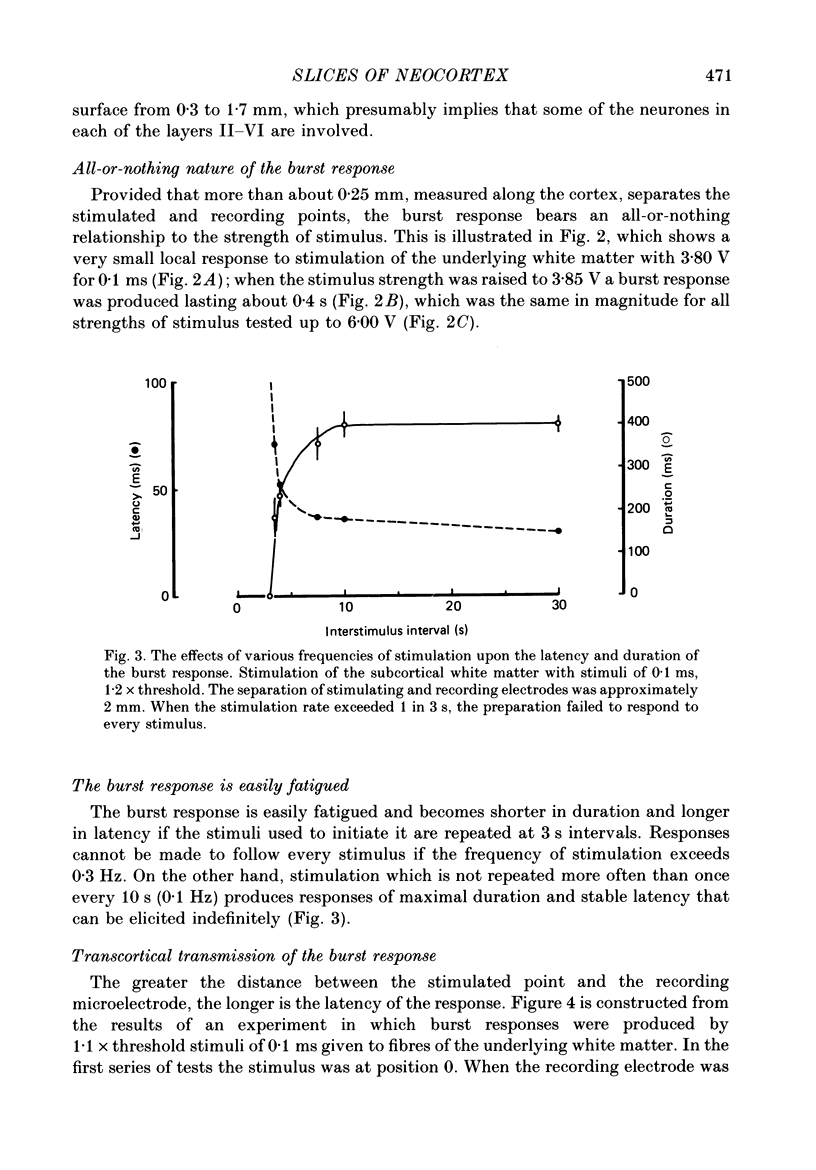
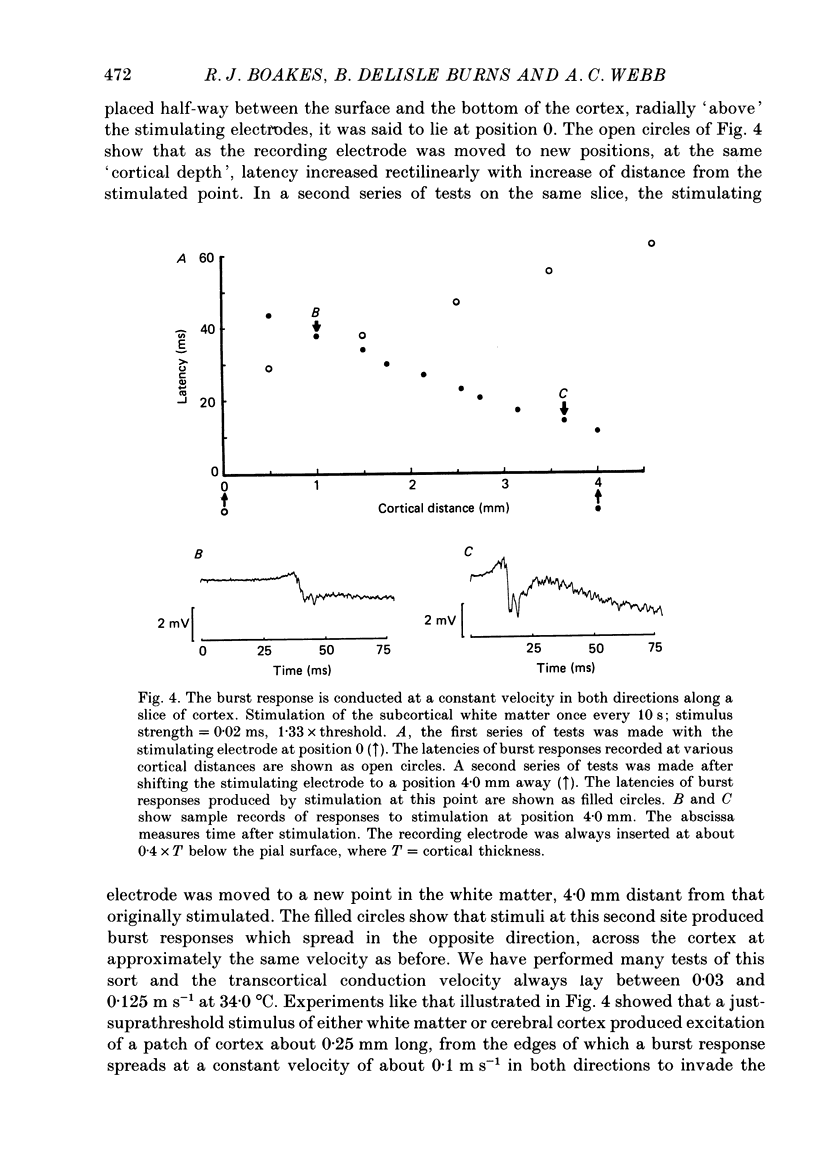
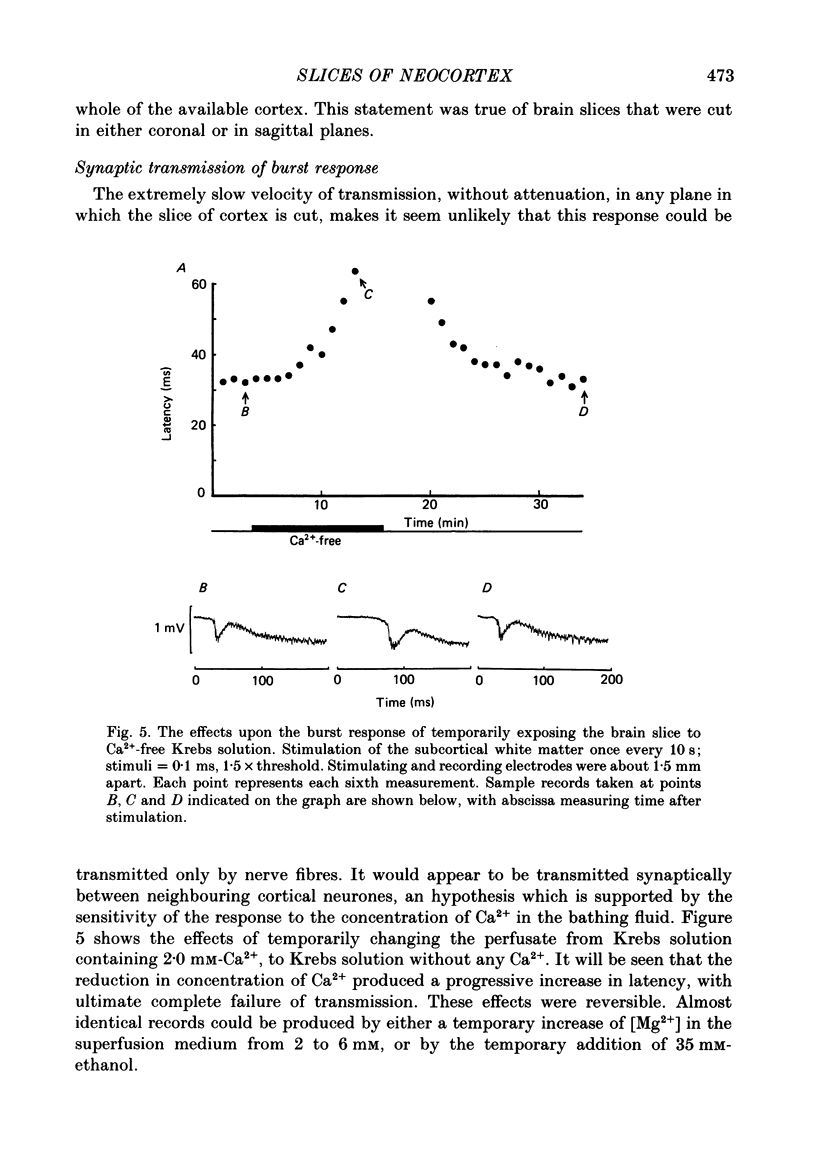
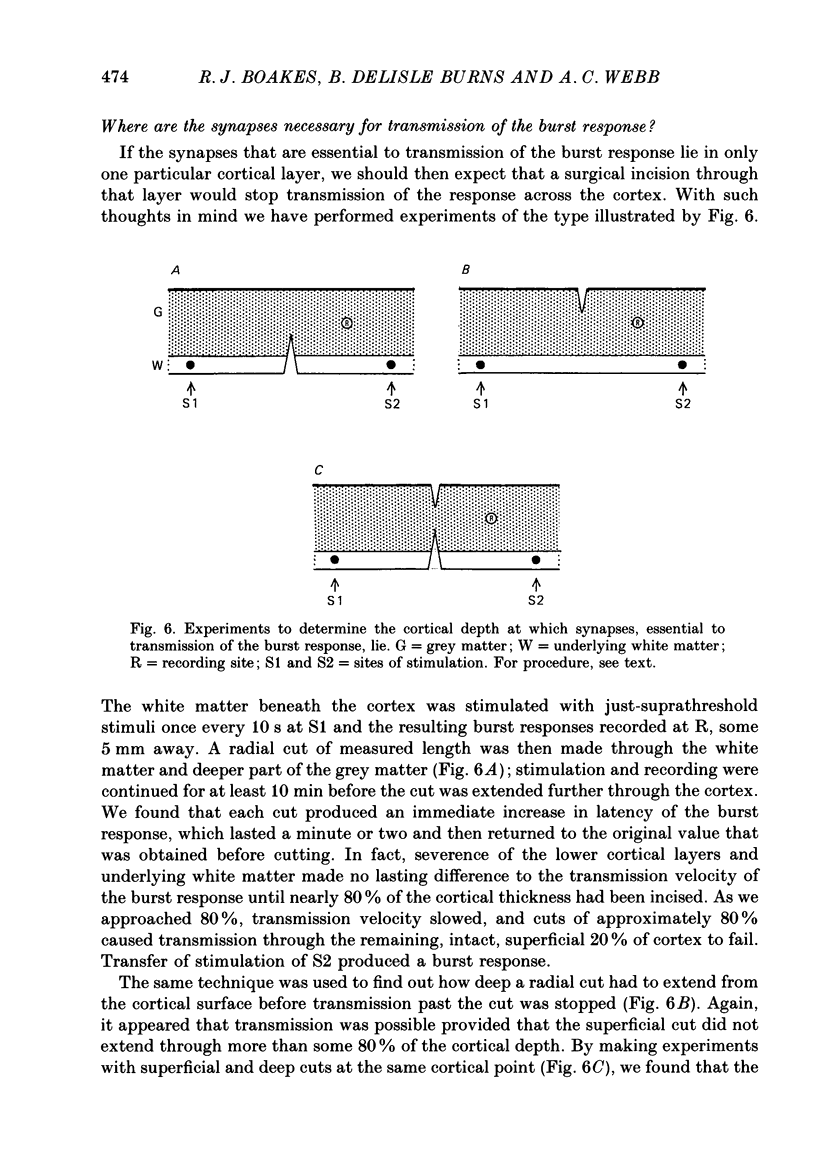
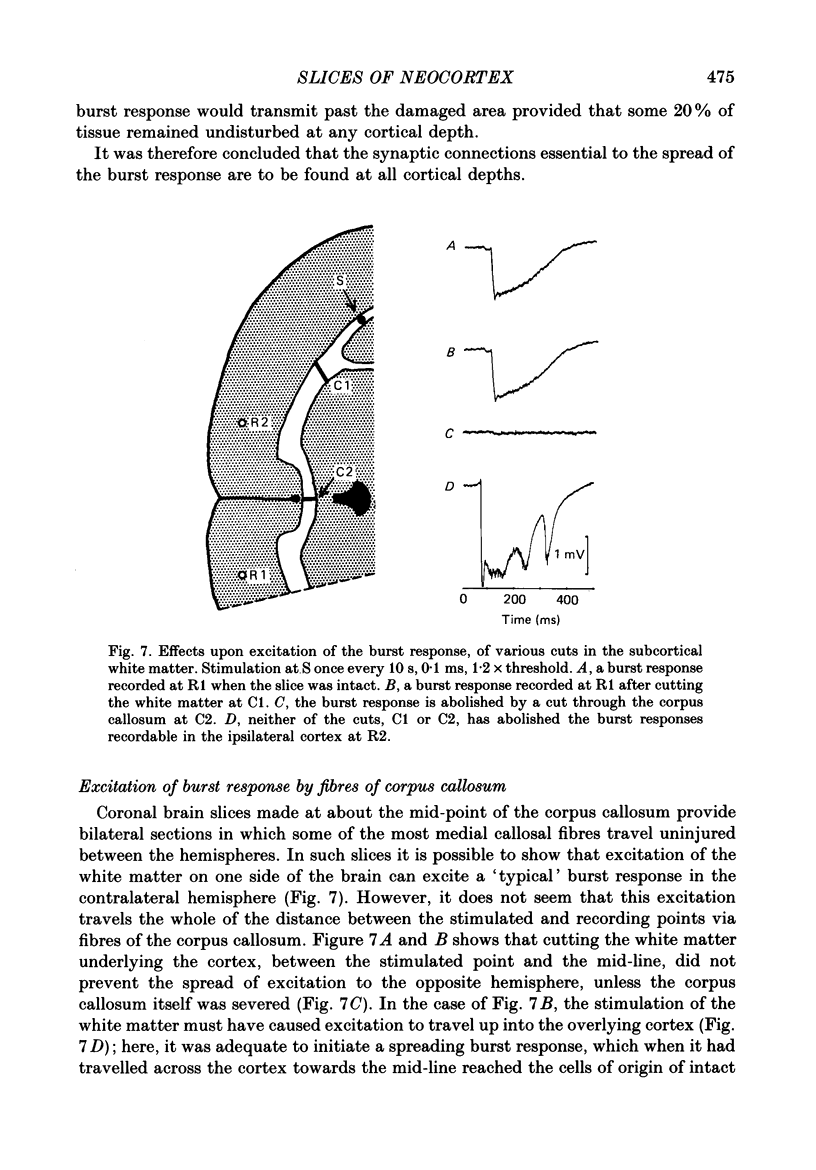
1. Slices of rat's forebrain, 400 micron thick, have been cut and maintained in a bath perfused with warm oxygenated Krebs solution. Records were made with extracellular micropipettes of the neural responses to local stimulation of the cortex itself or the underlying white matter. 2. Single stimuli at either of these sites could produce an all-or-nothing burst response among nearby neurones. This response usually lasted 0.2-0.5 s during which repetitively discharging cortical units could be recorded at all cortical depths. 3. This burst response was transmitted from the stimulated point across the cortex in all directions with a velocity of roughly 0.1 m s-1. 4. Complete recovery of excitability among neurones generating the burst response took about 10 s. 5. Removal of Ca2+ from the perfusate prevented transmission of this response, as did a high concentration of Mg2+ or 160 mg/100 ml of ethanol. 6. Propagation of the burst response was not dependent upon the integrity of the underlying white matter; it required only that any 20% of the cortical thickness was intact and undamaged. 7. In coronal sections of brain the response could be transmitted from one hemisphere to the other provided that the corpus callosum was intact.
Full text
PDF




Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- BURNS B. D., GRAFSTEIN B., OLSZEWSKI J. Identification of neurones giving burst response in isolated cerebral cortex. J Neurophysiol. 1957 Mar;20(2):200–210. doi: 10.1152/jn.1957.20.2.200. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- BURNS B. D., GRAFSTEIN B. The function and structure of some neurones in the cat's cerebral cortex. J Physiol. 1952 Nov;118(3):412–433. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1952.sp004805. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- BURNS B. D. Some properties of isolated cerebral cortex in the unanesthetized cat. J Physiol. 1951 Jan;112(1-2):156–175. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1951.sp004517. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bagust J., Herron C., Kerkut G. A. Spread of activity in thick cortical slices. Brain Res. 1984 Feb 13;293(1):168–172. doi: 10.1016/0006-8993(84)91465-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bindman L. J., Meyer T., Prince C. A. Comparison of the electrical properties of neocortical neurones in slices in vitro and in the anaesthetized rat. Exp Brain Res. 1988;69(3):489–496. doi: 10.1007/BF00247303. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Connors B. W., Gutnick M. J., Prince D. A. Electrophysiological properties of neocortical neurons in vitro. J Neurophysiol. 1982 Dec;48(6):1302–1320. doi: 10.1152/jn.1982.48.6.1302. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dingledine R., Dodd J., Kelly J. S. The in vitro brain slice as a useful neurophysiological preparation for intracellular recording. J Neurosci Methods. 1980 Aug;2(4):323–362. doi: 10.1016/0165-0270(80)90002-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- ECHLIN F. A., ARNETT V., ZOLL J. Paroxysmal high voltage discharges from isolated and partially isolated human and animal cerebral cortex. Electroencephalogr Clin Neurophysiol. 1952 May;4(2):147–164. doi: 10.1016/0013-4694(52)90004-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- HENRY C. E., SCOVILLE W. B. Suppression-burst activity from isolated cerebral cortex in man. Electroencephalogr Clin Neurophysiol. 1952 Feb;4(1):1–22. doi: 10.1016/0013-4694(52)90027-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- HILLMAN H. H., McILWAIN H. Membrane potentials in mammalian cerebral tissues in vitro: dependence on ionic environment. J Physiol. 1961 Jul;157:263–278. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1961.sp006720. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Haas H. L., Jefferys J. G. Low-calcium field burst discharges of CA1 pyramidal neurones in rat hippocampal slices. J Physiol. 1984 Sep;354:185–201. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1984.sp015371. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Knowles W. D., Traub R. D., Strowbridge B. W. The initiation and spread of epileptiform bursts in the in vitro hippocampal slice. Neuroscience. 1987 May;21(2):441–455. doi: 10.1016/0306-4522(87)90134-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- McCormick D. A., Prince D. A. Mechanisms of action of acetylcholine in the guinea-pig cerebral cortex in vitro. J Physiol. 1986 Jun;375:169–194. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1986.sp016112. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Prince D. A. The depolarization shift in "epileptic" neurons. Exp Neurol. 1968 Aug;21(4):467–485. doi: 10.1016/0014-4886(68)90066-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Prince D. A., Wong R. K. Human epileptic neurons studied in vitro. Brain Res. 1981 Apr 6;210(1-2):323–333. doi: 10.1016/0006-8993(81)90905-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Richards C. D., Sercombe R. Electrical activity observed in guinea-pig olfactory cortex maintained in vitro. J Physiol. 1968 Aug;197(3):667–683. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1968.sp008581. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Richards C. D., White A. E. The actions of volatile anaesthetics on synaptic transmission in the dentate gyrus. J Physiol. 1975 Oct;252(1):241–257. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1975.sp011142. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shaw C., Teyler T. J. The neural circuitry of the neocortex examined in the in vitro brain slice preparation. Brain Res. 1982 Jul 8;243(1):35–47. doi: 10.1016/0006-8993(82)91118-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Thomson A. M. A magnesium-sensitive post-synaptic potential in rat cerebral cortex resembles neuronal responses to N-methylaspartate. J Physiol. 1986 Jan;370:531–549. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1986.sp015949. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Vogt B. A., Gorman A. L. Responses of cortical neurons to stimulation of corpus callosum in vitro. J Neurophysiol. 1982 Dec;48(6):1257–1273. doi: 10.1152/jn.1982.48.6.1257. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


