Abstract
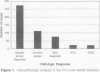
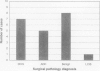
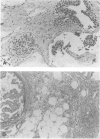
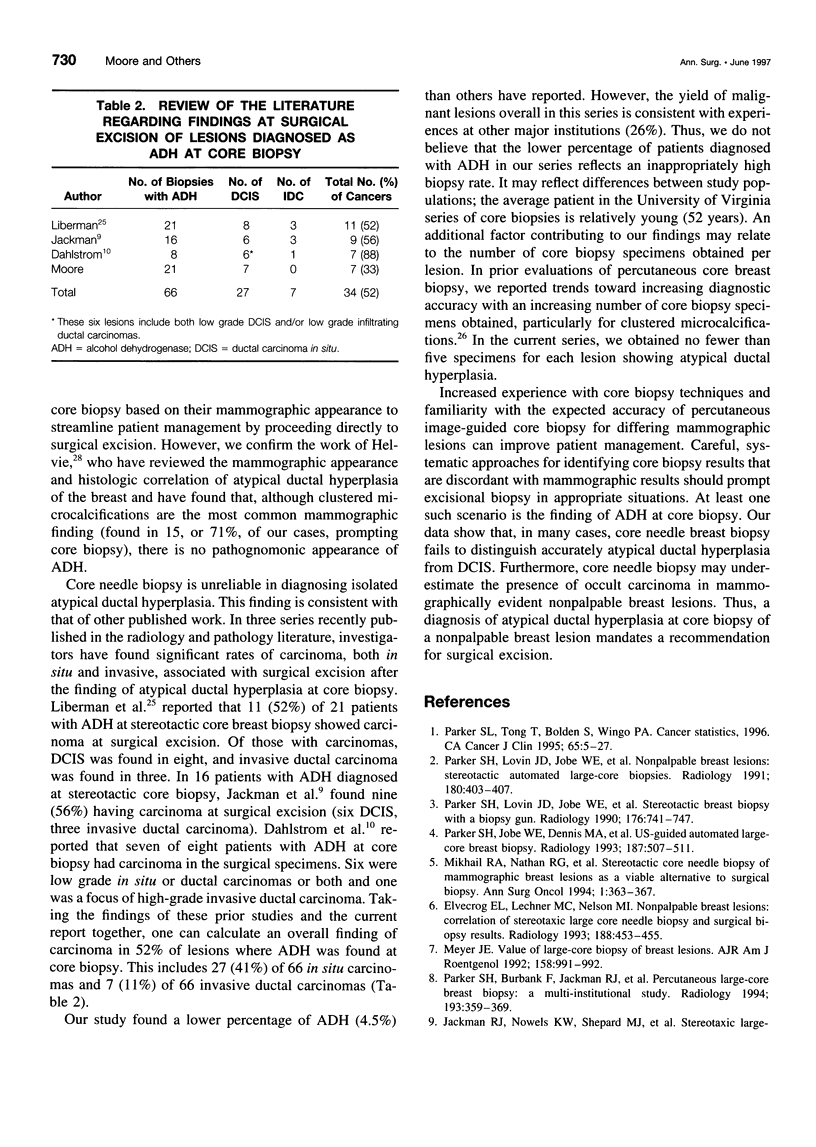
OBJECTIVE: The purpose of the study is to evaluate the prevalence of occult breast carcinoma in surgical breast biopsies performed on nonpalpable breast lesions diagnosed initially as atypical ductal hyperplasia (ADH) by core needle biopsy. BACKGROUND: Atypical ductal hyperplasia is a lesion with significant malignant potential. Some authors note that ADH and ductal carcinoma in situ (DCIS) frequently coexist in the same lesion. The criterion for the diagnosis of DCIS requires involvement of at least two ducts; otherwise, a lesion that is qualitatively consistent with DCIS but quantitatively insufficient is described as atypical ductal hyperplasia. Thus, the finding of ADH in a core needle breast biopsy specimen actually may represent a sample of a true in situ carcinoma. METHODS: Between May 3, 1994, and June 12, 1996, image-guided core biopsies of 510 mammographically identified lesions were performed using a 14-gauge automated device with an average of 7.5 cores obtained per lesion. Atypical ductal hyperplasia was found in 23 (4.5%) of 510 lesions, and surgical excision subsequently was performed in 21 of these cases. In these 21 cases, histopathologic results from core needle and surgical biopsies were reviewed and correlated. RESULTS: Histopathologic study of the 21 surgically excised lesions having ADH in their core needle specimens showed seven (33.3%) with DCIS. CONCLUSIONS: In the authors' patient population, one third of patients with ADH at core biopsy have an occult carcinoma. A core needle breast biopsy finding of ADH for nonpalpable lesions therefore warrants a recommendation for excisional biopsy.
Full text
PDF



Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Abendroth C. S., Wang H. H., Ducatman B. S. Comparative features of carcinoma in situ and atypical ductal hyperplasia of the breast on fine-needle aspiration biopsy specimens. Am J Clin Pathol. 1991 Nov;96(5):654–659. doi: 10.1093/ajcp/96.5.654. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bibbo M., Scheiber M., Cajulis R., Keebler C. M., Wied G. L., Dowlatshahi K. Stereotaxic fine needle aspiration cytology of clinically occult malignant and premalignant breast lesions. Acta Cytol. 1988 Mar-Apr;32(2):193–201. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Brenner R. J., Fajardo L., Fisher P. R., Dershaw D. D., Evans W. P., Bassett L., Feig S., Mendelson E., Jackson V., Margolin F. R. Percutaneous core biopsy of the breast: effect of operator experience and number of samples on diagnostic accuracy. AJR Am J Roentgenol. 1996 Feb;166(2):341–346. doi: 10.2214/ajr.166.2.8553943. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dahlstrom J. E., Sutton S., Jain S. Histological precision of stereotactic core biopsy in diagnosis of malignant and premalignant breast lesions. Histopathology. 1996 Jun;28(6):537–541. doi: 10.1046/j.1365-2559.1996.d01-463.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dupont W. D., Page D. L. Risk factors for breast cancer in women with proliferative breast disease. N Engl J Med. 1985 Jan 17;312(3):146–151. doi: 10.1056/NEJM198501173120303. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Elvecrog E. L., Lechner M. C., Nelson M. T. Nonpalpable breast lesions: correlation of stereotaxic large-core needle biopsy and surgical biopsy results. Radiology. 1993 Aug;188(2):453–455. doi: 10.1148/radiology.188.2.8327696. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Helvie M. A., Hessler C., Frank T. S., Ikeda D. M. Atypical hyperplasia of the breast: mammographic appearance and histologic correlation. Radiology. 1991 Jun;179(3):759–764. doi: 10.1148/radiology.179.3.2027988. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Is 'fibrocystic disease' of the breast precancerous? Arch Pathol Lab Med. 1986 Mar;110(3):171–173. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jackman R. J., Nowels K. W., Shepard M. J., Finkelstein S. I., Marzoni F. A., Jr Stereotaxic large-core needle biopsy of 450 nonpalpable breast lesions with surgical correlation in lesions with cancer or atypical hyperplasia. Radiology. 1994 Oct;193(1):91–95. doi: 10.1148/radiology.193.1.8090927. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lennington W. J., Jensen R. A., Dalton L. W., Page D. L. Ductal carcinoma in situ of the breast. Heterogeneity of individual lesions. Cancer. 1994 Jan 1;73(1):118–124. doi: 10.1002/1097-0142(19940101)73:1<118::aid-cncr2820730121>3.0.co;2-r. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Liberman L., Cohen M. A., Dershaw D. D., Abramson A. F., Hann L. E., Rosen P. P. Atypical ductal hyperplasia diagnosed at stereotaxic core biopsy of breast lesions: an indication for surgical biopsy. AJR Am J Roentgenol. 1995 May;164(5):1111–1113. doi: 10.2214/ajr.164.5.7717215. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Meyer J. E. Value of large-core biopsy of occult breast lesions. AJR Am J Roentgenol. 1992 May;158(5):991–992. doi: 10.2214/ajr.158.5.1566705. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mikhail R. A., Nathan R. C., Weiss M., Tummala R. M., Mullangi U. R., Lawrence L., Mukkamala A. Stereotactic core needle biopsy of mammographic breast lesions as a viable alternative to surgical biopsy. Ann Surg Oncol. 1994 Sep;1(5):363–367. doi: 10.1007/BF02303806. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Page D. L. Cancer risk assessment in benign breast biopsies. Hum Pathol. 1986 Sep;17(9):871–874. doi: 10.1016/s0046-8177(86)80636-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Page D. L., Dupont W. D., Rogers L. W. Ductal involvement by cells of atypical lobular hyperplasia in the breast: a long-term follow-up study of cancer risk. Hum Pathol. 1988 Feb;19(2):201–207. doi: 10.1016/s0046-8177(88)80350-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Page D. L., Dupont W. D., Rogers L. W., Rados M. S. Atypical hyperplastic lesions of the female breast. A long-term follow-up study. Cancer. 1985 Jun 1;55(11):2698–2708. doi: 10.1002/1097-0142(19850601)55:11<2698::aid-cncr2820551127>3.0.co;2-a. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Page D. L., Rogers L. W. Combined histologic and cytologic criteria for the diagnosis of mammary atypical ductal hyperplasia. Hum Pathol. 1992 Oct;23(10):1095–1097. doi: 10.1016/0046-8177(92)90026-y. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Page D. L. The woman at high risk for breast cancer. Importance of hyperplasia. Surg Clin North Am. 1996 Apr;76(2):221–230. doi: 10.1016/s0039-6109(05)70435-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Parker S. H., Burbank F., Jackman R. J., Aucreman C. J., Cardenosa G., Cink T. M., Coscia J. L., Jr, Eklund G. W., Evans W. P., 3rd, Garver P. R. Percutaneous large-core breast biopsy: a multi-institutional study. Radiology. 1994 Nov;193(2):359–364. doi: 10.1148/radiology.193.2.7972743. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Parker S. H., Jobe W. E., Dennis M. A., Stavros A. T., Johnson K. K., Yakes W. F., Truell J. E., Price J. G., Kortz A. B., Clark D. G. US-guided automated large-core breast biopsy. Radiology. 1993 May;187(2):507–511. doi: 10.1148/radiology.187.2.8475299. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Parker S. H., Lovin J. D., Jobe W. E., Burke B. J., Hopper K. D., Yakes W. F. Nonpalpable breast lesions: stereotactic automated large-core biopsies. Radiology. 1991 Aug;180(2):403–407. doi: 10.1148/radiology.180.2.1648757. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Parker S. H., Lovin J. D., Jobe W. E., Luethke J. M., Hopper K. D., Yakes W. F., Burke B. J. Stereotactic breast biopsy with a biopsy gun. Radiology. 1990 Sep;176(3):741–747. doi: 10.1148/radiology.176.3.2167501. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rosai J. Borderline epithelial lesions of the breast. Am J Surg Pathol. 1991 Mar;15(3):209–221. doi: 10.1097/00000478-199103000-00001. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schnitt S. J., Connolly J. L., Tavassoli F. A., Fechner R. E., Kempson R. L., Gelman R., Page D. L. Interobserver reproducibility in the diagnosis of ductal proliferative breast lesions using standardized criteria. Am J Surg Pathol. 1992 Dec;16(12):1133–1143. doi: 10.1097/00000478-199212000-00001. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sneige N., Staerkel G. A. Fine-needle aspiration cytology of ductal hyperplasia with and without atypia and ductal carcinoma in situ. Hum Pathol. 1994 May;25(5):485–492. doi: 10.1016/0046-8177(94)90120-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]