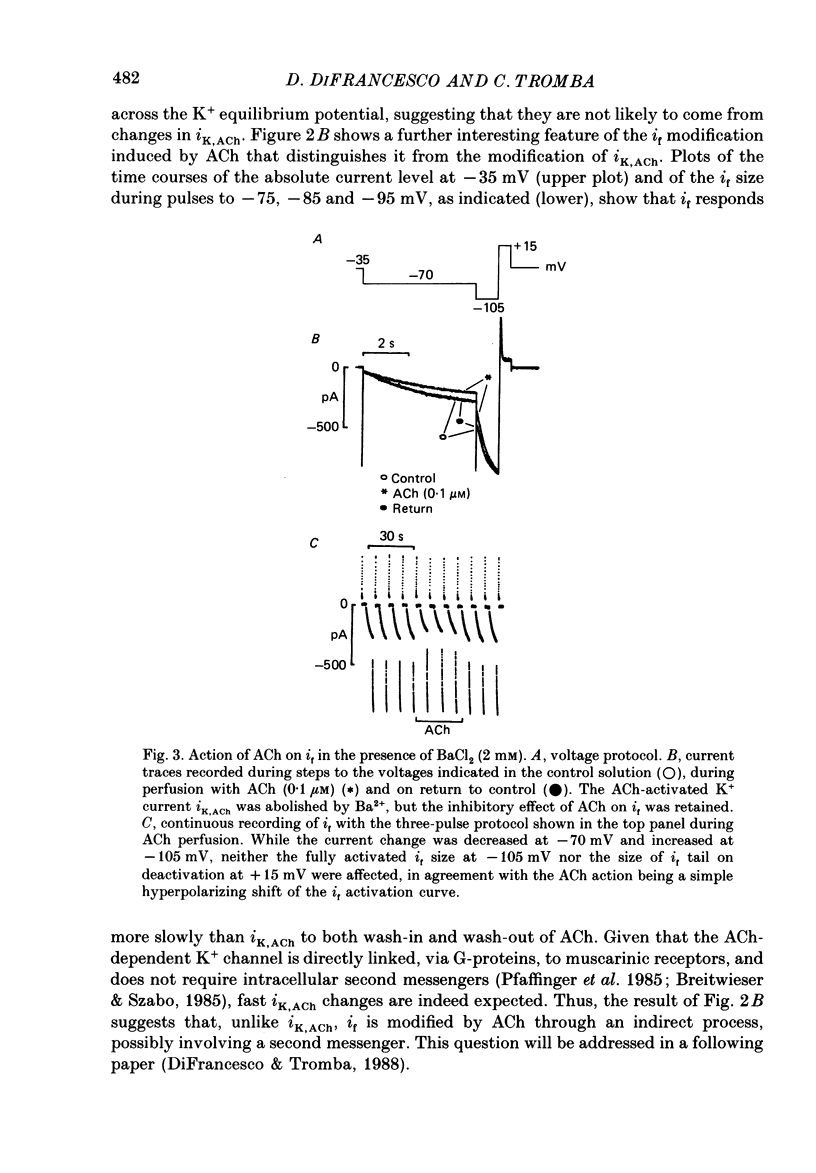
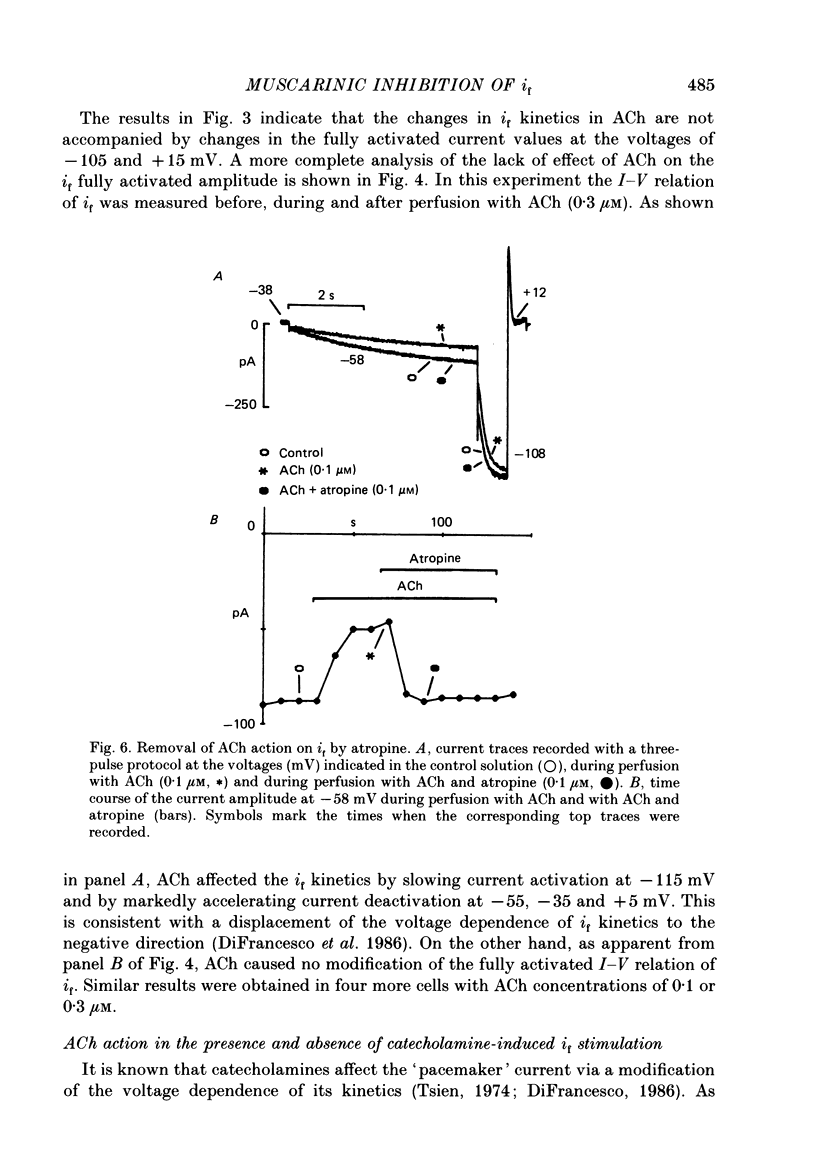
Abstract
1. The action of acetylcholine (ACh) on the hyperpolarization-activated ('pacemaker') current if was studied in single myocytes from the sino-atrial (SA) node region of the rabbit heart, where low doses of ACh slow spontaneous activity by prolonging the diastolic depolarization phase. 2. Besides activating an outward component at voltages positive to the K+ equilibrium potential (iK,ACh), ACh depressed the current if activated on hyperpolarization at concentrations in the range 0.03-1 microM. 3. The ACh-dependent if depression was dissected from modifications of iK,ACh by blocking iK,ACh with barium and was studied under conditions that minimized the interference of other current changes caused by ACh. 4. The study of if modification by ACh with three-pulse protocols and the measurement of fully activated I-V relations of if with and without ACh revealed that ACh acted on if by shifting the current activation range to more negative voltages, with no obvious alteration of the fully activated current amplitude. 5. The action of ACh on if was opposite to that caused by catecholamines. The presence of isoprenaline (IP) did not prevent ACh inhibition of if, nor did the presence of ACh prevent the if stimulation caused by IP. The effects of IP and ACh on if were additive. 6. The ACh-induced inhibition of if was reversed by addition of atropine and could be mimicked by muscarine, indicating that muscarinic receptors mediate it. The implications of these findings on the regulation of pacemaker activity by ACh is discussed.
Full text
PDF












Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Breitwieser G. E., Szabo G. Uncoupling of cardiac muscarinic and beta-adrenergic receptors from ion channels by a guanine nucleotide analogue. Nature. 1985 Oct 10;317(6037):538–540. doi: 10.1038/317538a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Brown H. F., DiFrancesco D., Noble S. J. How does adrenaline accelerate the heart? Nature. 1979 Jul 19;280(5719):235–236. doi: 10.1038/280235a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Brown H. F., Kimura J., Noble D., Noble S. J., Taupignon A. The ionic currents underlying pacemaker activity in rabbit sino-atrial node: experimental results and computer simulations. Proc R Soc Lond B Biol Sci. 1984 Sep 22;222(1228):329–347. doi: 10.1098/rspb.1984.0067. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Carmeliet E., Mubagwa K. Changes by acetylcholine of membrane currents in rabbit cardiac Purkinje fibres. J Physiol. 1986 Feb;371:201–217. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1986.sp015969. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Carmeliet E., Mubagwa K. Characterization of the acetylcholine-induced potassium current in rabbit cardiac Purkinje fibres. J Physiol. 1986 Feb;371:219–237. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1986.sp015970. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Carmeliet E., Ramon J. Effects of acetylcholine on time-dependent currents in sheep cardiac Purkinje fibers. Pflugers Arch. 1980 Sep;387(3):217–223. doi: 10.1007/BF00580973. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- DiFrancesco D. A study of the ionic nature of the pace-maker current in calf Purkinje fibres. J Physiol. 1981 May;314:377–393. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1981.sp013714. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- DiFrancesco D. Characterization of single pacemaker channels in cardiac sino-atrial node cells. Nature. 1986 Dec 4;324(6096):470–473. doi: 10.1038/324470a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- DiFrancesco D., Ferroni A., Mazzanti M., Tromba C. Properties of the hyperpolarizing-activated current (if) in cells isolated from the rabbit sino-atrial node. J Physiol. 1986 Aug;377:61–88. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1986.sp016177. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- DiFrancesco D., Ferroni A., Visentin S. Barium-induced blockade of the inward rectifier in calf Purkinje fibres. Pflugers Arch. 1984 Dec;402(4):446–453. doi: 10.1007/BF00583946. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- DiFrancesco D., Noma A., Trautwein W. Separation of current induced by potassium accumulation from acetylcholine-induced relaxation current in the rabbit S-A node. Pflugers Arch. 1980 Sep;387(2):83–90. doi: 10.1007/BF00584257. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- DiFrancesco D., Tromba C. Acetylcholine inhibits activation of the cardiac hyperpolarizing-activated current, if. Pflugers Arch. 1987 Sep;410(1-2):139–142. doi: 10.1007/BF00581906. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- DiFrancesco D., Tromba C. Muscarinic control of the hyperpolarization-activated current (if) in rabbit sino-atrial node myocytes. J Physiol. 1988 Nov;405:493–510. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1988.sp017344. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Eckstein F., Cassel D., Levkovitz H., Lowe M., Selinger Z. Guanosine 5'-O-(2-thiodiphosphate). An inhibitor of adenylate cyclase stimulation by guanine nucleotides and fluoride ions. J Biol Chem. 1979 Oct 10;254(19):9829–9834. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Egan T. M., Noble S. J. Acetylcholine and the mammalian 'slow inward' current: a computer investigation. Proc R Soc Lond B Biol Sci. 1987 Apr 22;230(1260):315–337. doi: 10.1098/rspb.1987.0022. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Endoh M., Maruyama M., Iijima T. Attenuation of muscarinic cholinergic inhibition by islet-activating protein in the heart. Am J Physiol. 1985 Aug;249(2 Pt 2):H309–H320. doi: 10.1152/ajpheart.1985.249.2.H309. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fischmeister R., Hartzell H. C. Mechanism of action of acetylcholine on calcium current in single cells from frog ventricle. J Physiol. 1986 Jul;376:183–202. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1986.sp016148. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Garnier D., Nargeot J., Ojeda C., Rougier O. The action of acetylcholine on background conductance in frog atrial trabeculae. J Physiol. 1978 Jan;274:381–396. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1978.sp012154. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Giles W., Noble S. J. Changes in membrane currents in bullfrog atrium produced by acetylcholine. J Physiol. 1976 Sep;261(1):103–123. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1976.sp011550. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gilman A. G. G proteins and dual control of adenylate cyclase. Cell. 1984 Mar;36(3):577–579. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(84)90336-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- HUTTER O. F., TRAUTWEIN W. Effect of vagal stimulation on the sinus venosus of the frog's heart. Nature. 1955 Sep 10;176(4480):512–513. doi: 10.1038/176512a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- HUTTER O. F., TRAUTWEIN W. Vagal and sympathetic effects on the pacemaker fibers in the sinus venosus of the heart. J Gen Physiol. 1956 May 20;39(5):715–733. doi: 10.1085/jgp.39.5.715. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hartzell H. C., Fischmeister R. Opposite effects of cyclic GMP and cyclic AMP on Ca2+ current in single heart cells. Nature. 1986 Sep 18;323(6085):273–275. doi: 10.1038/323273a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hauswirth O., Noble D., Tsien R. W. Adrenaline: mechanism of action on the pacemaker potential in cardiac Purkinje fibers. Science. 1968 Nov 22;162(3856):916–917. doi: 10.1126/science.162.3856.916. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hescheler J., Kameyama M., Trautwein W. On the mechanism of muscarinic inhibition of the cardiac Ca current. Pflugers Arch. 1986 Aug;407(2):182–189. doi: 10.1007/BF00580674. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hino N., Ochi R. Effect of acetylcholine on membrane currents in guinea-pig papillary muscle. J Physiol. 1980 Oct;307:183–197. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1980.sp013430. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Limbird L. E. Activation and attenuation of adenylate cyclase. The role of GTP-binding proteins as macromolecular messengers in receptor--cyclase coupling. Biochem J. 1981 Apr 1;195(1):1–13. doi: 10.1042/bj1950001. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Noma A., Peper K., Trautwein W. Acetylcholine-induced potassium current fluctuations in the rabbit sino-atrial node. Pflugers Arch. 1979 Sep;381(3):255–262. doi: 10.1007/BF00583257. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Noma A., Trautwein W. Relaxation of the ACh-induced potassium current in the rabbit sinoatrial node cell. Pflugers Arch. 1978 Nov 30;377(3):193–200. doi: 10.1007/BF00584272. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Osterrieder W., Noma A., Trautwein W. On the kinetics of the potassium channel activated by acetylcholine in the S-A node of the rabbit heart. Pflugers Arch. 1980 Jul;386(2):101–109. doi: 10.1007/BF00584196. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pfaffinger P. J., Martin J. M., Hunter D. D., Nathanson N. M., Hille B. GTP-binding proteins couple cardiac muscarinic receptors to a K channel. Nature. 1985 Oct 10;317(6037):536–538. doi: 10.1038/317536a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rodbell M. The role of hormone receptors and GTP-regulatory proteins in membrane transduction. Nature. 1980 Mar 6;284(5751):17–22. doi: 10.1038/284017a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sakmann B., Noma A., Trautwein W. Acetylcholine activation of single muscarinic K+ channels in isolated pacemaker cells of the mammalian heart. Nature. 1983 May 19;303(5914):250–253. doi: 10.1038/303250a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shibata E. F., Giles W., Pollack G. H. Threshold effects of acetylcholine on primary pacemaker cells of the rabbit sino-atrial node. Proc R Soc Lond B Biol Sci. 1985 Jan 22;223(1232):355–378. doi: 10.1098/rspb.1985.0006. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Soejima M., Noma A. Mode of regulation of the ACh-sensitive K-channel by the muscarinic receptor in rabbit atrial cells. Pflugers Arch. 1984 Apr;400(4):424–431. doi: 10.1007/BF00587544. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sorota S., Tsuji Y., Tajima T., Pappano A. J. Pertussis toxin treatment blocks hyperpolarization by muscarinic agonists in chick atrium. Circ Res. 1985 Nov;57(5):748–758. doi: 10.1161/01.res.57.5.748. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- TRAUTWEIN W., DUDEL J. Zum Mechanismus der Membranwirkung des Acetylcholin an der Herzmuskelfaser. Pflugers Arch. 1958;266(3):324–334. doi: 10.1007/BF00416781. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Trautwein W., Cavalié A. Cardiac calcium channels and their control by neurotransmitters and drugs. J Am Coll Cardiol. 1985 Dec;6(6):1409–1416. doi: 10.1016/s0735-1097(85)80233-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tsien R. W. Effects of epinephrine on the pacemaker potassium current of cardiac Purkinje fibers. J Gen Physiol. 1974 Sep;64(3):293–319. doi: 10.1085/jgp.64.3.293. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- de Carvalho A. P., Hoffman B. F., de Carvalho M. P. Two components of the cardiac action potential. I. Voltage-time course and the effect of acetylcholine on atrial and nodal cells of the rabbit heart. J Gen Physiol. 1969 Nov;54(5):607–635. doi: 10.1085/jgp.54.5.607. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


