Abstract
OBJECTIVE: To develop selection criteria based on the mechanical properties of pharyngoesophageal swallowing that indicate when patients with pharyngeal dysphagia will benefit from a myotomy. SUMMARY BACKGROUND DATA: The pathophysiology of pharyngoesophageal swallowing disorders is complex. The disorder is of interest to several medical specialists (gastroenterologists, otorhinolaryngologists, general and thoracic surgeons), which contributes to confusion about the entity. The management is compounded because it is most frequently seen in the elderly, is often associated with generalized neuromuscular disease, and occurs with a high prevalence of concomitant disease. The selection of patients for myotomy is difficult and of major importance to the quality of life of the affected patients. METHOD: One hundred seven patients without a Zenker diverticulum but with pharyngeal dysphagia underwent a detailed manometric assessment of the upper esophageal sphincter (UES). Cricopharyngeal opening was identified by the presence of a subatmospheric pressure drop before bolus arrival. Impaired pharyngoesophageal segment compliance resulting in a resistance to pharyngoesophageal flow was determined by measuring the intrabolus pressure generated by a 5-ml liquid bolus. RESULTS: Thirty-one of 107 patients underwent a myotomy (29%). Both impaired sphincter opening and increased intrabolus pressure predicted a good outcome. CONCLUSION: Myotomy is beneficial in patients with pharyngeal swallowing disorders and manometric evidence of defective sphincter opening and increased intrabolus pressure.
Full text
PDF


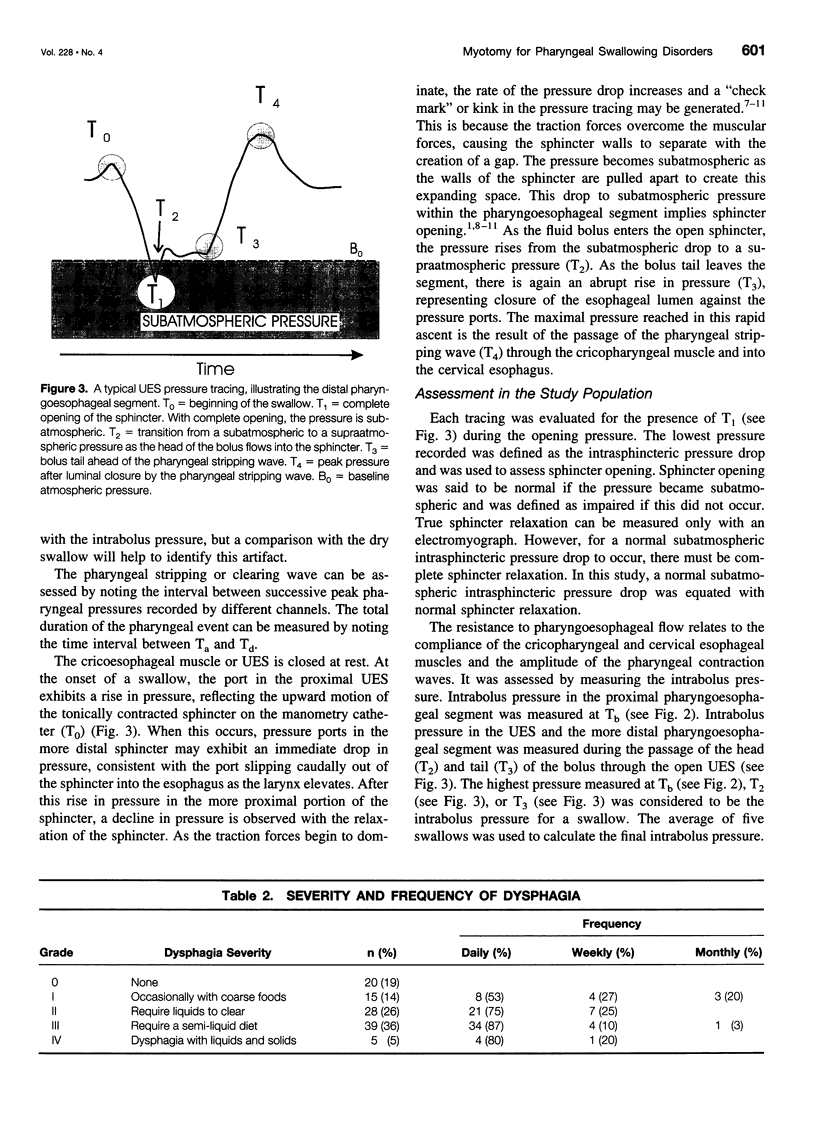

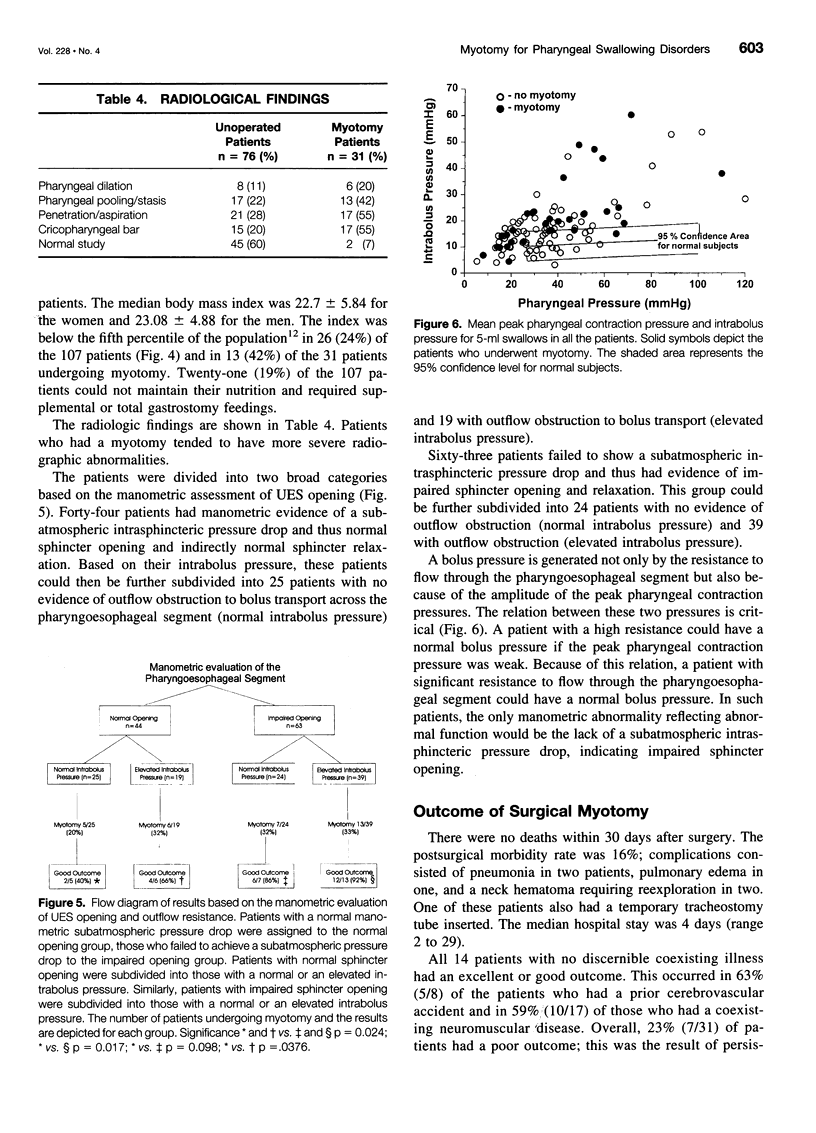
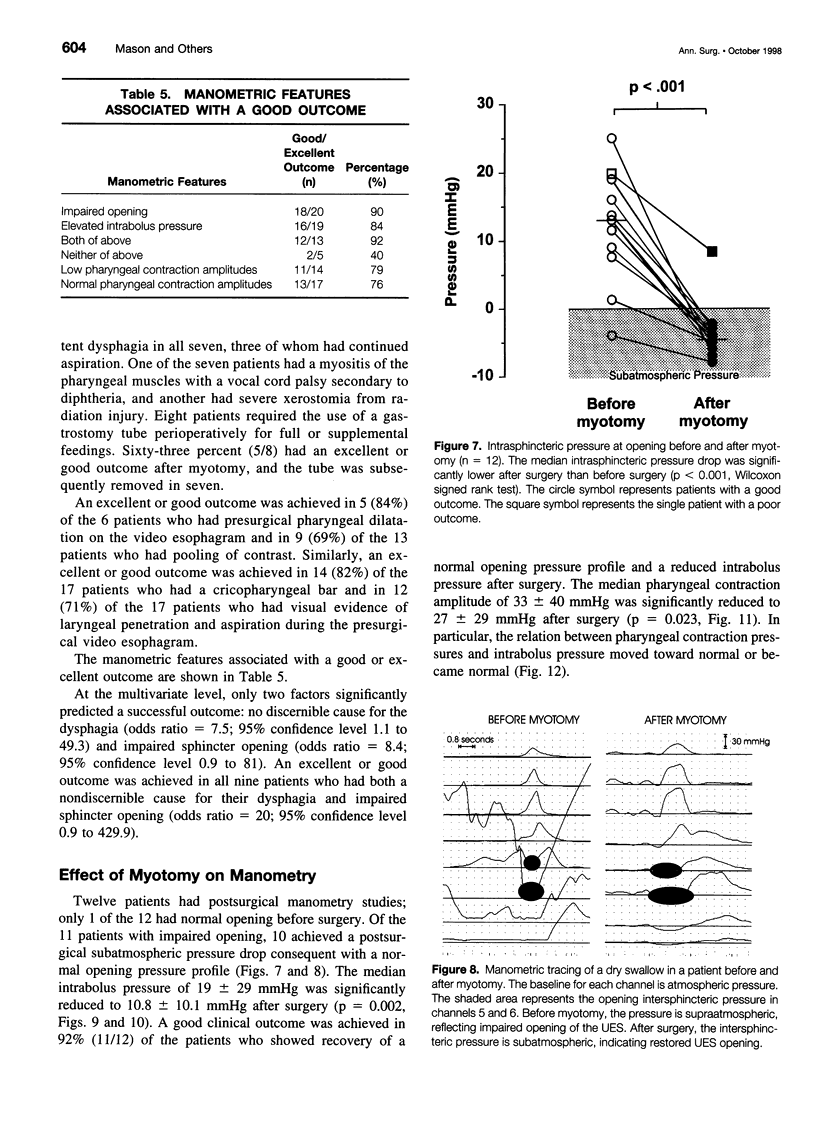
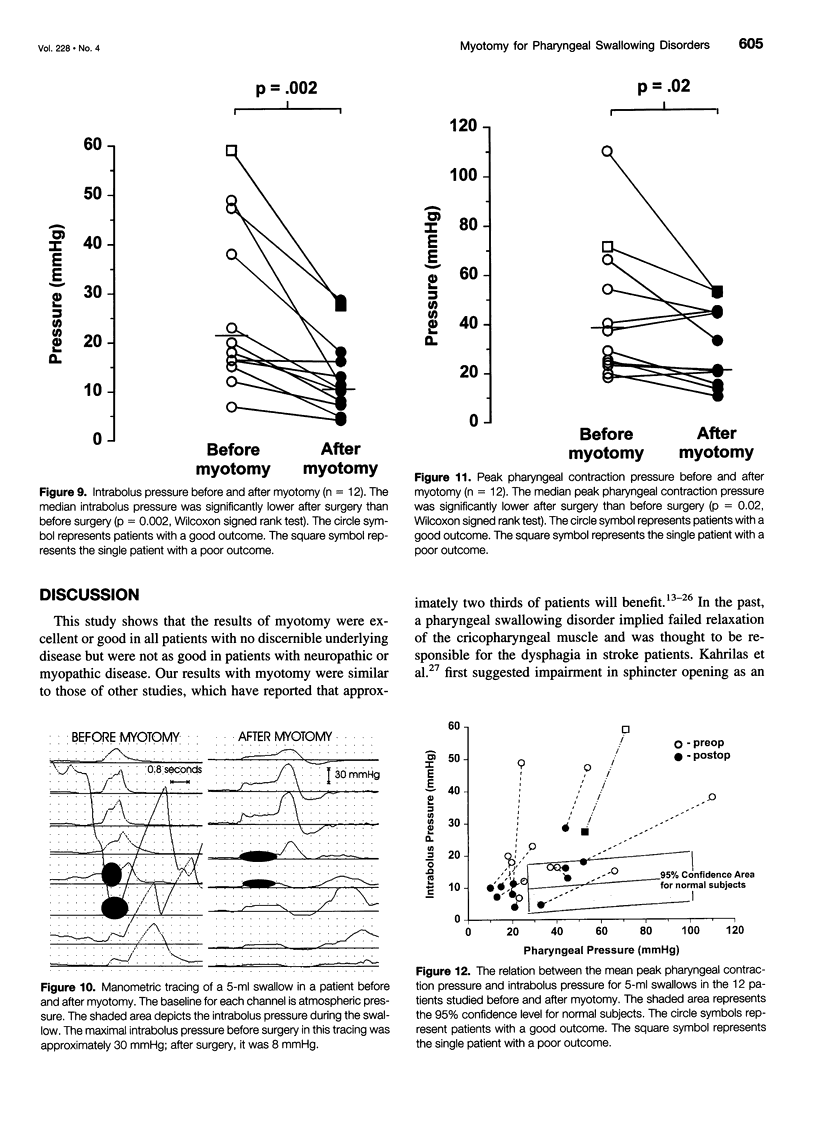


Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Ali G. N., Wallace K. L., Laundl T. M., Hunt D. R., deCarle D. J., Cook I. J. Predictors of outcome following cricopharyngeal disruption for pharyngeal dysphagia. Dysphagia. 1997 Summer;12(3):133–139. doi: 10.1007/PL00009527. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Asoh R., Goyal R. K. Manometry and electromyography of the upper esophageal sphincter in the opossum. Gastroenterology. 1978 Mar;74(3):514–520. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Berg H. M., Jacobs J. B., Persky M. S., Cohen N. L. Cricopharyngeal myotomy: a review of surgical results in patients with cricopharyngeal achalasia of neurogenic origin. Laryngoscope. 1985 Nov;95(11):1337–1340. doi: 10.1288/00005537-198511000-00008. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Black R. J. Cricopharyngeal myotomy. J Otolaryngol. 1981 Apr;10(2):145–148. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bonavina L., Khan N. A., DeMeester T. R. Pharyngoesophageal dysfunctions. The role of cricopharyngeal myotomy. Arch Surg. 1985 May;120(5):541–549. doi: 10.1001/archsurg.1985.01390290023004. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cook I. J., Dodds W. J., Dantas R. O., Massey B., Kern M. K., Lang I. M., Brasseur J. G., Hogan W. J. Opening mechanisms of the human upper esophageal sphincter. Am J Physiol. 1989 Nov;257(5 Pt 1):G748–G759. doi: 10.1152/ajpgi.1989.257.5.G748. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cruse J. P., Edwards D. A., Smith J. F., Wyllie J. H. The pathology of a cricopharyngeal dysphagia. Histopathology. 1979 May;3(3):223–232. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-2559.1979.tb02999.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dantas R. O., Cook I. J., Dodds W. J., Kern M. K., Lang I. M., Brasseur J. G. Biomechanics of cricopharyngeal bars. Gastroenterology. 1990 Nov;99(5):1269–1274. doi: 10.1016/0016-5085(90)91149-z. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ekberg O. The normal movements of the hyoid bone during swallow. Invest Radiol. 1986 May;21(5):408–410. doi: 10.1097/00004424-198605000-00009. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ellis F. H., Jr, Crozier R. E. Cervical esophageal dysphagia: indications for and results of cricopharyngeal myotomy. Ann Surg. 1981 Sep;194(3):279–289. doi: 10.1097/00000658-198109000-00005. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gagic N. M. Cricopharyngeal myotomy. Can J Surg. 1983 Jan;26(1):47–49. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gay I., Chisin R., Elidan J. Myotomy of the cricopharyngeal muscle. A treatment for dysphagia and aspiration in neurological disorders. Rev Laryngol Otol Rhinol (Bord) 1984;105(3):271–274. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kahrilas P. J., Dodds W. J., Dent J., Logemann J. A., Shaker R. Upper esophageal sphincter function during deglutition. Gastroenterology. 1988 Jul;95(1):52–62. doi: 10.1016/0016-5085(88)90290-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kahrilas P. J., Logemann J. A., Krugler C., Flanagan E. Volitional augmentation of upper esophageal sphincter opening during swallowing. Am J Physiol. 1991 Mar;260(3 Pt 1):G450–G456. doi: 10.1152/ajpgi.1991.260.3.G450. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kelly J. H. Use of manometry in the evaluation of dysphagia. Otolaryngol Head Neck Surg. 1997 Mar;116(3):355–357. doi: 10.1016/S0194-59989770273-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lacau St Guily J., Zhang K. X., Périé S., Copin H., Butler-Browne G. S., Barbet J. P. Improvement of dysphagia following cricopharyngeal myotomy in a group of elderly patients. Histochemical and biochemical assessment of the cricopharyngeal muscle. Ann Otol Rhinol Laryngol. 1995 Aug;104(8):603–609. doi: 10.1177/000348949510400803. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lindgren S., Ekberg O. Cricopharyngeal myotomy in the treatment of dysphagia. Clin Otolaryngol Allied Sci. 1990 Jun;15(3):221–227. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-2273.1990.tb00779.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Logemann J. A., Kahrilas P. J. Relearning to swallow after stroke--application of maneuvers and indirect biofeedback: a case study. Neurology. 1990 Jul;40(7):1136–1138. doi: 10.1212/wnl.40.7.1136. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- McConnel F. M., Cerenko D., Hersh T., Weil L. J. Evaluation of pharyngeal dysphagia with manofluorography. Dysphagia. 1988;2(4):187–195. doi: 10.1007/BF02414425. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- McConnel F. M., Cerenko D., Jackson R. T., Hersh T. Clinical application of the manofluorogram. Laryngoscope. 1988 Jul;98(7):705–711. doi: 10.1288/00005537-198807000-00003. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- McConnel F. M., Cerenko D., Mendelsohn M. S. Manofluorographic analysis of swallowing. Otolaryngol Clin North Am. 1988 Nov;21(4):625–635. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Migliore M., Payne H. R., Jeyasingham K. Pharyngo-oesophageal dysphagia: surgery based on clinical and manometric data. Eur J Cardiothorac Surg. 1996;10(5):365–371. doi: 10.1016/s1010-7940(96)80096-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Palmer J. B., Tanaka E., Siebens A. A. Electromyography of the pharyngeal musculature: technical considerations. Arch Phys Med Rehabil. 1989 Apr;70(4):283–287. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Poirier N. C., Bonavina L., Taillefer R., Nosadini A., Peracchia A., Duranceau A. Cricopharyngeal myotomy for neurogenic oropharyngeal dysphagia. J Thorac Cardiovasc Surg. 1997 Feb;113(2):233–241. doi: 10.1016/S0022-5223(97)70318-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ross E. R., Green R., Auslander M. O., Biller H. F. Cricopharyngeal myotomy: management of cervical dysphagia. Otolaryngol Head Neck Surg. 1982 Jul-Aug;90(4):434–441. doi: 10.1177/019459988209000413. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sato Y., Honda Y., Oizumi K., Kaku N., Furuno H., Ohta Y., Ito S., Higuchi I., Osame M. Morphological and histochemical study of nonhemiplegic muscle in acute stroke patients manifesting respiratory failure. Eur Neurol. 1996;36(1):13–19. doi: 10.1159/000117193. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shaker R., Ren J., Xie P., Lang I. M., Bardan E., Sui Z. Characterization of the pharyngo-UES contractile reflex in humans. Am J Physiol. 1997 Oct;273(4 Pt 1):G854–G858. doi: 10.1152/ajpgi.1997.273.4.G854. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shipp T., Deatsch W. W., Robertson K. Pharyngoesophageal muscle activity during swallowing in man. Laryngoscope. 1970 Jan;80(1):1–16. doi: 10.1288/00005537-197001000-00001. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Simopoulos A. P., Van Itallie T. B. Body weight, health, and longevity. Ann Intern Med. 1984 Feb;100(2):285–295. doi: 10.7326/0003-4819-100-2-285. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- St Guily J. L., Périé S., Willig T. N., Chaussade S., Eymard B., Angelard B. Swallowing disorders in muscular diseases: functional assessment and indications of cricopharyngeal myotomy. Ear Nose Throat J. 1994 Jan;73(1):34–40. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Taillefer R., Duranceau A. C. Manometric and radionuclide assessment of pharyngeal emptying before and after cricopharyngeal myotomy in patients with oculopharyngeal muscular dystrophy. J Thorac Cardiovasc Surg. 1988 May;95(5):868–875. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wilson P. S., Bruce-Lockhart F. J., Johnson A. P. Videofluoroscopy in motor neurone disease prior to cricopharyngeal myotomy. Ann R Coll Surg Engl. 1990 Nov;72(6):375–377. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]