Abstract
OBJECTIVE: To assess the feasibility, morbidity, mortality, and clinical success rate of surgical reconstruction of the biliary system in patients with ischemic-type biliary lesions in their liver graft. SUMMARY BACKGROUND DATA: After liver transplantation, strictures in the biliary tree with secondary sludge formation can occur in the absence of vascular problems. Jaundice, pruritus, and recurrent cholangitis are predominant clinical features leading to considerable morbidity. Interventional measures are the first-line treatment but are frequently only of transient success. Retransplantation is usually considered when interventional treatment is not effective. METHODS: Surgical exploration and reconstruction was performed in 17 patients with ischemic-type biliary strictures at a median of 2 years after liver transplantation. Findings during surgery, surgical strategies, and postsurgical courses are described. Clinical symptoms and biochemical parameters of cholestasis and liver function were analyzed in the postsurgical course. RESULTS: During surgery, all 17 patients were found to have strictures or sclerotic changes involving the hepatic bifurcation and extrahepatic bile duct. Sludge or stones were present in nine patients. In 14 patients with viable bile ducts proximal to the bifurcation, surgical reconstruction was performed by resection of the bifurcation and hepaticojejunostomy. In three patients with more extensive biliary destruction, portoenterostomy with or without peripheral hepatojejunostomy was performed. The prevalence rate of biliary infection at surgery was 93%; the predominant organisms were Candida and enterococci. The perioperative mortality rate was 0%. Clinical symptoms and biochemical parameters became normal or were considerably improved in 14 of 16 patients (88%). CONCLUSIONS: The hepatic bifurcation seems to be a predominant site for ischemic-type biliary changes after liver transplantation. Surgical treatment by resection of the bifurcation and reconstruction by high hepaticojejunostomy is a safe and highly effective approach leading to cure or persistent major improvement in most patients.
Full text
PDF


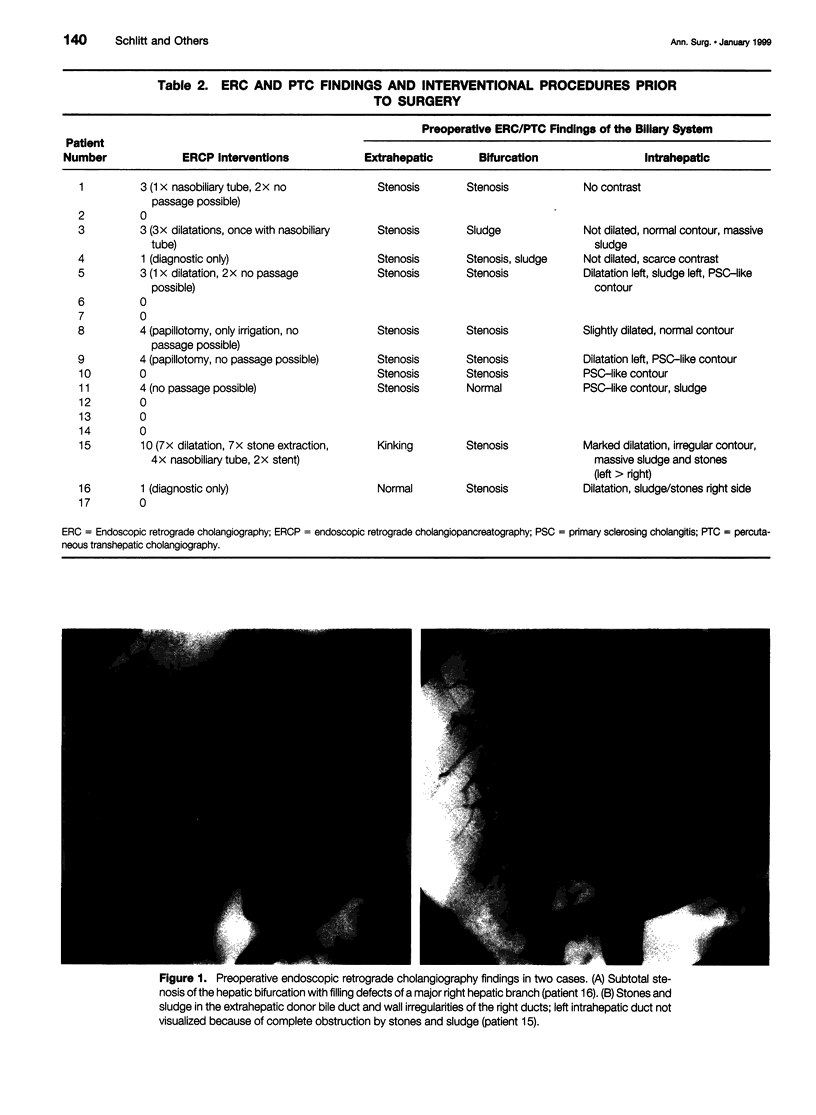


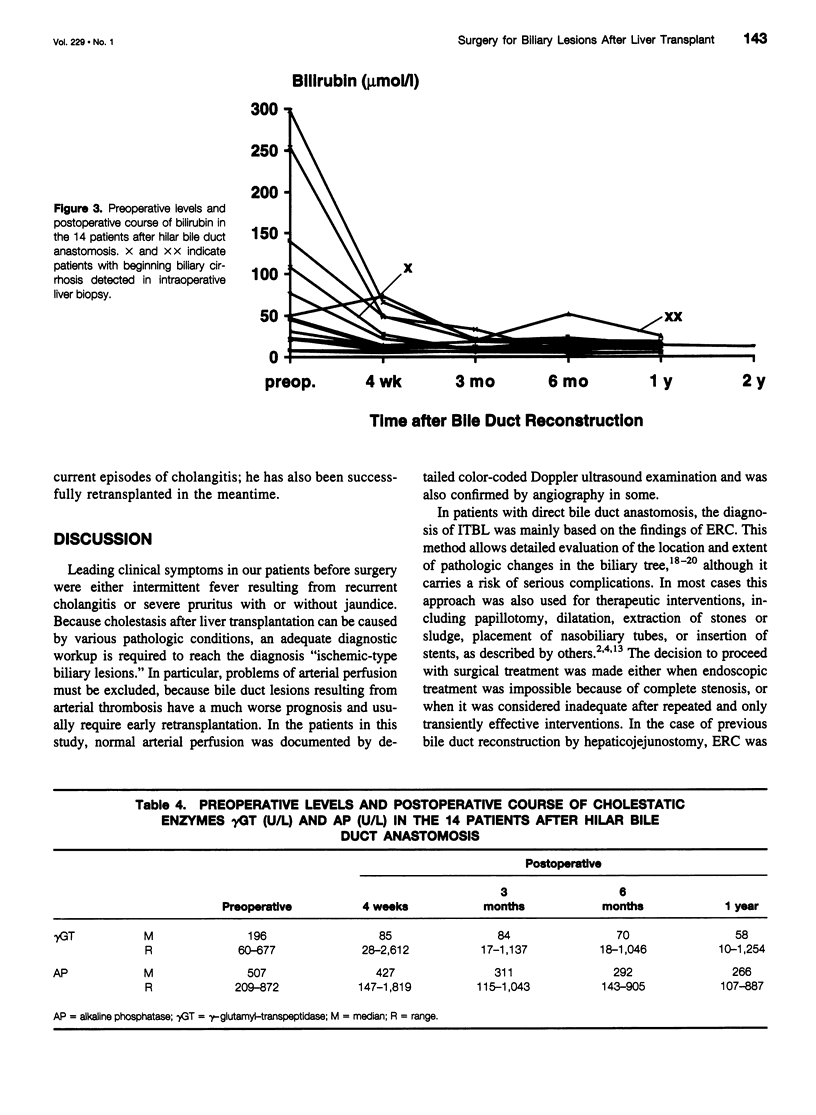


Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Barton P., Maier A., Steininger R., Mühlbacher F., Lechner G. Biliary sludge after liver transplantation: 1. Imaging findings and efficacy of various imaging procedures. AJR Am J Roentgenol. 1995 Apr;164(4):859–864. doi: 10.2214/ajr.164.4.7726038. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Barton P., Steininger R., Maier A., Mühlbacher F., Lechner G. Biliary sludge after liver transplantation: 2. Treatment with interventional techniques versus surgery and/or oral chemolysis. AJR Am J Roentgenol. 1995 Apr;164(4):865–869. doi: 10.2214/ajr.164.4.7537016. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chen C. L., Wang K. L., Chuang J. H., Lin J. N., Chu M. F., Chang C. H. Biliary sludge-cast formation following liver transplantation. Hepatogastroenterology. 1988 Feb;35(1):22–24. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Colonna J. O., 2nd, Shaked A., Gomes A. S., Colquhoun S. D., Jurim O., McDiarmid S. V., Millis J. M., Goldstein L. I., Busuttil R. W. Biliary strictures complicating liver transplantation. Incidence, pathogenesis, management, and outcome. Ann Surg. 1992 Sep;216(3):344–352. doi: 10.1097/00000658-199209000-00014. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Doillon C., Dureau G., Chignier E., Clendinnen G., Eloy R. Course of the initial epithelial lesions associated with autologous bile duct replacement. Experimental study in rats. Am J Surg. 1981 Feb;141(2):187–193. doi: 10.1016/0002-9610(81)90154-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fisher A., Miller C. H. Ischemic-type biliary strictures in liver allografts: the Achilles heel revisited? Hepatology. 1995 Feb;21(2):589–591. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Greif F., Bronsther O. L., Van Thiel D. H., Casavilla A., Iwatsuki S., Tzakis A., Todo S., Fung J. J., Starzl T. E. The incidence, timing, and management of biliary tract complications after orthotopic liver transplantation. Ann Surg. 1994 Jan;219(1):40–45. doi: 10.1097/00000658-199401000-00007. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hintze R. E., Adler A., Veltzke W., Abou-Rebyeh H., Felix R., Neuhaus P. Endoscopic management of biliary complications after orthotopic liver transplantation. Hepatogastroenterology. 1997 Jan-Feb;44(13):258–262. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kuo P. C., Lewis W. D., Stokes K., Pleskow D., Simpson M. A., Jenkins R. L. A comparison of operation, endoscopic retrograde cholangiopancreatography, and percutaneous transhepatic cholangiography in biliary complications after hepatic transplantation. J Am Coll Surg. 1994 Aug;179(2):177–181. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Langnas A. N., Stratta R. J., Wood R. P., Ozaki C. F., Bynon J. S., Shaw B. W., Jr The role of intrahepatic cholangiojejunostomy in liver transplant recipients after extensive destruction of the extrahepatic biliary system. Surgery. 1992 Oct;112(4):712–718. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ludwig J., Batts K. P., MacCarty R. L. Ischemic cholangitis in hepatic allografts. Mayo Clin Proc. 1992 Jun;67(6):519–526. doi: 10.1016/s0025-6196(12)60457-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- McMaster P., Herbertson B. M., Cusick C., Calne R. Y., Syrakos T., Marni A. The development of biliary "sludge" following liver transplantation. Transplant Proc. 1979 Mar;11(1):262–266. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Neuhaus P., Blumhardt G., Bechstein W. O., Steffen R., Platz K. P., Keck H. Technique and results of biliary reconstruction using side-to-side choledochocholedochostomy in 300 orthotopic liver transplants. Ann Surg. 1994 Apr;219(4):426–434. doi: 10.1097/00000658-199404000-00014. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- O'Connor H. J., Vickers C. R., Buckels J. A., McMaster P., Neuberger J. M., West R. J., Elias E. Role of endoscopic retrograde cholangiopancreatography after orthotopic liver transplantation. Gut. 1991 Apr;32(4):419–423. doi: 10.1136/gut.32.4.419. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Oguma S., Belle S., Starzl T. E., Demetris A. J. A histometric analysis of chronically rejected human liver allografts: insights into the mechanisms of bile duct loss: direct immunologic and ischemic factors. Hepatology. 1989 Feb;9(2):204–209. doi: 10.1002/hep.1840090207. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Otto G., Roeren T., Golling M., Datsis K., Hofmann W. J., Herfarth C., Theilmann L. Ischemic Type Lesions der Gallenwege nach Lebertransplantation: 2-Jahres-Ergebnisse. Zentralbl Chir. 1995;120(6):450–454. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sanchez-Urdazpal L., Batts K. P., Gores G. J., Moore S. B., Sterioff S., Wiesner R. H., Krom R. A. Increased bile duct complications in liver transplantation across the ABO barrier. Ann Surg. 1993 Aug;218(2):152–158. doi: 10.1097/00000658-199308000-00006. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sanchez-Urdazpal L., Gores G. J., Ward E. M., Maus T. P., Buckel E. G., Steers J. L., Wiesner R. H., Krom R. A. Diagnostic features and clinical outcome of ischemic-type biliary complications after liver transplantation. Hepatology. 1993 Apr;17(4):605–609. doi: 10.1002/hep.1840170413. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sanchez-Urdazpal L., Gores G. J., Ward E. M., Maus T. P., Wahlstrom H. E., Moore S. B., Wiesner R. H., Krom R. A. Ischemic-type biliary complications after orthotopic liver transplantation. Hepatology. 1992 Jul;16(1):49–53. doi: 10.1002/hep.1840160110. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sankary H. N., McChesney L., Frye E., Cohn S., Foster P., Williams J. A simple modification in operative technique can reduce the incidence of nonanastomotic biliary strictures after orthotopic liver transplantation. Hepatology. 1995 Jan;21(1):63–69. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sebagh M., Farges O., Kalil A., Samuel D., Bismuth H., Reynes M. Sclerosing cholangitis following human orthotopic liver transplantation. Am J Surg Pathol. 1995 Jan;19(1):81–90. doi: 10.1097/00000478-199501000-00010. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sheng R., Ramirez C. B., Zajko A. B., Campbell W. L. Biliary stones and sludge in liver transplant patients: a 13-year experience. Radiology. 1996 Jan;198(1):243–247. doi: 10.1148/radiology.198.1.8539387. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Starzl T. E., Putnam C. W., Hansbrough J. F., Porter K. A., Reid H. A. Biliary complications after liver transplantation: with special reference to the biliary cast syndrome and techniques of secondary duct repair. Surgery. 1977 Feb;81(2):212–221. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Theilmann L., Küppers B., Kadmon M., Roeren T., Notheisen H., Stiehl A., Otto G. Biliary tract strictures after orthotopic liver transplantation: diagnosis and management. Endoscopy. 1994 Aug;26(6):517–522. doi: 10.1055/s-2007-1009026. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ward E. M., Kiely M. J., Maus T. P., Wiesner R. H., Krom R. A. Hilar biliary strictures after liver transplantation: cholangiography and percutaneous treatment. Radiology. 1990 Oct;177(1):259–263. doi: 10.1148/radiology.177.1.2399328. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zemel G., Zajko A. B., Skolnick M. L., Bron K. M., Campbell W. L. The role of sonography and transhepatic cholangiography in the diagnosis of biliary complications after liver transplantation. AJR Am J Roentgenol. 1988 Nov;151(5):943–946. doi: 10.2214/ajr.151.5.943. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]




