Abstract
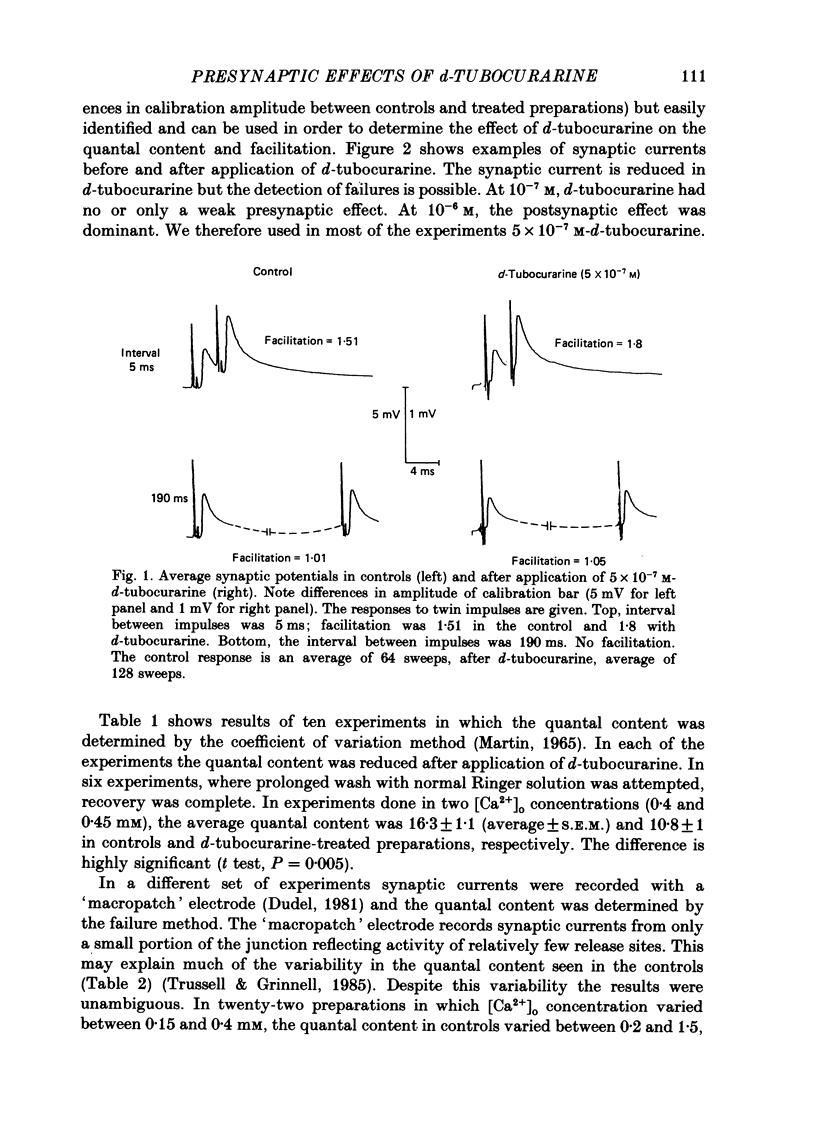
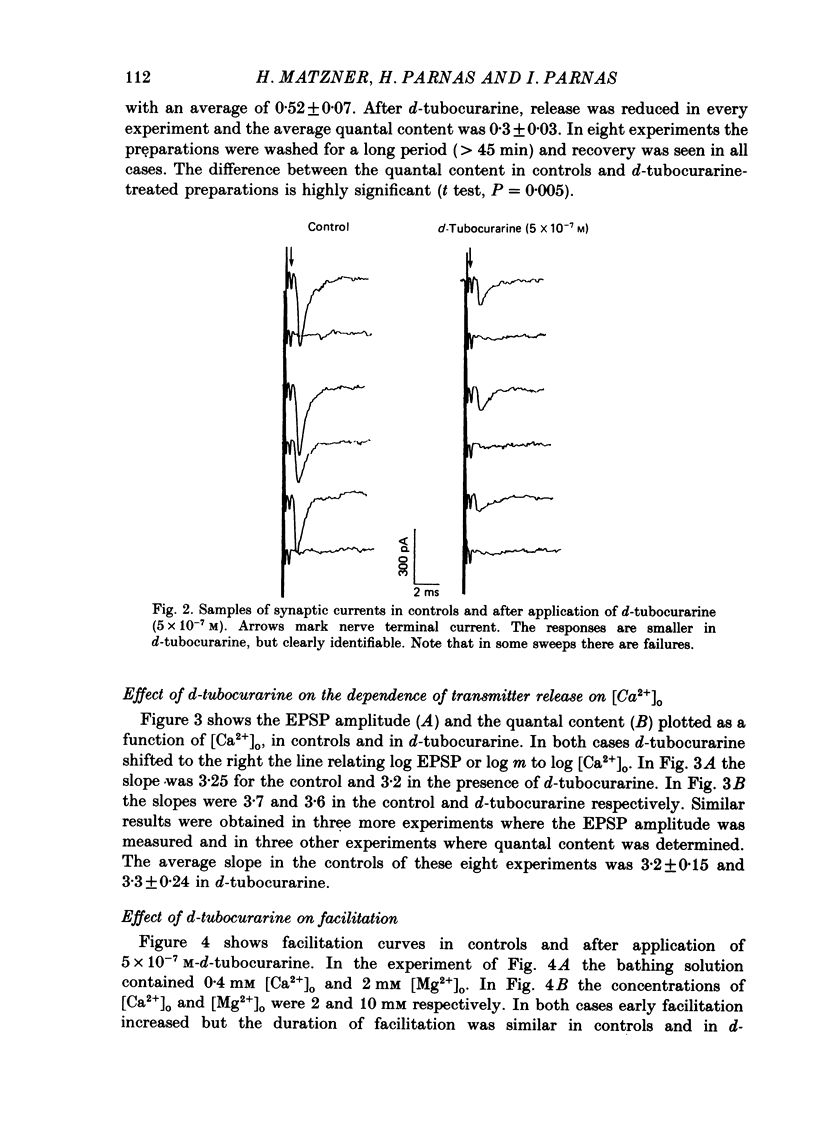
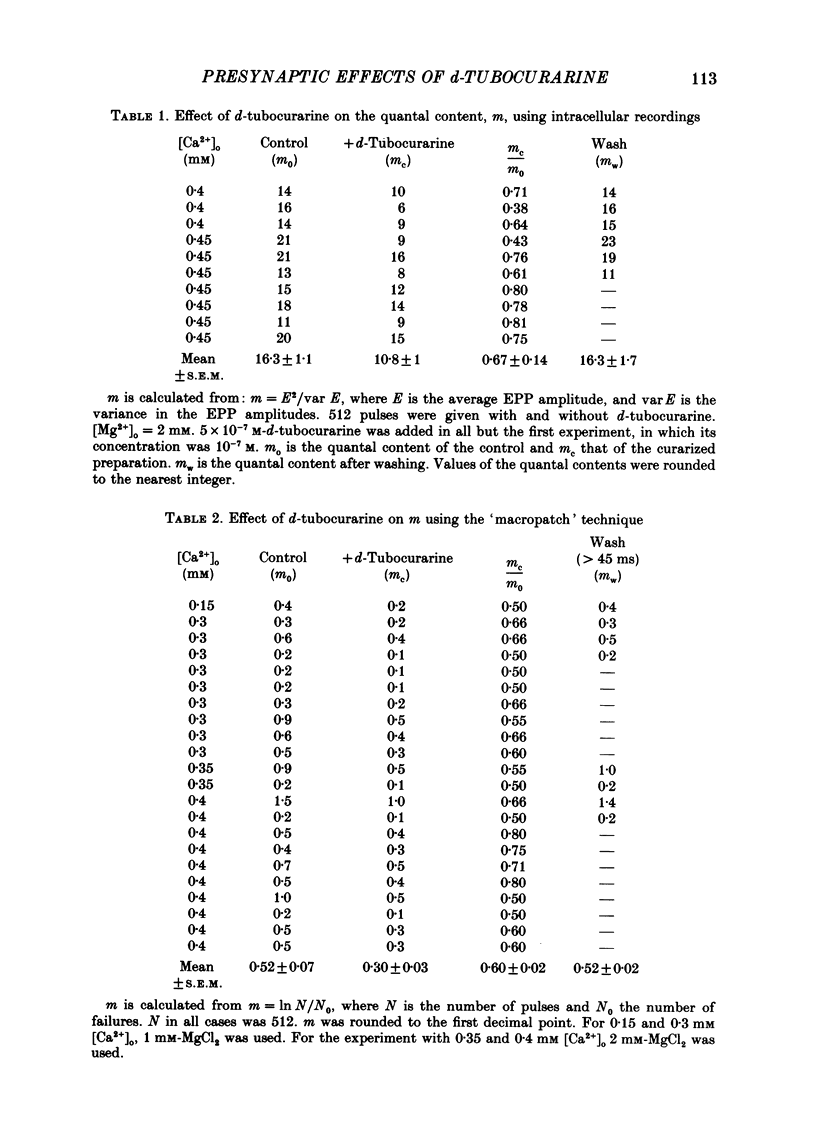
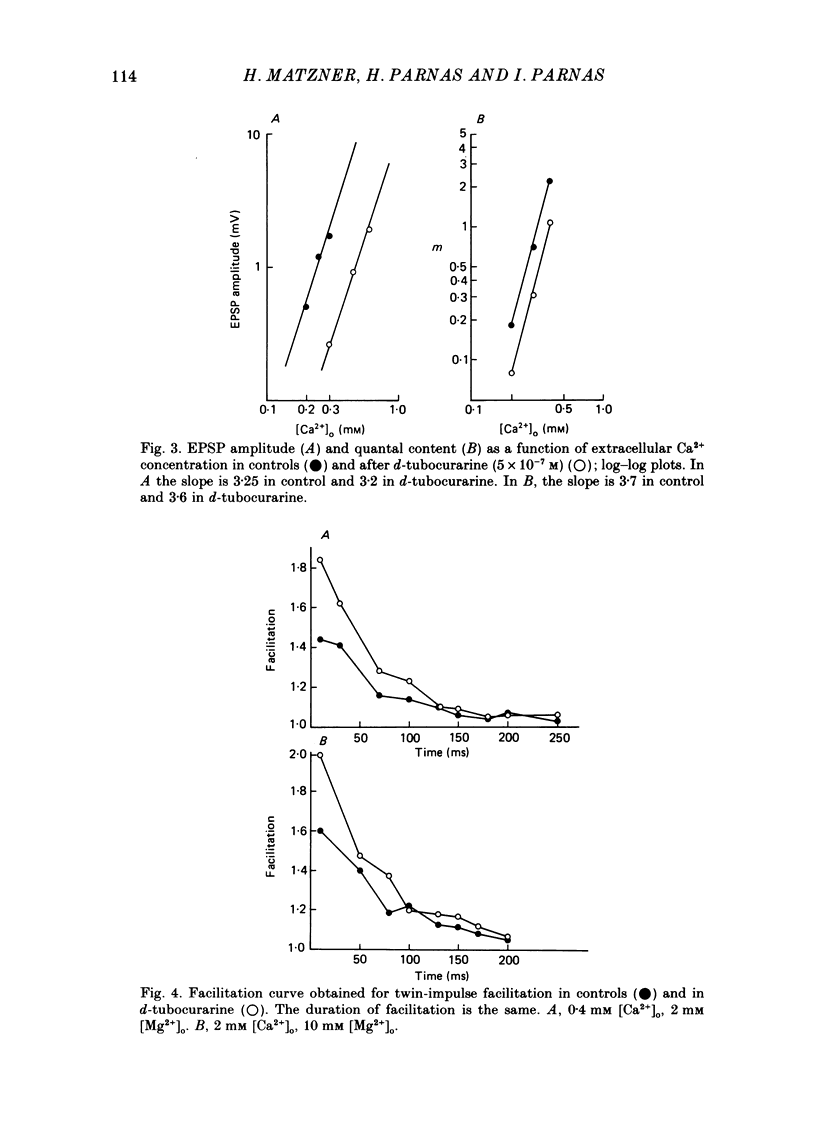
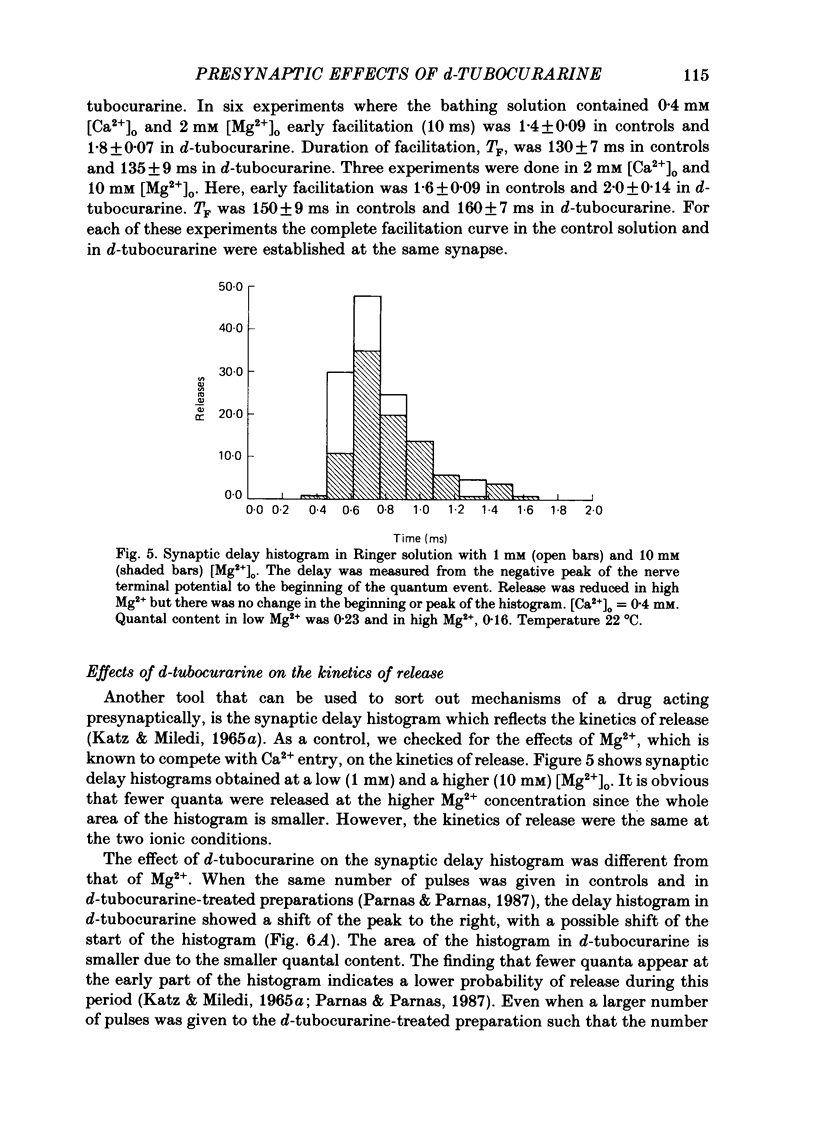
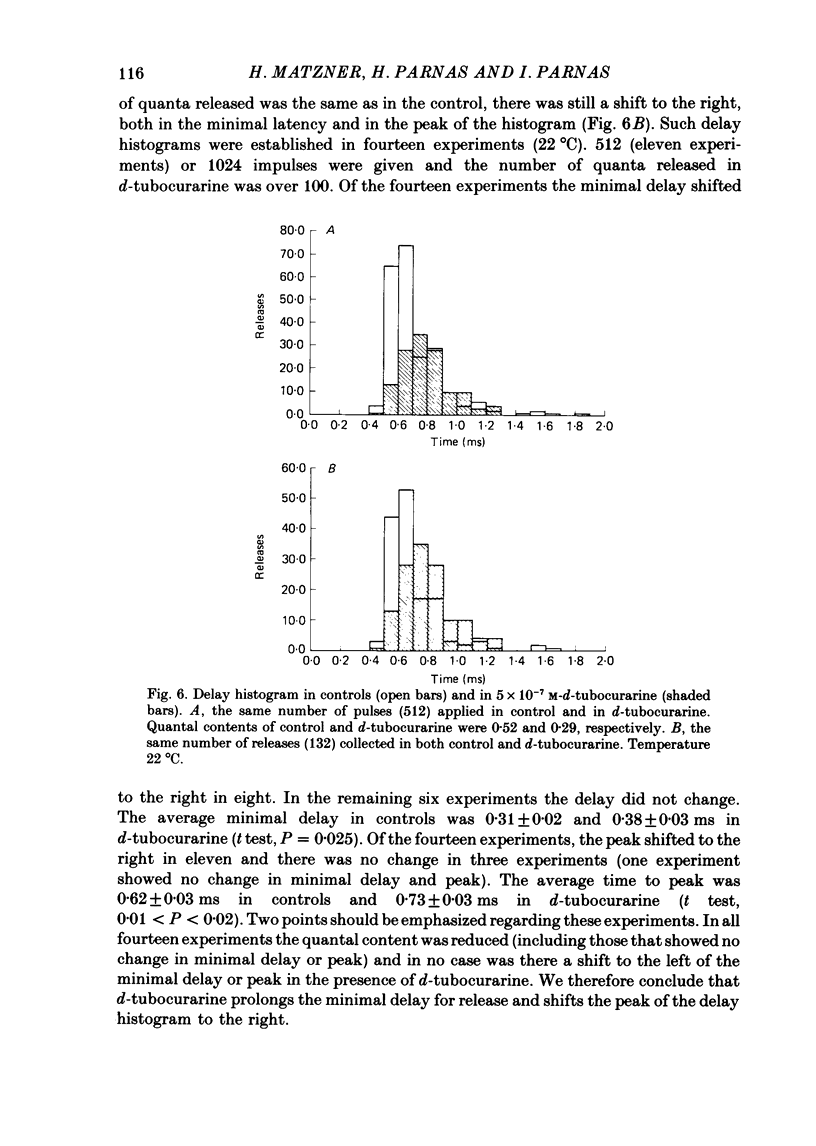
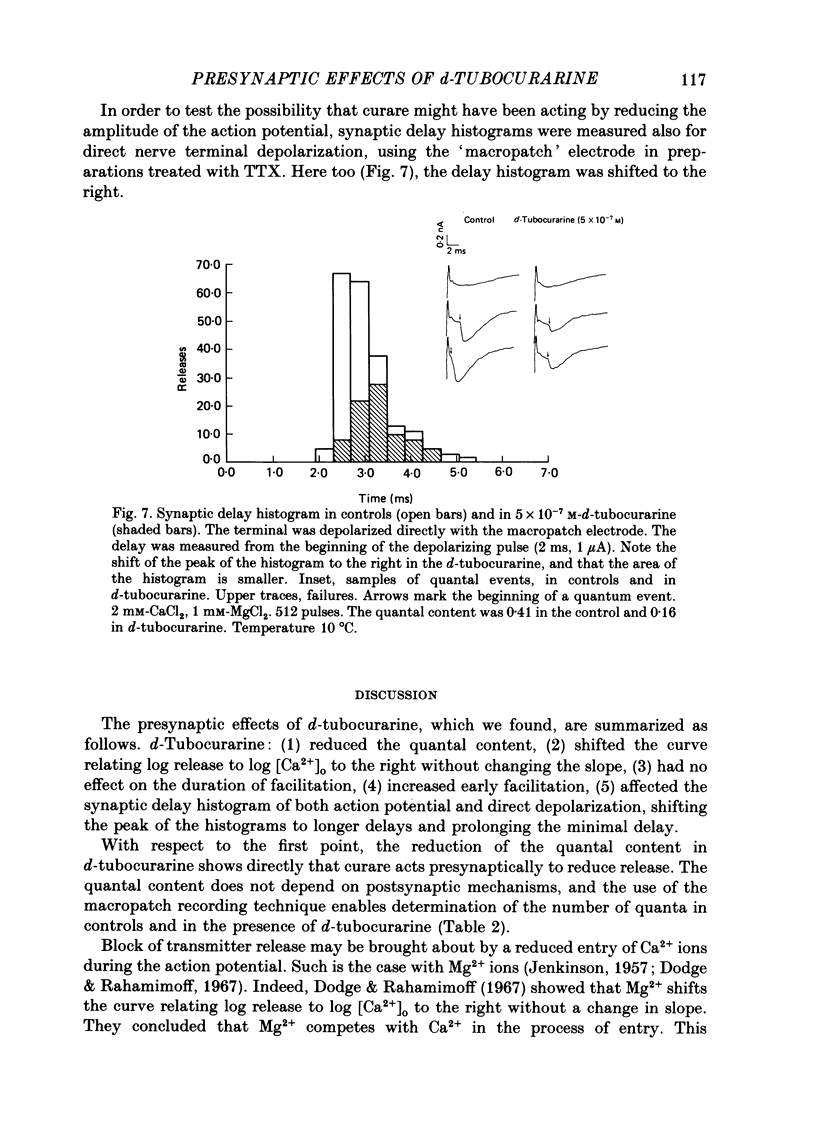
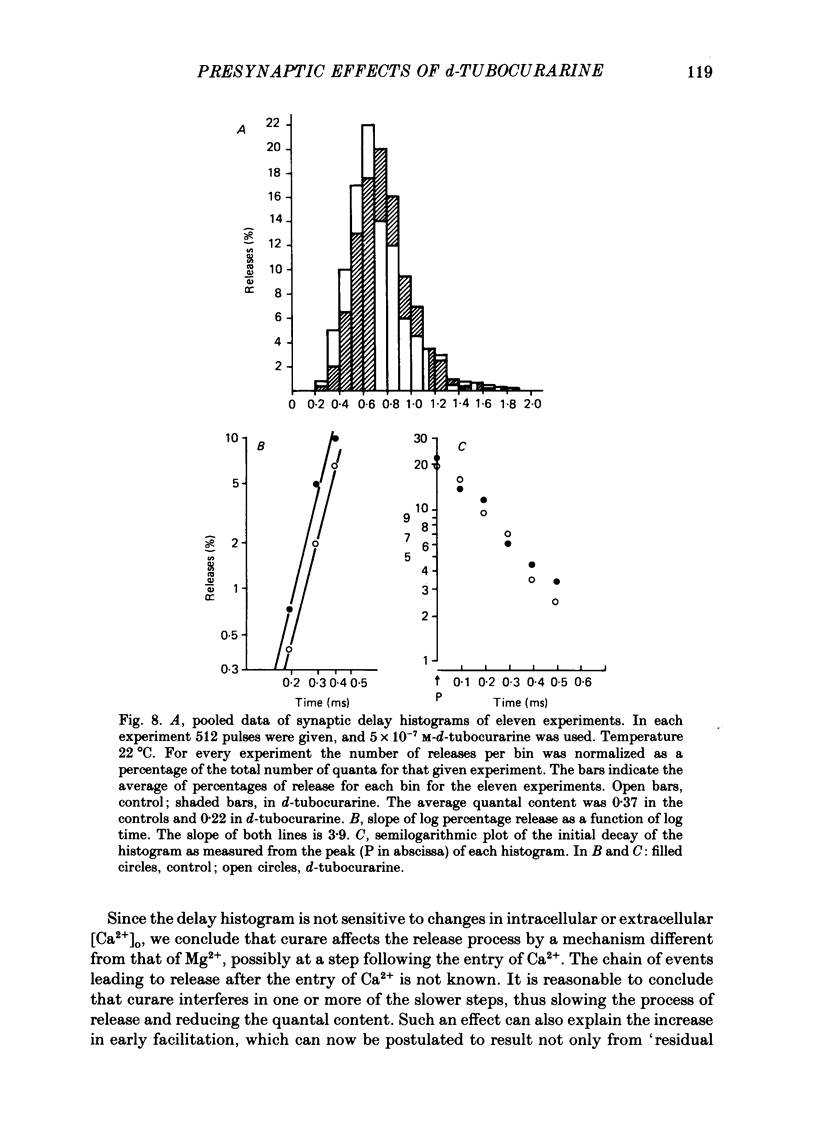
1. Presynaptic effects of d-tubocurarine on neurotransmitter release were examined at the frog neuromuscular junction, using intracellular and extracellular recording techniques. 2. d-Tubocurarine in concentrations of 10(-7)-10(-6) M decreased the quantal content (m) measured by the coefficient of variation and failure methods. 3. d-Tubocurarine produced a shift to the right of the curve relating log quantal content to log [Ca2+]o without changing the slope. 4. The duration of twin-impulse facilitation was not affected by 5 x 10(-7) M-d-tubocurarine. Early facilitation was higher in d-tubocurarine. 5. d-Tubocurarine altered the synaptic delay histogram. The peak of the histogram was shifted to longer delays. Prolongation of the minimal delay was seen in most but not all experiments. 6. These results suggest that d-tubocurarine inhibits release of neurotransmitter by affecting a stage in the process of release, which occurs after the entry of Ca2+ ions.
Full text
PDF




Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Adams P. R. Drug interactions at the motor endplate. Pflugers Arch. 1975 Oct 28;360(2):155–164. doi: 10.1007/BF00580538. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Auerbach A., Betz W. Does curare affect transmitter release? J Physiol. 1971 Mar;213(3):691–705. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1971.sp009409. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Barrett E. F., Stevens C. F. The kinetics of transmitter release at the frog neuromuscular junction. J Physiol. 1972 Dec;227(3):691–708. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1972.sp010054. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Baux G., Tauc L. Presynaptic actions of curare and atropine on quantal acetylcholine release at a central synapse of Aplysia. J Physiol. 1987 Jul;388:665–680. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1987.sp016637. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Beránek R., Vyskocil F. The action of tubocurarine and atropine on the normal and denervated rat diaphragm. J Physiol. 1967 Jan;188(1):53–66. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1967.sp008123. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chang C. C., Cheng H. C., Chen T. F. Does d-tubocurarine inhibit the release of acetylcholine from motor nerve endings? Jpn J Physiol. 1967 Oct 15;17(5):505–515. doi: 10.2170/jjphysiol.17.505. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Colquhoun D., Dreyer F., Sheridan R. E. The actions of tubocurarine at the frog neuromuscular junction. J Physiol. 1979 Aug;293:247–284. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1979.sp012888. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- DEL CASTILLO J., KATZ B. Quantal components of the end-plate potential. J Physiol. 1954 Jun 28;124(3):560–573. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1954.sp005129. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Datyner N. B., Gage P. W. Phasic secretion of acetylcholine at a mammalian neuromuscular junction. J Physiol. 1980 Jun;303:299–314. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1980.sp013286. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dodge F. A., Jr, Rahamimoff R. Co-operative action a calcium ions in transmitter release at the neuromuscular junction. J Physiol. 1967 Nov;193(2):419–432. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1967.sp008367. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dudel J. The effect of reduced calcium on quantal unit current and release at the crayfish neuromuscular junction. Pflugers Arch. 1981 Jul;391(1):35–40. doi: 10.1007/BF00580691. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dunant Y., Walker A. I. Cholinergic inhibition of acetylcholine release in the electric organ of Torpedo. Eur J Pharmacol. 1982 Feb 26;78(2):201–212. doi: 10.1016/0014-2999(82)90237-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- FATT P., KATZ B. An analysis of the end-plate potential recorded with an intracellular electrode. J Physiol. 1951 Nov 28;115(3):320–370. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1951.sp004675. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Galindo A. Prejunctional effect of curare: its relative importance. J Neurophysiol. 1971 Mar;34(2):289–301. doi: 10.1152/jn.1971.34.2.289. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Glavinović M. I. Presynaptic action of curare. J Physiol. 1979 May;290(2):499–506. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1979.sp012786. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hubbard J. I., Wilson D. F., Miyamoto M. Reduction of transmitter release by D-tubocurarine. Nature. 1969 Aug 2;223(5205):531–533. doi: 10.1038/223531a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hubbard J. I., Wilson D. F. Neuromuscular transmission in a mammalian preparation in the absence of blocking drugs and the effect of D-tubocurarine. J Physiol. 1973 Jan;228(2):307–325. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1973.sp010088. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- JENKINSON D. H. The antagonism between tubocurarine and substances which depolarize the motor end-plate. J Physiol. 1960 Jul;152:309–324. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1960.sp006489. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- JENKINSON D. H. The nature of the antagonism between calcium and magnesium ions at the neuromuscular junction. J Physiol. 1957 Oct 30;138(3):434–444. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1957.sp005860. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- KATZ B., MILEDI R. THE MEASUREMENT OF SYNAPTIC DELAY, AND THE TIME COURSE OF ACETYLCHOLINE RELEASE AT THE NEUROMUSCULAR JUNCTION. Proc R Soc Lond B Biol Sci. 1965 Feb 16;161:483–495. doi: 10.1098/rspb.1965.0016. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Katz B., Miledi R. A re-examination of curare action at the motor endplate. Proc R Soc Lond B Biol Sci. 1978 Dec 4;203(1151):119–133. doi: 10.1098/rspb.1978.0096. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Katz B., Miledi R. The effect of temperature on the synaptic delay at the neuromuscular junction. J Physiol. 1965 Dec;181(3):656–670. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1965.sp007790. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Katz B., Miledi R. The role of calcium in neuromuscular facilitation. J Physiol. 1968 Mar;195(2):481–492. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1968.sp008469. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kloog Y., Galron R., Sokolovsky M. Bisquaternary pyridinium oximes as presynaptic agonists and postsynaptic antagonists of muscarinic receptors. J Neurochem. 1986 Mar;46(3):767–772. doi: 10.1111/j.1471-4159.1986.tb13038.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Magleby K. L., Pallotta B. S., Terrar D. A. The effect of (+)-tubocurarine on neuromuscular transmission during repetitive stimulation in the rat, mouse, and frog. J Physiol. 1981 Mar;312:97–113. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1981.sp013618. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Manalis R. S. Voltage-dependent effect of curare at the frog neuromuscular junction. Nature. 1977 May 26;267(5609):366–368. doi: 10.1038/267366a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- McLachlan E. M., Martin A. R. Non-linear summation of end-plate potentials in the frog and mouse. J Physiol. 1981 Feb;311:307–324. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1981.sp013586. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Michaelson D. M., Avissar S., Kloog Y., Sokolovsky M. Mechanism of acetylcholine release: possible involvement of presynaptic muscarinic receptors in regulation of acetylcholine release and protein phosphorylation. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1979 Dec;76(12):6336–6340. doi: 10.1073/pnas.76.12.6336. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Miller M. W., Parnas H., Parnas I. Dopaminergic modulation of neuromuscular transmission in the prawn. J Physiol. 1985 Jun;363:363–375. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1985.sp015716. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Parnas H., Dudel J., Parnas I. Neurotransmitter release and its facilitation in crayfish. I. Saturation kinetics of release, and of entry and removal of calcium. Pflugers Arch. 1982 Mar;393(1):1–14. doi: 10.1007/BF00582384. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Parnas H., Dudel J., Parnas I. Neurotransmitter release and its facilitation in crayfish. VII. Another voltage dependent process beside Ca entry controls the time course of phasic release. Pflugers Arch. 1986 Feb;406(2):121–130. doi: 10.1007/BF00586672. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Parnas H., Parnas I. Influence of depolarizing pulse duration on the time course of transmitter release in lobster. J Physiol. 1987 Jul;388:487–494. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1987.sp016626. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Parnas H., Parnas I., Segel L. A new method for determining co-operativity in neurotransmitter release. J Theor Biol. 1986 Apr 21;119(4):481–499. doi: 10.1016/s0022-5193(86)80197-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Parnas H., Segel L. A. Ways to discern the presynaptic effect of drugs on neurotransmitter release. J Theor Biol. 1982 Feb 21;94(4):923–941. doi: 10.1016/0022-5193(82)90087-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Trussell L. O., Grinnell A. D. The regulation of synaptic strength within motor units of the frog cutaneous pectoris muscle. J Neurosci. 1985 Jan;5(1):243–254. doi: 10.1523/JNEUROSCI.05-01-00243.1985. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wilson D. F. Influence of presynaptic receptors on neuromuscular transmission in rat. Am J Physiol. 1982 May;242(5):C366–C372. doi: 10.1152/ajpcell.1982.242.5.C366. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


