Abstract
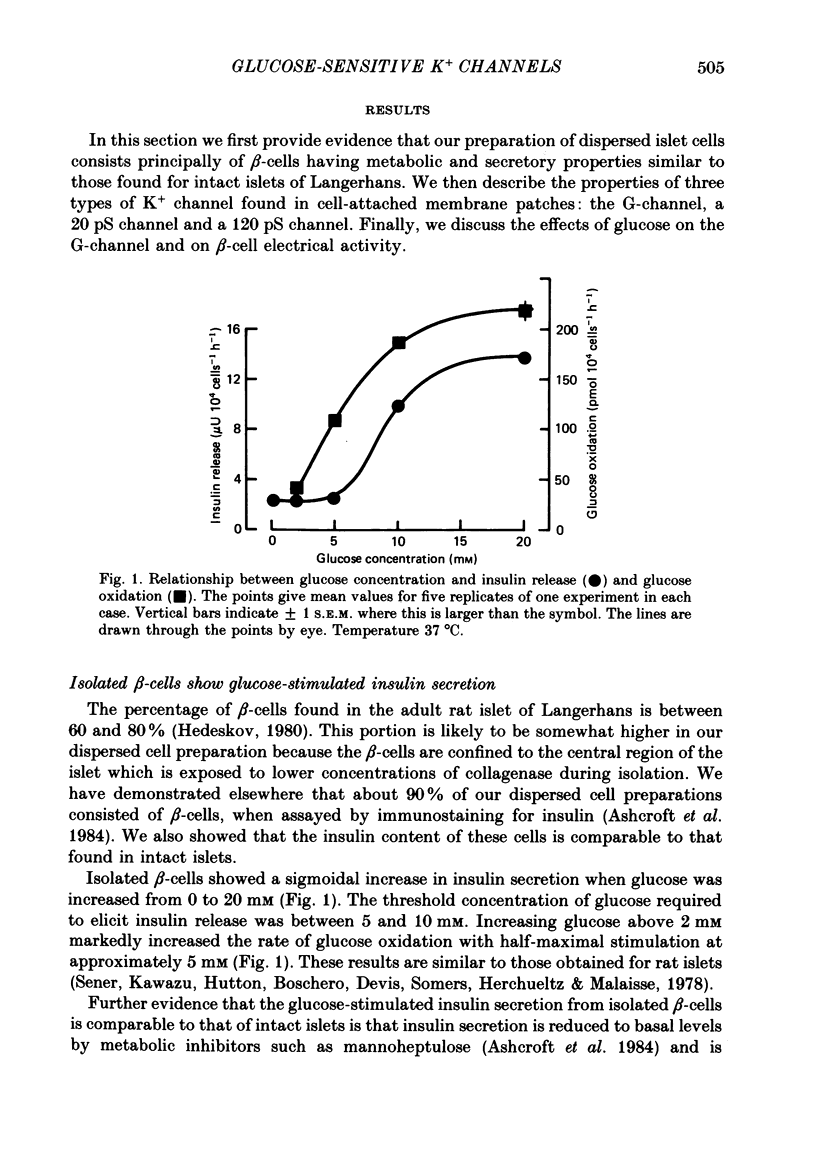
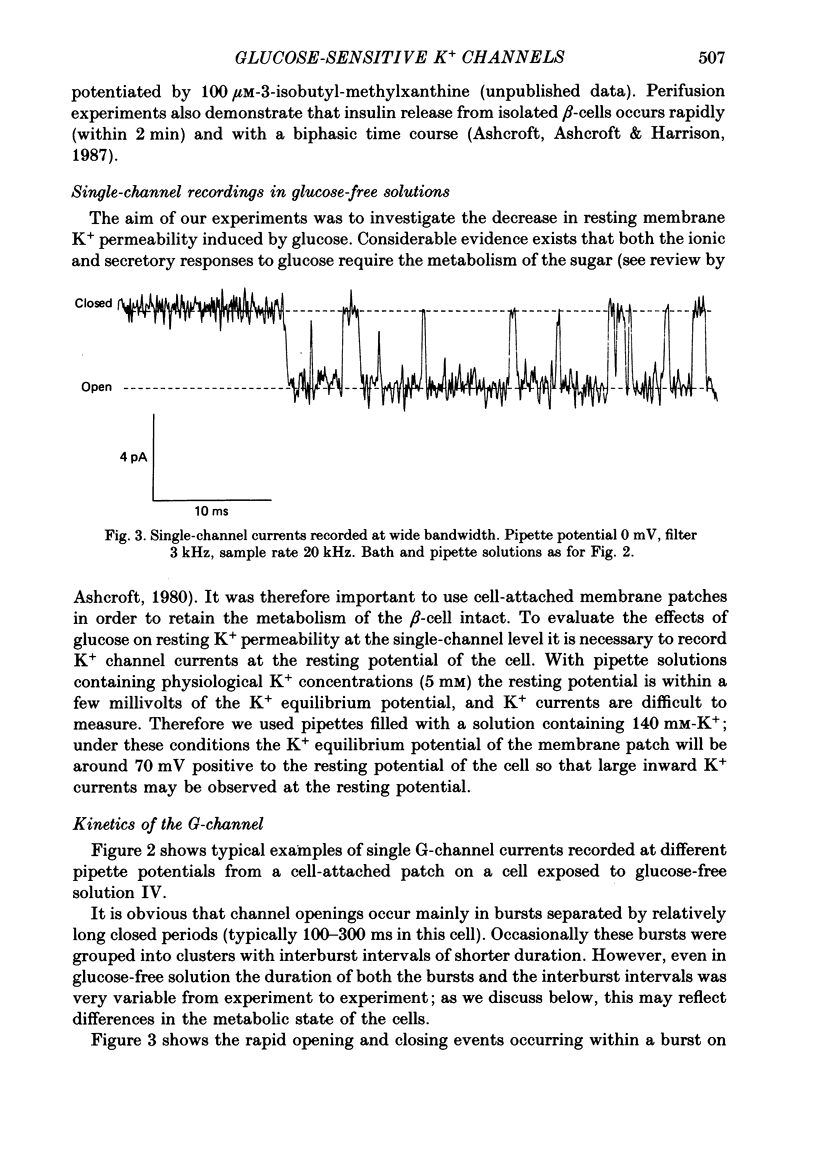
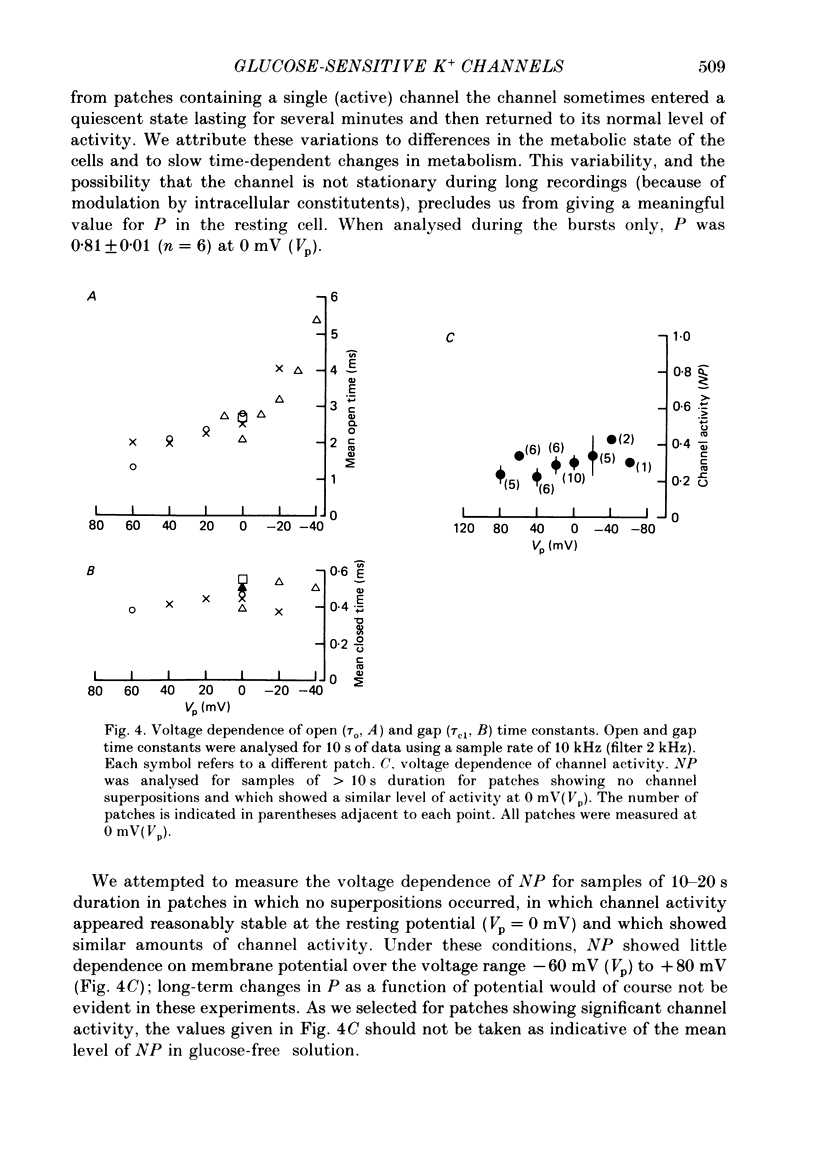
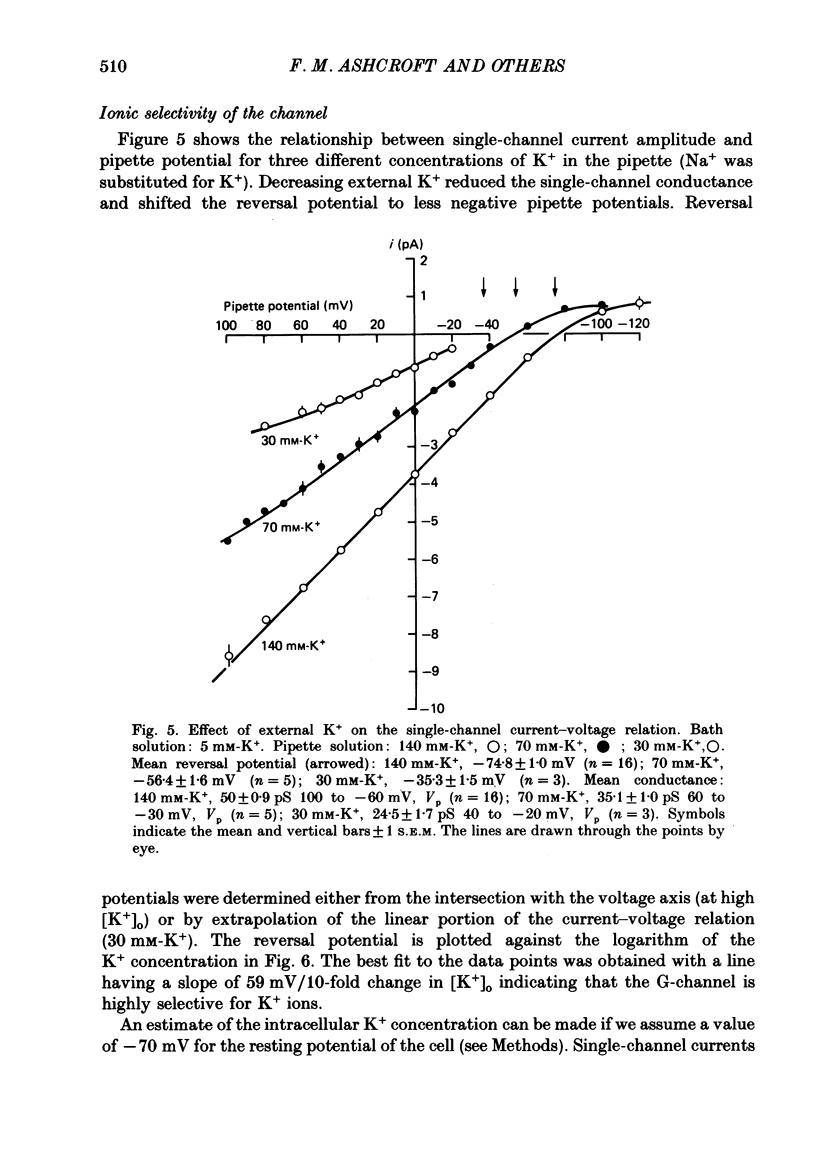
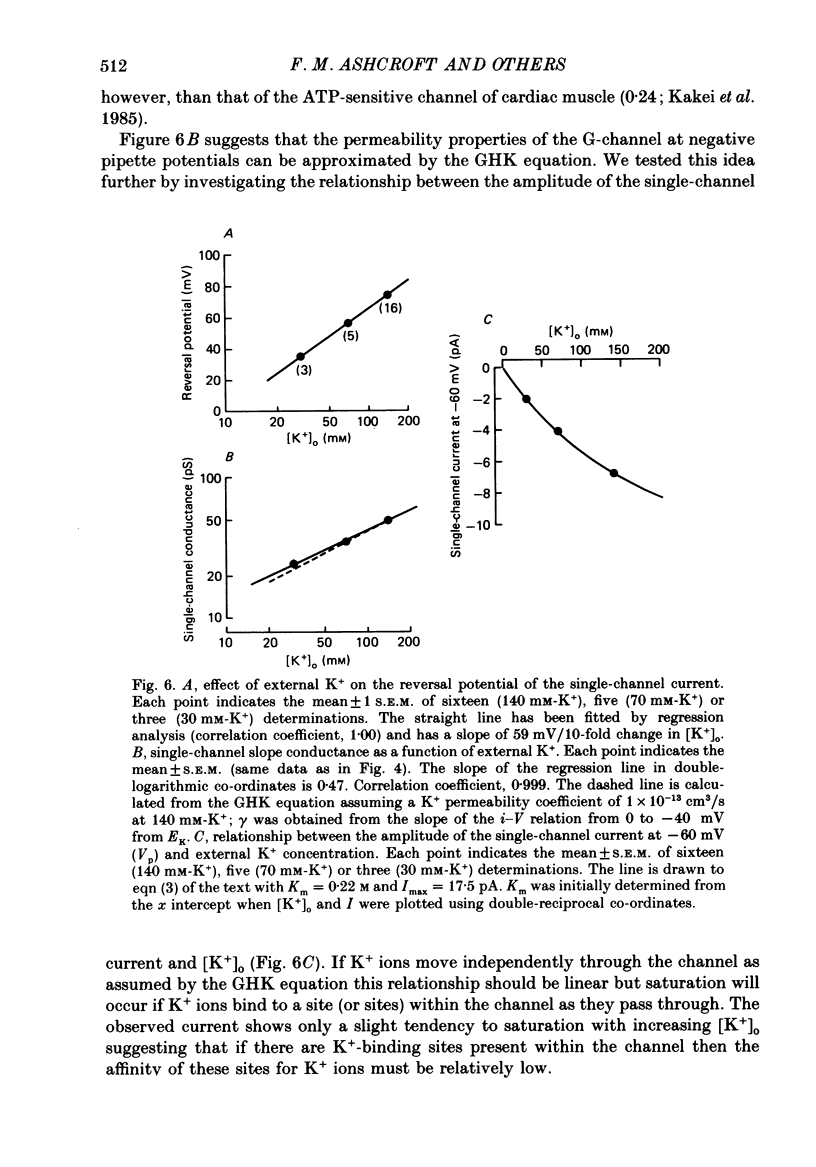
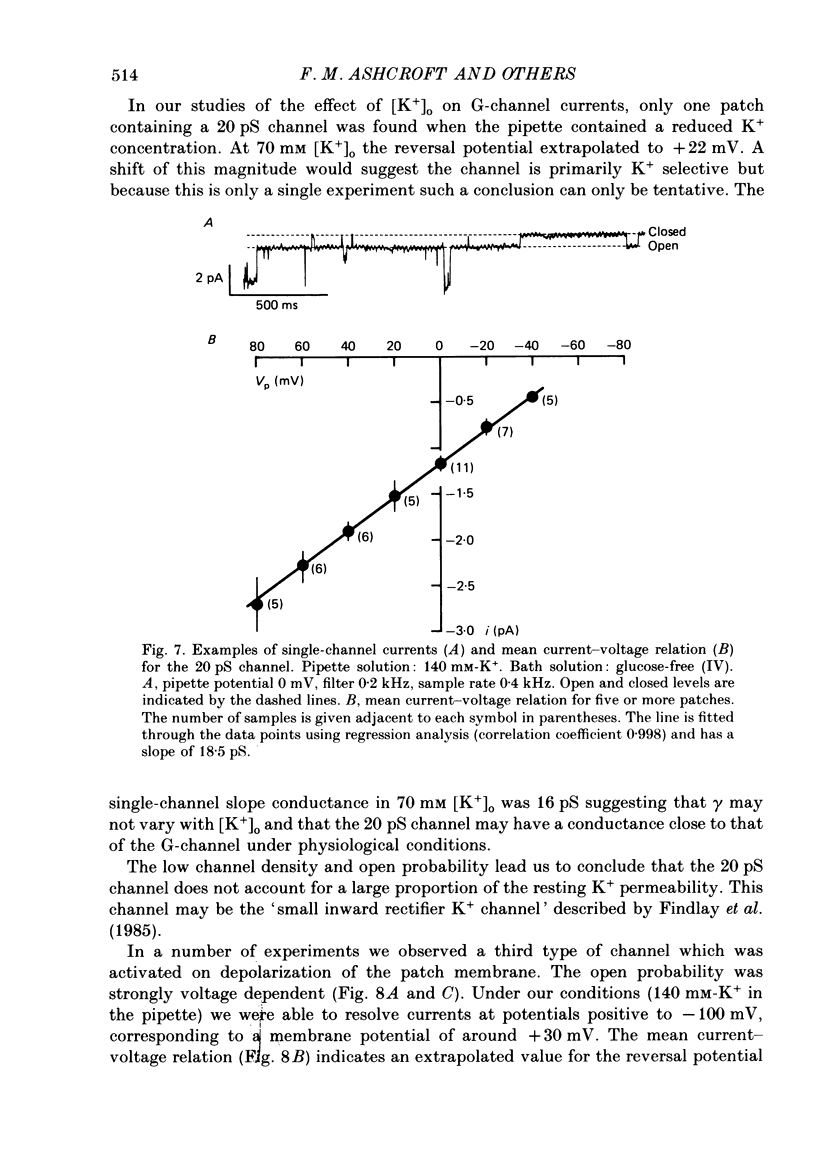
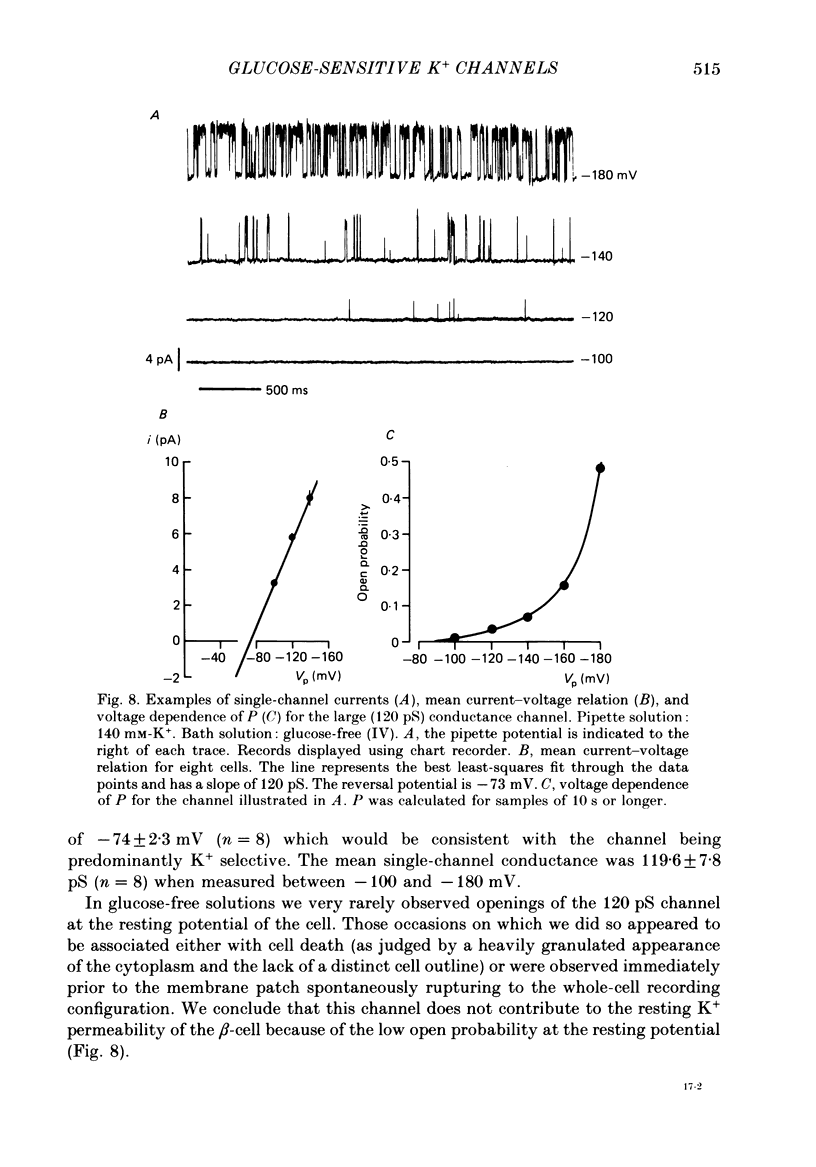
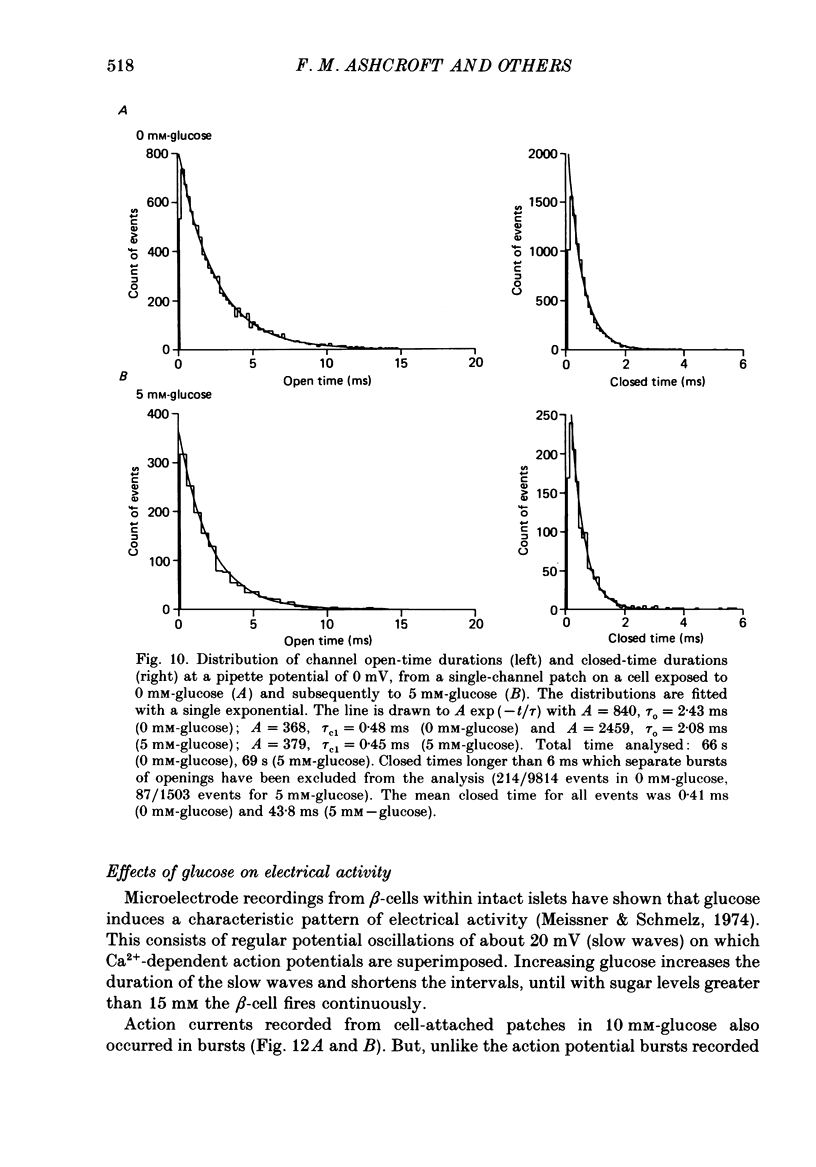
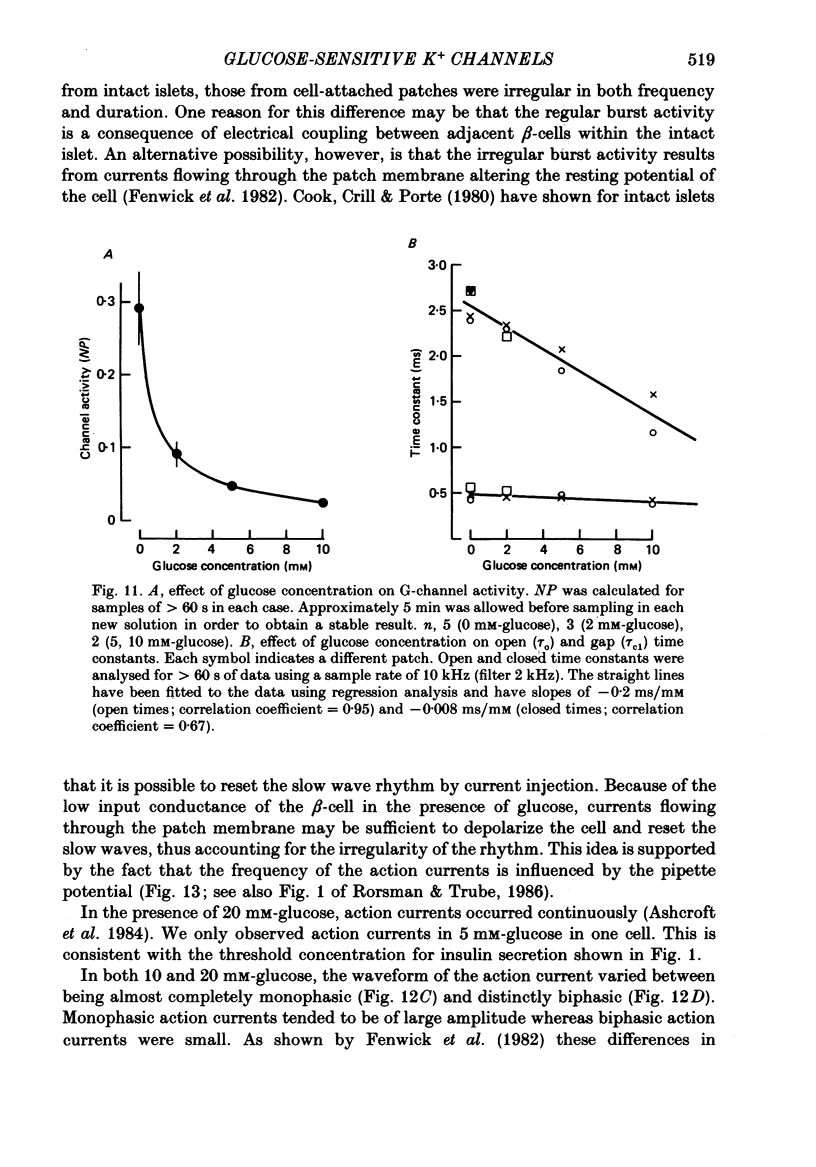
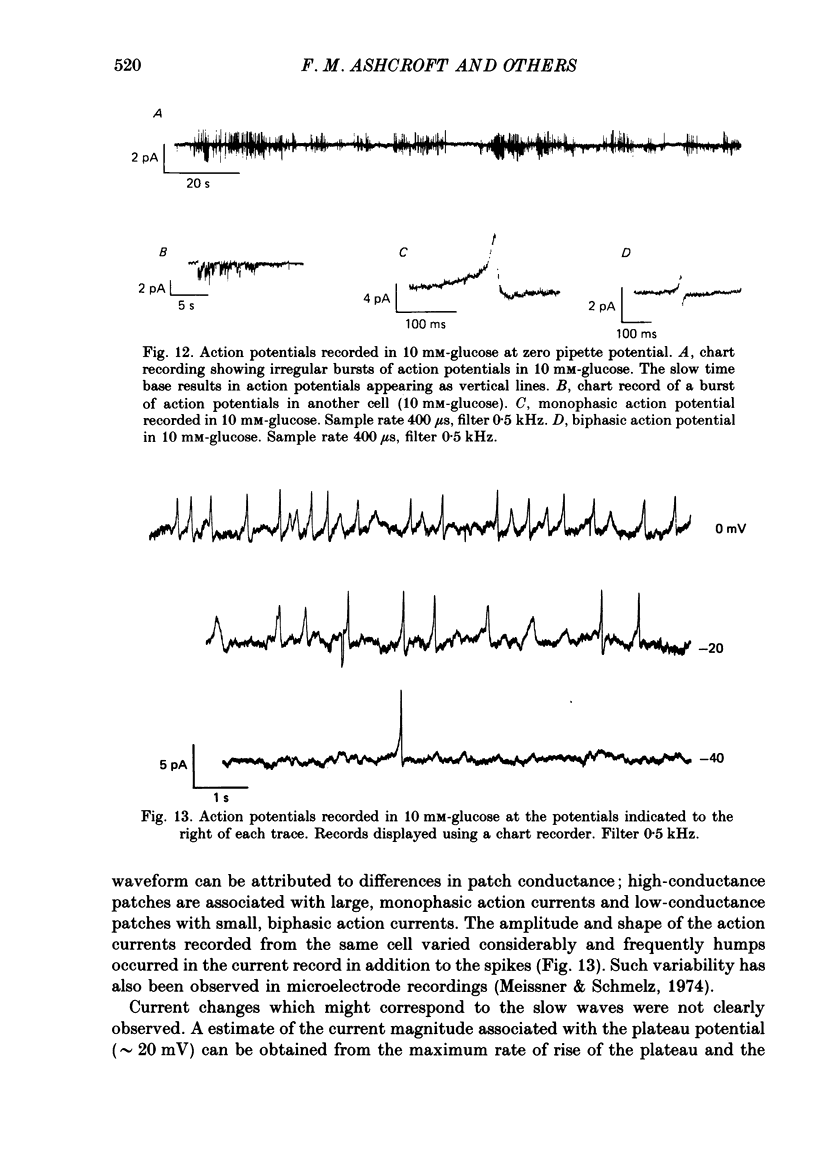
1. The patch clamp method has been used to examine the effect of glucose on single K+ channel currents recorded from cell-attached patches on dissociated rat pancreatic beta-cells. Patch pipettes contained a 140 mM-K+ solution. 2. In glucose-free solution three types of K+ channels were observed. Two of these, having conductances of around 50 pS (G-channel) and 20 pS when the external K+ concentration, [K+]0, was 140 mM, were active at the resting potential of the cell. The G-channel was observed in more patches and showed higher activity; it therefore appears to contribute the major fraction of the resting K+ permeability of the beta-cell. At membrane potentials positive to about +20 mV a third type of K+ channel, having a mean conductance of 120 pS, was activated. The open probability of this channel was strongly voltage dependent and increased with depolarization. 3. The reversal potential of the G-channel current was shifted 59 mV by a 10-fold change in external K+ (Na+ substitution) indicating the channel is highly K+ selective. The single-channel conductance varied with [K+]o as predicted from the Goldman-Hodgkin-Katz equation; at physiological [K+]o (5 mM-K+) an inward conductance of around 10 pS is predicted. The amplitude of the single-channel current showed a tendency to saturate with increasing [K+]o. 4. Single G-channel currents show burst kinetics indicating at least two closed states. The open and closed (gap) times within the bursts were distributed exponentially with time constants of 2.5 ms (tau o) and 0.5 ms (tau c1) respectively at the resting potential of the cell. There was little change in tau c1 over the voltage range -40 to 60 mV (pipette potential) but tau o increased slightly with membrane depolarization. 5. The addition of glucose to the bath solution produced a reversible, dose-dependent decrease in G-channel activity. This decrease results principally from a reduction in the frequency and duration of the bursts of openings with increasing glucose. In addition, the mean open time decreases. The short gaps during the bursts were little affected by glucose. 6. At glucose concentrations of .10 mM and above the decrease in G-channel activity is accompanied by an increase in the input resistance of the cell and by the initiation of action potentials. 7. It is concluded that glucose metabolism results in a reduction of G-channel open probability and thereby produces depolarization of the beta-cell.
Full text
PDF
















Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Ashcroft F. M. Adenosine 5'-triphosphate-sensitive potassium channels. Annu Rev Neurosci. 1988;11:97–118. doi: 10.1146/annurev.ne.11.030188.000525. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ashcroft F. M., Ashcroft S. J., Harrison D. E. Effects of 2-ketoisocaproate on insulin release and single potassium channel activity in dispersed rat pancreatic beta-cells. J Physiol. 1987 Apr;385:517–529. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1987.sp016505. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ashcroft F. M., Harrison D. E., Ashcroft S. J. Glucose induces closure of single potassium channels in isolated rat pancreatic beta-cells. 1984 Nov 29-Dec 5Nature. 312(5993):446–448. doi: 10.1038/312446a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ashcroft S. J., Crossley J. R. The effects of glucose, N-acetylglucosamine, glyceraldehyde and other sugars on insulin release in vivo. Diabetologia. 1975 Aug;11(4):279–284. doi: 10.1007/BF00422392. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ashcroft S. J. Glucoreceptor mechanisms and the control of insulin release and biosynthesis. Diabetologia. 1980 Jan;18(1):5–15. doi: 10.1007/BF01228295. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ashcroft S. J., Hedeskov C. J., Randle P. J. Glucose metabolism in mouse pancreatic islets. Biochem J. 1970 Jun;118(1):143–154. doi: 10.1042/bj1180143. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ashcroft S. J., Weerasinghe L. C., Randle P. J. Interrelationship of islet metabolism, adenosine triphosphate content and insulin release. Biochem J. 1973 Feb;132(2):223–231. doi: 10.1042/bj1320223. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Atwater I., Dawson C. M., Scott A., Eddlestone G., Rojas E. The nature of the oscillatory behaviour in electrical activity from pancreatic beta-cell. Horm Metab Res Suppl. 1980;Suppl 10:100–107. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Atwater I., Frankel B. J., Rojas E., Grodsky G. M. Beta cell membrane potential and insulin release; role of calcium and calcium:magnesium ratio. Q J Exp Physiol. 1983 Apr;68(2):233–245. doi: 10.1113/expphysiol.1983.sp002715. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Atwater I., Ribalet B., Rojas E. Cyclic changes in potential and resistance of the beta-cell membrane induced by glucose in islets of Langerhans from mouse. J Physiol. 1978 May;278:117–139. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1978.sp012296. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bennett J. A., Goodchild C. S., Kidd C., McWilliam P. N. Neurones in the brain stem of the cat excited by vagal afferent fibres from the heart and lungs. J Physiol. 1985 Dec;369:1–15. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1985.sp015884. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Christie M. R., Ashcroft S. J. Cyclic AMP-dependent protein phosphorylation and insulin secretion in intact islets of Langerhans. Biochem J. 1984 Feb 15;218(1):87–99. doi: 10.1042/bj2180087. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Coll-Garcia E., Gill J. R. Insulin release by isolated pancreatic islets of the mouse incubated in vitro. Diabetologia. 1969 Apr;5(2):61–66. doi: 10.1007/BF01211999. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Colquhoun D., Hawkes A. G. On the stochastic properties of bursts of single ion channel openings and of clusters of bursts. Philos Trans R Soc Lond B Biol Sci. 1982 Dec 24;300(1098):1–59. doi: 10.1098/rstb.1982.0156. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Colquhoun D., Hawkes A. G. On the stochastic properties of single ion channels. Proc R Soc Lond B Biol Sci. 1981 Mar 6;211(1183):205–235. doi: 10.1098/rspb.1981.0003. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Colquhoun D., Sakmann B. Fast events in single-channel currents activated by acetylcholine and its analogues at the frog muscle end-plate. J Physiol. 1985 Dec;369:501–557. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1985.sp015912. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cook D. L., Crill W. E., Porte D., Jr Plateau potentials in pancreatic islet cells are voltage-dependent action potentials. Nature. 1980 Jul 24;286(5771):404–406. doi: 10.1038/286404a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cook D. L., Hales C. N. Intracellular ATP directly blocks K+ channels in pancreatic B-cells. Nature. 1984 Sep 20;311(5983):271–273. doi: 10.1038/311271a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dean P. M., Matthews E. K., Sakamoto Y. Pancreatic islet cells: effects of monosaccharides, glycolytic intermediates and metabolic inhibitors on membrane potential and electrical activity. J Physiol. 1975 Mar;246(2):459–478. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1975.sp010899. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fenwick E. M., Marty A., Neher E. A patch-clamp study of bovine chromaffin cells and of their sensitivity to acetylcholine. J Physiol. 1982 Oct;331:577–597. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1982.sp014393. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Findlay I., Dunne M. J. ATP maintains ATP-inhibited K+ channels in an operational state. Pflugers Arch. 1986 Aug;407(2):238–240. doi: 10.1007/BF00580683. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Findlay I., Dunne M. J., Petersen O. H. ATP-sensitive inward rectifier and voltage- and calcium-activated K+ channels in cultured pancreatic islet cells. J Membr Biol. 1985;88(2):165–172. doi: 10.1007/BF01868430. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fischmeister R., Ayer R. K., Jr, DeHaan R. L. Some limitations of the cell-attached patch clamp technique: a two-electrode analysis. Pflugers Arch. 1986 Jan;406(1):73–82. doi: 10.1007/BF00582957. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- HODGKIN A. L., KATZ B. The effect of sodium ions on the electrical activity of giant axon of the squid. J Physiol. 1949 Mar 1;108(1):37–77. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1949.sp004310. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hamill O. P., Marty A., Neher E., Sakmann B., Sigworth F. J. Improved patch-clamp techniques for high-resolution current recording from cells and cell-free membrane patches. Pflugers Arch. 1981 Aug;391(2):85–100. doi: 10.1007/BF00656997. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hedeskov C. J. Mechanism of glucose-induced insulin secretion. Physiol Rev. 1980 Apr;60(2):442–509. doi: 10.1152/physrev.1980.60.2.442. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Henquin J. C. D-glucose inhibits potassium efflux from pancreatic islet cells. Nature. 1978 Jan 19;271(5642):271–273. doi: 10.1038/271271a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Henquin J. C., Meissner H. P. Significance of ionic fluxes and changes in membrane potential for stimulus-secretion coupling in pancreatic B-cells. Experientia. 1984 Oct 15;40(10):1043–1052. doi: 10.1007/BF01971450. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kakei M., Noma A. Adenosine-5'-triphosphate-sensitive single potassium channel in the atrioventricular node cell of the rabbit heart. J Physiol. 1984 Jul;352:265–284. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1984.sp015290. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kakei M., Noma A., Shibasaki T. Properties of adenosine-triphosphate-regulated potassium channels in guinea-pig ventricular cells. J Physiol. 1985 Jun;363:441–462. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1985.sp015721. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lernmark A. The preparation of, and studies on, free cell suspensions from mouse pancreatic islets. Diabetologia. 1974 Oct;10(5):431–438. doi: 10.1007/BF01221634. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lindström P., Sehlin J. Effect of glucose on the intracellular pH of pancreatic islet cells. Biochem J. 1984 Mar 15;218(3):887–892. doi: 10.1042/bj2180887. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Malaisse W. J., Hutton J. C., Kawazu S., Herchuelz A., Valverde I., Sener A. The stimulus-secretion coupling of glucose-induced insulin release. XXXV. The links between metabolic and cationic events. Diabetologia. 1979 May;16(5):331–341. doi: 10.1007/BF01223623. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Malaisse W. J., Hutton J. C., Kawazu S., Sener A. The stimulus-secretion coupling of glucose-induced insulin release. Metabolic effects of menadione in isolated islets. Eur J Biochem. 1978 Jun 1;87(1):121–130. doi: 10.1111/j.1432-1033.1978.tb12357.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Meissner H. P., Henquin J. C., Preissler M. Potassium dependence of the membrane potential of pancreatic B-cells. FEBS Lett. 1978 Oct 1;94(1):87–89. doi: 10.1016/0014-5793(78)80912-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Meissner H. P., Schmelz H. Membrane potential of beta-cells in pancreatic islets. Pflugers Arch. 1974;351(3):195–206. doi: 10.1007/BF00586918. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Moody W. J., Hagiwara S. Block of inward rectification by intracellular H+ in immature oocytes of the starfish Mediaster aequalis. J Gen Physiol. 1982 Jan;79(1):115–130. doi: 10.1085/jgp.79.1.115. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ohmori H. Inactivation kinetics and steady-state current noise in the anomalous rectifier of tunicate egg cell membranes. J Physiol. 1978 Aug;281:77–99. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1978.sp012410. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pace C. S., Tarvin J. T., Smith J. S. Stimulus-secretion coupling in beta-cells: modulation by pH. Am J Physiol. 1983 Jan;244(1):E3–18. doi: 10.1152/ajpendo.1983.244.1.E3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Panten U., Christians J., von Kriegstein E., Poser W., Hasselblatt A. Effect of carbohydrates upon fluorescence of reduced pyridine nucleotides from perifused isolated pancreatic islets. Diabetologia. 1973 Dec;9(6):477–482. doi: 10.1007/BF00461692. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pipeleers D., in't Veld P. I., Maes E., Van De Winkel M. Glucose-induced insulin release depends on functional cooperation between islet cells. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1982 Dec;79(23):7322–7325. doi: 10.1073/pnas.79.23.7322. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Prentki M., Wollheim C. B. Cytosolic free Ca2+ in insulin secreting cells and its regulation by isolated organelles. Experientia. 1984 Oct 15;40(10):1052–1060. doi: 10.1007/BF01971451. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rorsman P., Abrahamsson H., Gylfe E., Hellman B. Dual effects of glucose on the cytosolic Ca2+ activity of mouse pancreatic beta-cells. FEBS Lett. 1984 May 7;170(1):196–200. doi: 10.1016/0014-5793(84)81398-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rorsman P., Trube G. Calcium and delayed potassium currents in mouse pancreatic beta-cells under voltage-clamp conditions. J Physiol. 1986 May;374:531–550. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1986.sp016096. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rorsman P., Trube G. Glucose dependent K+-channels in pancreatic beta-cells are regulated by intracellular ATP. Pflugers Arch. 1985 Dec;405(4):305–309. doi: 10.1007/BF00595682. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sakmann B., Trube G. Conductance properties of single inwardly rectifying potassium channels in ventricular cells from guinea-pig heart. J Physiol. 1984 Feb;347:641–657. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1984.sp015088. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sener A., Kawazu S., Hutton J. C., Boschero A. C., Devis G., Somers G., Herchuelz A., Malaisse W. J. The stimulus-secretion coupling of glucose-induced insulin release. Effect of exogenous pyruvate on islet function. Biochem J. 1978 Oct 15;176(1):217–232. doi: 10.1042/bj1760217. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Spruce A. E., Standen N. B., Stanfield P. R. Voltage-dependent ATP-sensitive potassium channels of skeletal muscle membrane. Nature. 1985 Aug 22;316(6030):736–738. doi: 10.1038/316736a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Standen N. B., Stanfield P. R. Potassium depletion and sodium block of potassium currents under hyperpolarization in frog sartorius muscle. J Physiol. 1979 Sep;294:497–520. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1979.sp012943. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Standen N. B., Stanfield P. R., Ward T. A. Properties of single potassium channels in vesicles formed from the sarcolemma of frog skeletal muscle. J Physiol. 1985 Jul;364:339–358. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1985.sp015749. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Trube G., Hescheler J. Inward-rectifying channels in isolated patches of the heart cell membrane: ATP-dependence and comparison with cell-attached patches. Pflugers Arch. 1984 Jun;401(2):178–184. doi: 10.1007/BF00583879. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


