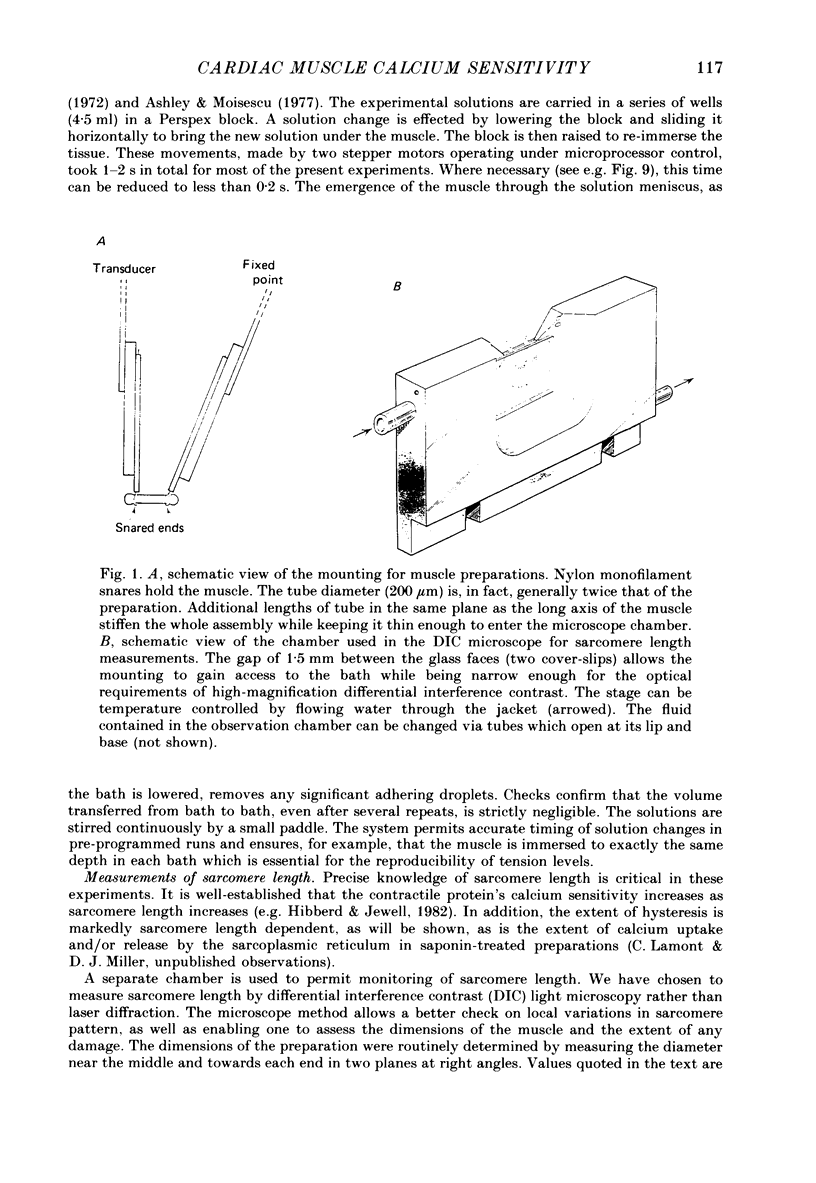
Abstract
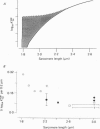
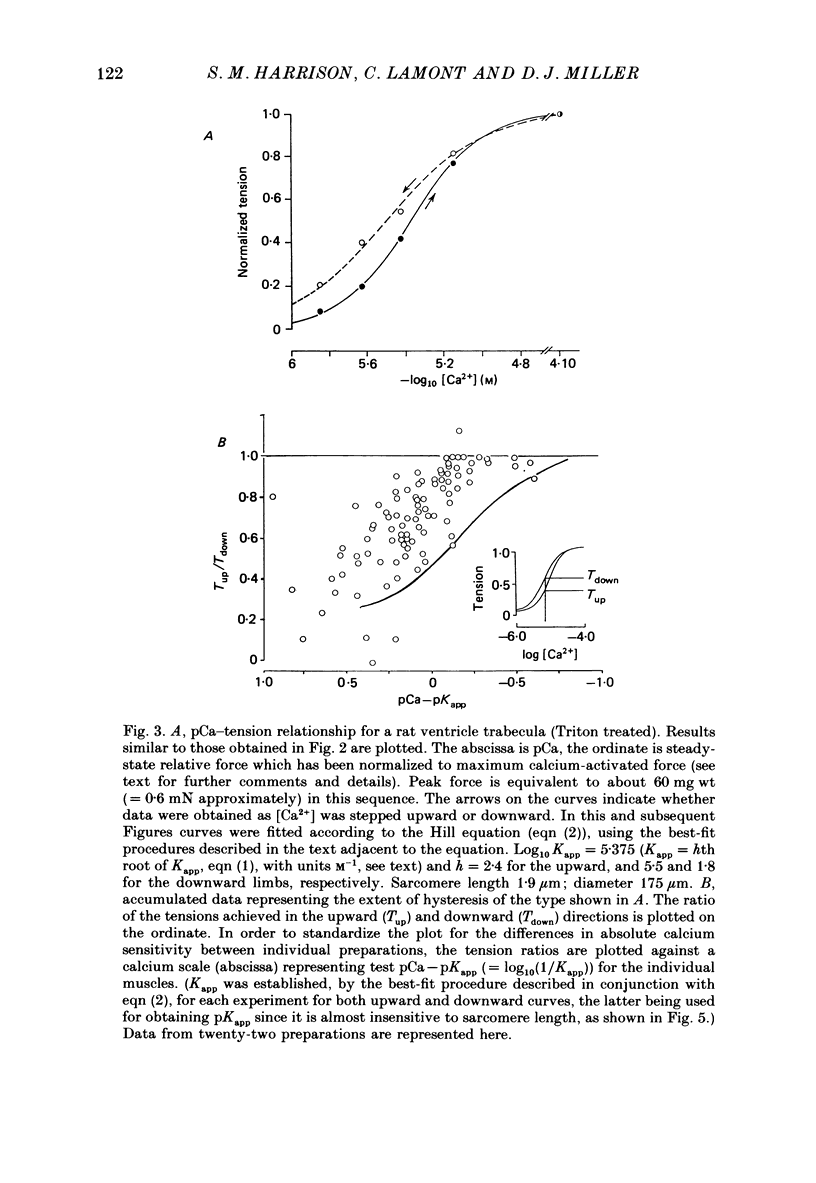
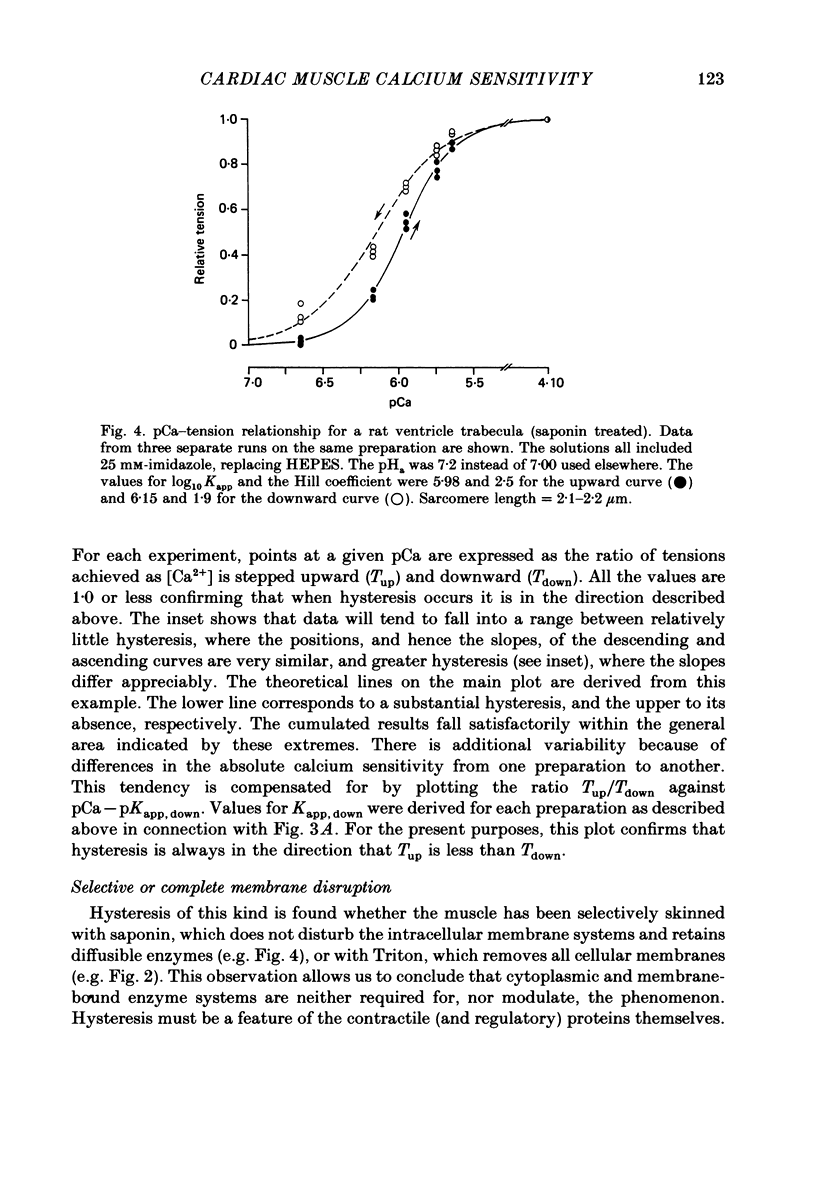
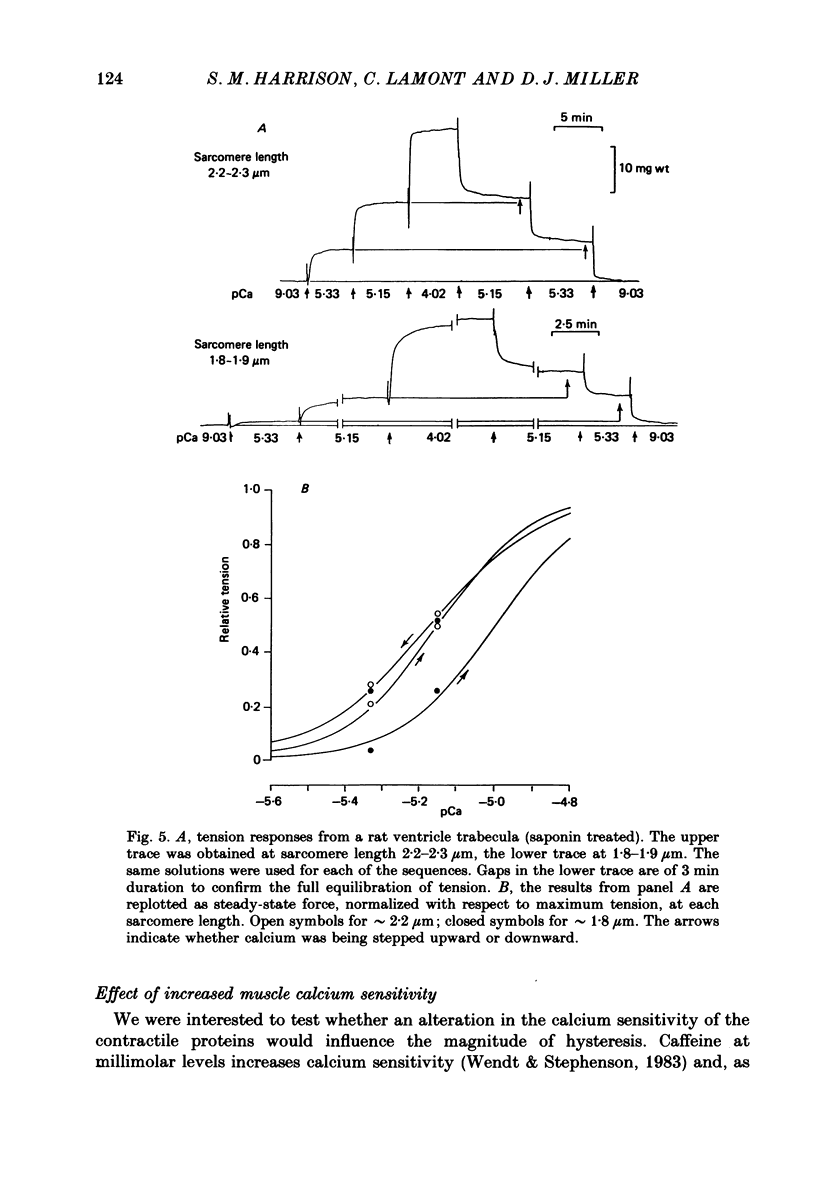
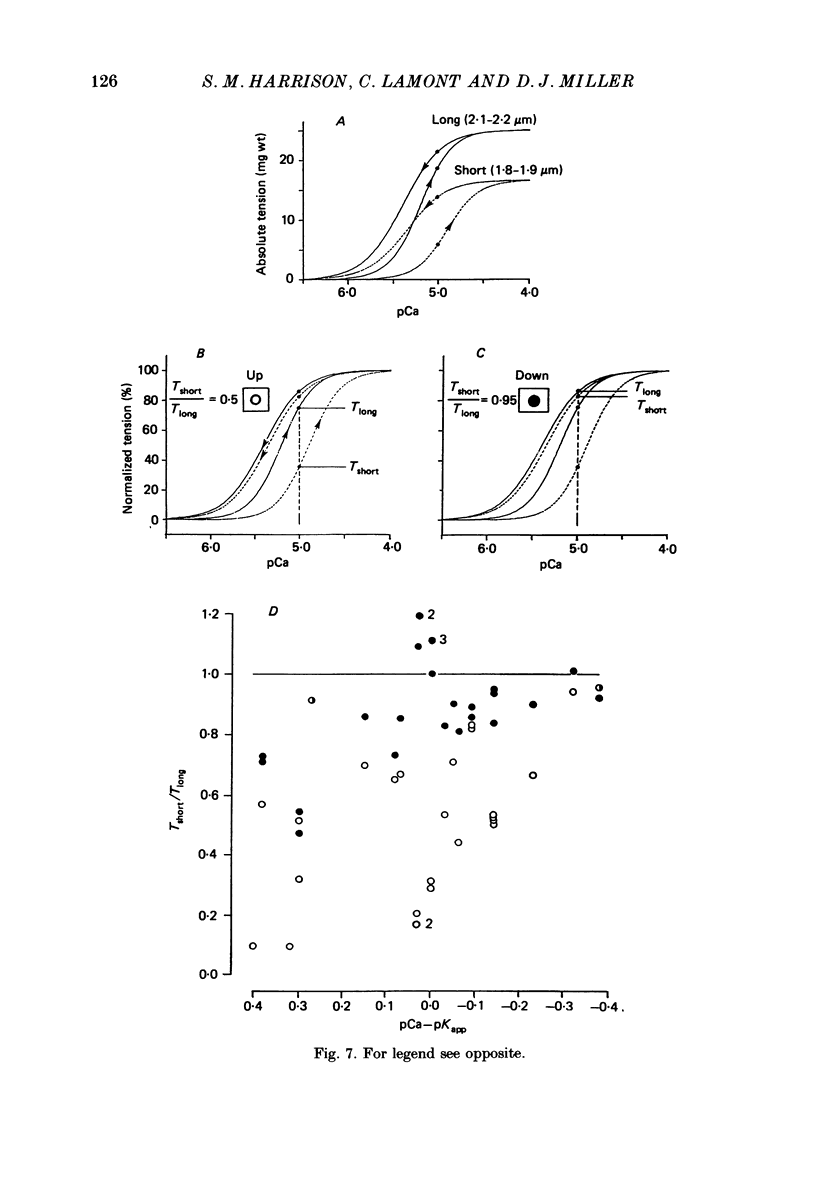
1. The relationship between pCa (-log10[Ca2+]) and steady-state isometric tension has been investigated in saponin- or Triton-treated (chemically 'skinned') cardiac muscle of rat. 2. Hysteresis exists in the relationship such that the muscle is less sensitive to Ca2+ during increasing activation (as [Ca2+] is stepped upward) than during reducing activation (as [Ca2+] is stepped downward). 3. The extent of the hysteresis is insensitive to interventions that increase overall calcium sensitivity by chemical means, such as caffeine, carnosine or increased pH. 4. The extent of the hysteresis is sensitive to sarcomere length. The phenomenon is virtually absent above sarcomere lengths of about 2.2-2.3 microns but becomes progressively greater at shorter sarcomere lengths. 5. The effect of sarcomere length on calcium sensitivity is restricted to the upward-going (increasing activation) part of the pCa-tension loop below 2.2 microns. The downward-going (decreasing activation) part of the hysteretic relationship is virtually unaffected by sarcomere length up to 2.2 microns. 6. Significant alterations in sarcomere length do not occur during tension development in the experiments described here: the phenomenon is not attributable to experimental artifacts of this kind. 7. Hysteresis develops sufficiently rapidly to be consistent with a physiological relevance during the normal heart beat. 8. The effects of sarcomere length show that the phenomenon is not due to force per se since, for example, greater peak force produces less hysteresis as sarcomere length is increased towards 2.2 microns. 9. Tonicity increase (by high-molecular-weight dextran), which shrinks the myofilament lattice, increases calcium sensitivity but reduces the effect of sarcomere length on calcium sensitivity. 10. The results suggest that lattice shrinkage is the mechanism which accounts for hysteresis in, and the sarcomere length dependence of, calcium sensitivity in cardiac muscle.
Full text
PDF






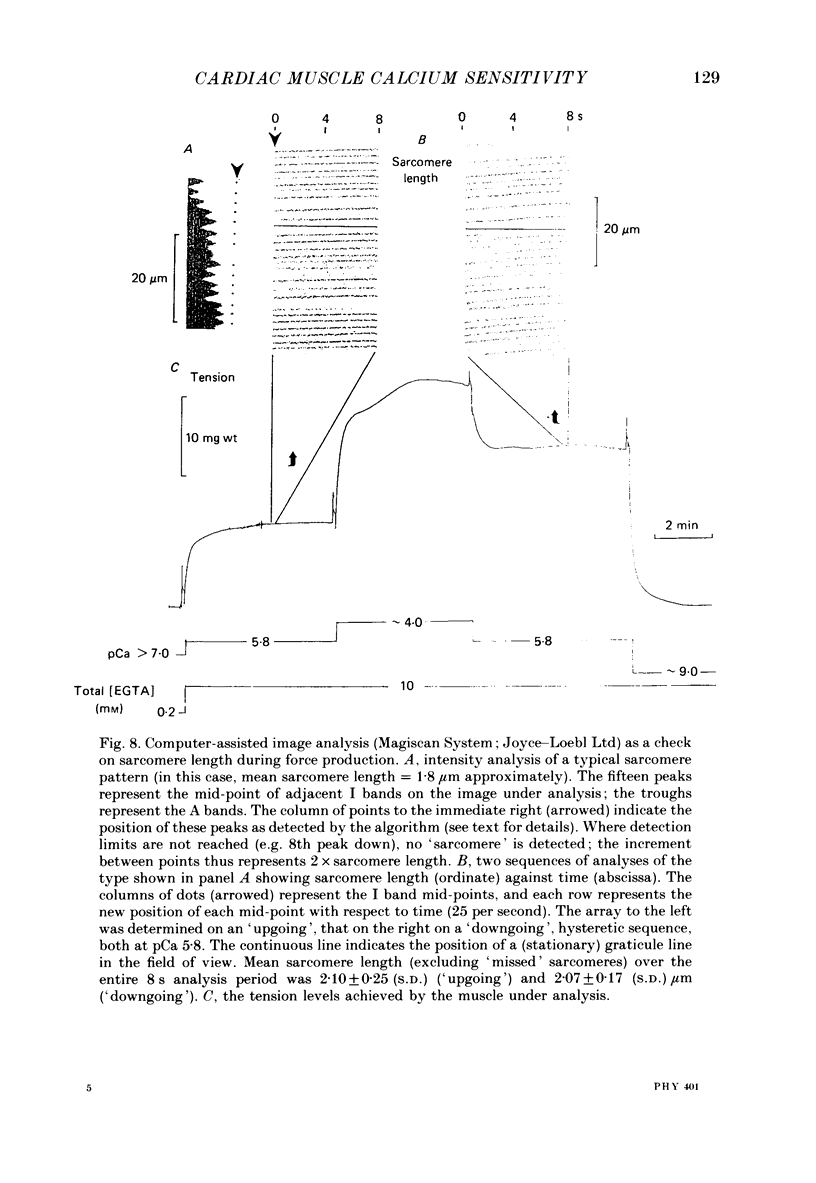

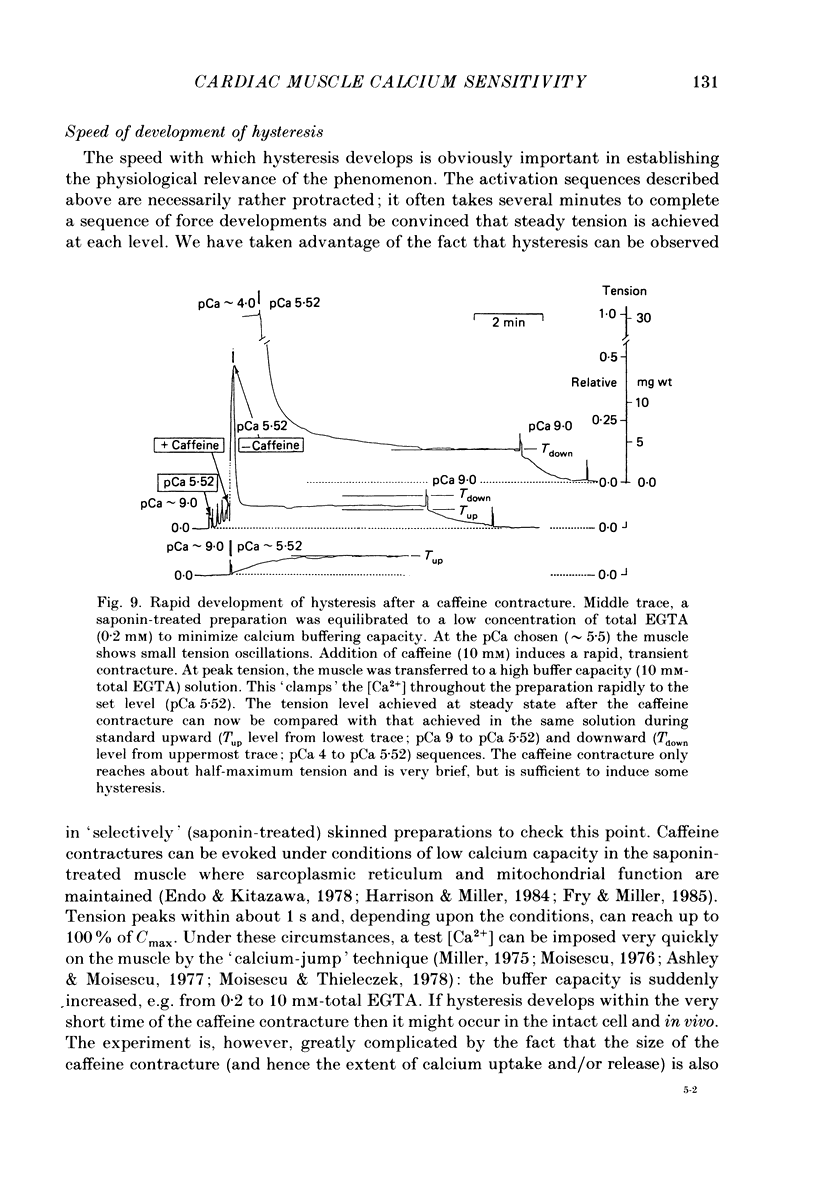
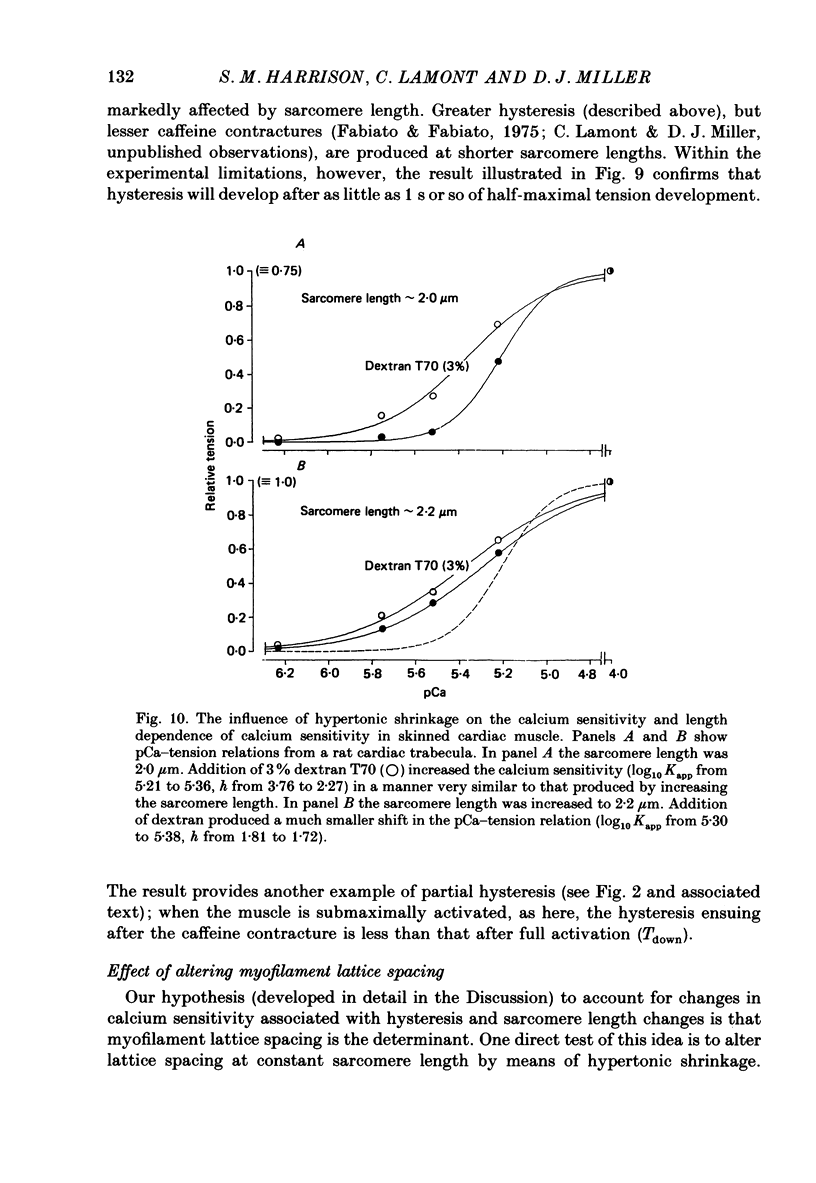





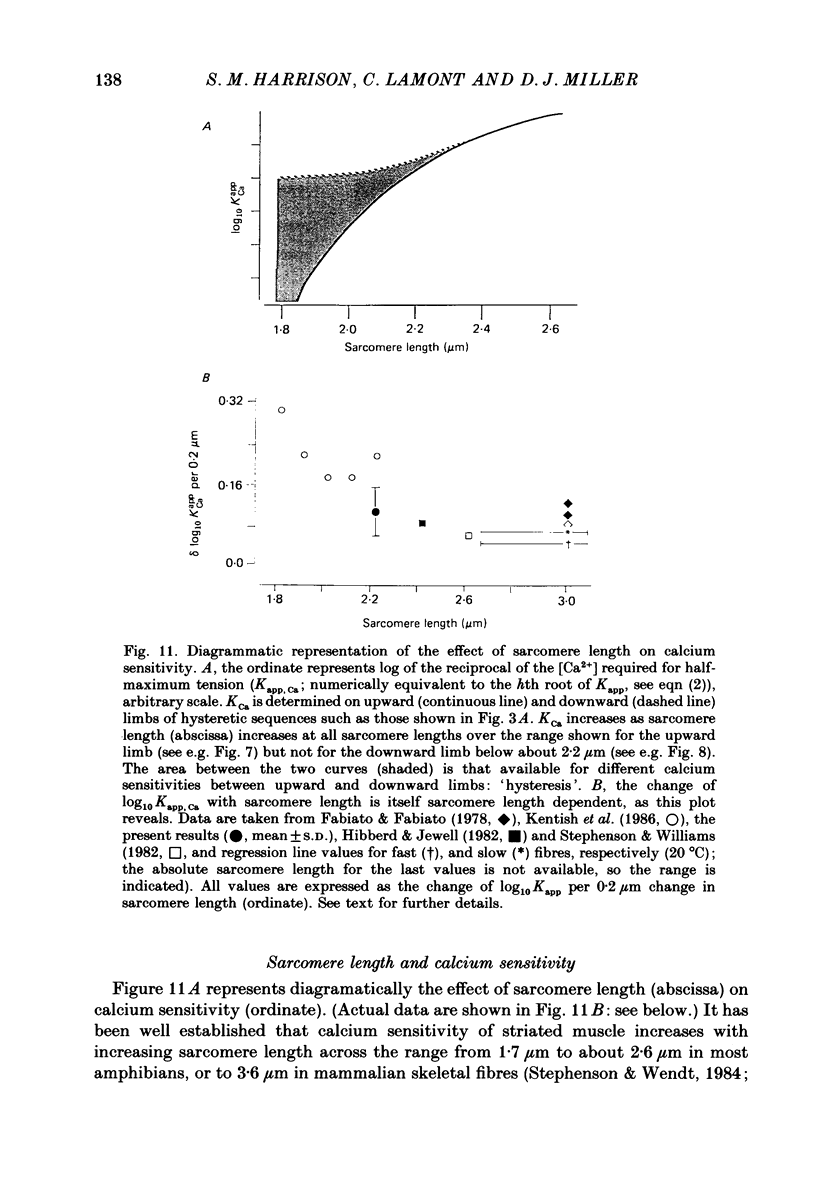





Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Allen D. G., Kentish J. C. The cellular basis of the length-tension relation in cardiac muscle. J Mol Cell Cardiol. 1985 Sep;17(9):821–840. doi: 10.1016/s0022-2828(85)80097-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Allen D. G., Kurihara S. The effects of muscle length on intracellular calcium transients in mammalian cardiac muscle. J Physiol. 1982 Jun;327:79–94. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1982.sp014221. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ashley C. C., Moisescu D. G. Effect of changing the composition of the bathing solutions upon the isometric tension-pCa relationship in bundles of crustacean myofibrils. J Physiol. 1977 Sep;270(3):627–652. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1977.sp011972. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bates R. G., Roy R. N., Robinson R. A. Buffer standards of tris(hydroxymethyl)methylglycine ("tricine") for the physiological range pH 7.2 to 8.5. Anal Chem. 1973 Aug;45(9):1663–1666. doi: 10.1021/ac60331a022. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Blinks J. R., Wier W. G., Hess P., Prendergast F. G. Measurement of Ca2+ concentrations in living cells. Prog Biophys Mol Biol. 1982;40(1-2):1–114. doi: 10.1016/0079-6107(82)90011-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Brandt P. W., Diamond M. S., Schachat F. H. The thin filament of vertebrate skeletal muscle co-operatively activates as a unit. J Mol Biol. 1984 Dec 5;180(2):379–384. doi: 10.1016/s0022-2836(84)80010-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Brandt P. W., Gluck B., Mini M., Cerri C. Hysteresis of the mammalian pCa/tension relation is small and muscle specific. J Muscle Res Cell Motil. 1985 Apr;6(2):197–205. doi: 10.1007/BF00713061. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bremel R. D., Weber A. Cooperation within actin filament in vertebrate skeletal muscle. Nat New Biol. 1972 Jul 26;238(82):97–101. doi: 10.1038/newbio238097a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fabiato A., Fabiato F. Contractions induced by a calcium-triggered release of calcium from the sarcoplasmic reticulum of single skinned cardiac cells. J Physiol. 1975 Aug;249(3):469–495. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1975.sp011026. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fabiato A., Fabiato F. Myofilament-generated tension oscillations during partial calcium activation and activation dependence of the sarcomere length-tension relation of skinned cardiac cells. J Gen Physiol. 1978 Nov;72(5):667–699. doi: 10.1085/jgp.72.5.667. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fellows S. J., Rack P. M. Changes in the length of the human biceps brachii muscle during elbow movements. J Physiol. 1987 Feb;383:405–412. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1987.sp016416. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ford L. E., Podolsky R. J. Calcium uptake and force development by skinned muscle fibres in EGTA buffered solutions. J Physiol. 1972 May;223(1):1–19. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1972.sp009830. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fuchs F. The binding of calcium to detergent-extracted rabbit psoas muscle fibres during relaxation and force generation. J Muscle Res Cell Motil. 1985 Aug;6(4):477–486. doi: 10.1007/BF00712584. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Godt R. E., Maughan D. W. Influence of osmotic compression on calcium activation and tension in skinned muscle fibers of the rabbit. Pflugers Arch. 1981 Oct;391(4):334–337. doi: 10.1007/BF00581519. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Godt R. E., Maughan D. W. Swelling of skinned muscle fibers of the frog. Experimental observations. Biophys J. 1977 Aug;19(2):103–116. doi: 10.1016/S0006-3495(77)85573-2. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gordon A. M., Ridgway E. B., Martyn D. A. Calcium sensitivity is modified by contraction. Adv Exp Med Biol. 1984;170:553–563. doi: 10.1007/978-1-4684-4703-3_49. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hibberd M. G., Jewell B. R. Calcium- and length-dependent force production in rat ventricular muscle. J Physiol. 1982 Aug;329:527–540. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1982.sp014317. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Illingworth J. A. A common source of error in pH measurements. Biochem J. 1981 Apr 1;195(1):259–262. doi: 10.1042/bj1950259. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jewell B. R. A reexamination of the influence of muscle length on myocardial performance. Circ Res. 1977 Mar;40(3):221–230. doi: 10.1161/01.res.40.3.221. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kentish J. C., ter Keurs H. E., Ricciardi L., Bucx J. J., Noble M. I. Comparison between the sarcomere length-force relations of intact and skinned trabeculae from rat right ventricle. Influence of calcium concentrations on these relations. Circ Res. 1986 Jun;58(6):755–768. doi: 10.1161/01.res.58.6.755. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Krueger J. W., Forletti D., Wittenberg B. A. Uniform sarcomere shortening behavior in isolated cardiac muscle cells. J Gen Physiol. 1980 Nov;76(5):587–607. doi: 10.1085/jgp.76.5.587. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Krueger J. W., Pollack G. H. Myocardial sarcomere dynamics during isometric contraction. J Physiol. 1975 Oct;251(3):627–643. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1975.sp011112. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Matsubara I., Elliott G. F. X-ray diffraction studies on skinned single fibres of frog skeletal muscle. J Mol Biol. 1972 Dec 30;72(3):657–669. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(72)90183-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Matsubara I., Goldman Y. E., Simmons R. M. Changes in the lateral filament spacing of skinned muscle fibres when cross-bridges attach. J Mol Biol. 1984 Feb 15;173(1):15–33. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(84)90401-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Matsubara I., Umazume Y., Yagi N. Lateral filamentary spacing in chemically skinned murine muscles during contraction. J Physiol. 1985 Mar;360:135–148. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1985.sp015608. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Matsubara I., Umazume Y., Yagi N. Lateral shrinkage of the myofilament lattice in chemically skinned muscles during contraction. Adv Exp Med Biol. 1984;170:711–720. doi: 10.1007/978-1-4684-4703-3_66. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Miller D. J., Smith G. L. EGTA purity and the buffering of calcium ions in physiological solutions. Am J Physiol. 1984 Jan;246(1 Pt 1):C160–C166. doi: 10.1152/ajpcell.1984.246.1.C160. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Miller D. J., Smith G. L. The contractile behaviour of EGTA- and detergent-treated heart muscle. J Muscle Res Cell Motil. 1985 Oct;6(5):541–567. doi: 10.1007/BF00711914. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Moisescu D. G. Kinetics of reaction in calcium-activated skinned muscle fibres. Nature. 1976 Aug 12;262(5569):610–613. doi: 10.1038/262610a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Moisescu D. G., Thieleczek R. Calcium and strontium concentration changes within skinned muscle preparations following a change in the external bathing solution. J Physiol. 1978 Feb;275:241–262. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1978.sp012188. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Moisescu D. G., Thieleczek R. Sarcomere length effects on the Sr2+- and Ca2+-activation curves in skinned frog muscle fibres. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1979 Apr 11;546(1):64–76. doi: 10.1016/0005-2728(79)90170-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pagani E. D., Shemin R., Julian F. J. Tension-pCa relations of saponin-skinned rabbit and human heart muscle. J Mol Cell Cardiol. 1986 Jan;18(1):55–66. doi: 10.1016/s0022-2828(86)80982-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ridgway E. B., Gordon A. M., Martyn D. A. Hysteresis in the force-calcium relation in muscle. Science. 1983 Mar 4;219(4588):1075–1077. doi: 10.1126/science.6823567. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rome E. X-ray diffraction studies of the filament lattice of striated muscle in various bathing media. J Mol Biol. 1968 Oct 28;37(2):331–344. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(68)90272-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Silver P. J. Pharmacological modulation of cardiac and vascular contractile protein function. J Cardiovasc Pharmacol. 1986;8 (Suppl 9):S34–S46. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Smith G. L., Miller D. J. Potentiometric measurements of stoichiometric and apparent affinity constants of EGTA for protons and divalent ions including calcium. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1985 May 8;839(3):287–299. doi: 10.1016/0304-4165(85)90011-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stephenson D. G., Wendt I. R. Length dependence of changes in sarcoplasmic calcium concentration and myofibrillar calcium sensitivity in striated muscle fibres. J Muscle Res Cell Motil. 1984 Jun;5(3):243–272. doi: 10.1007/BF00713107. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stephenson D. G., Williams D. A. Effects of sarcomere length on the force-pCa relation in fast- and slow-twitch skinned muscle fibres from the rat. J Physiol. 1982 Dec;333:637–653. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1982.sp014473. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stephenson D. G., Williams D. A. Slow amphibian muscle fibres become less sensitive to Ca2+ with increasing sarcomere length. Pflugers Arch. 1983 May;397(3):248–250. doi: 10.1007/BF00584366. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Vega C. A., Bates R. G. Buffers for the physiological pH range: thermodynamic constants of four substituted aminoethanesulfonic acids from 5 to 50 degrees C. Anal Chem. 1976 Aug;48(9):1293–1296. doi: 10.1021/ac50003a010. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wendt I. R., Stephenson D. G. Effects of caffeine on Ca-activated force production in skinned cardiac and skeletal muscle fibres of the rat. Pflugers Arch. 1983 Aug;398(3):210–216. doi: 10.1007/BF00657153. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Winegrad S. Resting sarcomere length-tension relation in living frog heart. J Gen Physiol. 1974 Sep;64(3):343–355. doi: 10.1085/jgp.64.3.343. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]