Abstract
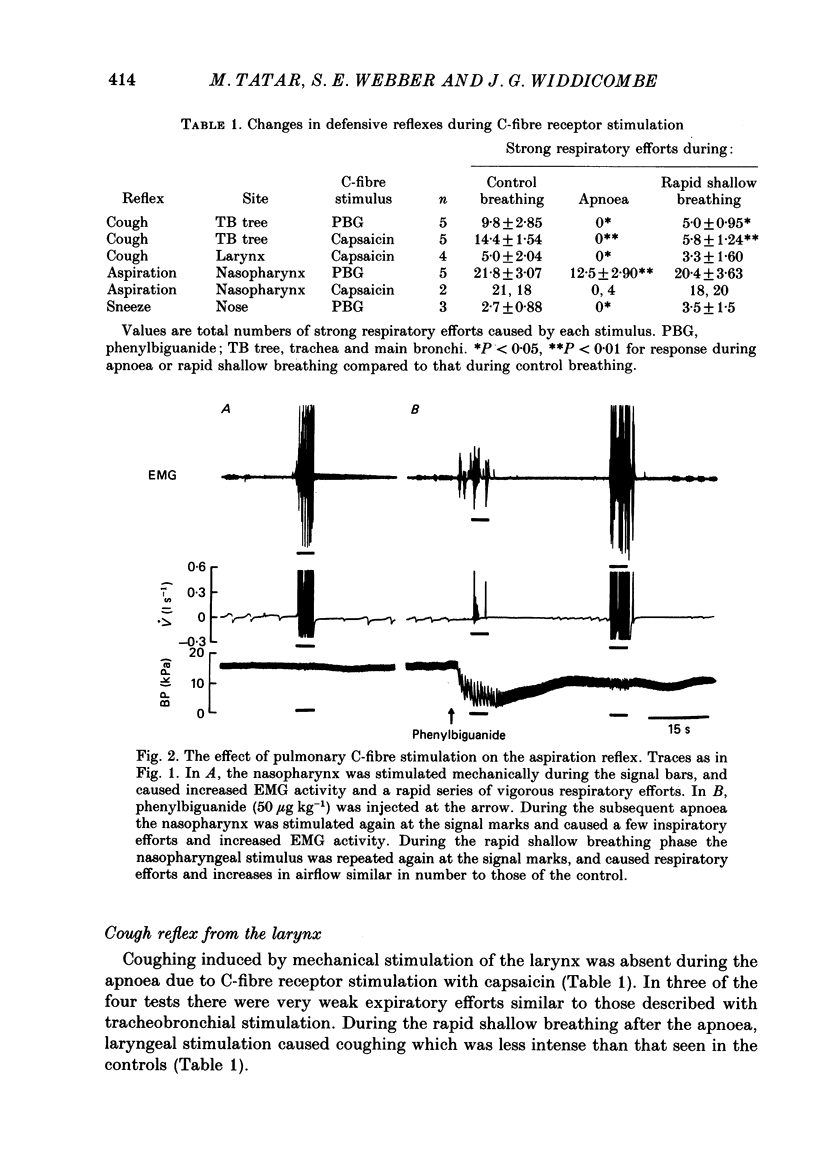
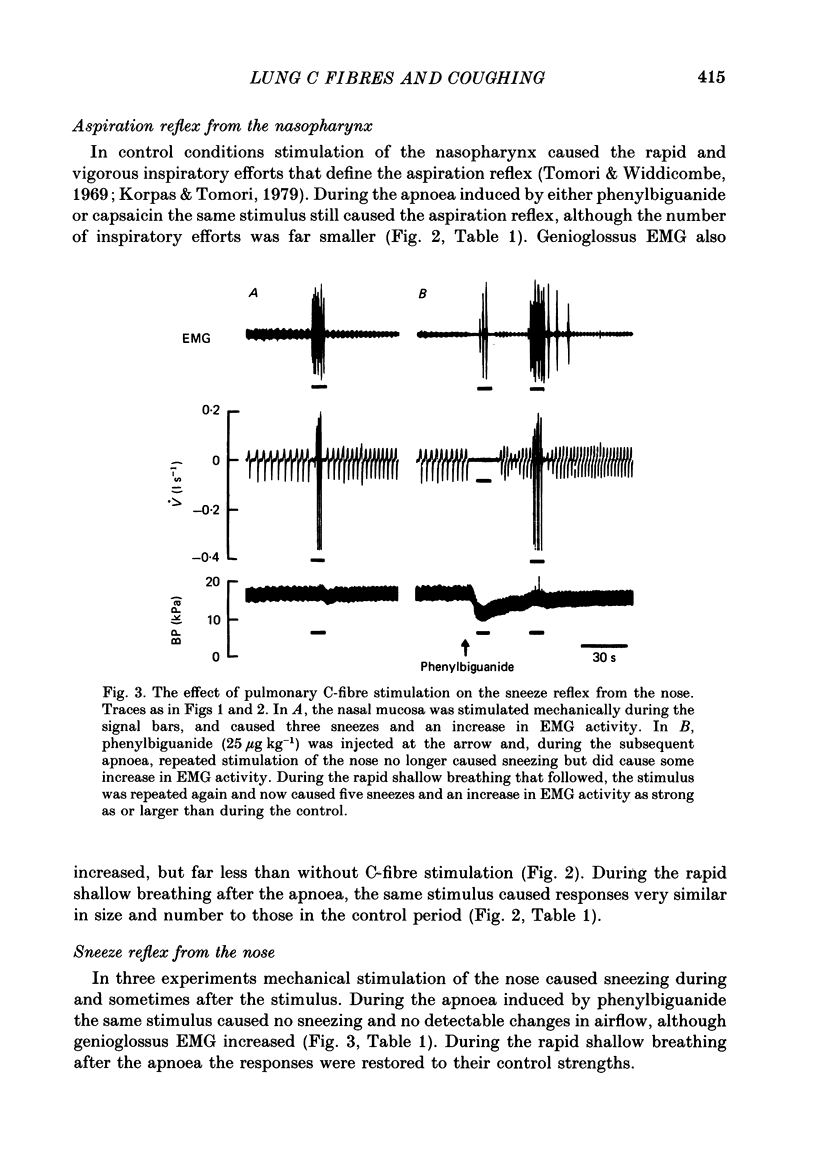
1. With pentobarbitone-anaesthetized cats we have elicited cough reflexes from the tracheobronchial tree and the larynx, and the aspiration and sneeze reflexes from the nasopharynx and the nose respectively. The reflexes were induced by mechanical stimulation of the mucosa, before and during activation of pulmonary C-fibre receptors by intravenous injections of capsaicin or phenylbiguanide. 2. During the 20-30 s apnoea due to C-fibre stimulation, the cough reflex from both sites and the sneeze reflex were completely abolished, whereas the aspiration reflex response was approximately halved. Reflex contractions of genioglossus muscle still occurred at this time, but were far weaker than in the control state. 3. During the rapid shallow breathing that immediately followed apnoea due to C-fibre receptor stimulation, the defensive reflexes recovered: the aspiration and sneeze reflexes fully and the cough reflexes to about half of the control response. 4. Acute hypotension due to haemorrhage, of a size considerably greater than that due to stimulation of the pulmonary C-fibre receptors, caused no significant inhibition of the cough reflex from the tracheobronchial tree. 5. We conclude that the pulmonary C-fibre reflex powerfully inhibits airway defensive reflexes, and that its activation is unlikely to contribute positively to coughing induced by aerosols of capsaicin and similar agents.
Full text
PDF







Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Armstrong D. J., Luck J. C. A comparative study of irritant and type J receptors in the cat. Respir Physiol. 1974 Jul;21(1):47–60. doi: 10.1016/0034-5687(74)90006-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Boushey H. A., Richardson P. S., Widdicombe J. G., Wise J. C. The response of laryngeal afferent fibres to mechanical and chemical stimuli. J Physiol. 1974 Jul;240(1):153–175. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1974.sp010605. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Buck S. H., Burks T. F. The neuropharmacology of capsaicin: review of some recent observations. Pharmacol Rev. 1986 Sep;38(3):179–226. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Clifford P. S., Litzow J. T., Coon R. L. Pulmonary depressor reflex elicited by capsaicin in conscious intact and lung-denervated dogs. Am J Physiol. 1987 Feb;252(2 Pt 2):R394–R397. doi: 10.1152/ajpregu.1987.252.2.R394. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Coleridge H. M., Coleridge J. C., Roberts A. M. Rapid shallow breathing evoked by selective stimulation of airway C fibres in dogs. J Physiol. 1983 Jul;340:415–433. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1983.sp014770. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Collier J. G., Fuller R. W. Capsaicin inhalation in man and the effects of sodium cromoglycate. Br J Pharmacol. 1984 Jan;81(1):113–117. doi: 10.1111/j.1476-5381.1984.tb10750.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- DAWES G. S., COMROE J. H., Jr Chemoreflexes from the heart and lungs. Physiol Rev. 1954 Apr;34(2):167–201. doi: 10.1152/physrev.1954.34.2.167. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Das R. M., Jeffrey P. K., Widdicombe J. G. The epithelial innervation of the lower respiratory tract of the cat. J Anat. 1978 May;126(Pt 1):123–131. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Forsberg K., Karlsson J. A. Cough induced by stimulation of capsaicin-sensitive sensory neurons in conscious guinea-pigs. Acta Physiol Scand. 1986 Oct;128(2):319–320. doi: 10.1111/j.1748-1716.1986.tb07981.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fuller R. W., Dixon C. M., Cuss F. M., Barnes P. J. Bradykinin-induced bronchoconstriction in humans. Mode of action. Am Rev Respir Dis. 1987 Jan;135(1):176–180. doi: 10.1164/arrd.1987.135.1.176. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hanácek J., Davies A., Widdicombe J. G. Influence of lung stretch receptors on the cough reflex in rabbits. Respiration. 1984;45(3):161–168. doi: 10.1159/000194614. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hoyes A. D., Barber P., Jagessar H. Effect of capsaicin on the intraperitoneal axons of the rat trachea. Neurosci Lett. 1981 Nov 4;26(3):329–334. doi: 10.1016/0304-3940(81)90154-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jonzon A., Pisarri T. E., Coleridge J. C., Coleridge H. M. Rapidly adapting receptor activity in dogs is inversely related to lung compliance. J Appl Physiol (1985) 1986 Nov;61(5):1980–1987. doi: 10.1152/jappl.1986.61.5.1980. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kaufman M. P., Coleridge H. M., Coleridge J. C., Baker D. G. Bradykinin stimulates afferent vagal C-fibers in intrapulmonary airways of dogs. J Appl Physiol Respir Environ Exerc Physiol. 1980 Mar;48(3):511–517. doi: 10.1152/jappl.1980.48.3.511. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Paintal A. S. The visceral sensations--some basic mechanisms. Prog Brain Res. 1986;67:3–19. doi: 10.1016/s0079-6123(08)62752-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Polácek H., Korpás J., Tatár M., Plank L., Pullmann R. Study of cough in anaesthetized cats with experimental pulmonary oedema. Physiol Bohemoslov. 1986;35(6):481–489. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Roberts A. M., Kaufman M. P., Baker D. G., Brown J. K., Coleridge H. M., Coleridge J. C. Reflex tracheal contraction induced by stimulation of bronchial C-fibers in dogs. J Appl Physiol Respir Environ Exerc Physiol. 1981 Aug;51(2):485–493. doi: 10.1152/jappl.1981.51.2.485. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sant'Ambrogio G. Information arising from the tracheobronchial tree of mammals. Physiol Rev. 1982 Apr;62(2):531–569. doi: 10.1152/physrev.1982.62.2.531. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sant'Ambrogio G. Nervous receptors of the tracheobronchial tree. Annu Rev Physiol. 1987;49:611–627. doi: 10.1146/annurev.ph.49.030187.003143. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sant'Ambrogio G., Sant'Ambrogio F. B., Davies A. Airway receptors in cough. Bull Eur Physiopathol Respir. 1984 Jan-Feb;20(1):43–47. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Simonsson B. G., Skoogh B. E., Bergh N. P., Andersson R., Svedmyr N. In vivo and in vitro effect of bradykinin on bronchial motor tone in normal subjects and patients with airways obstruction. Respiration. 1973;30(4):378–388. doi: 10.1159/000193051. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Such G., Jancsó G. Axonal effects of capsaicin: an electrophysiological study. Acta Physiol Hung. 1986;67(1):53–63. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tomori Z., Widdicombe J. G. Muscular, bronchomotor and cardiovascular reflexes elicited by mechanical stimulation of the respiratory tract. J Physiol. 1969 Jan;200(1):25–49. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1969.sp008680. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Widdicombe J. G. Sensory innervation of the lungs and airways. Prog Brain Res. 1986;67:49–64. doi: 10.1016/s0079-6123(08)62756-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Winning A. J., Hamilton R. D., Shea S. A., Guz A. Respiratory and cardiovascular effects of central and peripheral intravenous injections of capsaicin in man: evidence for pulmonary chemosensitivity. Clin Sci (Lond) 1986 Nov;71(5):519–526. doi: 10.1042/cs0710519. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- van Lunteren E., Strohl K. P. The muscles of the upper airways. Clin Chest Med. 1986 Jun;7(2):171–188. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


