Abstract
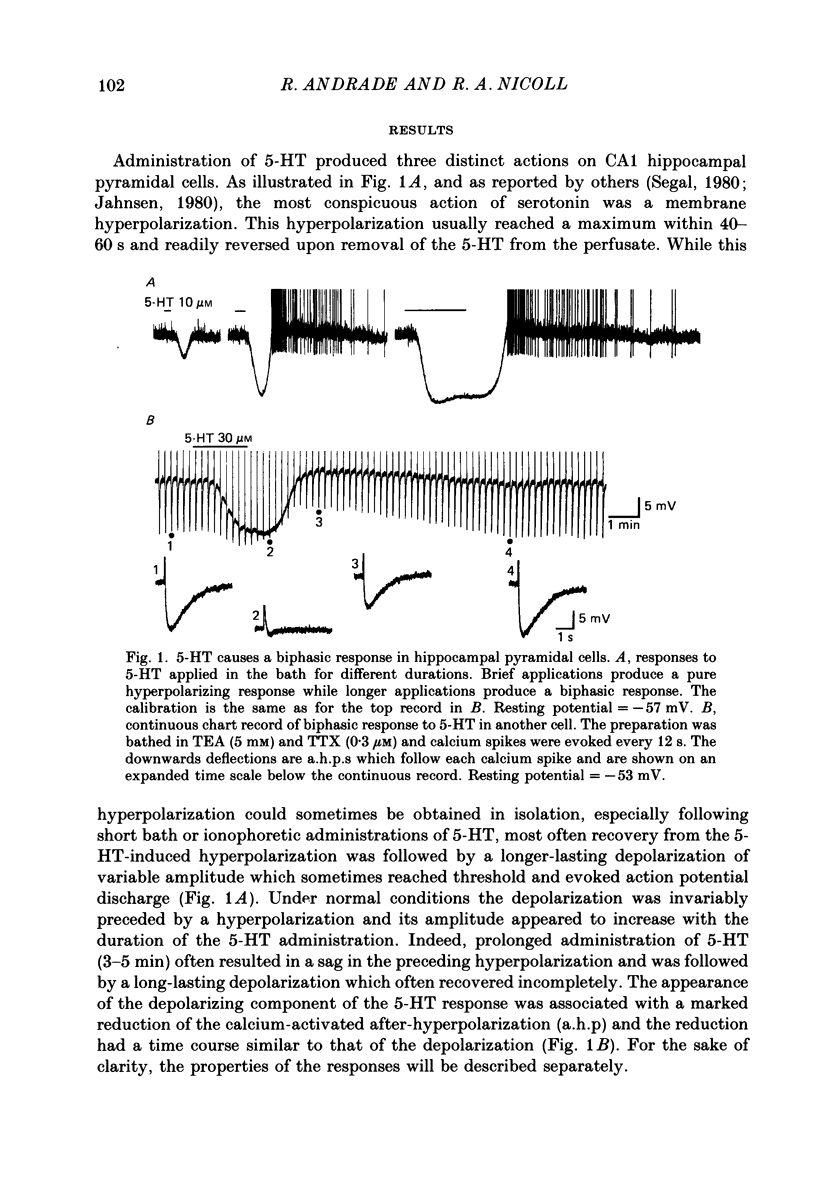
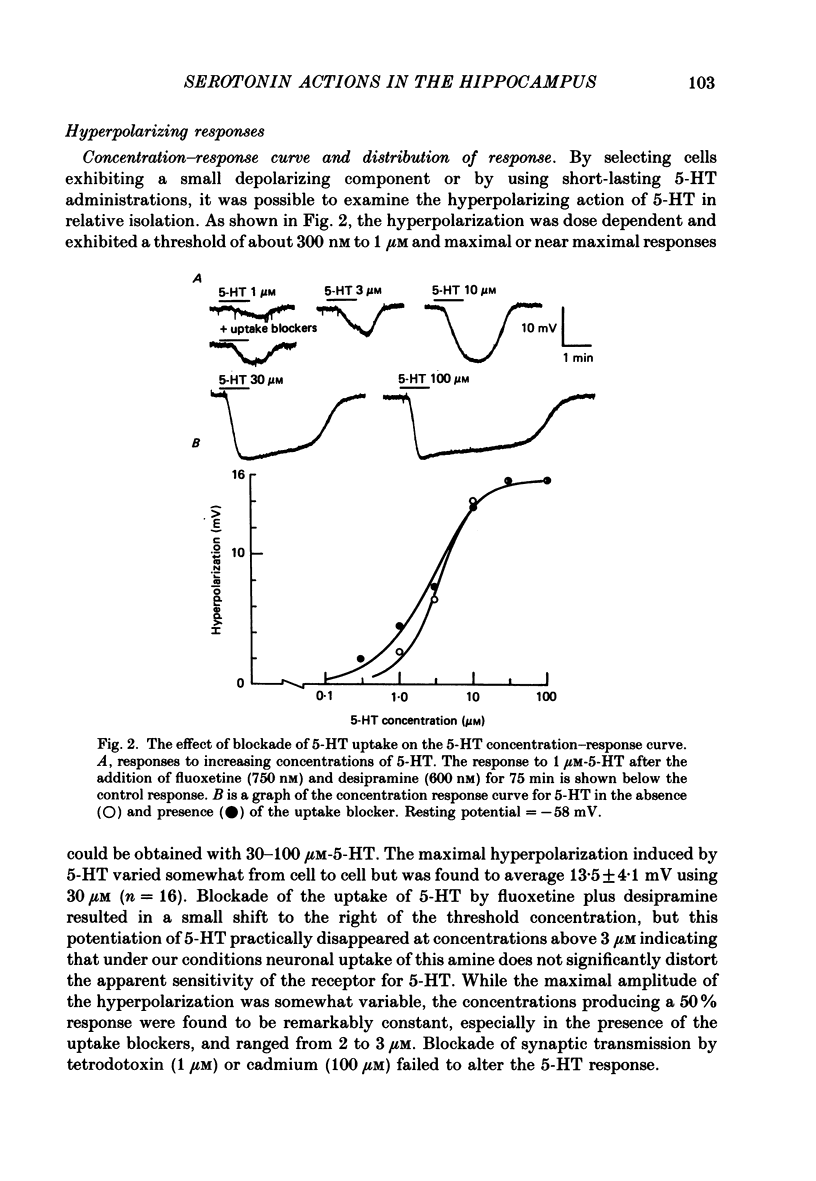
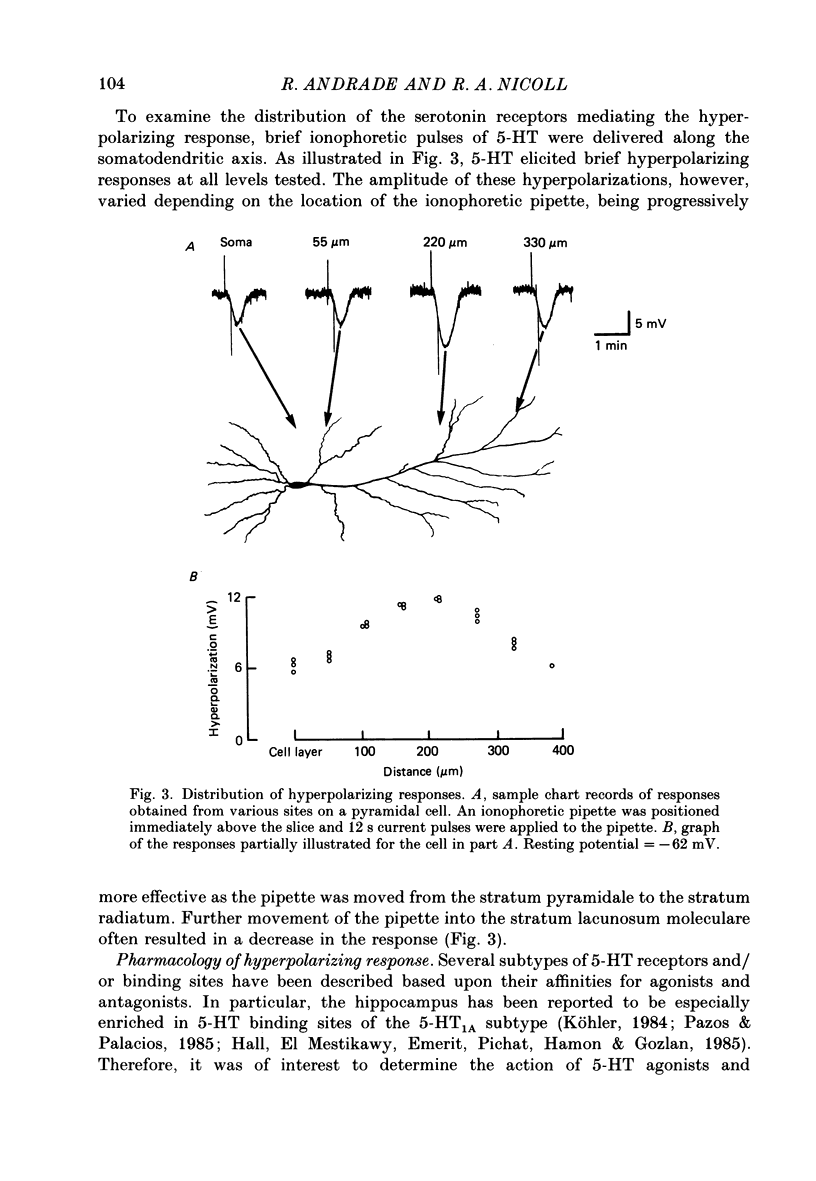
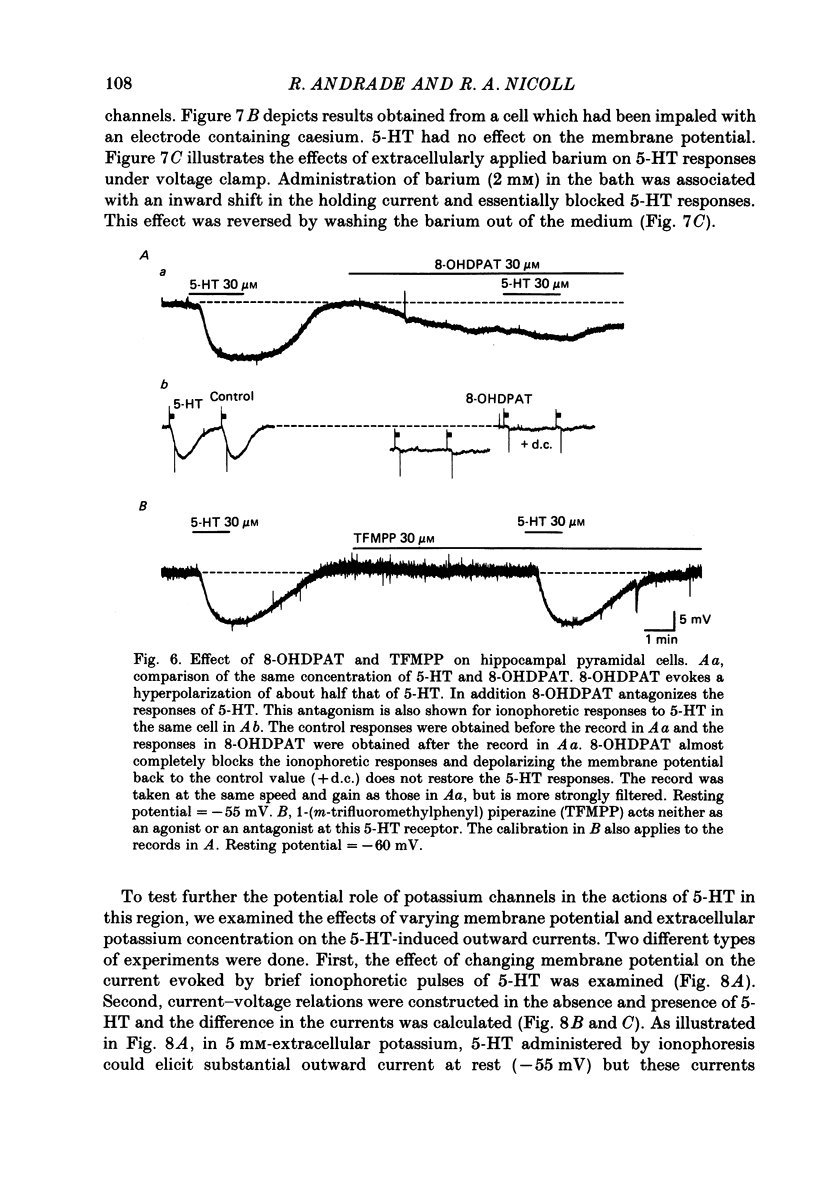
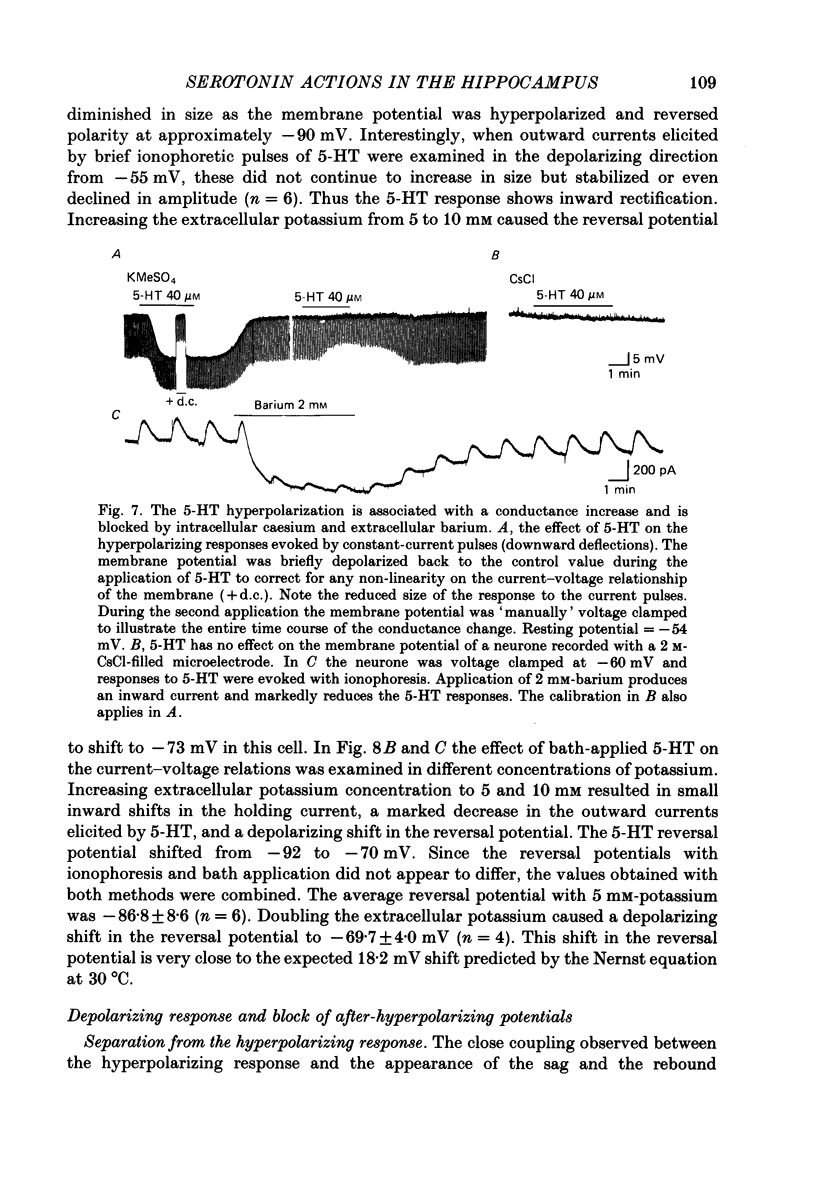
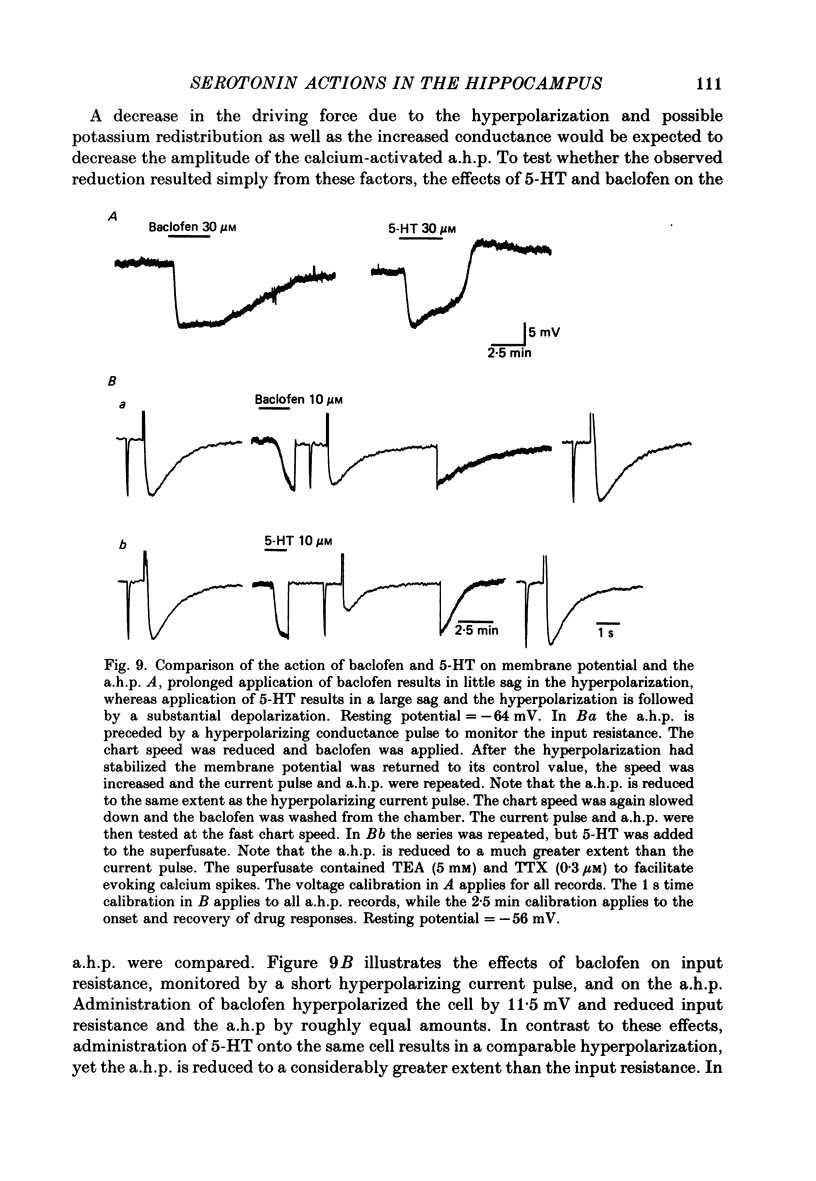
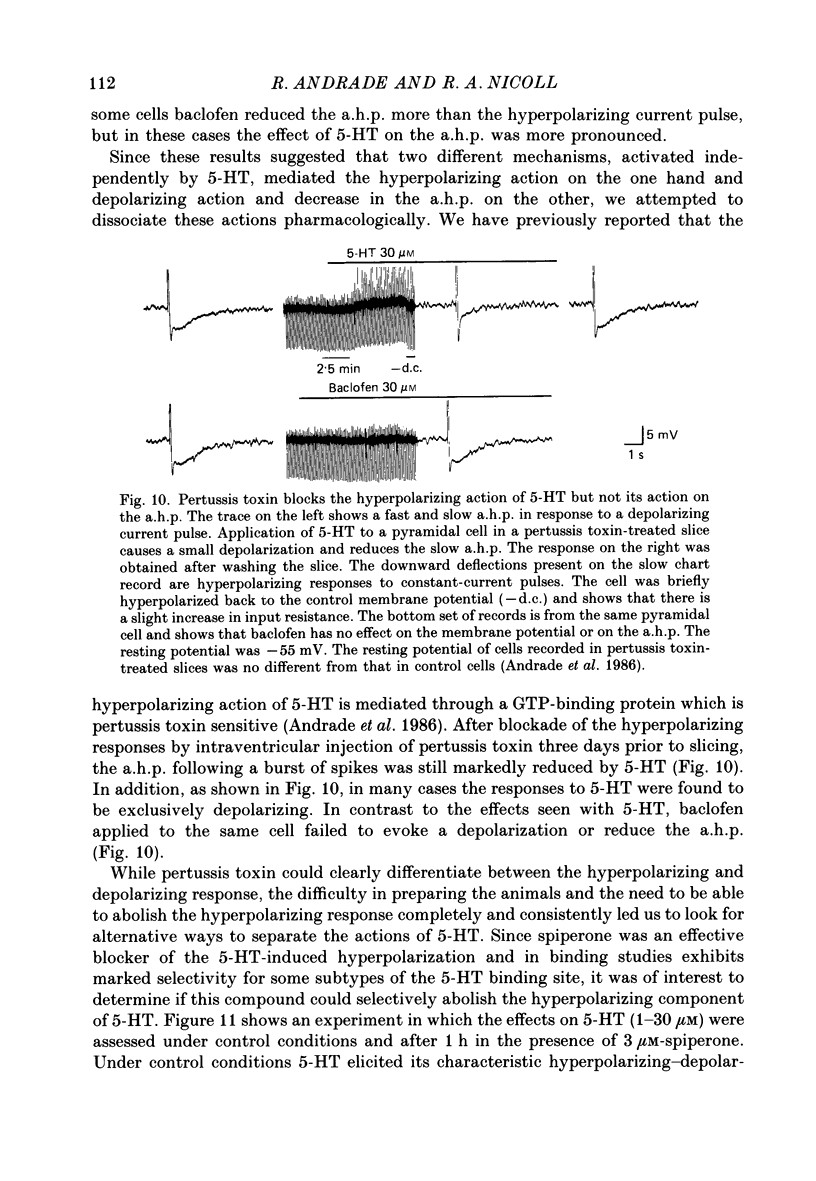
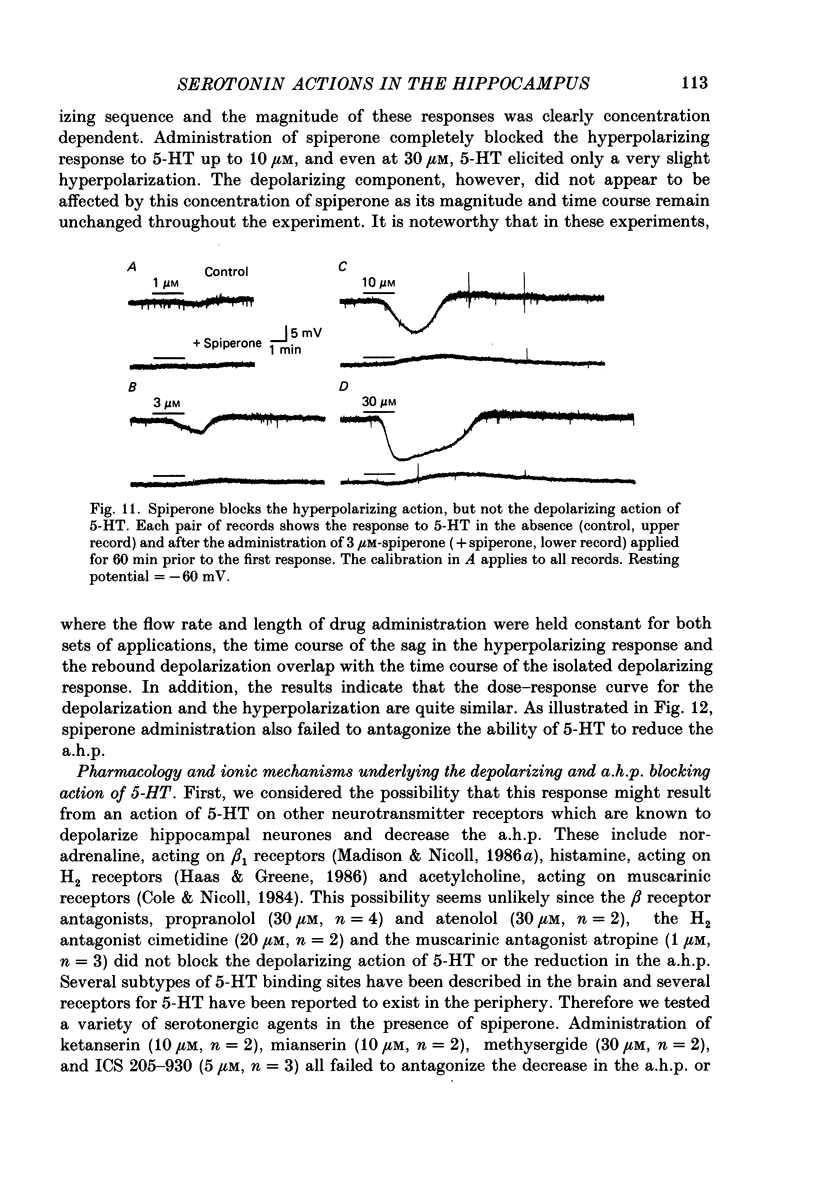
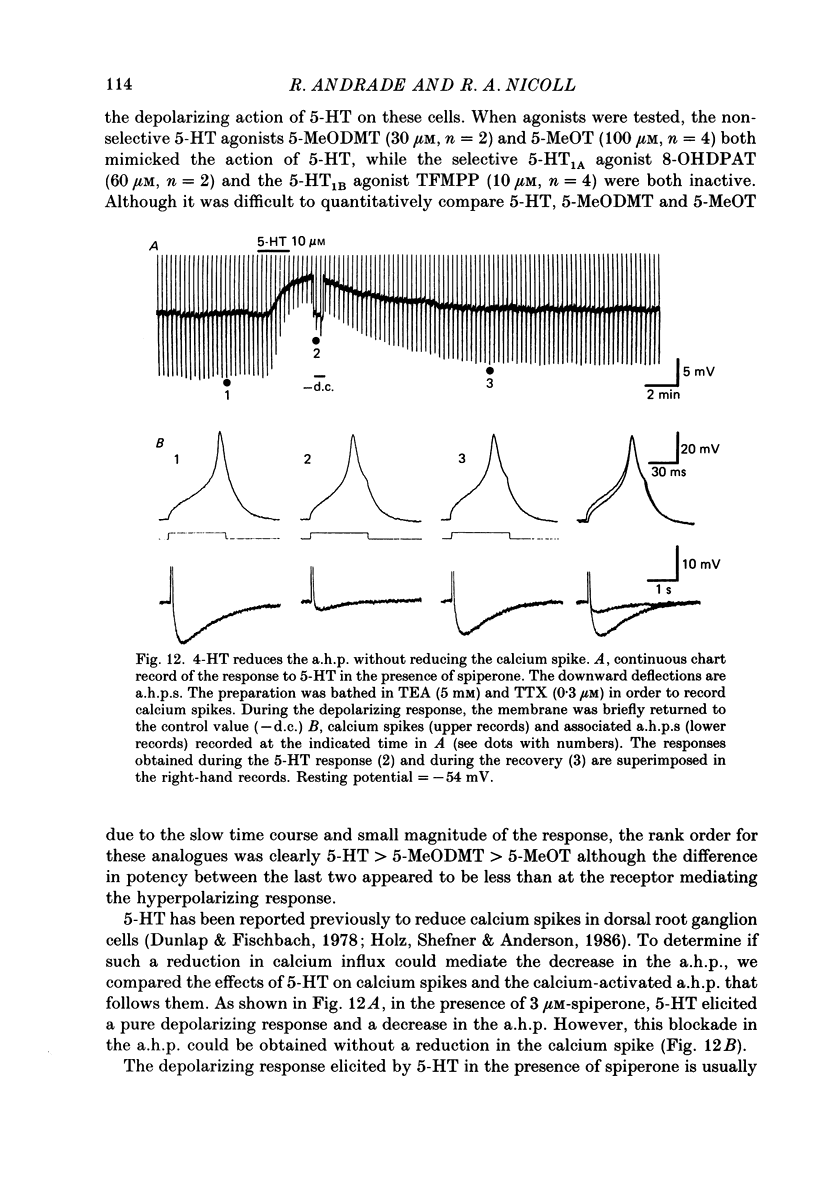
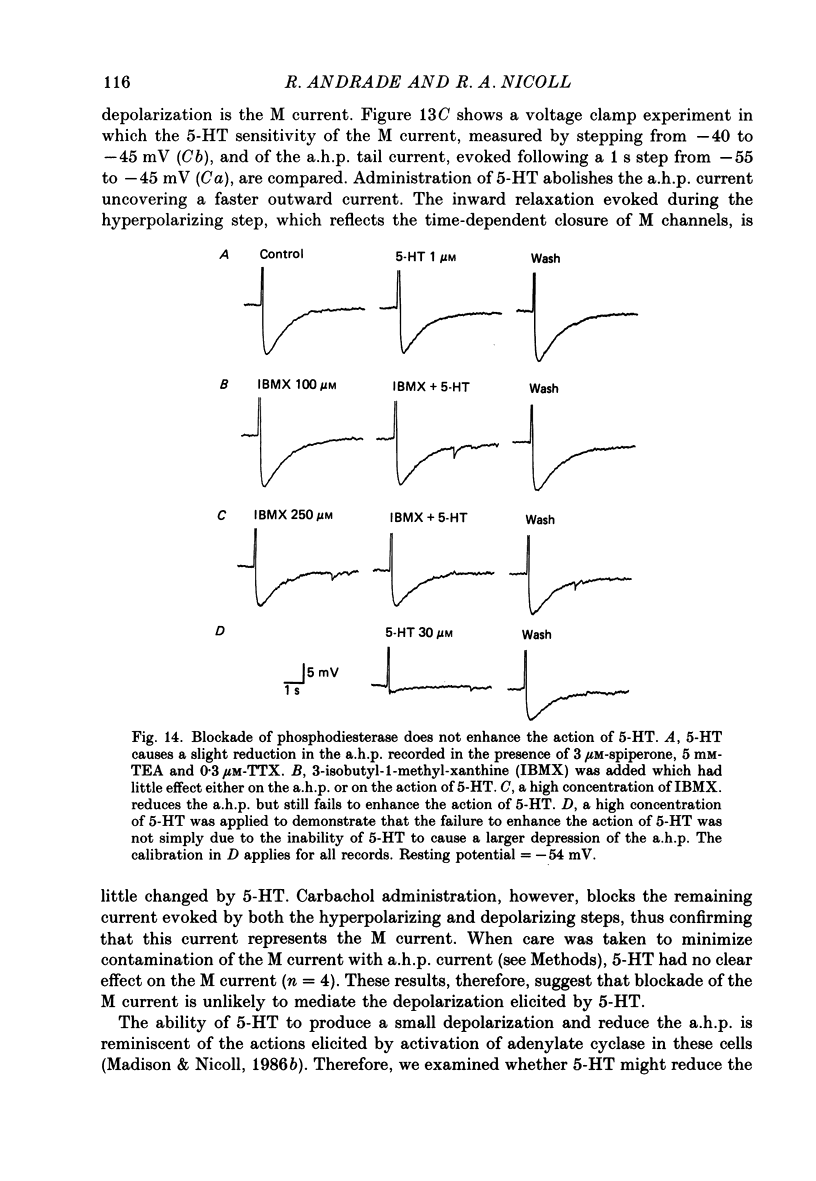
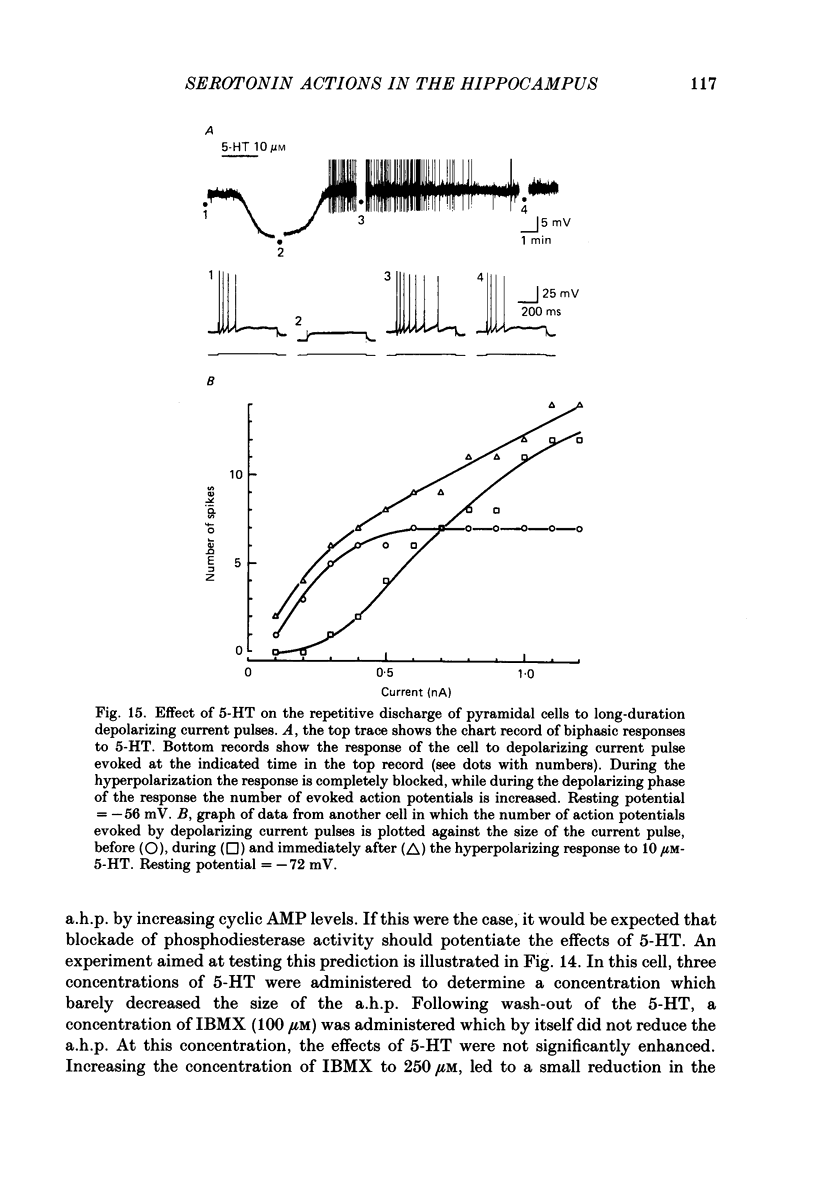
1. The actions of serotonin (5-HT) on pyramidal cells of the CA1 region of the rat hippocampus were characterized using intracellular recording in in vitro brain slices. 2. 5-HT typically evokes a biphasic response consisting of a hyperpolarization which is followed by a longer-lasting depolarization. These effects on membrane potential are accompanied by a decrease in the calcium-activated after-hyperpolarization (a.h.p). 3. Detailed analysis using 5-HT antagonists and agonists indicates that the hyperpolarization is mediated by a 5-HT1A receptor. Spiperone is the most effective antagonist of the response and the selective 5-HT1A agonist, 8-OHDPAT, behaves as a partial agonist at this receptor. In agreement with the distribution of 5-HT1A binding sites, responses to 5-HT were most prominent in the stratum radiatum. 4. The hyperpolarizing response is associated with a decrease in input resistance, is blocked by extracellular barium and intracellular caesium, is unaffected by the chloride gradient, and its reversal potential shifts with the extracellular concentration of potassium as predicted for a response mediated by a selective increase in potassium permeability. 5. The depolarizing response and reduction in the a.h.p. could be studied in isolation by blocking the hyperpolarizing response with either pertussis toxin or spiperone. The pharmacology of these responses did not correspond to that of any of the 5-HT binding sites reported in C.N.S. tissue. Although the depolarization and blockade of the a.h.p. have the same time course it is unclear if they are mediated by the same or different receptors. 6. The depolarization most likely results from a decrease in resting potassium conductance. However, neither a blockade of the M current nor the a.h.p. current can account for the depolarization. 7. Blockade of phosphodiesterase activity by 3-isobutyl-1-methylxanthine (IBMX) did not enhance the depressant action of 5-HT on the a.h.p., making it unlikely that this action is mediated by cyclic AMP. 8. Blockade of the a.h.p. by 5-HT reduces spike frequency adaptation and counteracts the inhibitory action of 5-HT on 5-HT1A receptors. This excitatory action outlasts the hyperpolarizing action. 9. In summary 5-HT acts on at least two distinct receptors on hippocampal pyramidal cells, one coupled to the opening of potassium channels and a second coupled to a decrease in a resting potassium conductance and a decrease in the a.h.p.
Full text
PDF














Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Andrade R., Malenka R. C., Nicoll R. A. A G protein couples serotonin and GABAB receptors to the same channels in hippocampus. Science. 1986 Dec 5;234(4781):1261–1265. doi: 10.1126/science.2430334. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Baraban J. M., Snyder S. H., Alger B. E. Protein kinase C regulates ionic conductance in hippocampal pyramidal neurons: electrophysiological effects of phorbol esters. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1985 Apr;82(8):2538–2542. doi: 10.1073/pnas.82.8.2538. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Barbaccia M. L., Brunello N., Chuang D. M., Costa E. Serotonin-elicited amplification of adenylate cyclase activity in hippocampal membranes from adult rat. J Neurochem. 1983 Jun;40(6):1671–1679. doi: 10.1111/j.1471-4159.1983.tb08141.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Beck S. G., Clarke W. P., Goldfarb J. Spiperone differentiates multiple 5-hydroxytryptamine responses in rat hippocampal slices in vitro. Eur J Pharmacol. 1985 Oct 8;116(1-2):195–197. doi: 10.1016/0014-2999(85)90206-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bloom F. E., Hoffer B. J., Siggins G. R., Barker J. L., Nicoll R. A. Effects of serotonin on central neurons: microiontophoretic administration. Fed Proc. 1972 Jan-Feb;31(1):97–106. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Boakes R. J., Bradley P. B., Briggs I., Dray A. Antagonism of 5-hydroxytryptamine by LSD 25 in the central nervous system: a possible neuronal basis for the actions of LSD 25. Br J Pharmacol. 1970 Oct;40(2):202–218. doi: 10.1111/j.1476-5381.1970.tb09914.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cole A. E., Nicoll R. A. Characterization of a slow cholinergic post-synaptic potential recorded in vitro from rat hippocampal pyramidal cells. J Physiol. 1984 Jul;352:173–188. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1984.sp015285. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Colino A., Halliwell J. V. 8-OH-DPAT is a strong antagonist of 5-HT action in rat hippocampus. Eur J Pharmacol. 1986 Oct 14;130(1-2):151–152. doi: 10.1016/0014-2999(86)90196-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Conn P. J., Sanders-Bush E. Serotonin-stimulated phosphoinositide turnover: mediation by the S2 binding site in rat cerebral cortex but not in subcortical regions. J Pharmacol Exp Ther. 1985 Jul;234(1):195–203. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Devivo M., Maayani S. Inhibition of forskolin-stimulated adenylate cyclase activity by 5-HT receptor agonists. Eur J Pharmacol. 1985 Dec 17;119(3):231–234. doi: 10.1016/0014-2999(85)90300-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Drummond A. H., Benson J. A., Levitan I. B. Serotonin-induced hyperpolarization of an indentified Aplysia neuron is mediated by cyclic AMP. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1980 Aug;77(8):5013–5017. doi: 10.1073/pnas.77.8.5013. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dunlap K., Fischbach G. D. Neurotransmitters decrease the calcium ocmponent of sensory neurone action potentials. Nature. 1978 Dec 21;276(5690):837–839. doi: 10.1038/276837a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Engel G., Göthert M., Hoyer D., Schlicker E., Hillenbrand K. Identity of inhibitory presynaptic 5-hydroxytryptamine (5-HT) autoreceptors in the rat brain cortex with 5-HT1B binding sites. Naunyn Schmiedebergs Arch Pharmacol. 1986 Jan;332(1):1–7. doi: 10.1007/BF00633189. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gershon M. D., Takaki M., Tamir H., Branchek T. The enteric neural receptor for 5-hydroxytryptamine. Experientia. 1985 Jul 15;41(7):863–868. doi: 10.1007/BF01970002. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gozlan H., El Mestikawy S., Pichat L., Glowinski J., Hamon M. Identification of presynaptic serotonin autoreceptors using a new ligand: 3H-PAT. Nature. 1983 Sep 8;305(5930):140–142. doi: 10.1038/305140a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Haas H. L., Greene R. W. Effects of histamine on hippocampal pyramidal cells of the rat in vitro. Exp Brain Res. 1986;62(1):123–130. doi: 10.1007/BF00237408. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hall M. D., el Mestikawy S., Emerit M. B., Pichat L., Hamon M., Gozlan H. [3H]8-hydroxy-2-(di-n-propylamino)tetralin binding to pre- and postsynaptic 5-hydroxytryptamine sites in various regions of the rat brain. J Neurochem. 1985 Jun;44(6):1685–1696. doi: 10.1111/j.1471-4159.1985.tb07155.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Holz G. G., 4th, Shefner S. A., Anderson E. G. Serotonin decreases the duration of action potentials recorded from tetraethylammonium-treated bullfrog dorsal root ganglion cells. J Neurosci. 1986 Mar;6(3):620–626. doi: 10.1523/JNEUROSCI.06-03-00620.1986. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Horn A. S., Coyle J. T., Snyder S. H. Catecholamine uptake by synaptosomes from rat brain. Structure-activity relationships of drugs with differential effects on dopamine and norepinephrine neurons. Mol Pharmacol. 1971 Jan;7(1):66–80. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hoyer D., Engel G., Kalkman H. O. Molecular pharmacology of 5-HT1 and 5-HT2 recognition sites in rat and pig brain membranes: radioligand binding studies with [3H]5-HT, [3H]8-OH-DPAT, (-)[125I]iodocyanopindolol, [3H]mesulergine and [3H]ketanserin. Eur J Pharmacol. 1985 Nov 26;118(1-2):13–23. doi: 10.1016/0014-2999(85)90658-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jahnsen H. The action of 5-hydroxytryptamine on neuronal membranes and synaptic transmission in area CA1 of the hippocampus in vitro. Brain Res. 1980 Sep 15;197(1):83–94. doi: 10.1016/0006-8993(80)90436-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Janowsky A., Labarca R., Paul S. M. Characterization of neurotransmitter receptor-mediated phosphatidylinositol hydrolysis in the rat hippocampus. Life Sci. 1984 Nov 5;35(19):1953–1961. doi: 10.1016/0024-3205(84)90476-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Joëls M., Twery M. J., Shinnick-Gallagher P., Gallagher J. P. Multiple actions of serotonin on lateral septal neurons in rat brain. Eur J Pharmacol. 1986 Sep 23;129(1-2):203–204. doi: 10.1016/0014-2999(86)90357-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Madison D. V., Lancaster B., Nicoll R. A. Voltage clamp analysis of cholinergic action in the hippocampus. J Neurosci. 1987 Mar;7(3):733–741. doi: 10.1523/JNEUROSCI.07-03-00733.1987. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Madison D. V., Nicoll R. A. Actions of noradrenaline recorded intracellularly in rat hippocampal CA1 pyramidal neurones, in vitro. J Physiol. 1986 Mar;372:221–244. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1986.sp016006. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Madison D. V., Nicoll R. A. Control of the repetitive discharge of rat CA 1 pyramidal neurones in vitro. J Physiol. 1984 Sep;354:319–331. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1984.sp015378. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Madison D. V., Nicoll R. A. Cyclic adenosine 3',5'-monophosphate mediates beta-receptor actions of noradrenaline in rat hippocampal pyramidal cells. J Physiol. 1986 Mar;372:245–259. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1986.sp016007. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Malenka R. C., Madison D. V., Andrade R., Nicoll R. A. Phorbol esters mimic some cholinergic actions in hippocampal pyramidal neurons. J Neurosci. 1986 Feb;6(2):475–480. doi: 10.1523/JNEUROSCI.06-02-00475.1986. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Markstein R., Hoyer D., Engel G. 5-HT1A-receptors mediate stimulation of adenylate cyclase in rat hippocampus. Naunyn Schmiedebergs Arch Pharmacol. 1986 Aug;333(4):335–341. doi: 10.1007/BF00500006. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Martin L. L., Sanders-Bush E. Comparison of the pharmacological characteristics of 5 HT1 and 5 HT2 binding sites with those of serotonin autoreceptors which modulate serotonin release. Naunyn Schmiedebergs Arch Pharmacol. 1982 Dec;321(3):165–170. doi: 10.1007/BF00505480. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nicoll R. A., Alger B. E. A simple chamber for recording from submerged brain slices. J Neurosci Methods. 1981 Aug;4(2):153–156. doi: 10.1016/0165-0270(81)90049-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Paupardin-Tritsch D., Hammond C., Gerschenfeld H. M. Serotonin and cyclic GMP both induce an increase of the calcium current in the same identified molluscan neurons. J Neurosci. 1986 Sep;6(9):2715–2723. doi: 10.1523/JNEUROSCI.06-09-02715.1986. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pazos A., Palacios J. M. Quantitative autoradiographic mapping of serotonin receptors in the rat brain. I. Serotonin-1 receptors. Brain Res. 1985 Nov 4;346(2):205–230. doi: 10.1016/0006-8993(85)90856-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Peroutka S. J., Lebovitz R. M., Snyder S. H. Two distinct central serotonin receptors with different physiological functions. Science. 1981 May 15;212(4496):827–829. doi: 10.1126/science.7221567. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Peroutka S. J. Pharmacological differentiation and characterization of 5-HT1A, 5-HT1B, and 5-HT1C binding sites in rat frontal cortex. J Neurochem. 1986 Aug;47(2):529–540. doi: 10.1111/j.1471-4159.1986.tb04532.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Richardson B. P., Engel G., Donatsch P., Stadler P. A. Identification of serotonin M-receptor subtypes and their specific blockade by a new class of drugs. Nature. 1985 Jul 11;316(6024):126–131. doi: 10.1038/316126a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Roberts M. H., Straughan D. W. Excitation and depression of cortical neurones by 5-hydroxytryptamine. J Physiol. 1967 Nov;193(2):269–294. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1967.sp008357. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Segal M. The action of serotonin in the rat hippocampal slice preparation. J Physiol. 1980 Jun;303:423–439. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1980.sp013297. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shaskan E. G., Snyder S. H. Kinetics of serotonin accumulation into slices from rat brain: relationship to catecholamine uptake. J Pharmacol Exp Ther. 1970 Nov;175(2):404–418. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Siegelbaum S. A., Camardo J. S., Kandel E. R. Serotonin and cyclic AMP close single K+ channels in Aplysia sensory neurones. Nature. 1982 Sep 30;299(5882):413–417. doi: 10.1038/299413a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sills M. A., Wolfe B. B., Frazer A. Determination of selective and nonselective compounds for the 5-HT 1A and 5-HT 1B receptor subtypes in rat frontal cortex. J Pharmacol Exp Ther. 1984 Dec;231(3):480–487. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sprouse J. S., Aghajanian G. K. Electrophysiological responses of serotoninergic dorsal raphe neurons to 5-HT1A and 5-HT1B agonists. Synapse. 1987;1(1):3–9. doi: 10.1002/syn.890010103. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Van Dongen P. A., Grillner S., Hökfelt T. 5-Hydroxytryptamine (serotonin) causes a reduction in the afterhyperpolarization following the action potential in lamprey motoneurons and premotor interneurons. Brain Res. 1986 Feb 26;366(1-2):320–325. doi: 10.1016/0006-8993(86)91310-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- VanderMaelen C. P., Aghajanian G. K. Intracellular studies showing modulation of facial motoneurone excitability by serotonin. Nature. 1980 Sep 25;287(5780):346–347. doi: 10.1038/287346a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Vandermaelen C. P., Aghajanian G. K. Serotonin-induced depolarization of rat facial motoneurons in vivo: comparison with amino acid transmitters. Brain Res. 1982 May 6;239(1):139–152. doi: 10.1016/0006-8993(82)90838-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wong D. T., Bymaster F. P., Horng J. S., Molloy B. B. A new selective inhibitor for uptake of serotonin into synaptosomes of rat brain: 3-(p-trifluoromethylphenoxy). N-methyl-3-phenylpropylamine. J Pharmacol Exp Ther. 1975 Jun;193(3):804–811. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wood J. D., Mayer C. J. Serotonergic activation of tonic-type enteric neurons in guinea pig small bowel. J Neurophysiol. 1979 Mar;42(2):582–593. doi: 10.1152/jn.1979.42.2.582. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]





