Abstract
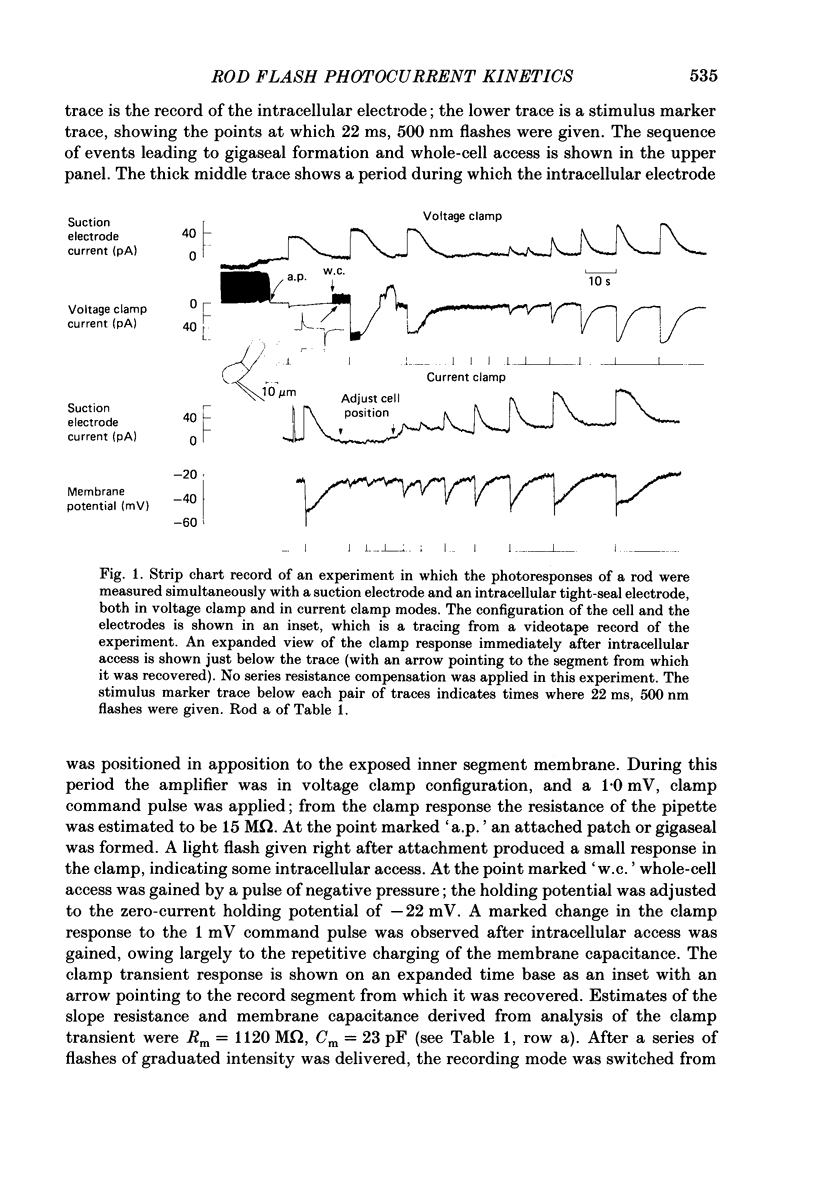
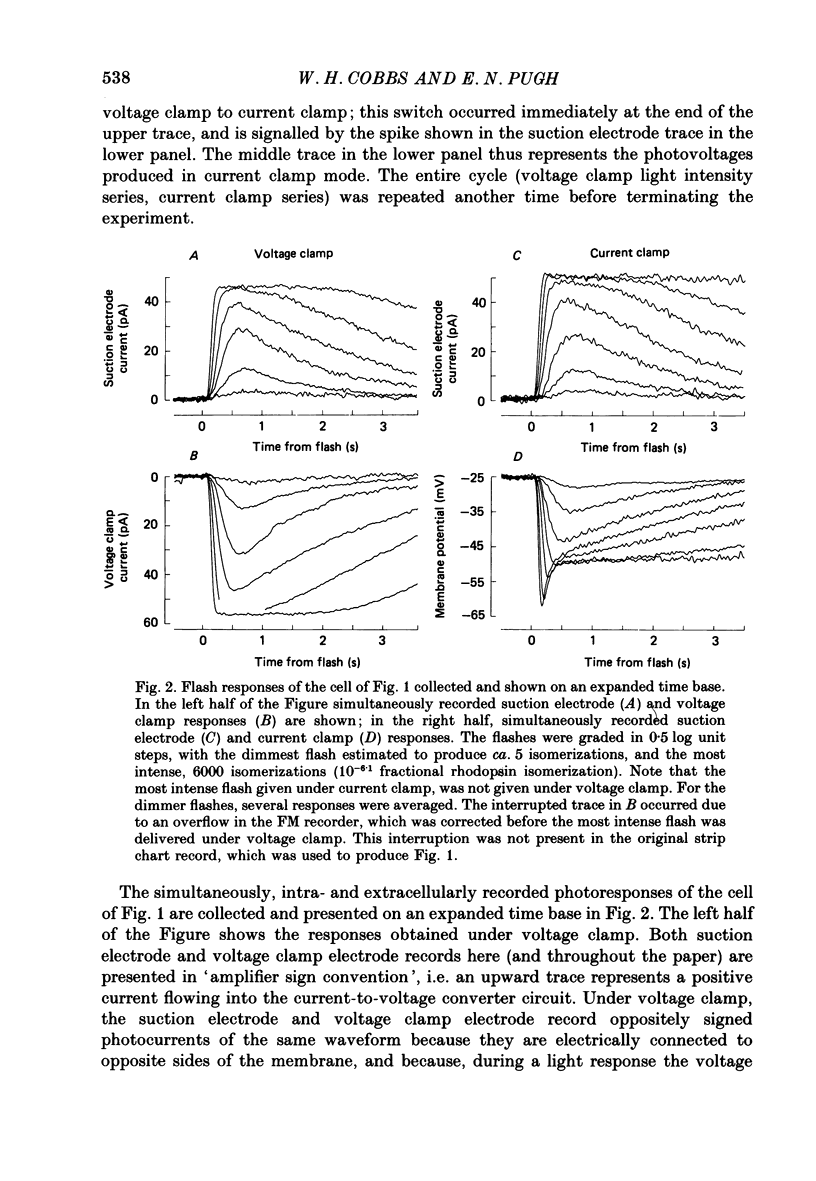
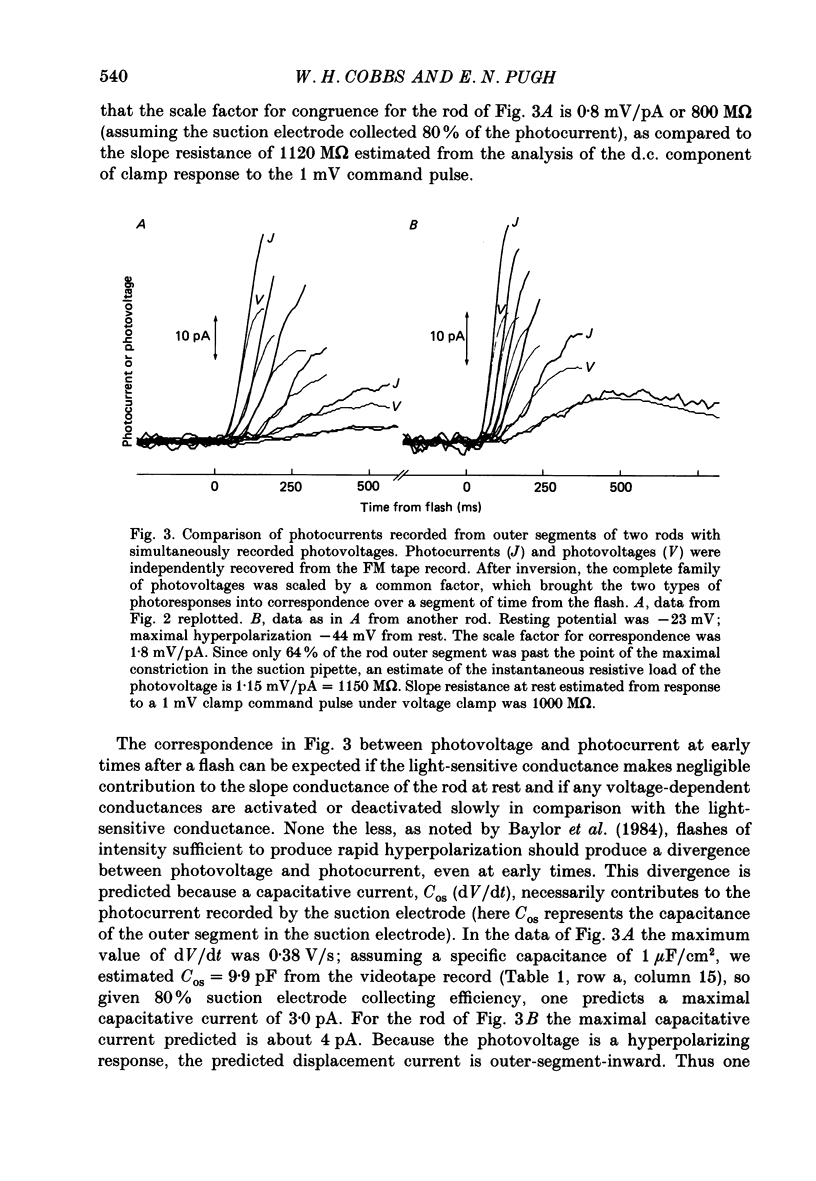
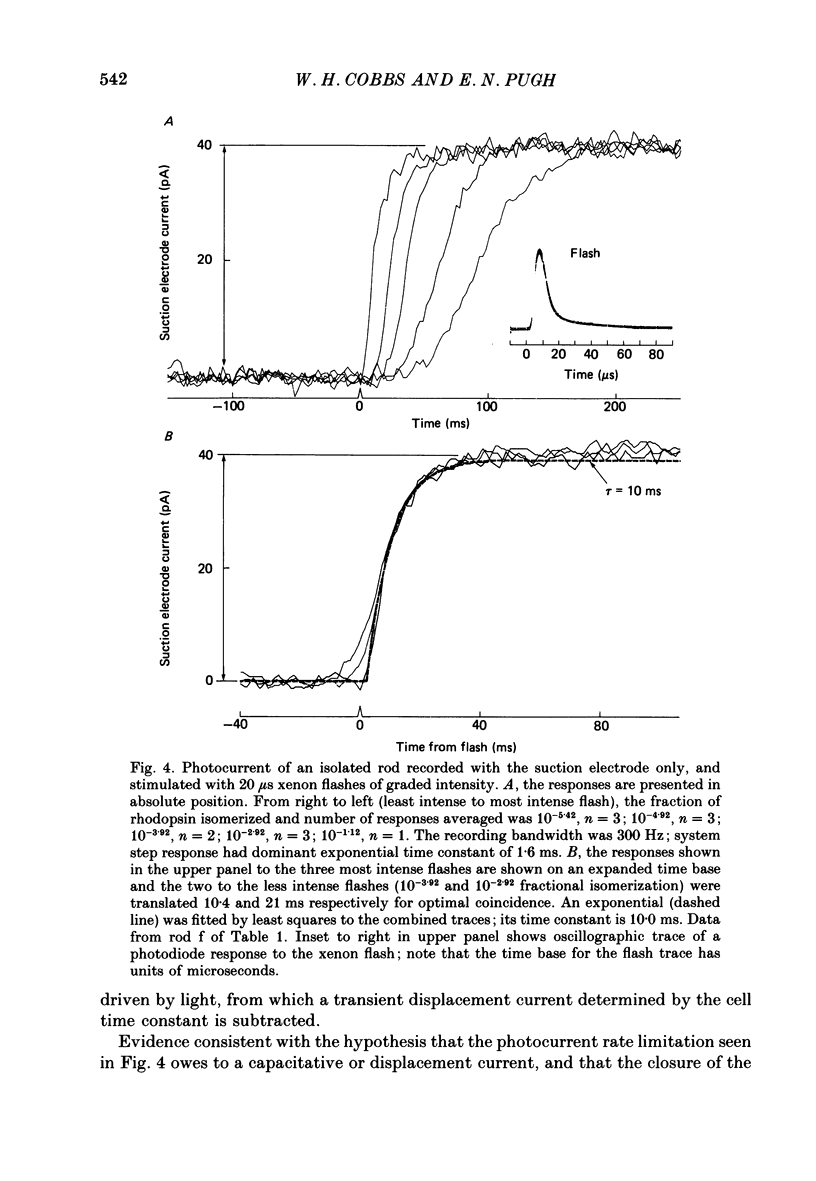
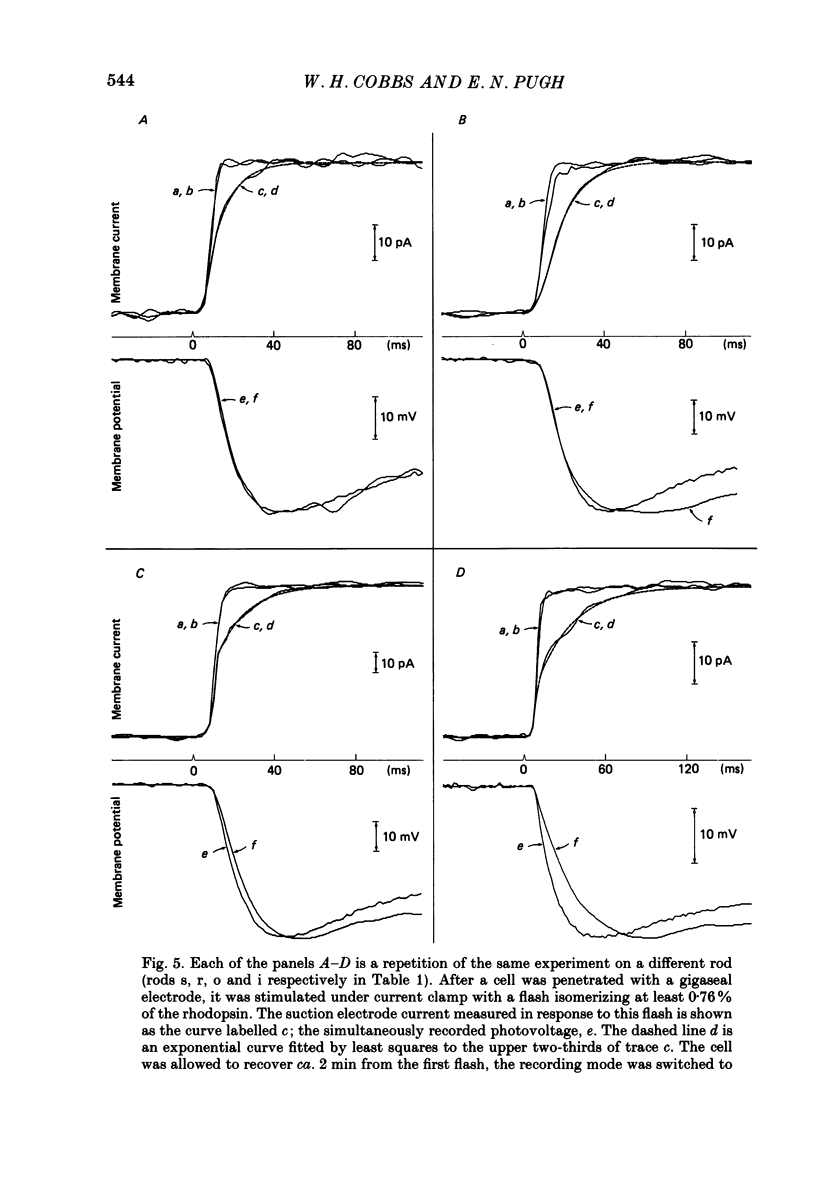
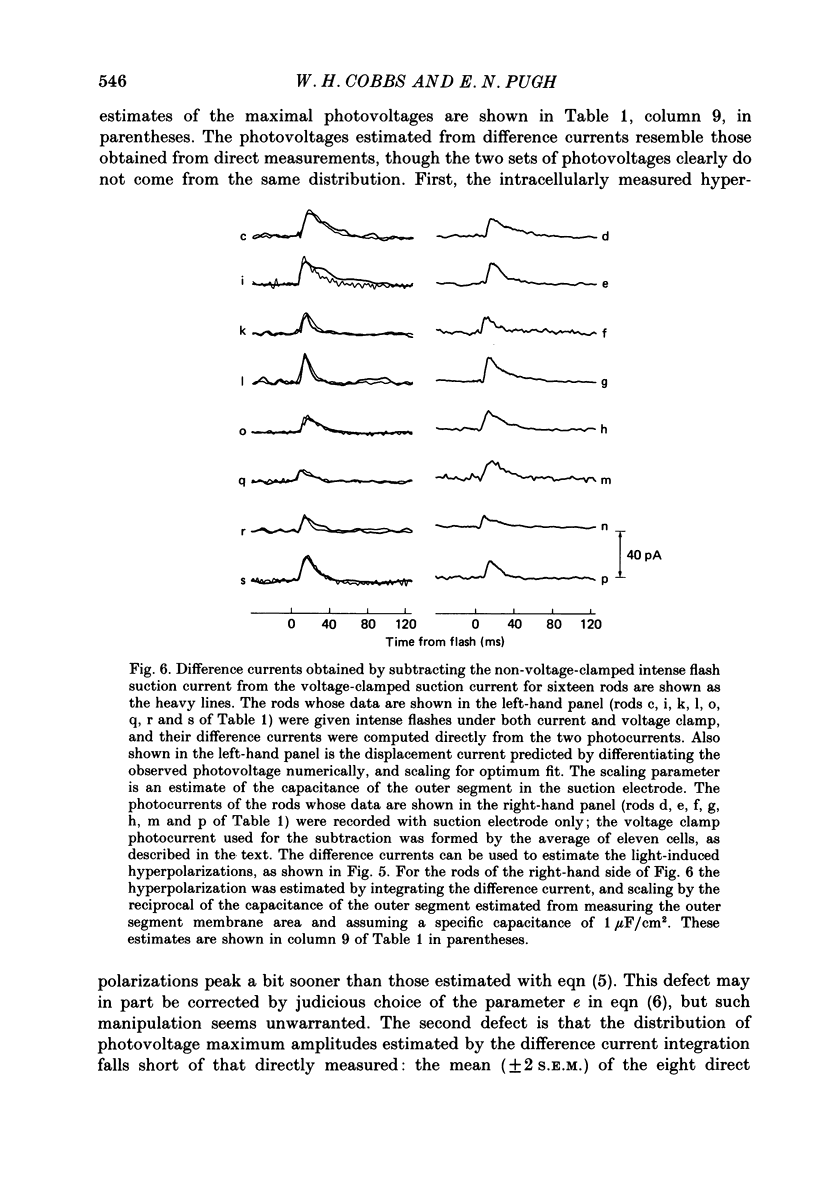
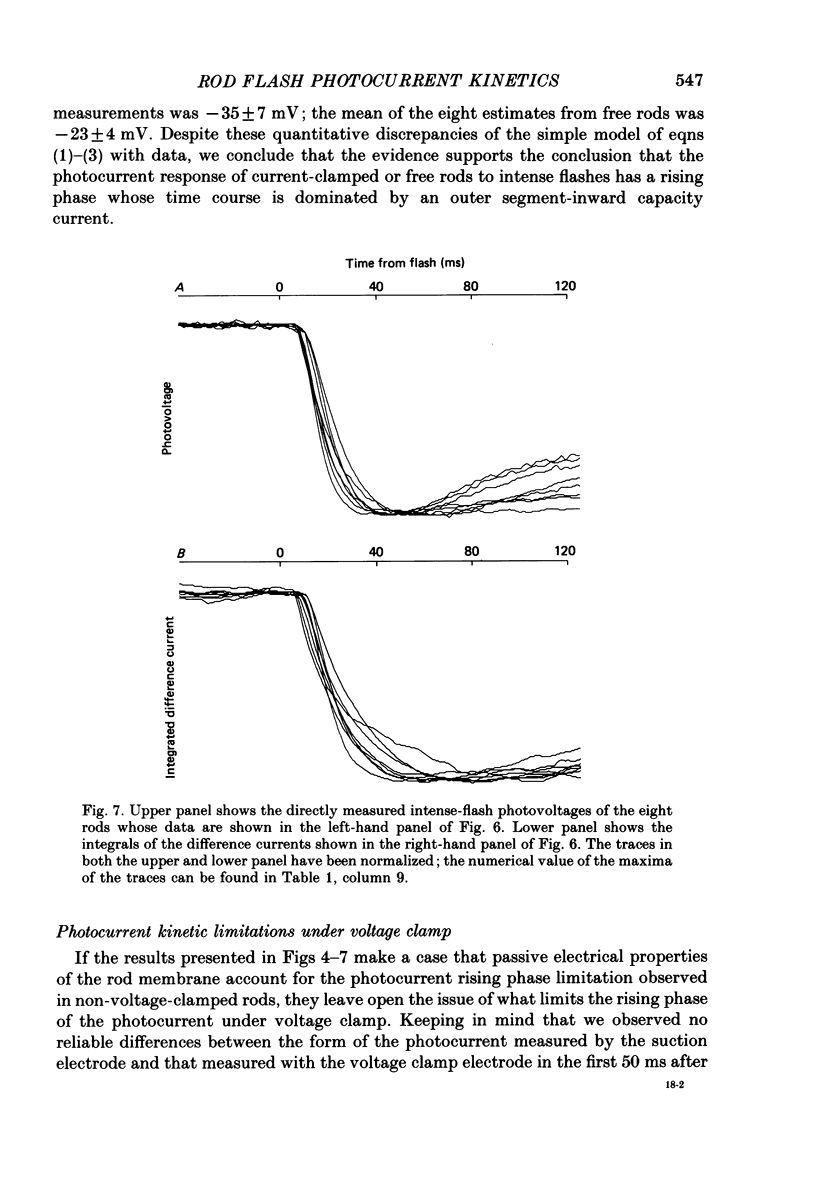
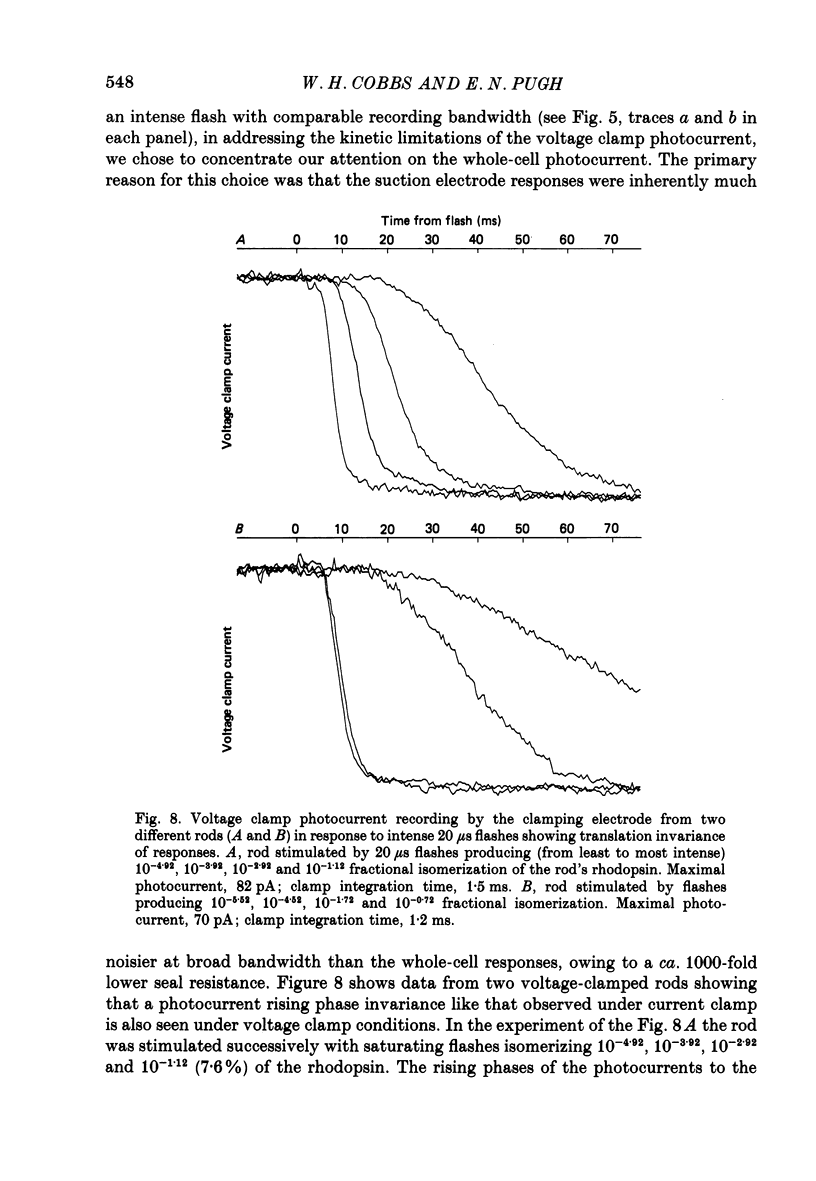
1. Membrane currents initiated by intense, 20 microseconds flashes (photocurrents) were recorded from isolated salamander rods by combined extracellular suction electrodes and intracellular tight-seal electrodes either in current or voltage clamp mode. The magnitudes (mean +/- 2 S.E.M.) of the maximal photoresponses recorded by the suction and by the intracellular electrode respectively were 40 +/- 5 pA (n = 18) and 35 +/- 7 mV (n = 8) for current clamp at zero current; 43 +/- 9 pA and 66 +/- 13 (n = 11) pA for voltage clamp at the zero-current holding potential, -24 +/- 3 mV. 2. Photocurrents initiated by flashes isomerizing 0.1% or more of the outer segment's rhodopsin achieved a saturated velocity and were 95% complete in less than 50 ms. The effect of incrementing flash intensity above 0.1% isomerization can be described as a translation of the photocurrent along the time axis towards the origin. Within the interval 0-50 ms the latter two-thirds of the velocity-saturated photocurrent is well described as a single-exponential decay. The decay was much faster in voltage clamp (2.8 +/- 1.2 ms, n = 11) than in current clamp mode (17 +/- 5 ms, n = 17). 3. The initial third of the velocity-saturated photocurrent, occurring over the interval from the flash to the onset of exponential decay, followed about the same time course in current and voltage clamp. The time interval occupied by this initial 'latent' phase decreased with increasing flash intensity and attained an apparent minimum of about 7 ms in response to flashes isomerizing 10% or more of the rhodopsin at ca. 22 degrees C. 4. The hypothesis that the decay of outer segment light-sensitive membrane current is the same in current and voltage clamp was supported by an analysis of the difference between outer segment currents measured successively in the two recording modes. First, the tail of the difference current decayed exponentially with a time constant approximately equal to R x C, where R and C are independently estimated slope resistance and capacitance of the rod. Secondly, the integral of the difference current, when divided by outer segment capacitance, closely approximated the hyperpolarizing light response measured under current clamp. Thus, displacement current accounted for the difference between photocurrents measured in current and voltage clamp.(ABSTRACT TRUNCATED AT 400 WORDS)
Full text
PDF



























Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Bader C. R., Bertrand D., Schwartz E. A. Voltage-activated and calcium-activated currents studied in solitary rod inner segments from the salamander retina. J Physiol. 1982 Oct;331:253–284. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1982.sp014372. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bader C. R., Macleish P. R., Schwartz E. A. A voltage-clamp study of the light response in solitary rods of the tiger salamander. J Physiol. 1979 Nov;296:1–26. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1979.sp012988. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Baehr W., Devlin M. J., Applebury M. L. Isolation and characterization of cGMP phosphodiesterase from bovine rod outer segments. J Biol Chem. 1979 Nov 25;254(22):11669–11677. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Baumann C. The equilibrium between metarhodopsin I and metarhodopsin II in the isolated frog retina. J Physiol. 1978 Jun;279:71–80. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1978.sp012331. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Baylor D. A., Hodgkin A. L., Lamb T. D. The electrical response of turtle cones to flashes and steps of light. J Physiol. 1974 Nov;242(3):685–727. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1974.sp010731. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Baylor D. A., Lamb T. D. Local effects of bleaching in retinal rods of the toad. J Physiol. 1982 Jul;328:49–71. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1982.sp014252. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Baylor D. A., Lamb T. D., Yau K. W. Responses of retinal rods to single photons. J Physiol. 1979 Mar;288:613–634. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Baylor D. A., Lamb T. D., Yau K. W. The membrane current of single rod outer segments. J Physiol. 1979 Mar;288:589–611. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Baylor D. A., Matthews G., Nunn B. J. Location and function of voltage-sensitive conductances in retinal rods of the salamander, Ambystoma tigrinum. J Physiol. 1984 Sep;354:203–223. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1984.sp015372. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Baylor D. A., Nunn B. J. Electrical properties of the light-sensitive conductance of rods of the salamander Ambystoma tigrinum. J Physiol. 1986 Feb;371:115–145. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1986.sp015964. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bennett N., Michel-Villaz M., Kühn H. Light-induced interaction between rhodopsin and the GTP-binding protein. Metarhodopsin II is the major photoproduct involved. Eur J Biochem. 1982 Sep;127(1):97–103. doi: 10.1111/j.1432-1033.1982.tb06842.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bodoia R. D., Detwiler P. B. Patch-clamp recordings of the light-sensitive dark noise in retinal rods from the lizard and frog. J Physiol. 1985 Oct;367:183–216. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1985.sp015820. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cobbs W. H., Pugh E. N., Jr Cyclic GMP can increase rod outer-segment light-sensitive current 10-fold without delay of excitation. Nature. 1985 Feb 14;313(6003):585–587. doi: 10.1038/313585a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fesenko E. E., Kolesnikov S. S., Lyubarsky A. L. Induction by cyclic GMP of cationic conductance in plasma membrane of retinal rod outer segment. Nature. 1985 Jan 24;313(6000):310–313. doi: 10.1038/313310a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fung B. K., Hurley J. B., Stryer L. Flow of information in the light-triggered cyclic nucleotide cascade of vision. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1981 Jan;78(1):152–156. doi: 10.1073/pnas.78.1.152. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gray P., Attwell D. Kinetics of light-sensitive channels in vertebrate photoreceptors. Proc R Soc Lond B Biol Sci. 1985 Jan 22;223(1232):379–388. doi: 10.1098/rspb.1985.0007. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Haynes L. W., Kay A. R., Yau K. W. Single cyclic GMP-activated channel activity in excised patches of rod outer segment membrane. Nature. 1986 May 1;321(6065):66–70. doi: 10.1038/321066a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kwok-Keung Fung B., Stryer L. Photolyzed rhodopsin catalyzes the exchange of GTP for bound GDP in retinal rod outer segments. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1980 May;77(5):2500–2504. doi: 10.1073/pnas.77.5.2500. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- LIEBMAN P. A. In situ microspectrophotometric studies on the pigments of single retinal rods. Biophys J. 1962 Mar;2:161–178. doi: 10.1016/s0006-3495(62)86847-7. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lamb T. D., McNaughton P. A., Yau K. W. Spatial spread of activation and background desensitization in toad rod outer segments. J Physiol. 1981;319:463–496. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1981.sp013921. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Liebman P. A., Entine G. Lateral diffusion of visual pigment in photorecptor disk membranes. Science. 1974 Aug 2;185(4149):457–459. doi: 10.1126/science.185.4149.457. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Liebman P. A., Evanczuk A. T. Real time assay of rod disk membrane cGMP phosphodiesterase and its controller enzymes. Methods Enzymol. 1982;81:532–542. doi: 10.1016/s0076-6879(82)81074-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Liebman P. A., Pugh E. N., Jr Gain, speed and sensitivity of GTP binding vs PDE activation in visual excitation. Vision Res. 1982;22(12):1475–1480. doi: 10.1016/0042-6989(82)90212-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Matthews G. Single-channel recordings demonstrate that cGMP opens the light-sensitive ion channel of the rod photoreceptor. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1987 Jan;84(1):299–302. doi: 10.1073/pnas.84.1.299. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Penn R. D., Hagins W. A. Kinetics of the photocurrent of retinal rods. Biophys J. 1972 Aug;12(8):1073–1094. doi: 10.1016/S0006-3495(72)86145-9. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Poo M., Cone R. A. Lateral diffusion of rhodopsin in the photoreceptor membrane. Nature. 1974 Feb 15;247(5441):438–441. doi: 10.1038/247438a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pugh E. N., Jr, Cobbs W. H. Visual transduction in vertebrate rods and cones: a tale of two transmitters, calcium and cyclic GMP. Vision Res. 1986;26(10):1613–1643. doi: 10.1016/0042-6989(86)90051-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rae J. L., Levis R. A. Patch Clamp Recordings from the Epithelium of the Lens Obtained using Glasses Selected for Low Noise and Improved Sealing Properties. Biophys J. 1984 Jan;45(1):144–146. doi: 10.1016/S0006-3495(84)84142-9. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stryer L. Cyclic GMP cascade of vision. Annu Rev Neurosci. 1986;9:87–119. doi: 10.1146/annurev.ne.09.030186.000511. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Vuong T. M., Chabre M., Stryer L. Millisecond activation of transducin in the cyclic nucleotide cascade of vision. Nature. 1984 Oct 18;311(5987):659–661. doi: 10.1038/311659a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yau K. W., Nakatani K. Electrogenic Na-Ca exchange in retinal rod outer segment. Nature. 1984 Oct 18;311(5987):661–663. doi: 10.1038/311661a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yau K. W., Nakatani K. Light-induced reduction of cytoplasmic free calcium in retinal rod outer segment. Nature. 1985 Feb 14;313(6003):579–582. doi: 10.1038/313579a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yau K. W., Nakatani K. Light-suppressible, cyclic GMP-sensitive conductance in the plasma membrane of a truncated rod outer segment. Nature. 1985 Sep 19;317(6034):252–255. doi: 10.1038/317252a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zimmerman A. L., Baylor D. A. Cyclic GMP-sensitive conductance of retinal rods consists of aqueous pores. Nature. 1986 May 1;321(6065):70–72. doi: 10.1038/321070a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zimmerman A. L., Yamanaka G., Eckstein F., Baylor D. A., Stryer L. Interaction of hydrolysis-resistant analogs of cyclic GMP with the phosphodiesterase and light-sensitive channel of retinal rod outer segments. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1985 Dec;82(24):8813–8817. doi: 10.1073/pnas.82.24.8813. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


