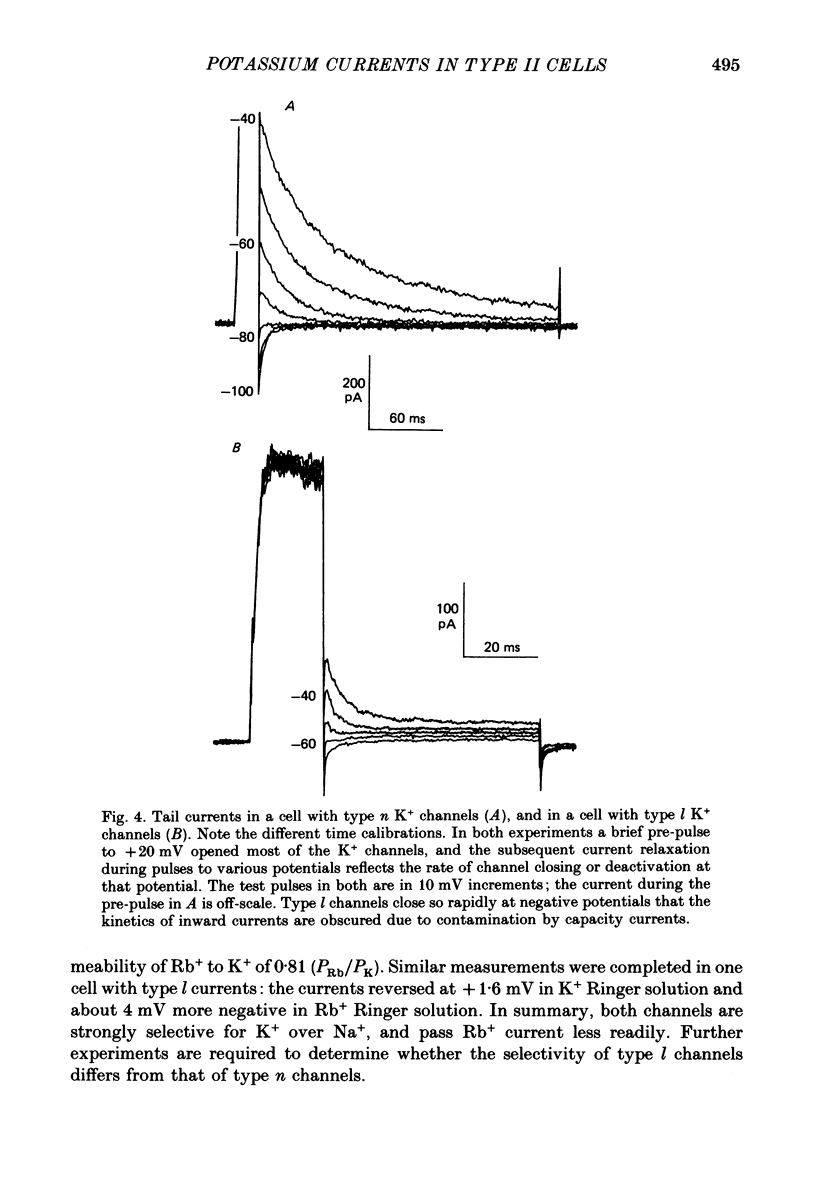
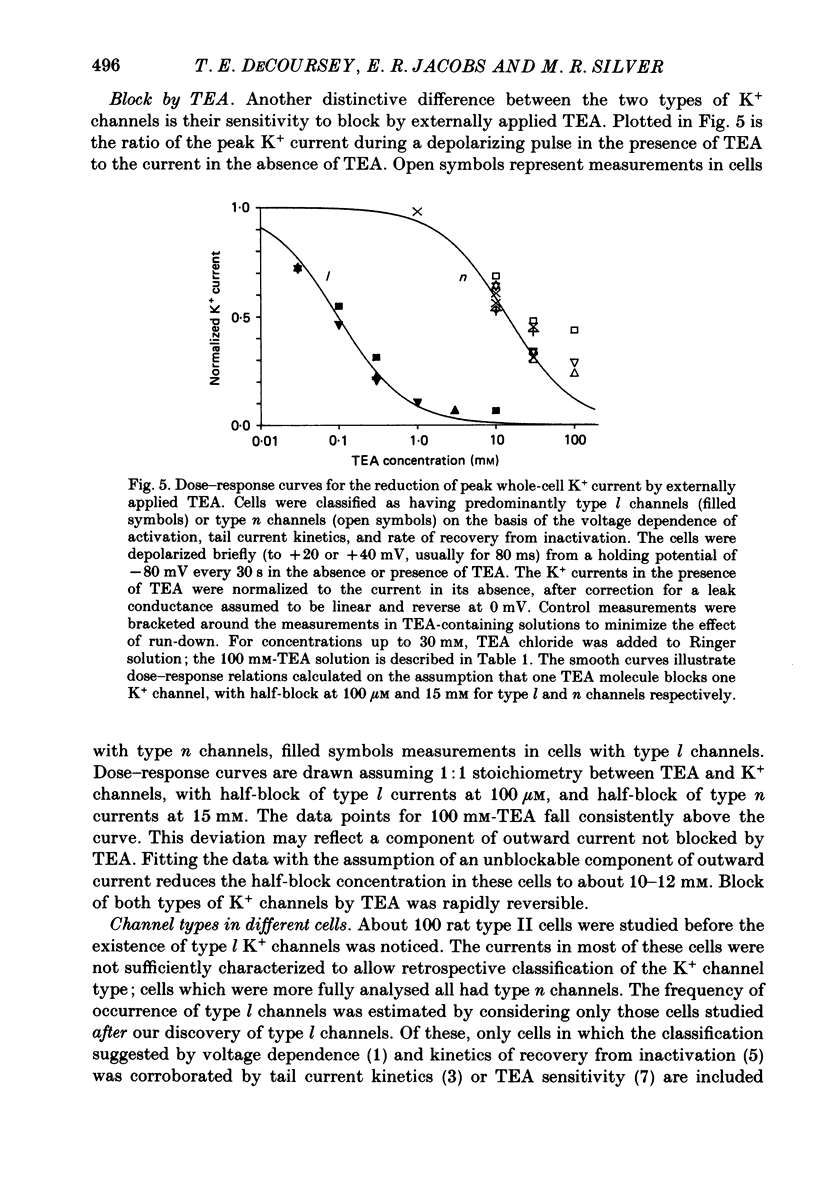
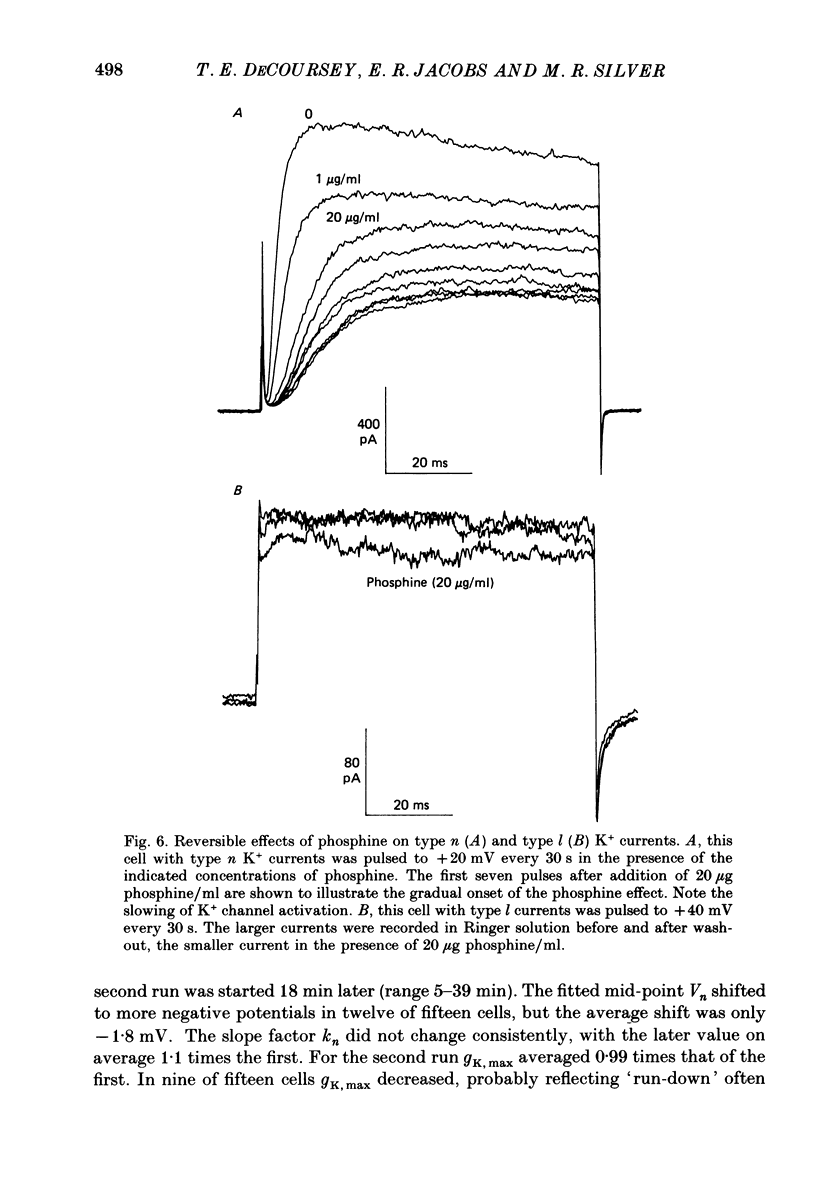
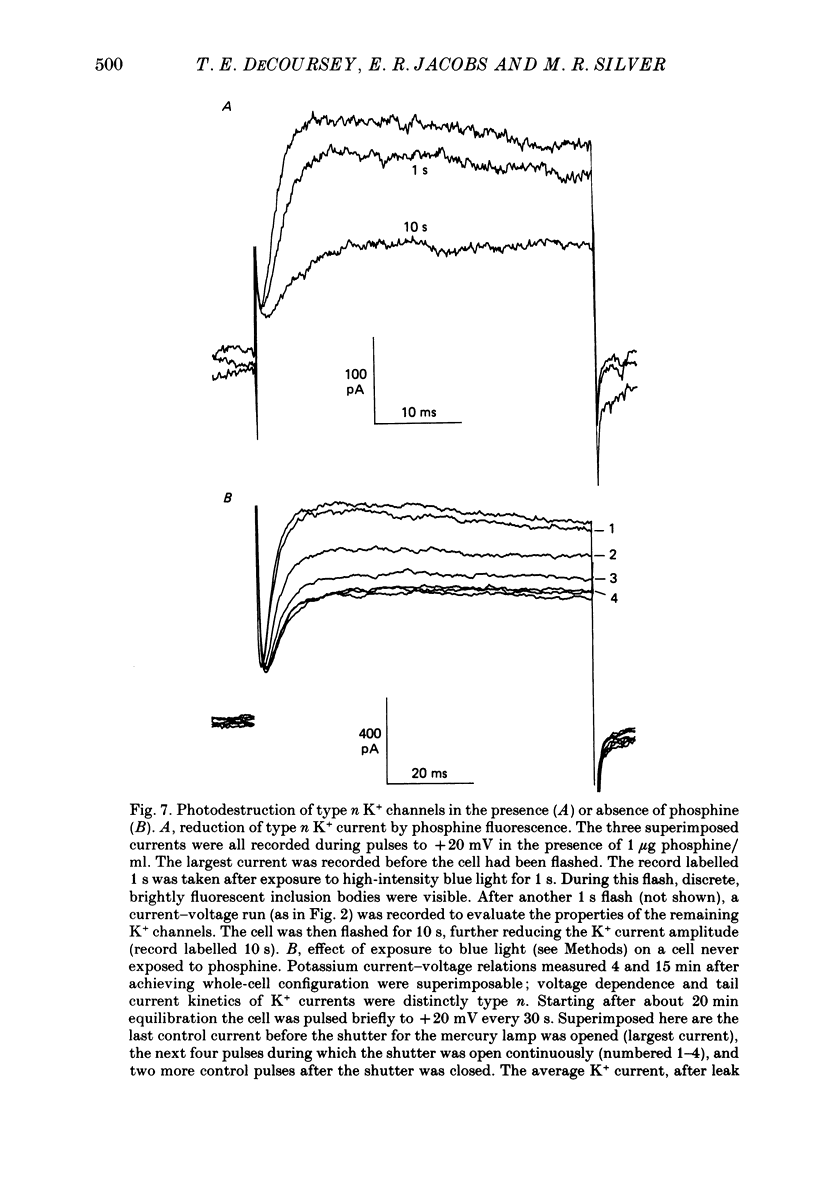
Abstract
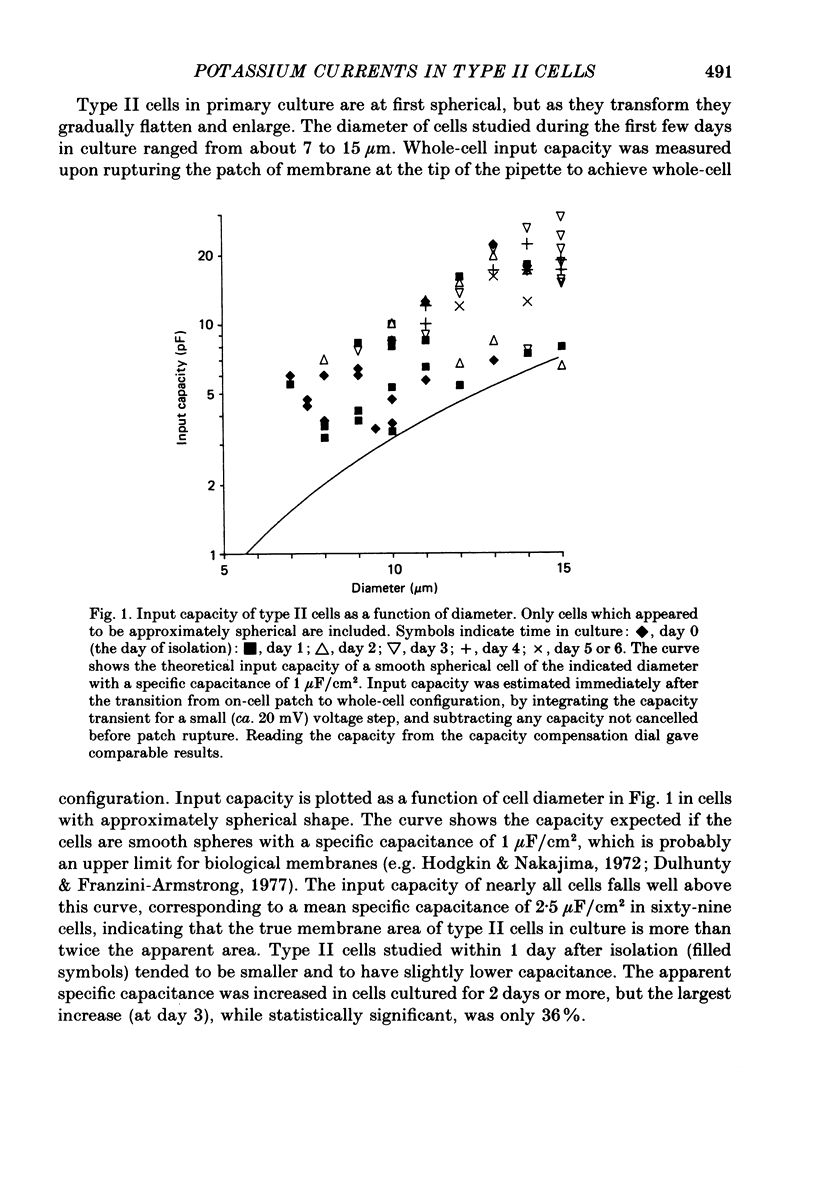
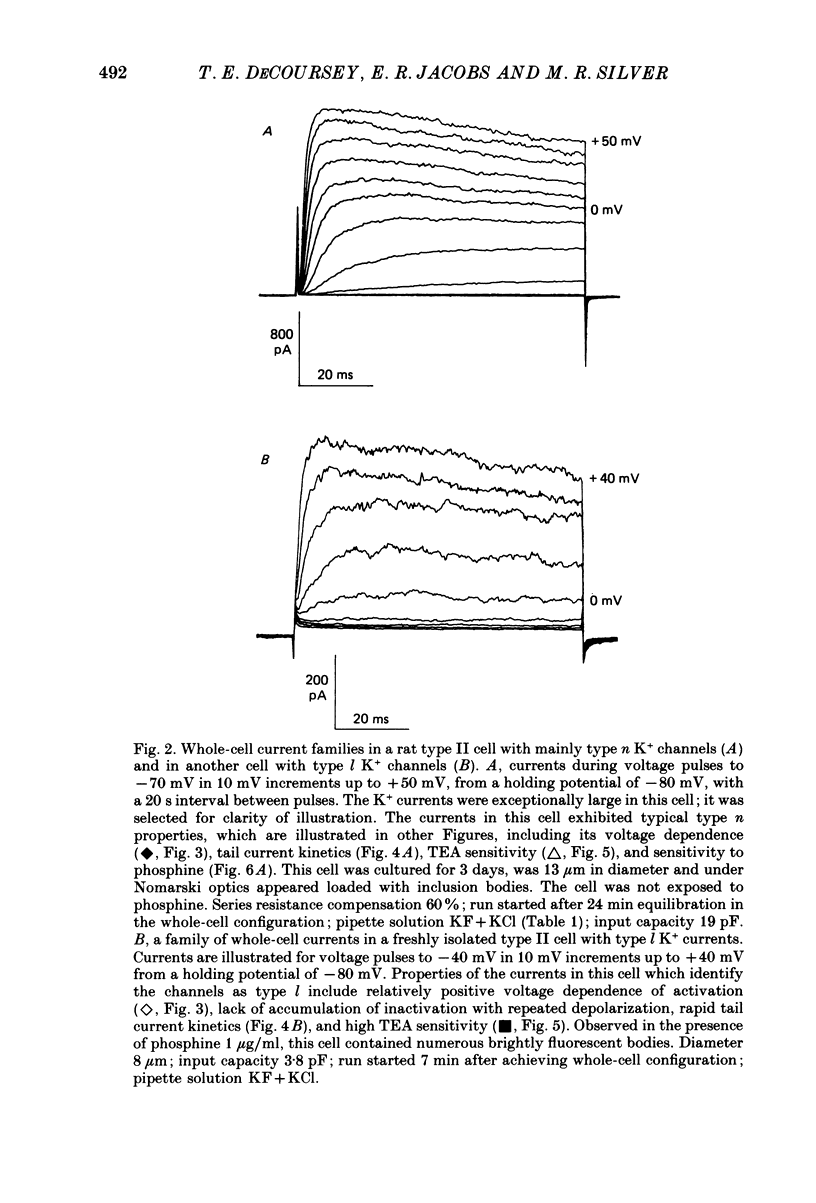
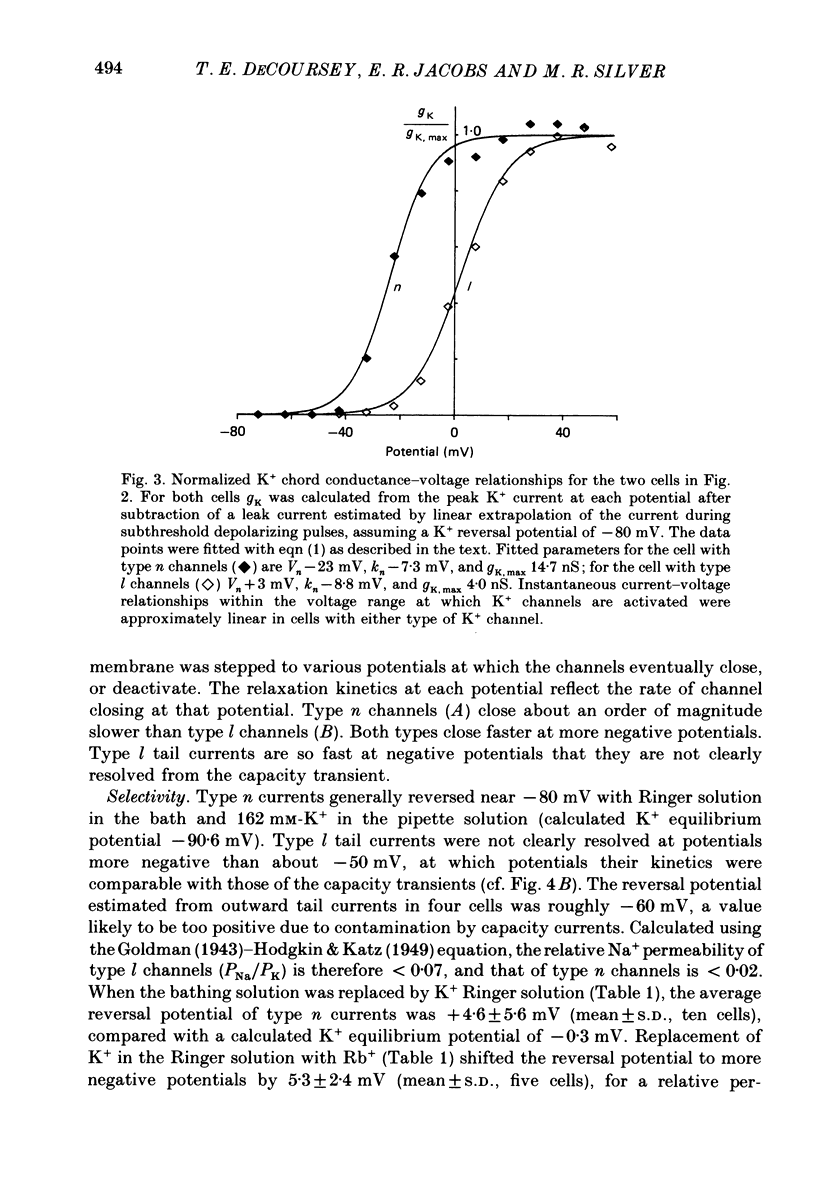
1. Type II alveolar epithelial cells isolated from adult rats and grown in primary culture were studied using the whole-cell configuration of the gigohm-seal voltage clamp technique. 2. The average specific capacitance of type II cells was 2.5 microF/cm2, suggesting that type II cell membranes in vitro are irregular, with an actual area more than twice the apparent area. 3. Most type II cells have time- and voltage-dependent outward currents carried by potassium ions. Potassium currents activate with a sigmoid time course upon membrane depolarization, and inactivate during maintained depolarization. The average maximum whole-cell K+ conductance was 1.6 nS. 4. Two distinct types of K+-selective channels underlie outward currents in type II cells. Most cells have currents resembling delayed rectifier K+ currents in skeletal muscle, nerve and immune cells. A few cells had a different type of K+ conductance which is more sensitive to block by tetraethylammonium ions, has faster 'tail currents', and activates at more positive potentials. 5. In some experiments, individual type II cells were identified by staining with phosphine, a fluorescent dye which is concentrated in lamellar bodies. Both types of K+ channels were seen in type II cells identified with this dye. 6. Phosphine added to the bathing solution reversibly reduced K+ currents and shifted K+ channel activation to more positive potentials. Excitation of phosphine to fluoresce reduced irreversibly K+ currents in type II cells. The usefulness of phosphine as a means of identifying cells for study is discussed.
Full text
PDF










Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Adrian R. H., Chandler W. K., Hodgkin A. L. Voltage clamp experiments in striated muscle fibres. J Physiol. 1970 Jul;208(3):607–644. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1970.sp009139. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Aldrich R. W., Jr, Getting P. A., Thompson S. H. Inactivation of delayed outward current in molluscan neurone somata. J Physiol. 1979 Jun;291:507–530. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1979.sp012828. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cahalan M. D., Chandy K. G., DeCoursey T. E., Gupta S. A voltage-gated potassium channel in human T lymphocytes. J Physiol. 1985 Jan;358:197–237. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1985.sp015548. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Castranova V., Jones G. S., Miles P. R. Transmembrane potential of isolated rat alveolar type II cells. J Appl Physiol Respir Environ Exerc Physiol. 1983 Jun;54(6):1511–1517. doi: 10.1152/jappl.1983.54.6.1511. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chander A., Johnson R. G., Reicherter J., Fisher A. B. Lung lamellar bodies maintain an acidic internal pH. J Biol Chem. 1986 May 5;261(13):6126–6131. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chandy K. G., DeCoursey T. E., Fischbach M., Talal N., Cahalan M. D., Gupta S. Altered K+ channel expression in abnormal T lymphocytes from mice with the lpr gene mutation. Science. 1986 Sep 12;233(4769):1197–1200. doi: 10.1126/science.2426784. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Decoursey T. E., Chandy K. G., Gupta S., Cahalan M. D. Mitogen induction of ion channels in murine T lymphocytes. J Gen Physiol. 1987 Mar;89(3):405–420. doi: 10.1085/jgp.89.3.405. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Decoursey T. E., Chandy K. G., Gupta S., Cahalan M. D. Two types of potassium channels in murine T lymphocytes. J Gen Physiol. 1987 Mar;89(3):379–404. doi: 10.1085/jgp.89.3.379. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Diglio C. A., Kikkawa Y. The type II epithelial cells of the lung. IV. Adaption and behavior of isolated type II cells in culture. Lab Invest. 1977 Dec;37(6):622–631. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dulhunty A. F., Franzini-Armstrong C. The passive electrical properties of frog skeletal muscle fibres at different sarcomere lengths. J Physiol. 1977 Apr;266(3):687–711. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1977.sp011788. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fenwick E. M., Marty A., Neher E. Sodium and calcium channels in bovine chromaffin cells. J Physiol. 1982 Oct;331:599–635. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1982.sp014394. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fernandez J. M., Fox A. P., Krasne S. Membrane patches and whole-cell membranes: a comparison of electrical properties in rat clonal pituitary (GH3) cells. J Physiol. 1984 Nov;356:565–585. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1984.sp015483. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fisher A. B., Furia L., Berman H. Metabolism of rat granular pneumocytes isolated in primary culture. J Appl Physiol Respir Environ Exerc Physiol. 1980 Oct;49(4):743–750. doi: 10.1152/jappl.1980.49.4.743. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fukushima Y., Hagiwara S. Currents carried by monovalent cations through calcium channels in mouse neoplastic B lymphocytes. J Physiol. 1985 Jan;358:255–284. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1985.sp015550. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gallin E. K., Sheehy P. A. Differential expression of inward and outward potassium currents in the macrophage-like cell line J774.1. J Physiol. 1985 Dec;369:475–499. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1985.sp015911. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gallo R. L., Finkelstein J. N., Notter R. H. Characterization of the plasma and mitochondrial membrane potentials of alveolar type II cells by the use of ionic probes. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1984 Apr 11;771(2):217–227. doi: 10.1016/0005-2736(84)90536-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Goodman B. E., Crandall E. D. Dome formation in primary cultured monolayers of alveolar epithelial cells. Am J Physiol. 1982 Jul;243(1):C96–100. doi: 10.1152/ajpcell.1982.243.1.C96. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- HODGKIN A. L., HUXLEY A. F. A quantitative description of membrane current and its application to conduction and excitation in nerve. J Physiol. 1952 Aug;117(4):500–544. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1952.sp004764. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- HODGKIN A. L., KATZ B. The effect of sodium ions on the electrical activity of giant axon of the squid. J Physiol. 1949 Mar 1;108(1):37–77. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1949.sp004310. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hodgkin A. L., Nakajima S. Analysis of the membrane capacity in frog muscle. J Physiol. 1972 Feb;221(1):121–136. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1972.sp009743. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kikkawa Y., Yoneda K. The type II epithelial cell of the lung. I. Method of isolation. Lab Invest. 1974 Jan;30(1):76–84. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mason R. J., Dobbs L. G., Greenleaf R. D., Williams M. C. Alveolar type II cells. Fed Proc. 1977 Dec;36(13):2697–2702. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mason R. J., Williams M. C., Greenleaf R. D., Clements J. A. Isolation and properties of type II alveolar cells from rat lung. Am Rev Respir Dis. 1977 Jun;115(6):1015–1026. doi: 10.1164/arrd.1977.115.6.1015. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mason R., Williams M. C., Clements J. A. Isolation and identification of type 2 alveolar epithelial cells. Chest. 1975 Feb;67(2 Suppl):36S–37S. doi: 10.1378/chest.67.2_supplement.36s. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Messmer T. O., Armour R., Holley R. W. Factors influencing the growth of alveolar type II epithelial cells isolated from rat lungs. Exp Cell Res. 1982 Dec;142(2):417–426. doi: 10.1016/0014-4827(82)90383-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rooney S. A. The surfactant system and lung phospholipid biochemistry. Am Rev Respir Dis. 1985 Mar;131(3):439–460. doi: 10.1164/arrd.1985.131.3.439. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ross W. N., Salzberg B. M., Cohen L. B., Grinvald A., Davila H. V., Waggoner A. S., Wang C. H. Changes in absorption, fluorescence, dichroism, and Birefringence in stained giant axons: : optical measurement of membrane potential. J Membr Biol. 1977 May 6;33(1-2):141–183. doi: 10.1007/BF01869514. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schneider G. T., Cook D. I., Gage P. W., Young J. A. Voltage sensitive, high-conductance chloride channels in the luminal membrane of cultured pulmonary alveolar (type II) cells. Pflugers Arch. 1985 Aug;404(4):354–357. doi: 10.1007/BF00585348. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Simon R. H., McCoy J. P., Jr, Chu A. E., Dehart P. D., Goldstein I. J. Binding of Griffonia simplicifolia I lectin to rat pulmonary alveolar macrophages and its use in purifying type II alveolar epithelial cells. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1986 Jan 23;885(1):34–42. doi: 10.1016/0167-4889(86)90035-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Smith F. B., Kikkawa Y., Diglio C. A., Dalen R. C. The type II epithelial cells of the lung. VI. Incorporation of 3H-choline and 3H-palmitate into lipids of cultured type II cells. Lab Invest. 1980 Mar;42(3):296–301. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


