Abstract
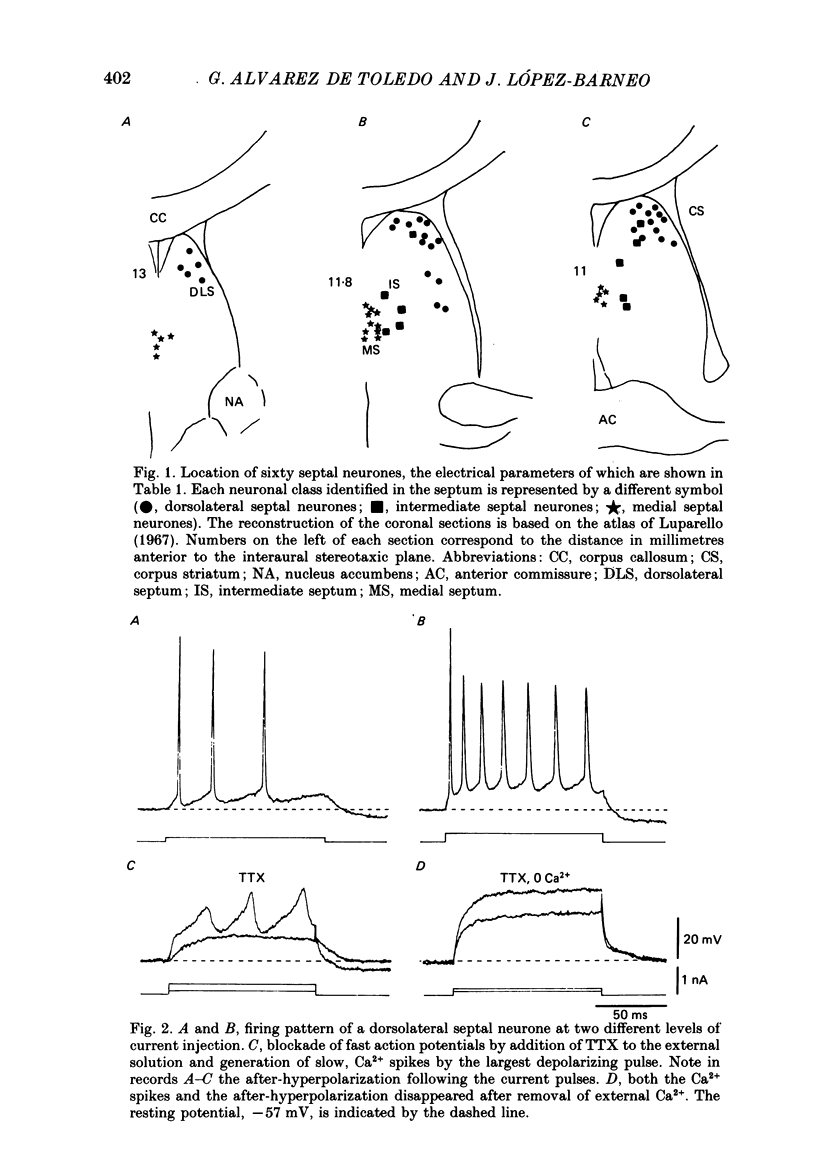
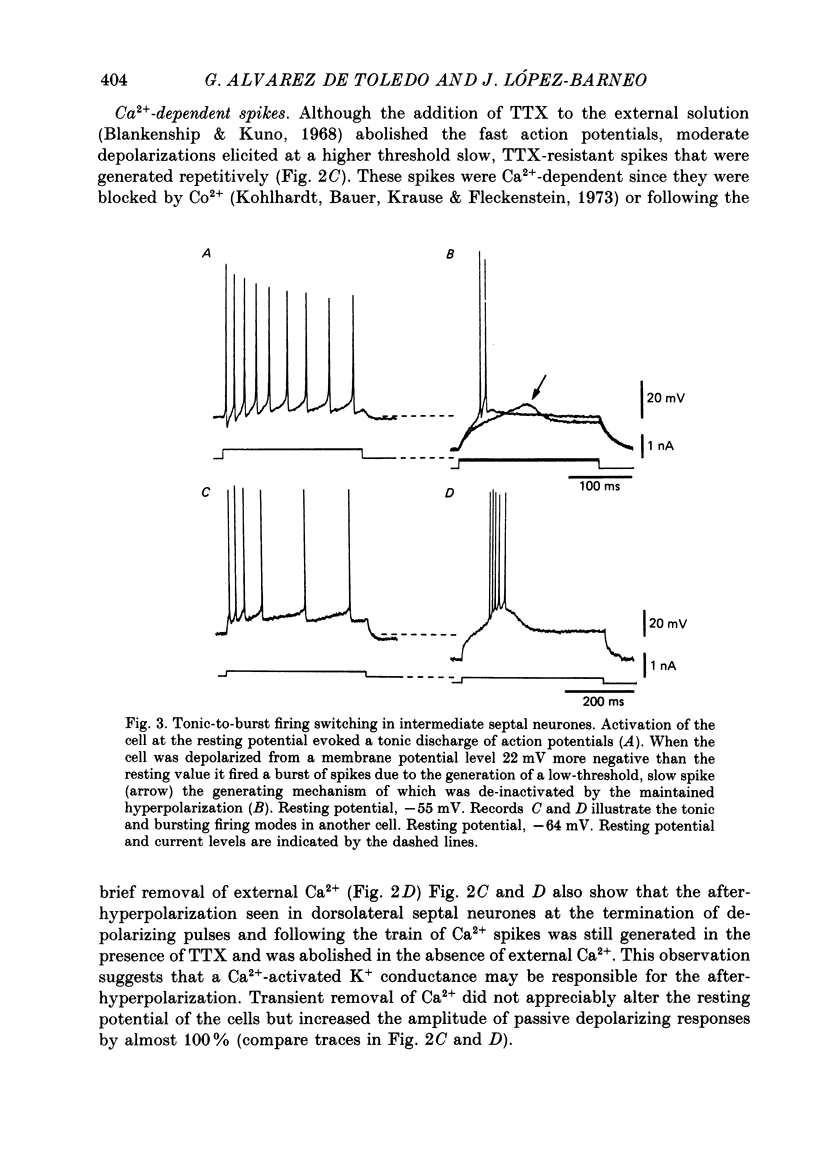
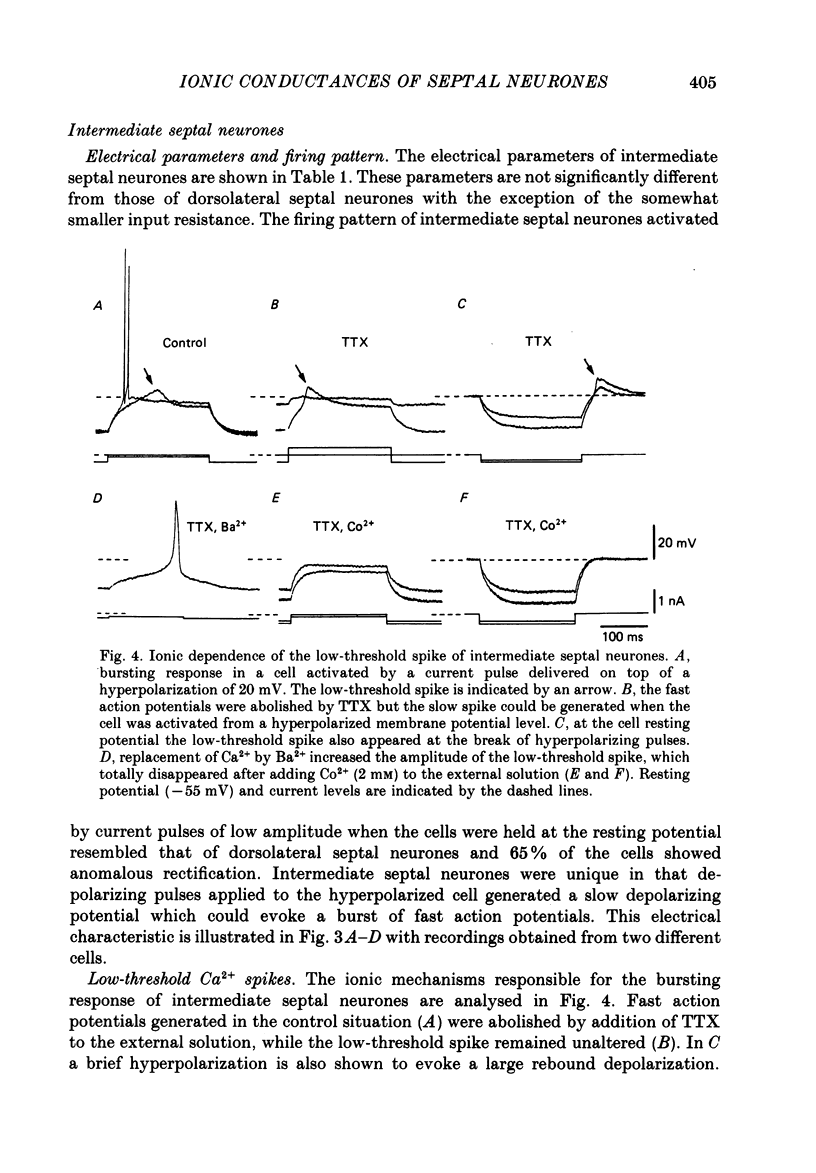
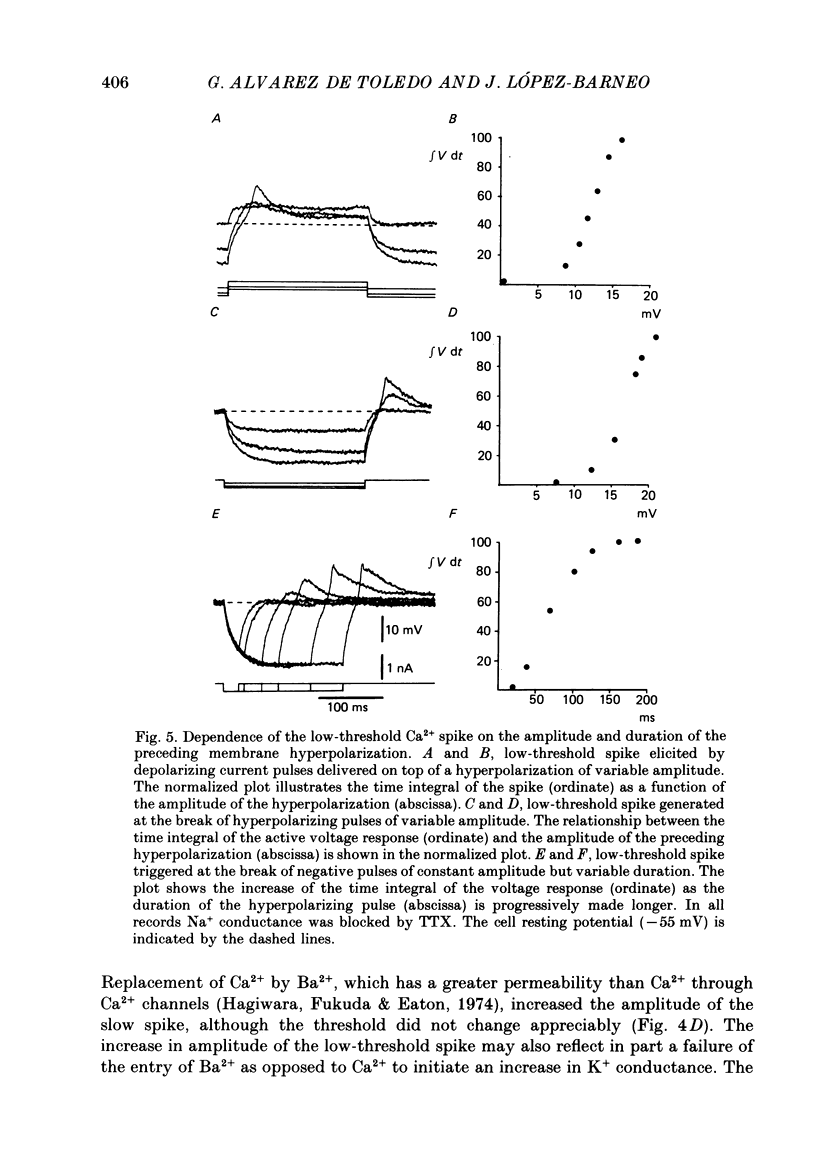
1. The electrical properties and ionic conductances of septal neurones were studied by intracellular recording in an in vitro slice preparation. Within the total number of cells recorded (n = 150) we identified three electrophysiological cell types, each one of them located in a separate septal region. Dorsolateral septal neurones comprised 60% of the cells, intermediate septal neurons 10%, and medical septal neurones 30%. 2. Passive electrical constants of dorsolateral, intermediate and medial septal neurones were, respectively:resting potential (-60.2 +/- 4.8, -59.8 +/- 3.3 and -56 +/- 4.3 mV); input resistance (82.5 +/- 17, 63 +/- 16 and 83 +/- 18 M omega) and membrane time constant (18.5 +/- 7.3, 14.2 +/- 6.8 and 10.7 +/- 3.4 ms). 3. Direct activation of dorsolateral septal neurones by current injection below 0.2 nA triggered repetitive firing of fast action potentials. Larger current pulses elicited a characteristic response consisting of an initial fast action potential followed by a train of slow spikes. An after-hyperpolarization followed termination of the pulse and the characteristic response. 4. In dorsolateral septal neurons tetrodotoxin (TTX) abolished the fast action potentials. The slow spikes and the after-hyperpolarization disappeared in presence of Co2+ or after brief removal of external Ca2+. This suggests that the characteristic response is mediated by Ca2+ and the after-hyperpolarization by a Ca2+-dependent K+ conductance. 5. The firing pattern of intermediate septal neurones activated from the resting potential spontaneously measured in the cells was similar to that of dorsolateral septal neurones; but direct activation from a hyperpolarized membrane potential evoked in intermediate septal cells a bursting response due to the generation of a low-threshold spike. The low-threshold spike was TTX-resistant but abolished by Co2+ and reached a maximal amplitude after hyperpolarization to -75 mV lasting for 100-150 ms. These results suggest the existence in intermediate septal neurons of a low-threshold Ca2+ conductance inactivated at the resting potential and deinactivated by hyperpolarization. 6. Depolarization of medial septal neurons by current pulses of amplitude greater than 0.2-0.3 nA elicited a typical burst of two to six action potentials. The bursts lasted for 20-50 ms and were followed by a marked after-hyperpolarization.(ABSTRACT TRUNCATED AT 400 WORDS)
Full text
PDF








Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
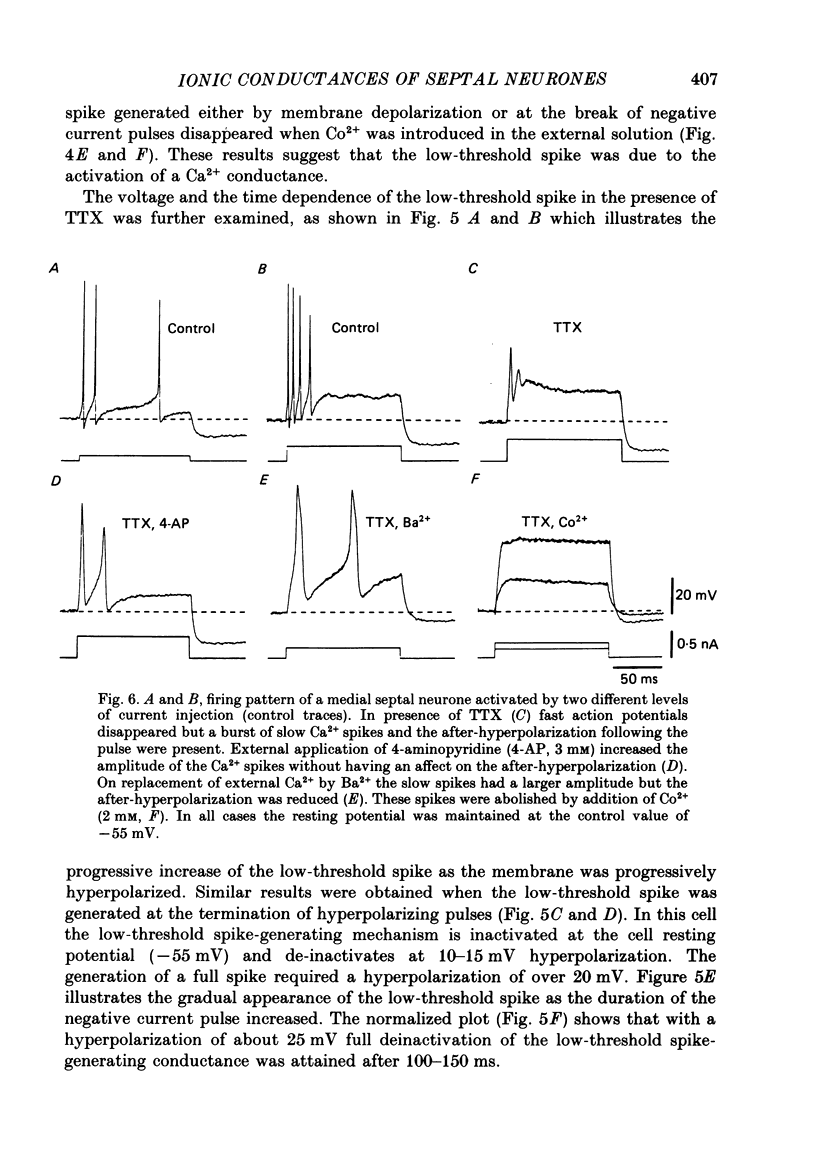
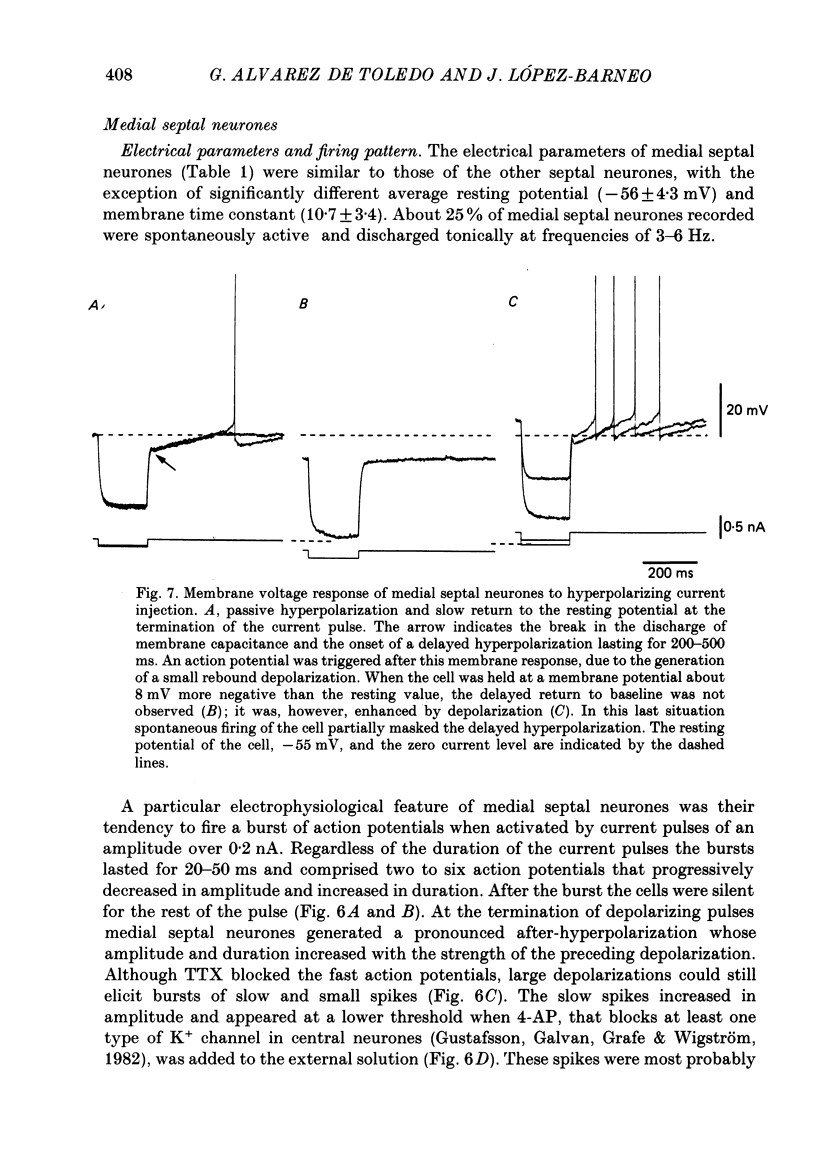
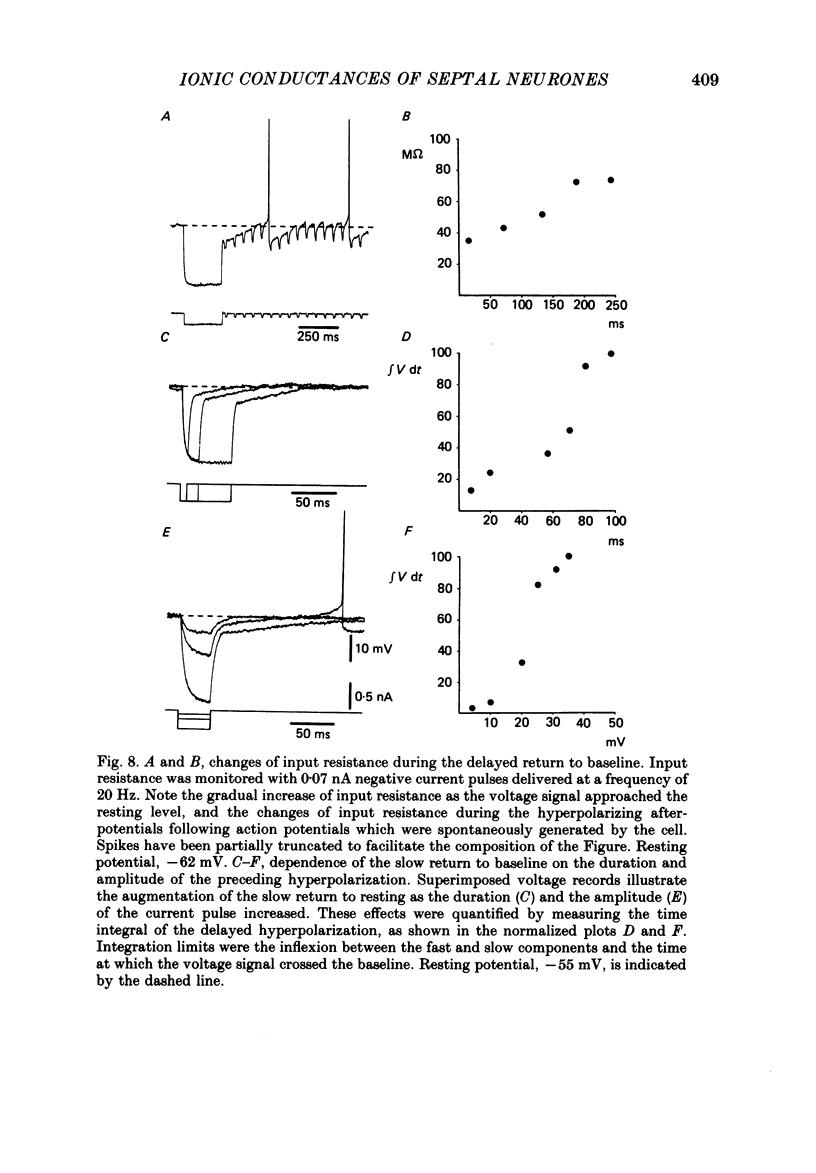
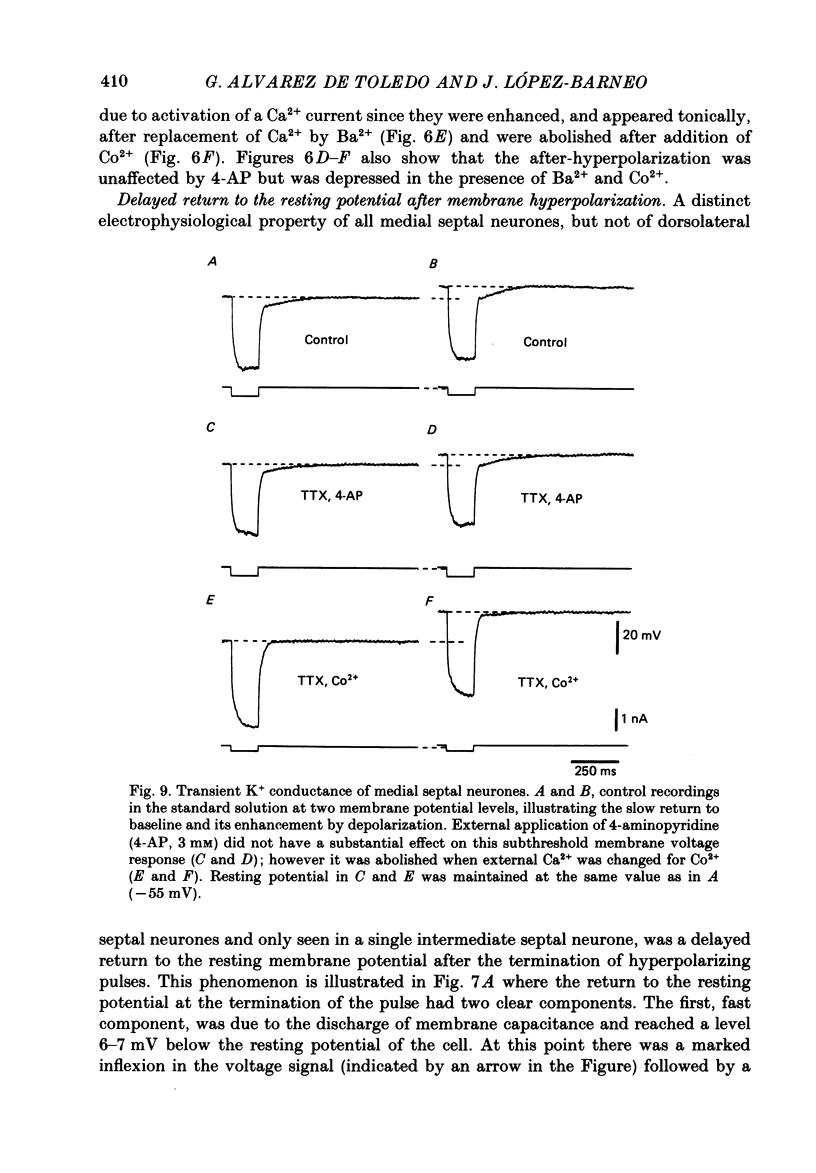
- ANDY O. J., STEPHAN H. Septal nuclei in the Soricidae (insectivors). Cyto-architectonic study. J Comp Neurol. 1961 Oct;117:251–273. doi: 10.1002/cne.901170211. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Apostol G., Creutzfeldt O. D. Crosscorrelation between the activity of septal units and hippocampal EEG during arousal. Brain Res. 1974 Feb 15;67(1):65–75. doi: 10.1016/0006-8993(74)90298-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- BRUECKE F., PETSCHE H., PILLAT B., DEISENHAMMER E. [The influencing of the "hippocampus arousal reaction" in the rabbit by electrical stimulation in the septum]. Pflugers Arch Gesamte Physiol Menschen Tiere. 1959;269:319–338. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Blankenship J. E., Kuno M. Analysis of spontaneous subthreshold activity in spinal motoneurons of the cat. J Neurophysiol. 1968 Mar;31(2):195–209. doi: 10.1152/jn.1968.31.2.195. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Brown D. A., Constanti A., Adams P. R. Ca-activated potassium current in vertebrate sympathetic neurons. Cell Calcium. 1983 Dec;4(5-6):407–420. doi: 10.1016/0143-4160(83)90017-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Brown T. H., Fricke R. A., Perkel D. H. Passive electrical constants in three classes of hippocampal neurons. J Neurophysiol. 1981 Oct;46(4):812–827. doi: 10.1152/jn.1981.46.4.812. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Connor J. A., Stevens C. F. Voltage clamp studies of a transient outward membrane current in gastropod neural somata. J Physiol. 1971 Feb;213(1):21–30. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1971.sp009365. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Connors B. W., Gutnick M. J., Prince D. A. Electrophysiological properties of neocortical neurons in vitro. J Neurophysiol. 1982 Dec;48(6):1302–1320. doi: 10.1152/jn.1982.48.6.1302. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- DeFrance J. F., Yoshihara H., Chronister R. B. Electrophysiological studies of the septal nuclei: I. The lateral septal region. Exp Neurol. 1976 Nov;53(2):399–419. doi: 10.1016/0014-4886(76)90081-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dutar P., Lamour Y., Jobert A. Activation of identified septo-hippocampal neurons by noxious peripheral stimulation. Brain Res. 1985 Feb 25;328(1):15–21. doi: 10.1016/0006-8993(85)91317-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- GREEN J. D., ARDUINI A. A. Hippocampal electrical activity in arousal. J Neurophysiol. 1954 Nov;17(6):533–557. doi: 10.1152/jn.1954.17.6.533. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Galvan M., Sedlmeir C. Outward currents in voltage-clamped rat sympathetic neurones. J Physiol. 1984 Nov;356:115–133. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1984.sp015456. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gustafsson B., Galvan M., Grafe P., Wigström H. A transient outward current in a mammalian central neurone blocked by 4-aminopyridine. Nature. 1982 Sep 16;299(5880):252–254. doi: 10.1038/299252a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hagiwara S., Fukuda J., Eaton D. C. Membrane currents carried by Ca, Sr, and Ba in barnacle muscle fiber during voltage clamp. J Gen Physiol. 1974 May;63(5):564–578. doi: 10.1085/jgp.63.5.564. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jahnsen H., Llinás R. Electrophysiological properties of guinea-pig thalamic neurones: an in vitro study. J Physiol. 1984 Apr;349:205–226. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1984.sp015153. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Joëls M., Twery M. J., Shinnick-Gallagher P., Gallagher J. P. Multiple actions of serotonin on lateral septal neurons in rat brain. Eur J Pharmacol. 1986 Sep 23;129(1-2):203–204. doi: 10.1016/0014-2999(86)90357-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Junge D. Calcium dependence of A-currents in perfused Aplysia neurons. Brain Res. 1985 Nov 4;346(2):294–300. doi: 10.1016/0006-8993(85)90863-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lamour Y., Dutar P., Jobert A. Septo-hippocampal and other medial septum-diagonal band neurons: electrophysiological and pharmacological properties. Brain Res. 1984 Sep 10;309(2):227–239. doi: 10.1016/0006-8993(84)90588-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lebrun C. J., Poulain D. A. Electrical activity of septal neurones during suckling and the milk ejection reflex in the lactating rat. Exp Brain Res. 1982;47(2):203–208. doi: 10.1007/BF00239379. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lebrun C. J., Poulain D. A., Theodosis D. T. The role of the septum in the control of the milk ejection reflex in the rat: effects of lesions and electrical stimulation. J Physiol. 1983 Jun;339:17–31. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1983.sp014699. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Llinás R., Sugimori M. Electrophysiological properties of in vitro Purkinje cell somata in mammalian cerebellar slices. J Physiol. 1980 Aug;305:171–195. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1980.sp013357. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Llinás R., Yarom Y. Electrophysiology of mammalian inferior olivary neurones in vitro. Different types of voltage-dependent ionic conductances. J Physiol. 1981 Jun;315:549–567. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1981.sp013763. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- López-Barneo J., Alvarez de Toledo G., Yarom Y. Electrophysiological properties of guinea pig septal neurons in vitro. Brain Res. 1985 Nov 18;347(2):358–362. doi: 10.1016/0006-8993(85)90199-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- López-Barneo J., Armstrong C. M. Depolarizing response of rat parathyroid cells to divalent cations. J Gen Physiol. 1983 Aug;82(2):269–294. doi: 10.1085/jgp.82.2.269. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- MacDermott A. B., Weight F. F. Action potential repolarization may involve a transient, Ca2+-sensitive outward current in a vertebrate neurone. Nature. 1982 Nov 11;300(5888):185–188. doi: 10.1038/300185a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- McLennan H., Miller J. J. Frequency-related inhibitory mechanisms controlling rhythmical activity in the septal area. J Physiol. 1976 Jan;254(3):827–841. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1976.sp011263. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- McLennan H., Miller J. J. The hippocampal control of neuronal discharges in the septum of the rat. J Physiol. 1974 Mar;237(3):607–624. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1974.sp010500. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Meibach R. C., Siegel A. Efferent connections of the septal area in the rat: an analysis utilizing retrograde and anterograde transport methods. Brain Res. 1977 Jan 1;119(1):1–20. doi: 10.1016/0006-8993(77)90088-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Murase K., Randić M. Electrophysiological properties of rat spinal dorsal horn neurones in vitro: calcium-dependent action potentials. J Physiol. 1983 Jan;334:141–153. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1983.sp014485. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Neher E. Two fast transient current components during voltage clamp on snail neurons. J Gen Physiol. 1971 Jul;58(1):36–53. doi: 10.1085/jgp.58.1.36. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- PETSCHE H., GOGOLAK G., VANZWIETEN P. A. RHYTHMICITY OF SEPTAL CELL DISCHARGES AT VARIOUS LEVELS OF RETICULAR EXCITATION. Electroencephalogr Clin Neurophysiol. 1965 Jul;19:25–33. doi: 10.1016/0013-4694(65)90004-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Raisman G. The connexions of the septum. Brain. 1966 Jun;89(2):317–348. doi: 10.1093/brain/89.2.317. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schwartzkroin P. A., Slawsky M. Probable calcium spikes in hippocampal neurons. Brain Res. 1977 Oct 21;135(1):157–161. doi: 10.1016/0006-8993(77)91060-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Segal M., Barker J. L. Rat hippocampal neurons in culture: potassium conductances. J Neurophysiol. 1984 Jun;51(6):1409–1433. doi: 10.1152/jn.1984.51.6.1409. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stevens D. R., Gallagher J. P., Shinnick-Gallagher P. Intracellular recordings from rat dorsolateral septal neurons, in vitro. Brain Res. 1984 Jul 9;305(2):353–356. doi: 10.1016/0006-8993(84)90441-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Thompson S. H. Three pharmacologically distinct potassium channels in molluscan neurones. J Physiol. 1977 Feb;265(2):465–488. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1977.sp011725. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Vinogradova O. S., Brazhnik E. S., Karanov A. M., Zhadina S. D. Neuronal activity of the septum following various types of deafferentation. Brain Res. 1980 Apr 14;187(2):353–368. doi: 10.1016/0006-8993(80)90208-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zbicz K. L., Weight F. F. Transient voltage and calcium-dependent outward currents in hippocampal CA3 pyramidal neurons. J Neurophysiol. 1985 Apr;53(4):1038–1058. doi: 10.1152/jn.1985.53.4.1038. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


