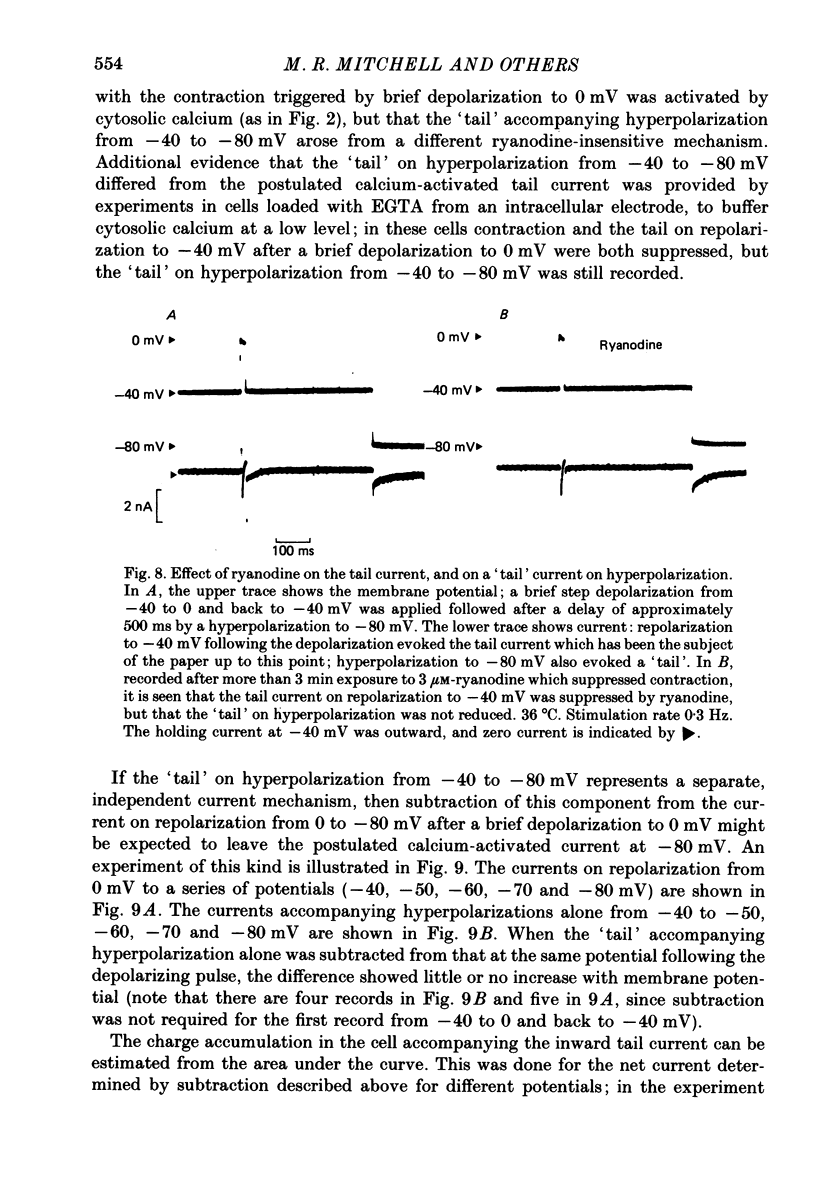
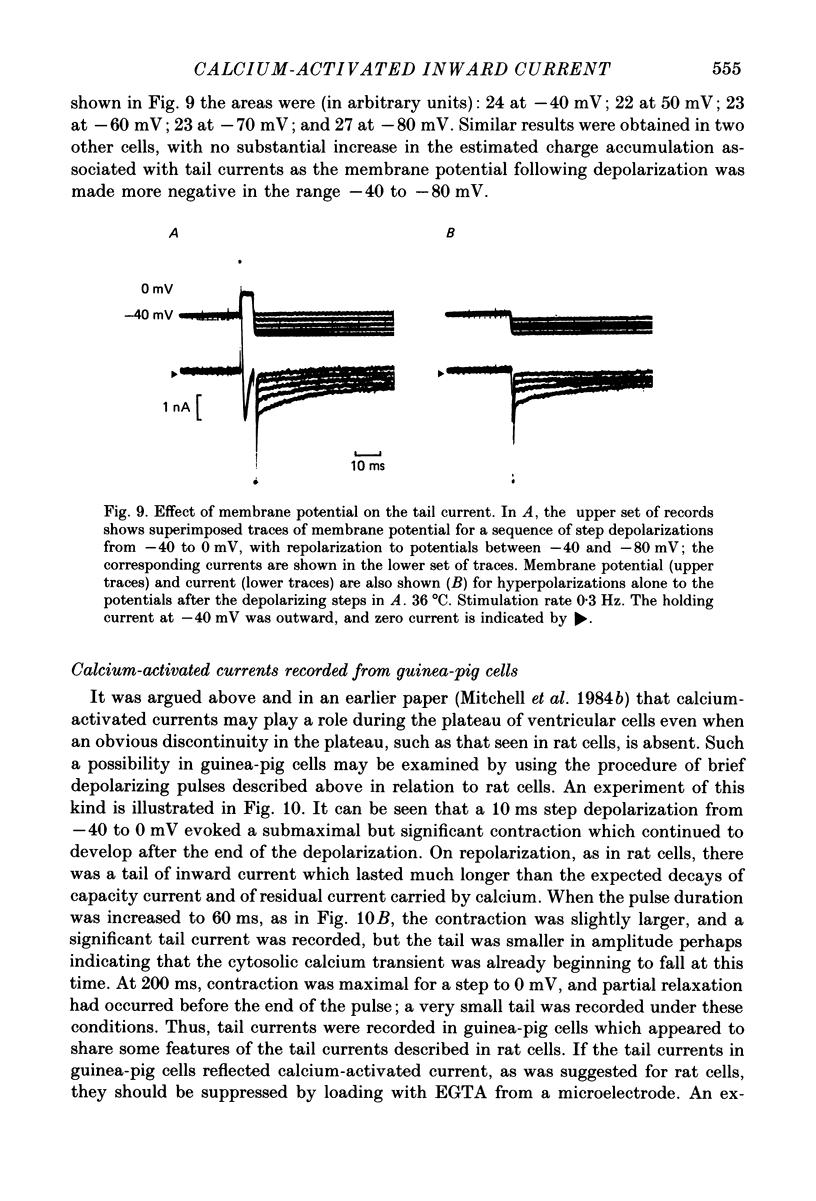
Abstract
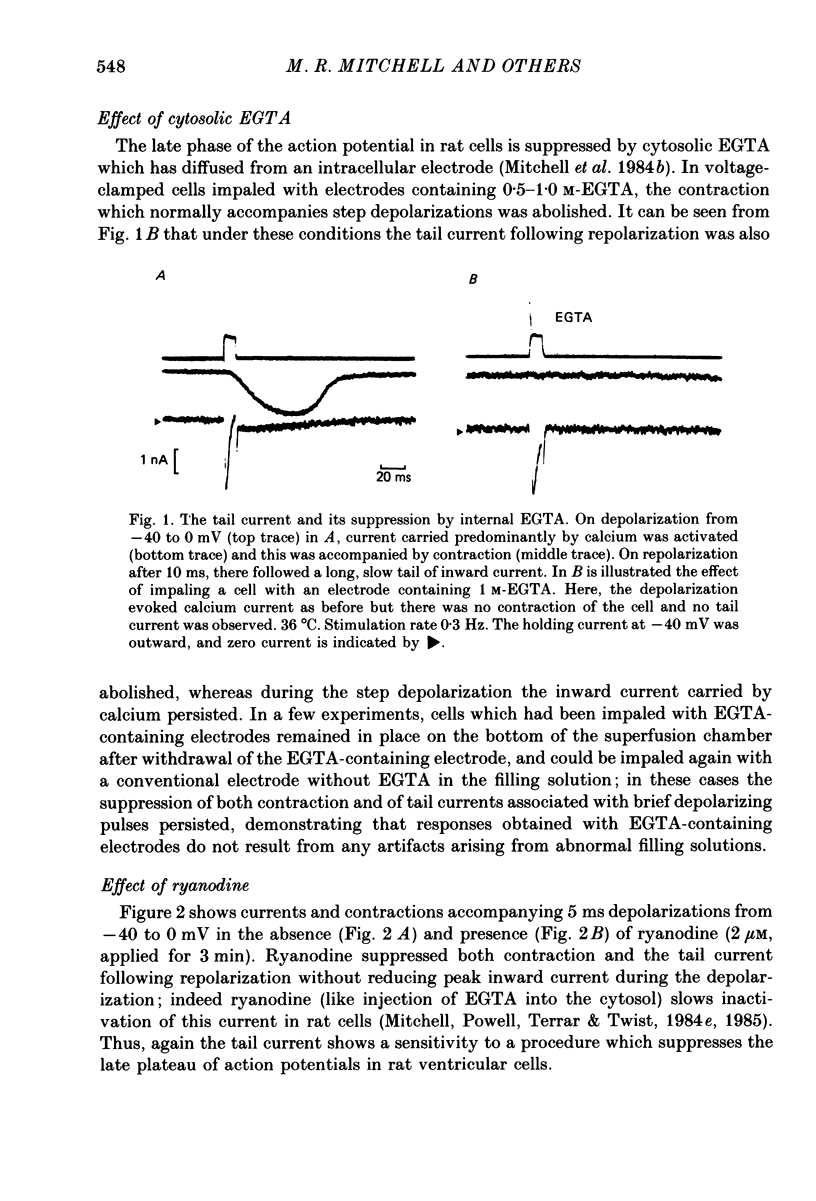
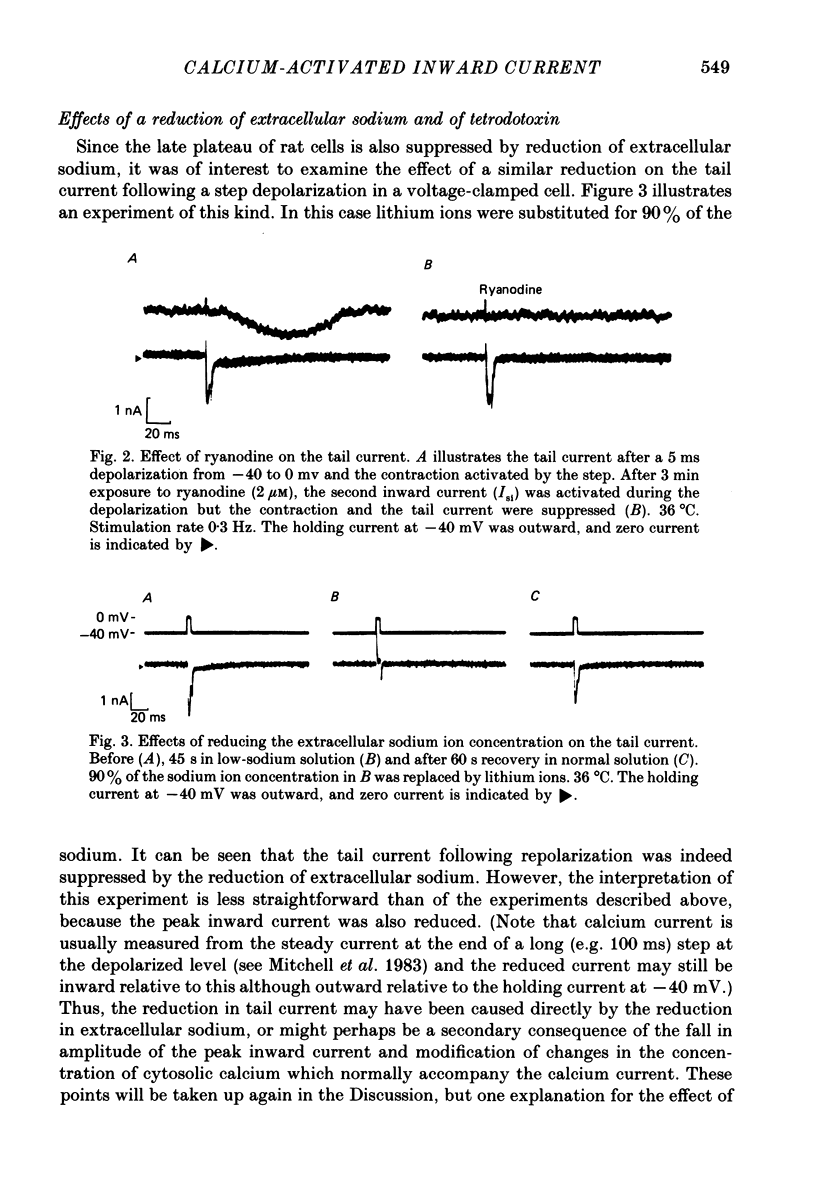
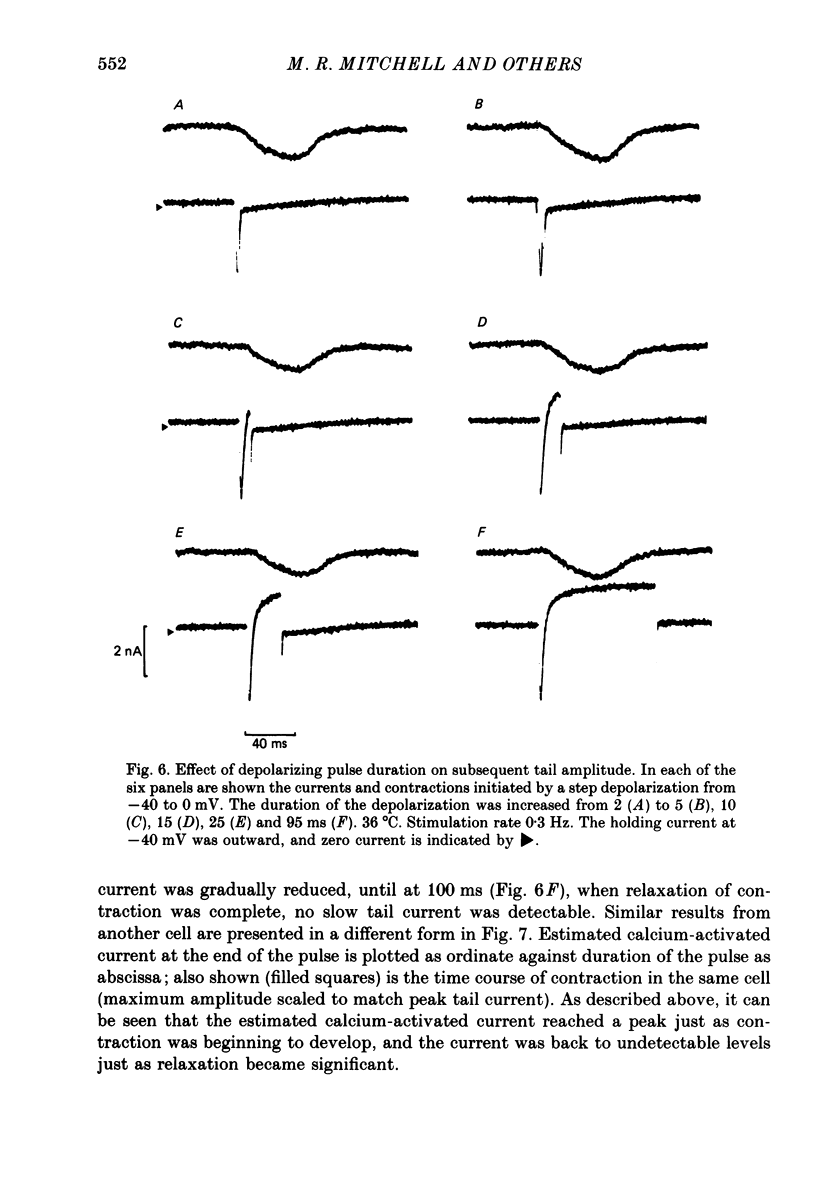
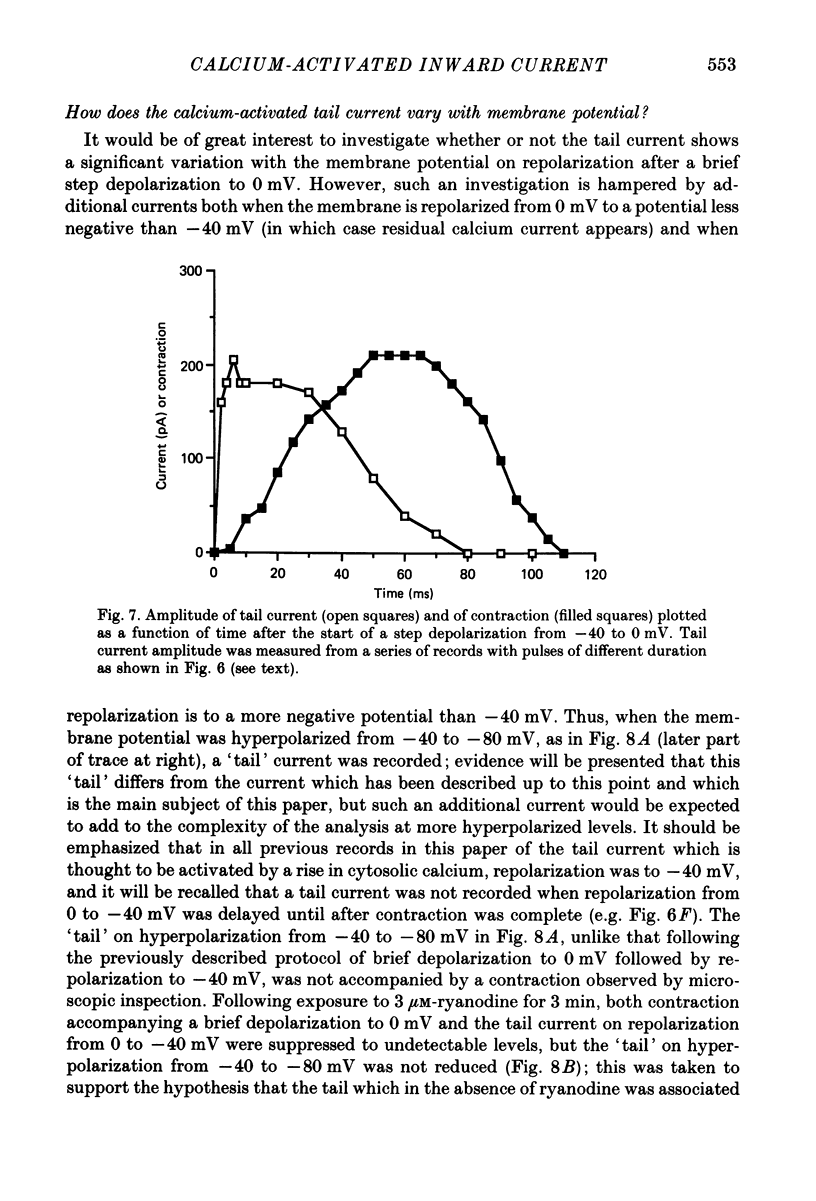
1. Single ventricular cells from rat and guinea-pig hearts were voltage clamped, and contraction was monitored with an optical method. 2. In rat cells, short (2-10 ms) depolarizing pulses to 0 mV from a holding potential of -40 mV evoked current carried by calcium, and on repolarization to -40 mV there was a slow 'tail' current which decayed much more slowly than the expected deactivation of calcium current at this potential. 3. When rat cells were loaded with EGTA diffusing into the cytosol from an intracellular electrode, contraction and the tail current were both abolished, whereas the peak calcium current was not reduced. 4. Exposure of rat cells to ryanodine (1-2 microM) suppressed both contraction and the tail current, but not peak calcium current. 5. The tail current was unaffected by tetrodotoxin (10 microM), but was reduced by lowering extracellular sodium to 10% by replacement with lithium or choline. 6. In rat cells, exposure to nifedipine (1-5 microM) initially caused a marked reduction of calcium current while substantial contraction and tail current remained; longer exposure to nifedipine suppressed both contraction and the tail current. Isoprenaline (50-100 nM) caused a marked increase in peak calcium current, while under these conditions there was little or no increase in either contraction or tail current. 7. The amplitude of the tail current in rat cells varied with the duration of the depolarization at 0 mV; the tail current evoked by repolarization to -40 mV reached a peak just as contraction was beginning to develop and was back to undetectable levels just as relaxation became significant, as might be expected if the tail current were determined by the cytosolic calcium transient which triggered contraction. 8. In guinea-pig cells, a tail current was also recorded on repolarization to a holding potential of -40 mV, and, as in rat cells, the tail was suppressed by cytosolic EGTA and reduced by exposure of the cells to low-sodium solution. 9. It is concluded that the tail currents recorded in both rat and guinea-pig cells represent current activated by a rise in cytosolic calcium; in rat cells this is markedly dependent on ryanodine-sensitive release of calcium from internal stores. The origin of this current, and its possible role during the plateaux of action potentials are discussed.
Full text
PDF









Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Allen D. G., Blinks J. R. Calcium transients in aequorin-injected frog cardiac muscle. Nature. 1978 Jun 15;273(5663):509–513. doi: 10.1038/273509a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Beeler G. W., Jr, Reuter H. Membrane calcium current in ventricular myocardial fibres. J Physiol. 1970 Mar;207(1):191–209. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1970.sp009056. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Colatsky T. J. Mechanisms of action of lidocaine and quinidine on action potential duration in rabbit cardiac Purkinje fibers. An effect on steady state sodium currents? Circ Res. 1982 Jan;50(1):17–27. doi: 10.1161/01.res.50.1.17. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Colquhoun D., Neher E., Reuter H., Stevens C. F. Inward current channels activated by intracellular Ca in cultured cardiac cells. Nature. 1981 Dec 24;294(5843):752–754. doi: 10.1038/294752a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- DiFrancesco D., Noble D. A model of cardiac electrical activity incorporating ionic pumps and concentration changes. Philos Trans R Soc Lond B Biol Sci. 1985 Jan 10;307(1133):353–398. doi: 10.1098/rstb.1985.0001. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Eisner D. A., Lederer W. J. Na-Ca exchange: stoichiometry and electrogenicity. Am J Physiol. 1985 Mar;248(3 Pt 1):C189–C202. doi: 10.1152/ajpcell.1985.248.3.C189. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fabiato A. Myoplasmic free calcium concentration reached during the twitch of an intact isolated cardiac cell and during calcium-induced release of calcium from the sarcoplasmic reticulum of a skinned cardiac cell from the adult rat or rabbit ventricle. J Gen Physiol. 1981 Nov;78(5):457–497. doi: 10.1085/jgp.78.5.457. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hume J. R., Giles W. Ionic currents in single isolated bullfrog atrial cells. J Gen Physiol. 1983 Feb;81(2):153–194. doi: 10.1085/jgp.81.2.153. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hume J. R., Uehara A. Ionic basis of the different action potential configurations of single guinea-pig atrial and ventricular myocytes. J Physiol. 1985 Nov;368:525–544. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1985.sp015874. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Isenberg G., Klöckner U. Calcium currents of isolated bovine ventricular myocytes are fast and of large amplitude. Pflugers Arch. 1982 Oct;395(1):30–41. doi: 10.1007/BF00584965. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kass R. S., Wiegers S. E. The ionic basis of concentration-related effects of noradrenaline on the action potential of calf cardiac purkinje fibres. J Physiol. 1982 Jan;322:541–558. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1982.sp014054. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kimura J., Noma A., Irisawa H. Na-Ca exchange current in mammalian heart cells. Nature. 1986 Feb 13;319(6054):596–597. doi: 10.1038/319596a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lee K. S., Marban E., Tsien R. W. Inactivation of calcium channels in mammalian heart cells: joint dependence on membrane potential and intracellular calcium. J Physiol. 1985 Jul;364:395–411. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1985.sp015752. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lee K. S., Noble D., Lee E., Spindler A. J. A new calcium current underlying the plateau of the cardiac action potential. Proc R Soc Lond B Biol Sci. 1984 Nov 22;223(1230):35–48. doi: 10.1098/rspb.1984.0081. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lee K. S., Tsien R. W. Mechanism of calcium channel blockade by verapamil, D600, diltiazem and nitrendipine in single dialysed heart cells. Nature. 1983 Apr 28;302(5911):790–794. doi: 10.1038/302790a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lee K. S., Tsien R. W. Reversal of current through calcium channels in dialysed single heart cells. Nature. 1982 Jun 10;297(5866):498–501. doi: 10.1038/297498a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Marban E., Tsien R. W. Effects of nystatin-mediated intracellular ion substitution on membrane currents in calf purkinje fibres. J Physiol. 1982 Aug;329:569–587. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1982.sp014320. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Marban E., Wier W. G. Ryanodine as a tool to determine the contributions of calcium entry and calcium release to the calcium transient and contraction of cardiac Purkinje fibers. Circ Res. 1985 Jan;56(1):133–138. doi: 10.1161/01.res.56.1.133. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Matsuda H., Noma A. Isolation of calcium current and its sensitivity to monovalent cations in dialysed ventricular cells of guinea-pig. J Physiol. 1984 Dec;357:553–573. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1984.sp015517. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mechmann S., Pott L. Identification of Na-Ca exchange current in single cardiac myocytes. Nature. 1986 Feb 13;319(6054):597–599. doi: 10.1038/319597a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mitchell M. R., Powell T., Terrar D. A., Twist V. W. Characteristics of the second inward current in cells isolated from rat ventricular muscle. Proc R Soc Lond B Biol Sci. 1983 Oct 22;219(1217):447–469. doi: 10.1098/rspb.1983.0084. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mitchell M. R., Powell T., Terrar D. A., Twist V. W. Electrical activity and contraction in cells isolated from rat and guinea-pig ventricular muscle: a comparative study. J Physiol. 1987 Oct;391:527–544. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1987.sp016754. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mitchell M. R., Powell T., Terrar D. A., Twist V. W. Influence of a change in stimulation rate on action potentials, currents and contractions in rat ventricular cells. J Physiol. 1985 Jul;364:113–130. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1985.sp015734. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mitchell M. R., Powell T., Terrar D. A., Twist V. W. Strontium, nifedipine and 4-aminopyridine modify the time course of the action potential in cells from rat ventricular muscle. Br J Pharmacol. 1984 Mar;81(3):551–556. doi: 10.1111/j.1476-5381.1984.tb10108.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mitchell M. R., Powell T., Terrar D. A., Twist V. W. The effects of ryanodine, EGTA and low-sodium on action potentials in rat and guinea-pig ventricular myocytes: evidence for two inward currents during the plateau. Br J Pharmacol. 1984 Mar;81(3):543–550. doi: 10.1111/j.1476-5381.1984.tb10107.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mullins L. J. The generation of electric currents in cardiac fibers by Na/Ca exchange. Am J Physiol. 1979 Mar;236(3):C103–C110. doi: 10.1152/ajpcell.1979.236.3.C103. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Niedergerke R., Orkand R. K. The dual effect of calcium on the action potential of the frog's heart. J Physiol. 1966 May;184(2):291–311. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1966.sp007916. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Noble D. The surprising heart: a review of recent progress in cardiac electrophysiology. J Physiol. 1984 Aug;353:1–50. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1984.sp015320. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schouten V. J., ter Keurs H. E. The slow repolarization phase of the action potential in rat heart. J Physiol. 1985 Mar;360:13–25. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1985.sp015601. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Watanabe T., Delbridge L. M., Bustamante J. O., McDonald T. F. Heterogeneity of the action potential in isolated rat ventricular myocytes and tissue. Circ Res. 1983 Mar;52(3):280–290. doi: 10.1161/01.res.52.3.280. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


