Abstract
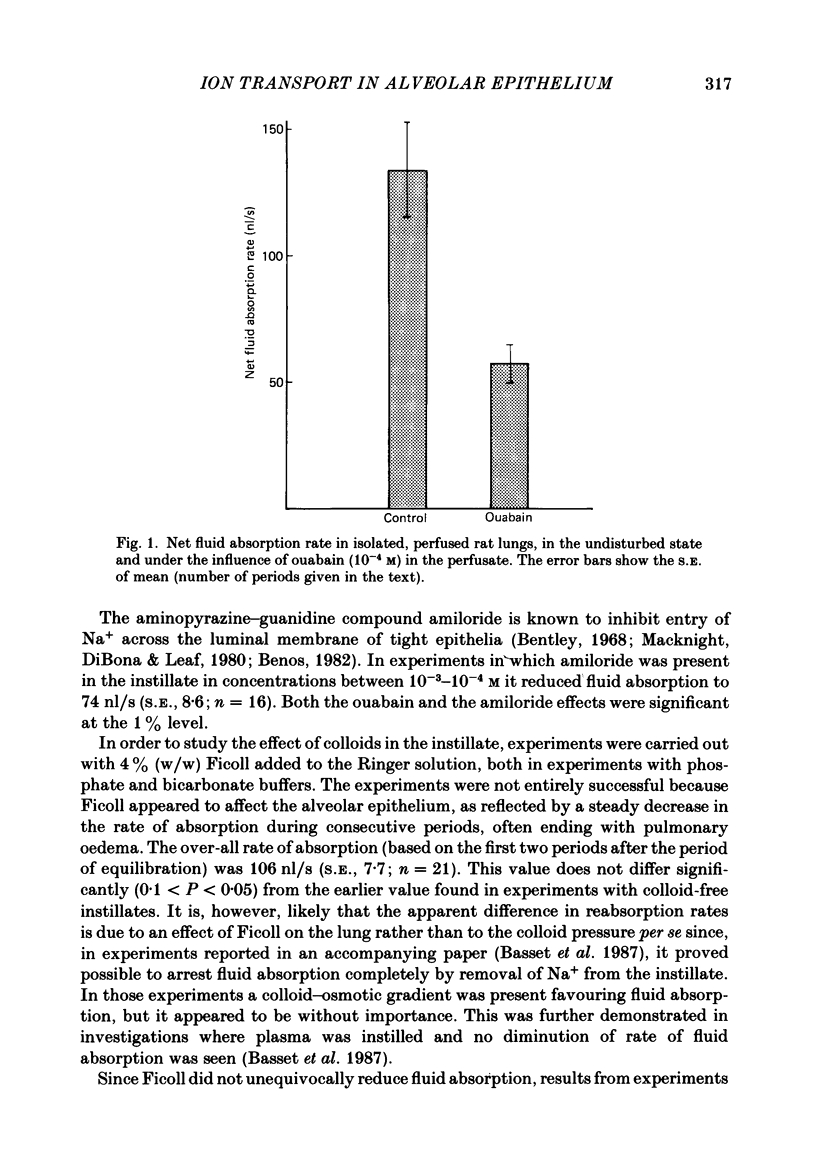
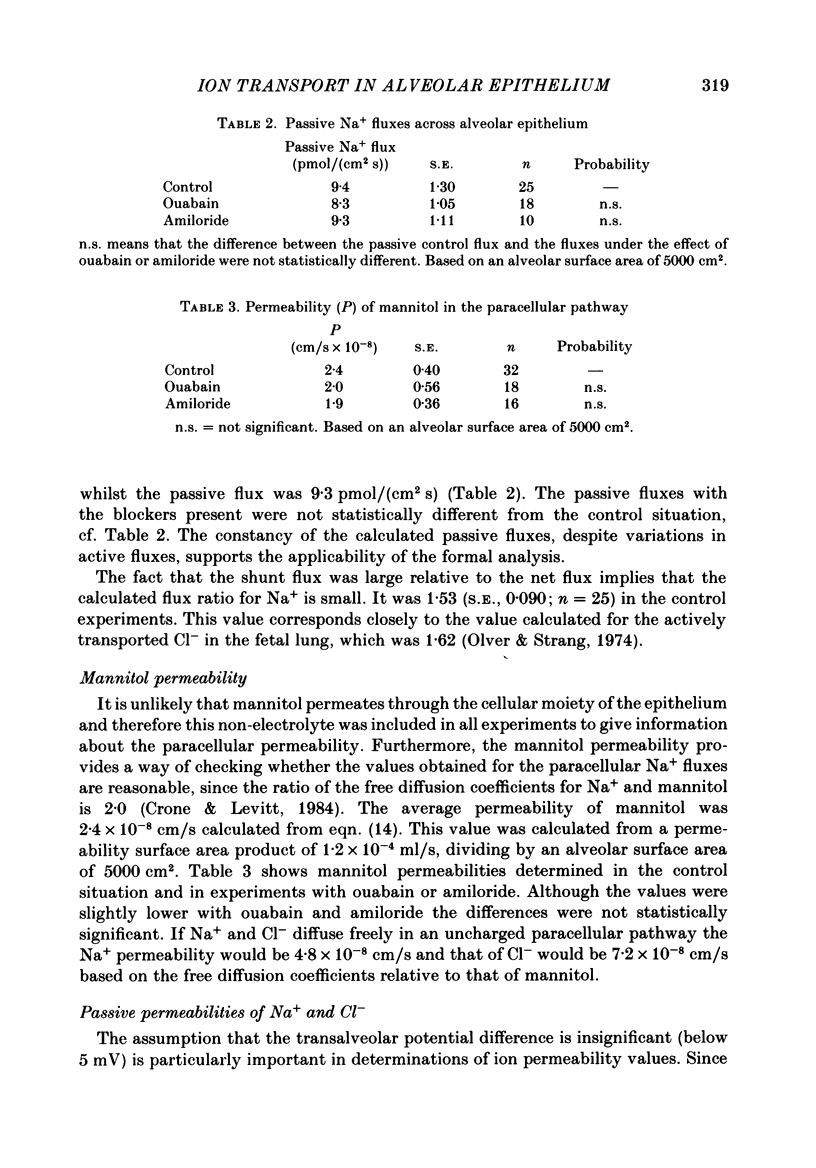
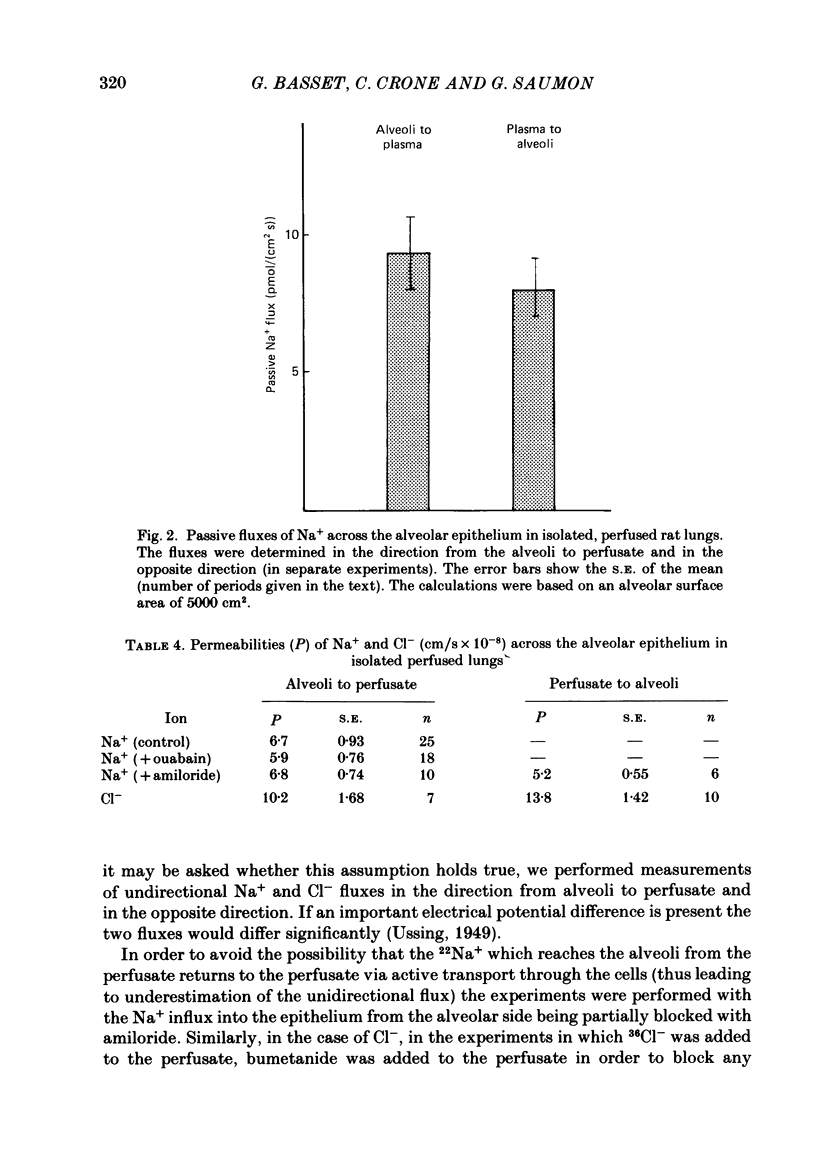
1. Experiments were performed on isolated rat lungs perfused with Ringer solutions containing red cells. The goal was to clarify the role of active transport of Na+ for the absorption of fluid across the alveolar membrane, and to characterize active and passive pathways. 2. Partially degassed lungs were filled with 5 ml of an isotonic Ringer solution containing 125I-labelled albumin in order to calculate the fluid movement, and 22Na+ or 36Cl- for measurement of ion fluxes. Passive non-electrolyte permeability was determined in all experiments using [3H]mannitol. 3. The average rate of fluid absorption in phosphate-buffered instillates was 134 nl/s (S.E., 18.5; n = 14). With ouabain (10(-4) M) in the perfusate the fluid absorption rate fell to 57 nl/s (S.E., 8.2; n = 18). Amiloride (10(-3)-10(-4) M) in the instillate reduced the absorption to 75 nl/s (S.E., 8.6; n = 16). These results show that fluid absorption depends on transcellular transport of Na+ and that alveolar epithelial cells have a Na+ entry system in the luminal membrane and a Na+-K+ pump in the abluminal membrane. 4. The transcellular ion transport operates in parallel with a paracellular, passive leak that allows mannitol to pass with a permeability surface area product of 1.2 X 10(-4) ml/s, corresponding to a permeability coefficient of 2.4 X 10(-8) cm/s, assuming an alveolar surface area of 5000 cm2. 5. The passive fluxes of Na+ were 9.4 pmol/(cm2s) (S.E., 1.3; n = 25) in the direction from alveoli to perfusate and 8.0 pmol/(cm2s) (S.E., 0.86; n = 6) from perfusate to plasma. The passive fluxes of Cl- in the two directions were not significantly different either. Thus the transalveolar electrical potential difference is too small to affect ion movements measurably. 6. The passive permeability to Na+ was 6.7 X 10(-8) cm/s and to Cl- was 10.2 X 10(-8) cm/s (alveolar surface area assumed to be 5000 cm2). The ratio of the permeabilities is close to the ratio of the diffusion coefficients in free solution, suggesting a neutral or weakly charged paracellular channel. 7. We conclude that the alveolar epithelium performs solute-coupled fluid transport from alveoli to plasma, and that it shows many features that are common to other fluid-transporting epithelia; with an approximate surface area of 100 m2 in humans it constitutes one of the largest epithelial surfaces in the body.(ABSTRACT TRUNCATED AT 400 WORDS)
Full text
PDF










Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Basset G., Crone C., Saumon G. Fluid absorption by rat lung in situ: pathways for sodium entry in the luminal membrane of alveolar epithelium. J Physiol. 1987 Mar;384:325–345. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1987.sp016457. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Benos D. J. Amiloride: a molecular probe of sodium transport in tissues and cells. Am J Physiol. 1982 Mar;242(3):C131–C145. doi: 10.1152/ajpcell.1982.242.3.C131. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bentley P. J. Amiloride: a potent inhibitor of sodium transport across the toad bladder. J Physiol. 1968 Mar;195(2):317–330. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1968.sp008460. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bruus K., Kristensen P., Larsen E. H. Pathways for chloride and sodium transport across toad skin. Acta Physiol Scand. 1976 Mar;97(1):31–47. doi: 10.1111/j.1748-1716.1976.tb10233.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Carrière S., Dandavino R. Bumetanide, a new loop diuretic. Clin Pharmacol Ther. 1976 Oct;20(4):424–438. doi: 10.1002/cpt1976204424. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Crapo J. D., Young S. L., Fram E. K., Pinkerton K. E., Barry B. E., Crapo R. O. Morphometric characteristics of cells in the alveolar region of mammalian lungs. Am Rev Respir Dis. 1983 Aug;128(2 Pt 2):S42–S46. doi: 10.1164/arrd.1983.128.2P2.S42. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- DiBona D. R., Mills J. W. Distribution of Na+-pump sites in transporting epithelia. Fed Proc. 1979 Feb;38(2):134–143. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Goodman B. E., Brown S. E., Crandall E. D. Regulation of transport across pulmonary alveolar epithelial cell monolayers. J Appl Physiol Respir Environ Exerc Physiol. 1984 Sep;57(3):703–710. doi: 10.1152/jappl.1984.57.3.703. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Goodman B. E., Fleischer R. S., Crandall E. D. Evidence for active Na+ transport by cultured monolayers of pulmonary alveolar epithelial cells. Am J Physiol. 1983 Jul;245(1):C78–C83. doi: 10.1152/ajpcell.1983.245.1.C78. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lewis S. A., Diamond J. M. Na+ transport by rabbit urinary bladder, a tight epithelium. J Membr Biol. 1976 Aug 27;28(1):1–40. doi: 10.1007/BF01869689. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lewis S. A., Eaton D. C., Diamond J. M. The mechanism of Na+ transport by rabbit urinary bladder. J Membr Biol. 1976 Aug 27;28(1):41–70. doi: 10.1007/BF01869690. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mason R. J., Williams M. C., Widdicombe J. H., Sanders M. J., Misfeldt D. S., Berry L. C., Jr Transepithelial transport by pulmonary alveolar type II cells in primary culture. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1982 Oct;79(19):6033–6037. doi: 10.1073/pnas.79.19.6033. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Matthay M. A., Berthiaume Y., Staub N. C. Long-term clearance of liquid and protein from the lungs of unanesthetized sheep. J Appl Physiol (1985) 1985 Sep;59(3):928–934. doi: 10.1152/jappl.1985.59.3.928. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Matthay M. A., Landolt C. C., Staub N. C. Differential liquid and protein clearance from the alveoli of anesthetized sheep. J Appl Physiol Respir Environ Exerc Physiol. 1982 Jul;53(1):96–104. doi: 10.1152/jappl.1982.53.1.96. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nielson D. W., Goerke J., Clements J. A. Alveolar subphase pH in the lungs of anesthetized rabbits. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1981 Nov;78(11):7119–7123. doi: 10.1073/pnas.78.11.7119. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Olver R. E., Strang L. B. Ion fluxes across the pulmonary epithelium and the secretion of lung liquid in the foetal lamb. J Physiol. 1974 Sep;241(2):327–357. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1974.sp010659. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schuurmans Stekhoven F., Bonting S. L. Transport adenosine triphosphatases: properties and functions. Physiol Rev. 1981 Jan;61(1):1–76. doi: 10.1152/physrev.1981.61.1.1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- TAYLOR A. E., GUYTON A. C., BISHOP V. S. PERMEABILITY OF THE ALVEOLAR MEMBRANE TO SOLUTES. Circ Res. 1965 Apr;16:353–362. doi: 10.1161/01.res.16.4.353. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wangensteen O. D., Wittmers L. E., Jr, Johnson J. A. Permeability of the mammalian blood-gas barrier and its components. Am J Physiol. 1969 Apr;216(4):719–727. doi: 10.1152/ajplegacy.1969.216.4.719. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Weibel E. R. Morphological basis of alveolar-capillary gas exchange. Physiol Rev. 1973 Apr;53(2):419–495. doi: 10.1152/physrev.1973.53.2.419. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


