Abstract
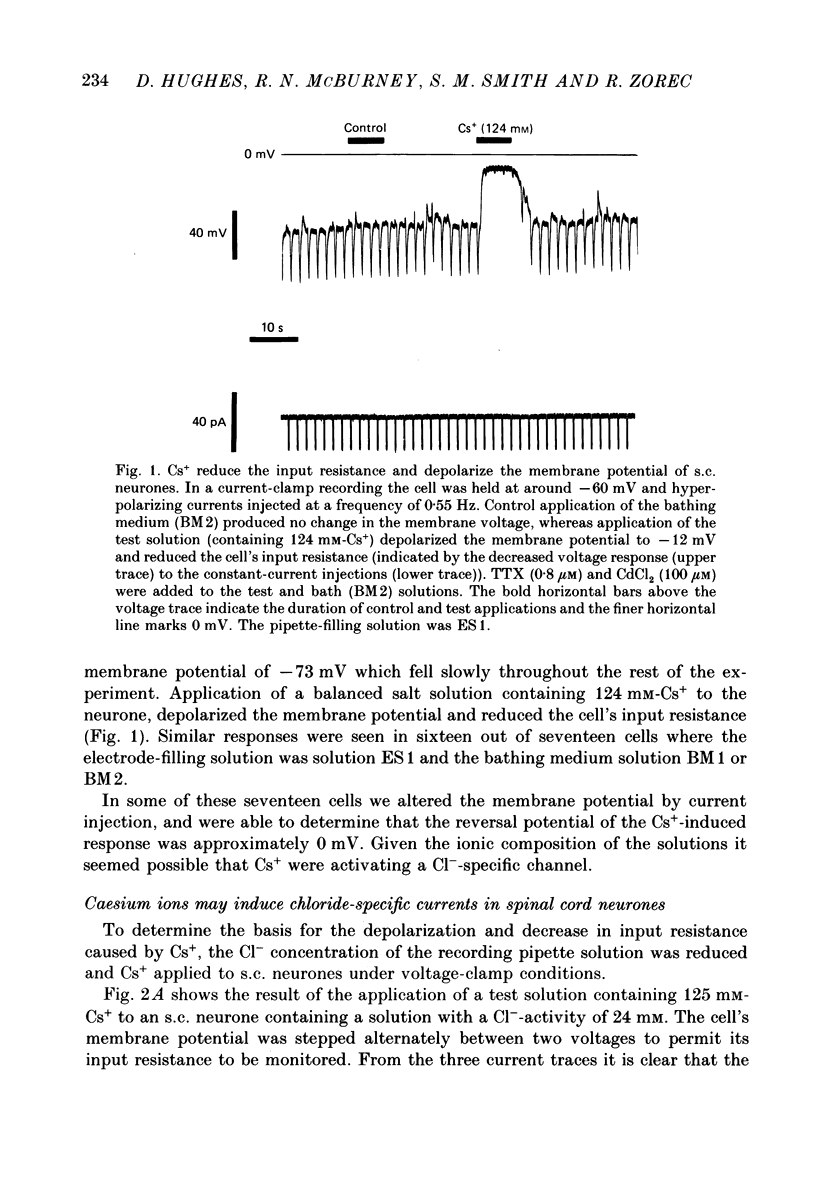
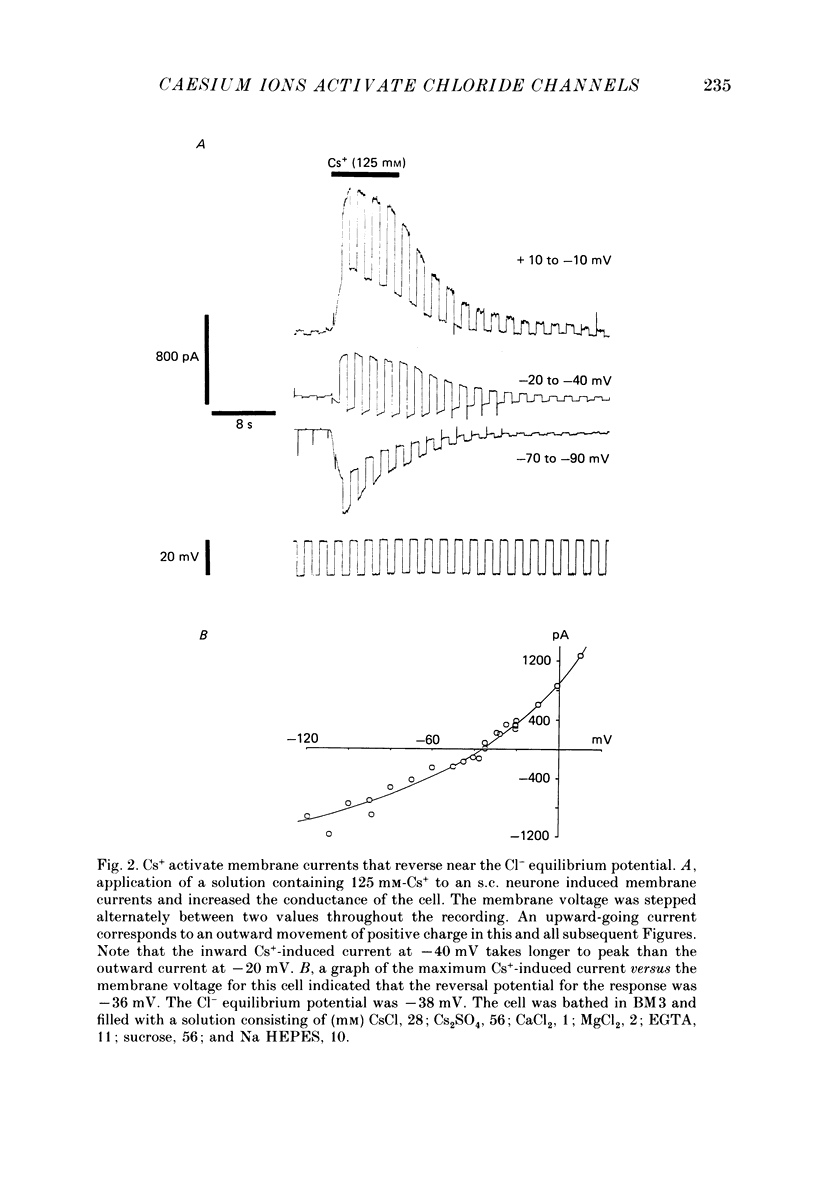
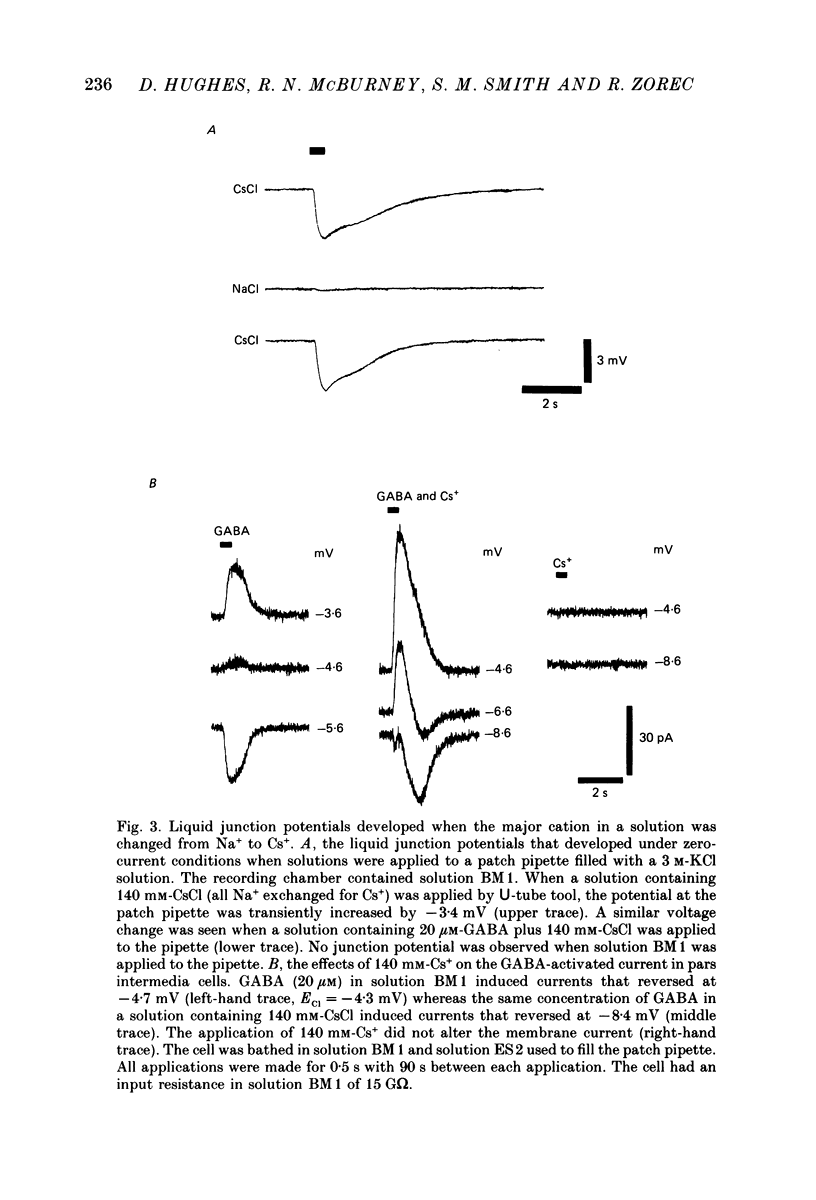
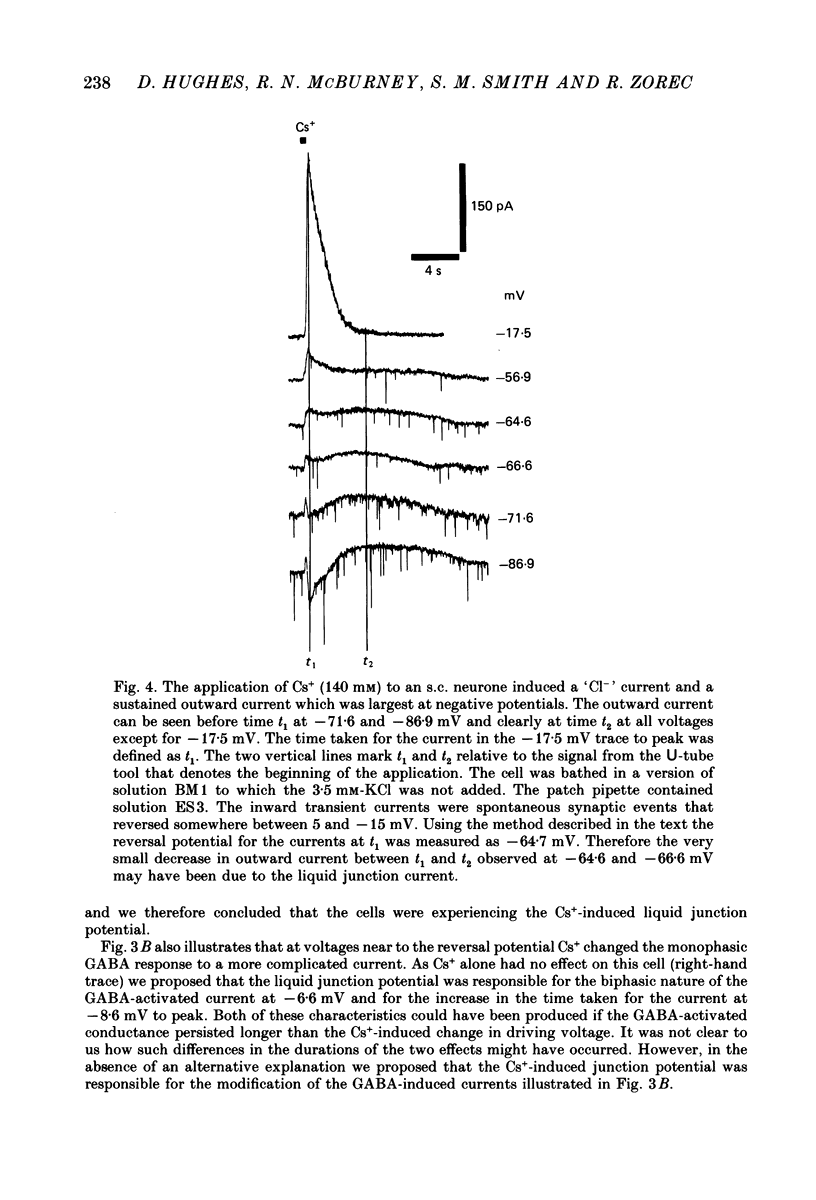
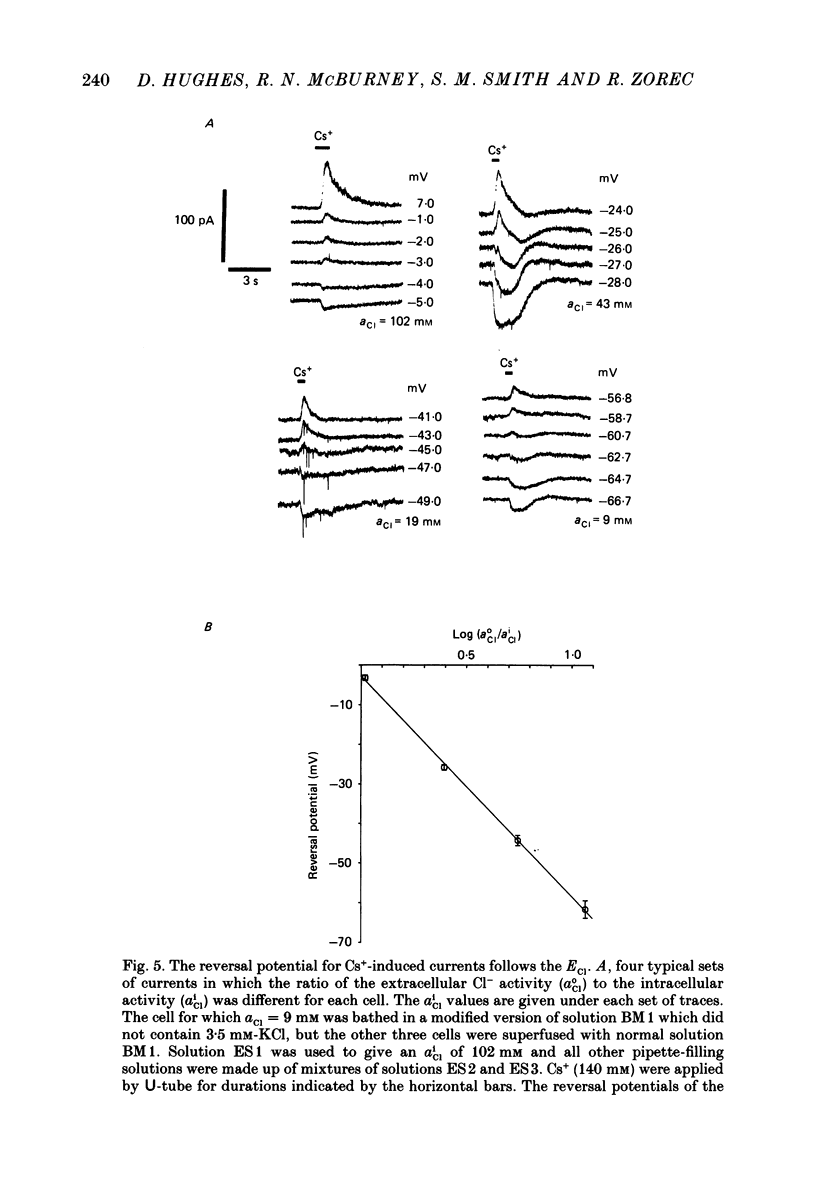
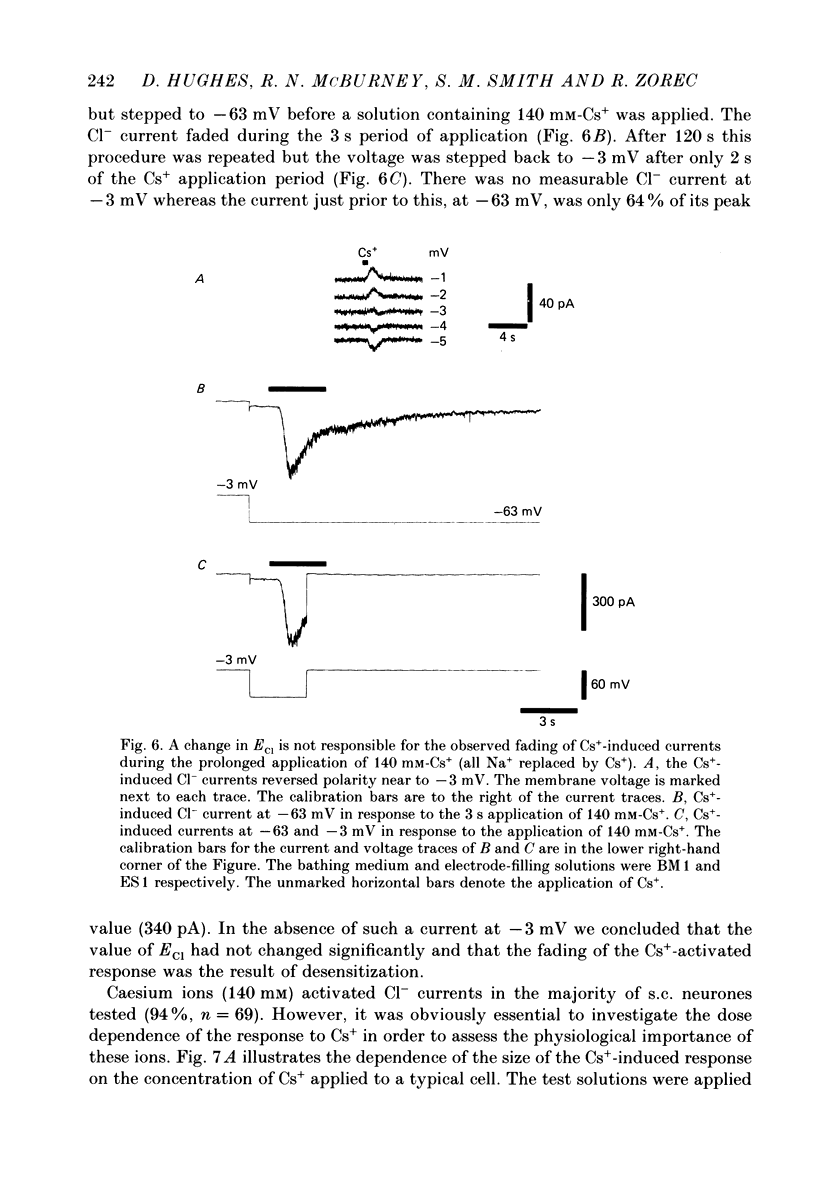
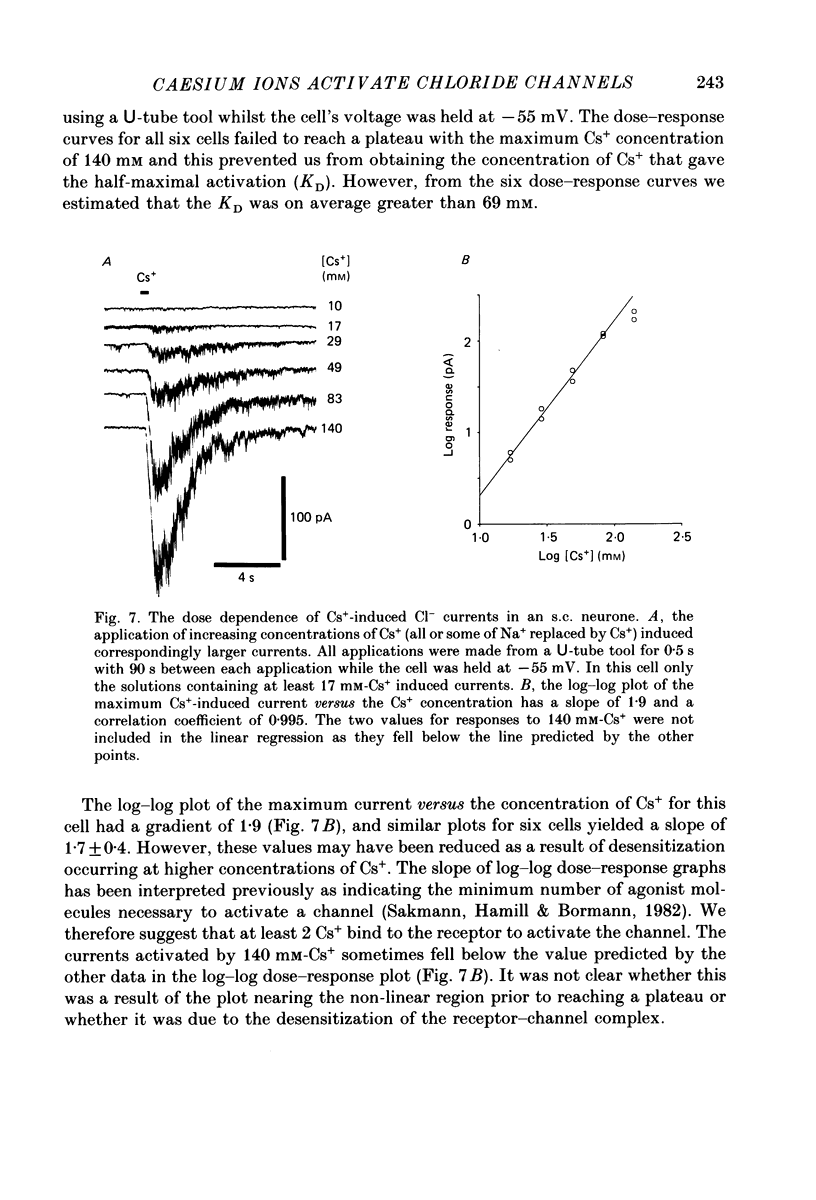
1. Caesium ions (Cs+), applied extracellularly, caused a decrease in the input resistance of cultured spinal cord (s.c.) neurones and depolarized the neurones when they contained 140 mM-CsCl. 2. The reversal potential for Cs+-activated currents shifted 56 mV on average for a 10-fold reduction in the intracellular chloride ion (Cl-) activity, indicating that the Cs+-activated currents were specific to Cl-. 3. The activation of Cl- currents by Cs+ was not due to the depolarization-evoked release of neurotransmitter from presynaptic terminals. We therefore suggest that Cs+ were acting directly on the extracellular surface of the s.c. neurones to activate Cl- currents. 4. Cs+-activated currents showed desensitization in the presence of 140 mM-Cs+. 5. The log-log plot of the dose-response data could be fitted with a straight line with a slope of 1.7 +/- 0.4 (n = 6), indicating that at least 2 Cs+ were needed to activate a single Cl- channel. The KD of the Cs+-induced response was greater than 69 mM. 6. In outside-out patches Cs+ activated single Cl- channels. These channels were not activated by sodium or potassium ions. 7. The Cs+-activated channels displayed a total of five distinct conductance states which had mean conductances of 20, 30, 43, 66 and 92 pS. The 30 and 43 pS states were the most frequently occurring states. 8. The conductance states of the Cs+-activated channel have the same conductances as those reported for gamma-aminobutyric acid (GABA)- and glycine-activated channels in rat s.c. neurones. We therefore conclude that Cs+ activate the same type of Cl- channel as GABA and glycine through an unidentified receptor.
Full text
PDF








Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Fenwick E. M., Marty A., Neher E. A patch-clamp study of bovine chromaffin cells and of their sensitivity to acetylcholine. J Physiol. 1982 Oct;331:577–597. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1982.sp014393. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
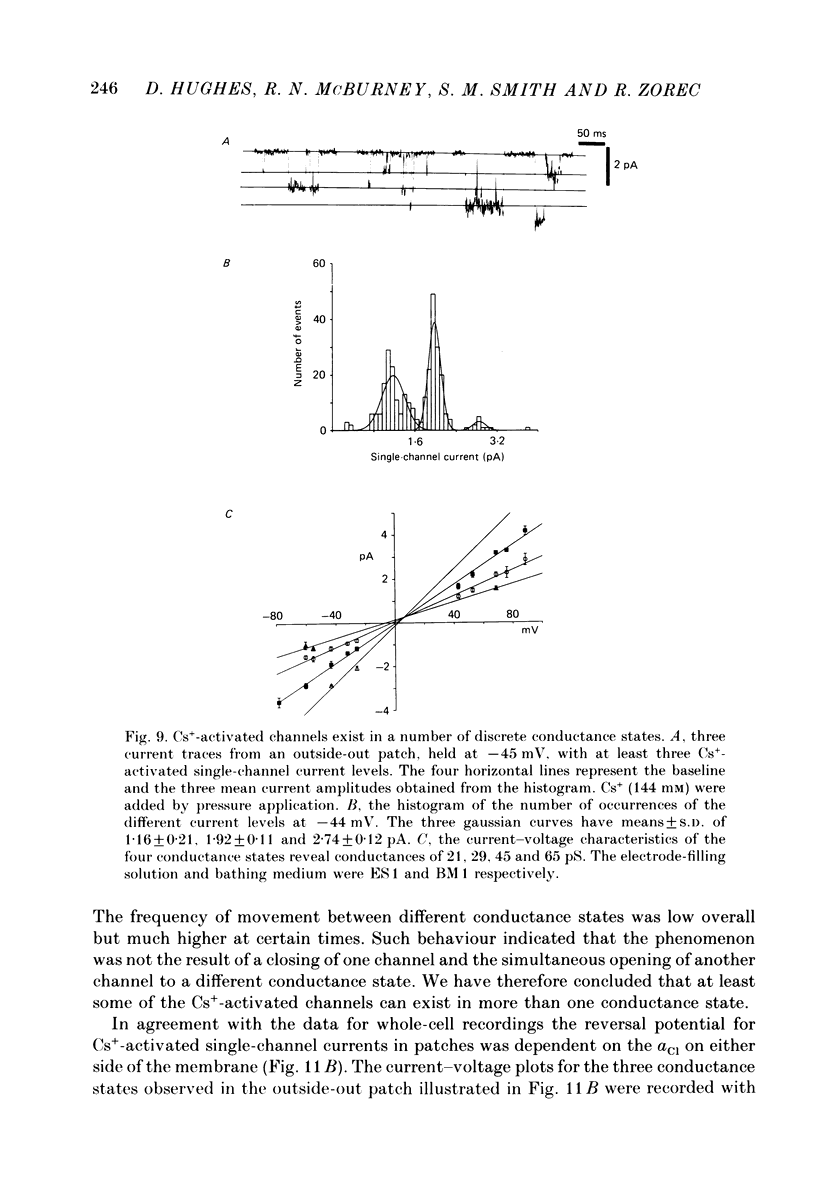
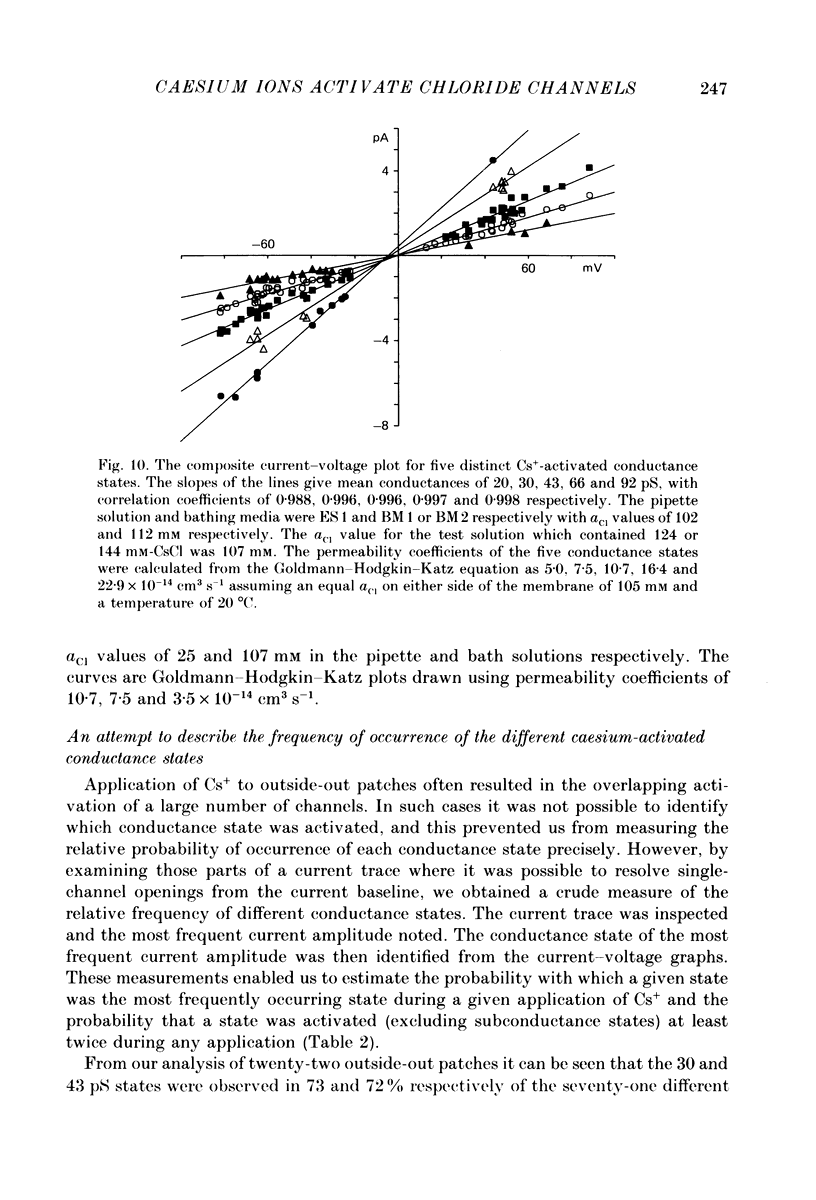
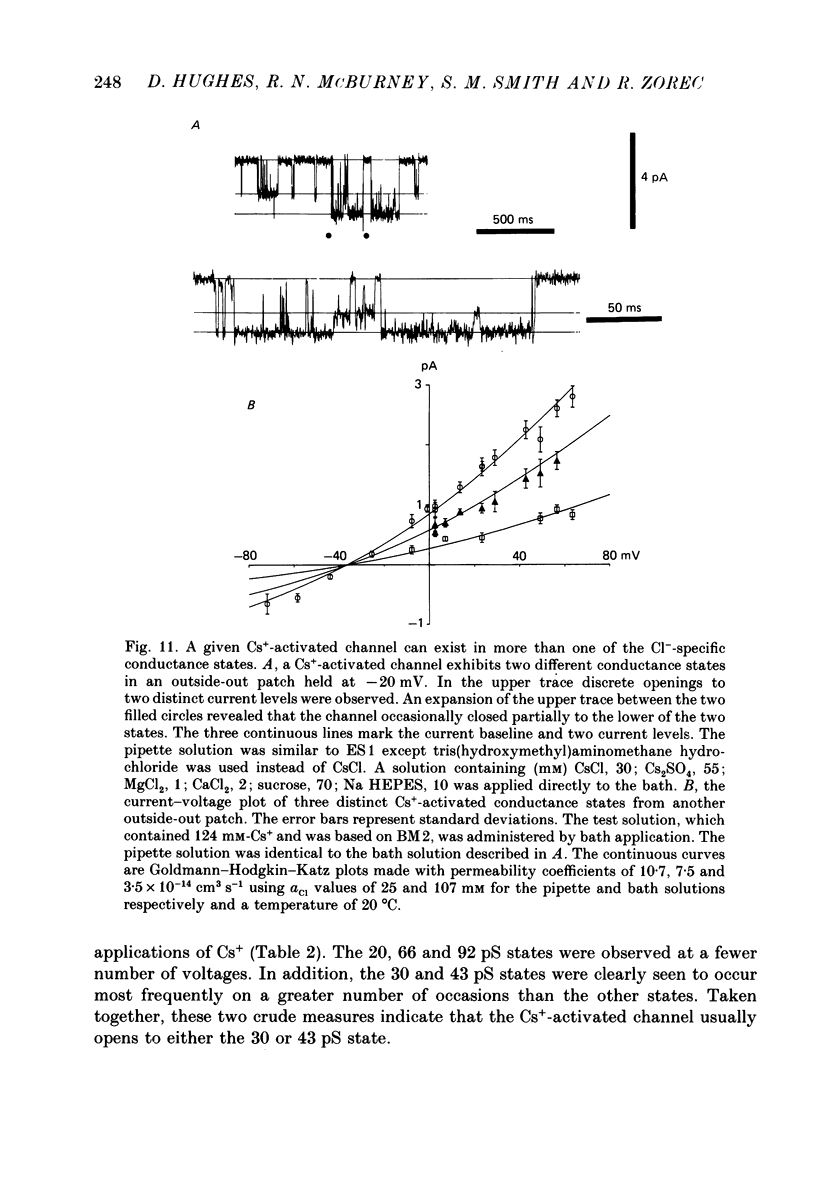
- Geletyuk V. I., Kazachenko V. N. Single Cl- channels in molluscan neurones: multiplicity of the conductance states. J Membr Biol. 1985;86(1):9–15. doi: 10.1007/BF01871605. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hamill O. P., Bormann J., Sakmann B. Activation of multiple-conductance state chloride channels in spinal neurones by glycine and GABA. 1983 Oct 27-Nov 2Nature. 305(5937):805–808. doi: 10.1038/305805a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hamill O. P., Marty A., Neher E., Sakmann B., Sigworth F. J. Improved patch-clamp techniques for high-resolution current recording from cells and cell-free membrane patches. Pflugers Arch. 1981 Aug;391(2):85–100. doi: 10.1007/BF00656997. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hodgkin A. L., McNaughton P. A., Nunn B. J. The ionic selectivity and calcium dependence of the light-sensitive pathway in toad rods. J Physiol. 1985 Jan;358:447–468. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1985.sp015561. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Huguenard J. R., Alger B. E. Whole-cell voltage-clamp study of the fading of GABA-activated currents in acutely dissociated hippocampal neurons. J Neurophysiol. 1986 Jul;56(1):1–18. doi: 10.1152/jn.1986.56.1.1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jefferys J. G., Haas H. L. Synchronized bursting of CA1 hippocampal pyramidal cells in the absence of synaptic transmission. Nature. 1982 Dec 2;300(5891):448–450. doi: 10.1038/300448a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- KATZ B., THESLEFF S. A study of the desensitization produced by acetylcholine at the motor end-plate. J Physiol. 1957 Aug 29;138(1):63–80. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1957.sp005838. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kaneko A., Tachibana M. Effects of gamma-aminobutyric acid on isolated cone photoreceptors of the turtle retina. J Physiol. 1986 Apr;373:443–461. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1986.sp016057. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- McBurney R. N., Barker J. L. GABA-induced conductance fluctuations in cultured spinal neurones. Nature. 1978 Aug 10;274(5671):596–597. doi: 10.1038/274596a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- McBurney R. N., Neering I. R. The measurement of changes in intracellular free calcium during action potentials in mammalian neurones. J Neurosci Methods. 1985 Mar;13(1):65–76. doi: 10.1016/0165-0270(85)90044-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Turnell D. C., Cooper J. D. Rapid assay for amino acids in serum or urine by pre-column derivatization and reversed-phase liquid chromatography. Clin Chem. 1982 Mar;28(3):527–531. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


