Abstract
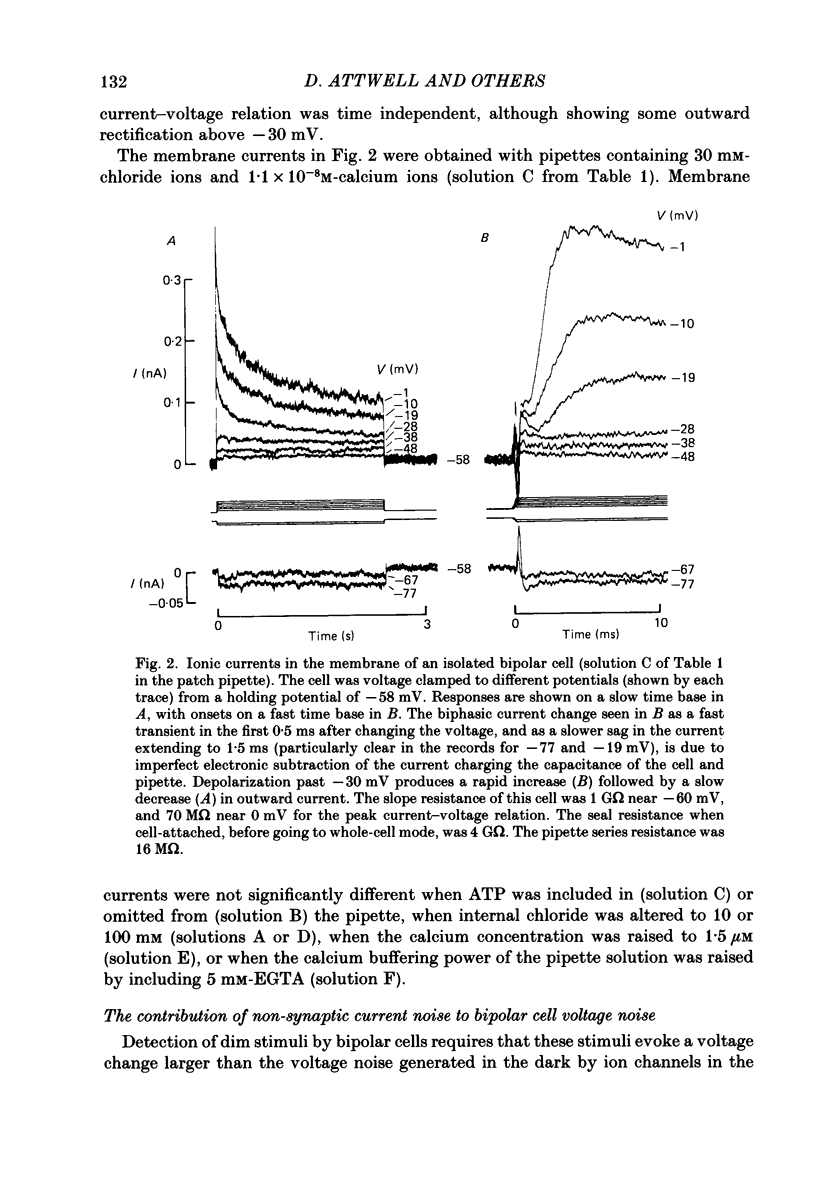
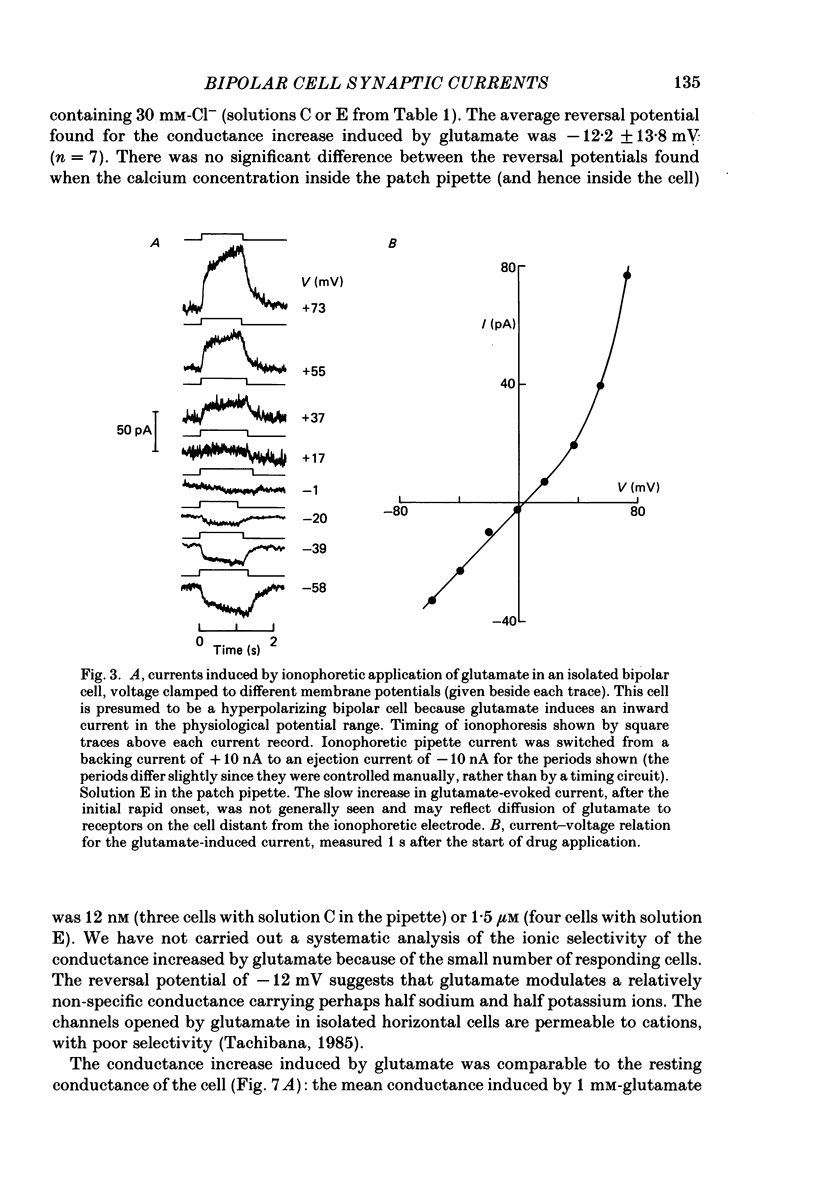
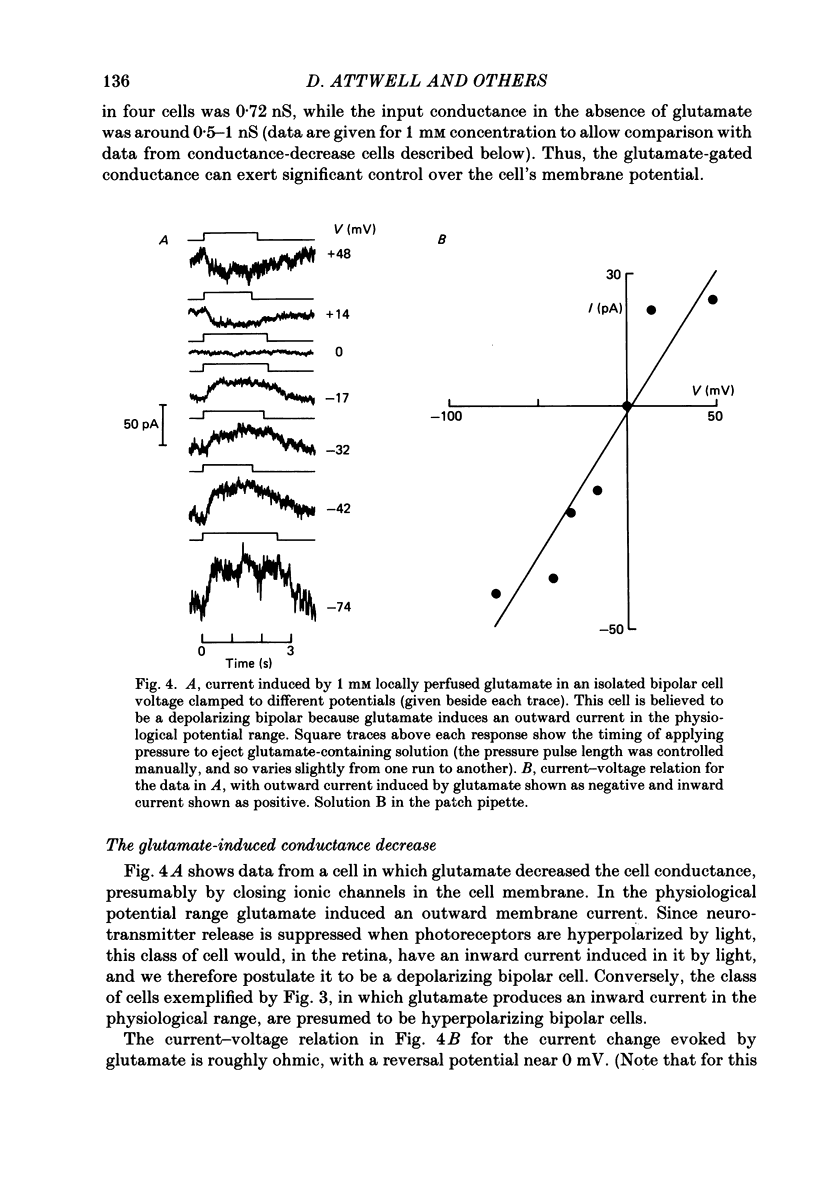
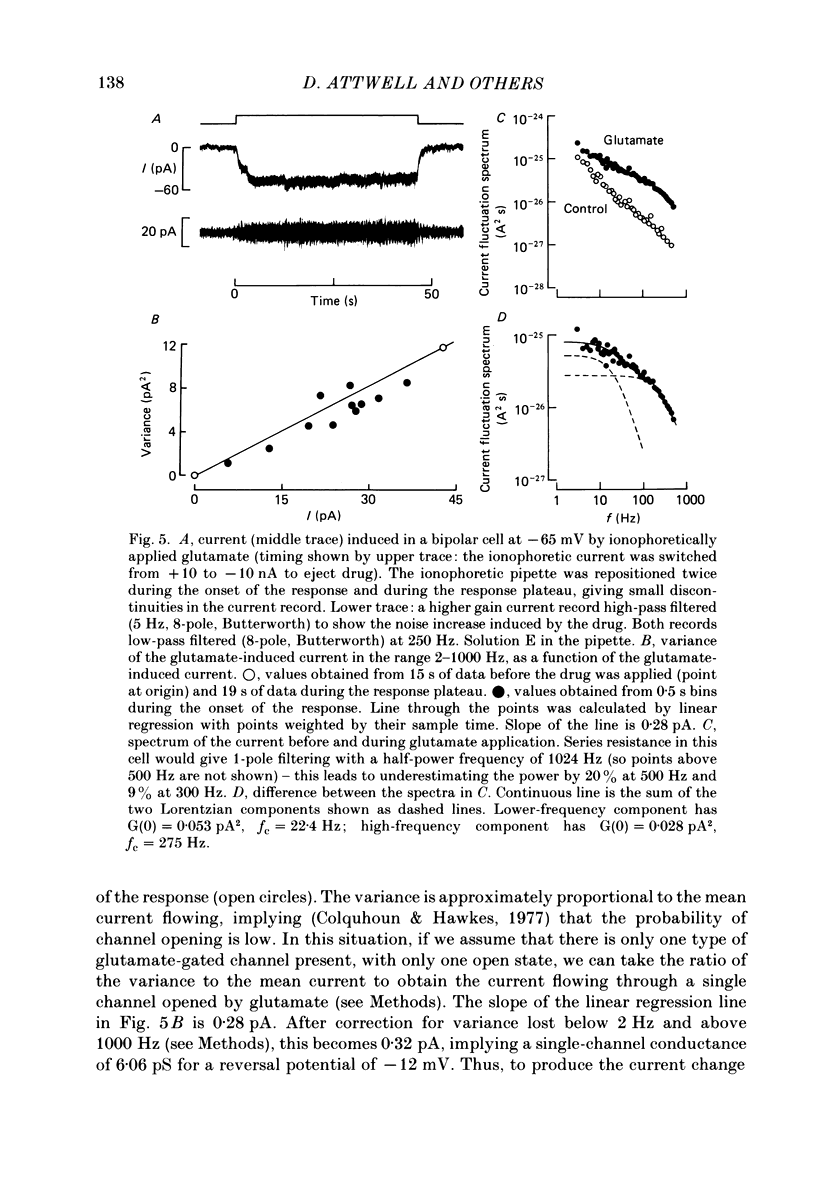
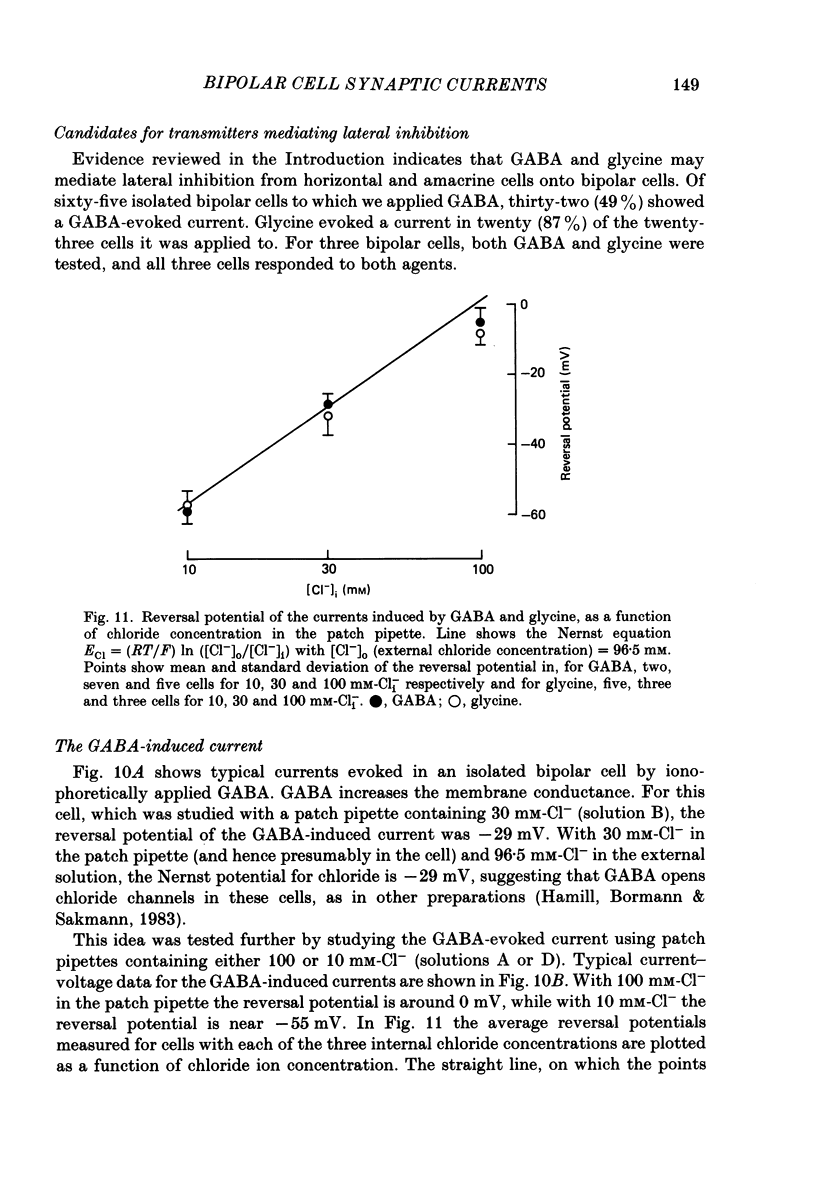
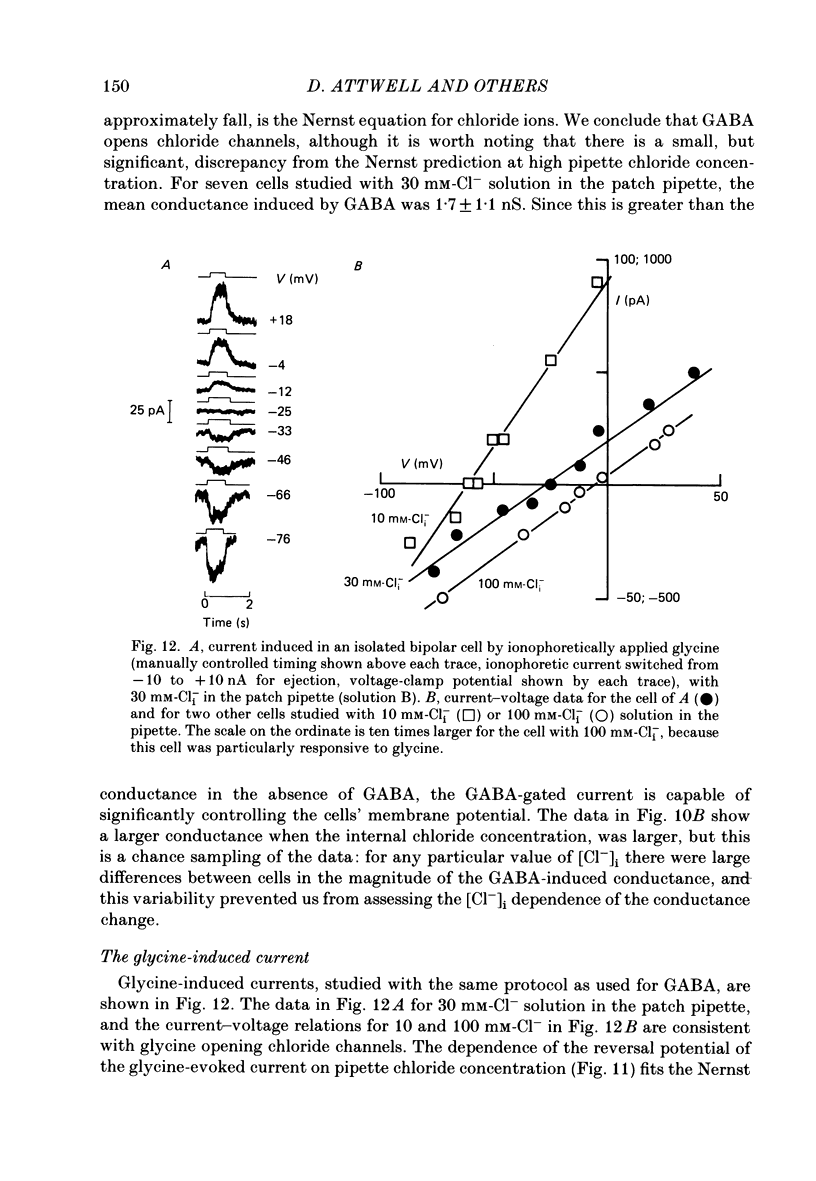
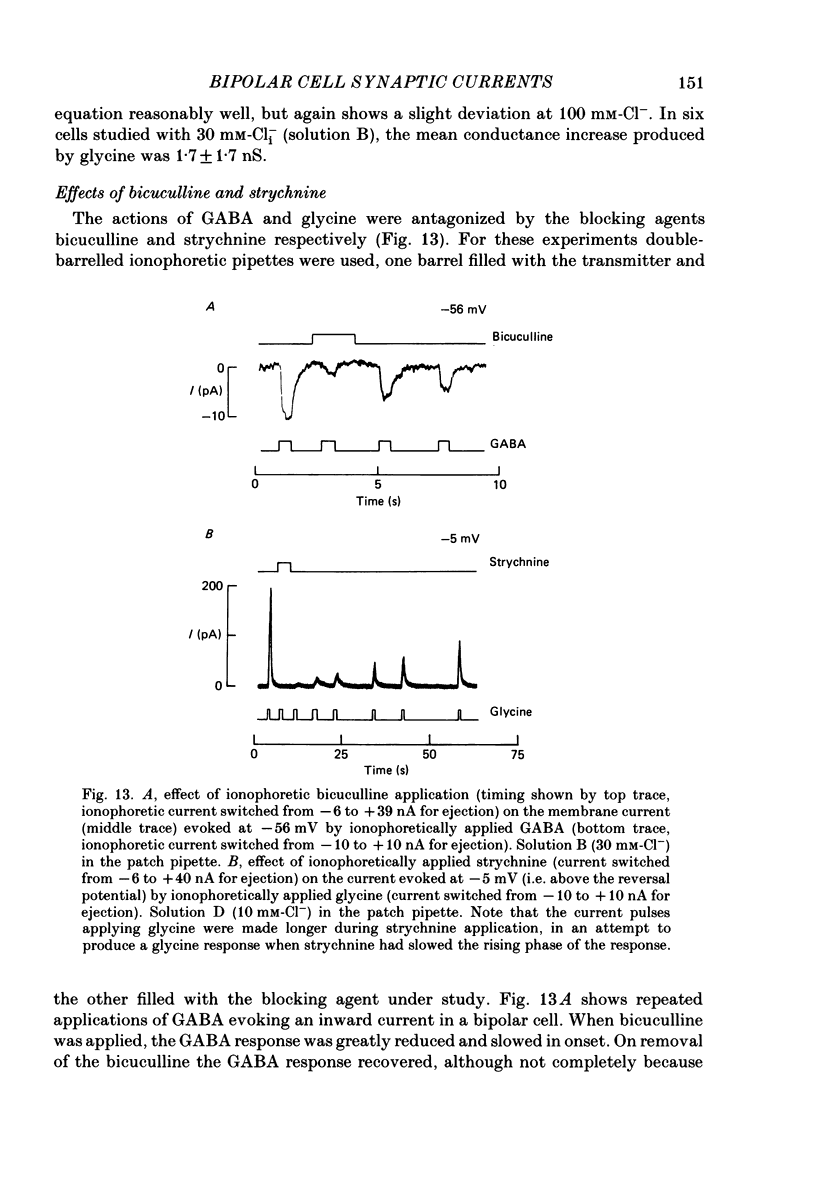
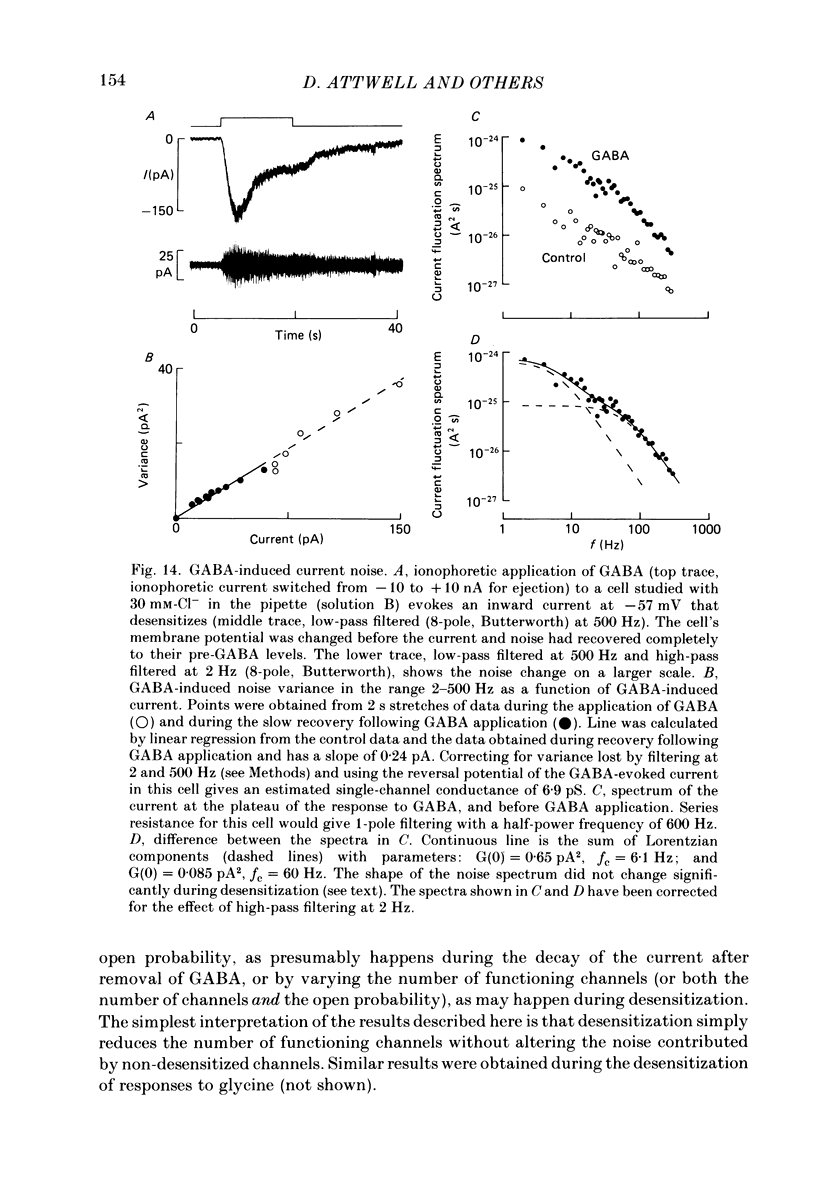
1. Whole-cell patch clamping was used to study the membrane properties of isolated bipolar cells and the currents evoked in them by putative retinal neurotransmitters. 2. Isolated bipolar cells show an approximately ohmic response to voltage steps over most of the physiological response range, with an average input resistance of 1.3 G omega and resting potential of -35 mV. These values are underestimates because of the shunting effect of the seal between the patch electrode and the cell membrane. Depolarization beyond -30 mV produces rapid activation (10-100 ms) of an outward current (carried largely by potassium ions), which then inactivates slowly (0.5-2 s). 3. Of five candidates for the photoreceptor transmitter, four (aspartate, N-acetylhistidine, cadaverine, putrescine) had no effect on bipolar cells. The fifth substance, L-glutamate, opened ionic channels with a mean reversal potential of -12 mV in some cells (presumed hyperpolarizing bipolar cells), and closed channels with a mean reversal potential of -13 mV in other cells (presumed depolarizing bipolar cells). 4. The conductance increase induced by glutamate in presumed hyperpolarizing bipolar cells was associated with an increase in membrane current noise. Noise analysis suggested a single-channel conductance for the glutamate-gated channel of 5.4 pS. The power spectrum of the noise increase required the sum of two Lorentzian curves to fit it, suggesting that the channel can exist in three states. 5. The conductance decrease induced by glutamate in presumed depolarizing bipolar cells was associated with a decrease in membrane current noise that could be described as the sum of two Lorentzian spectra, and which suggested a single-channel conductance of 11 pS. The noise decrease implies that the channels closed by glutamate are not all open in the absence of the transmitter. 6. GABA (gamma-aminobutyric acid) and glycine, transmitters believed to mediate lateral inhibition in the retina, open chloride channels in isolated bipolar cells, and increase the membrane current noise. Noise analysis suggested that the channels gated by GABA and glycine have conductances of 4.4 and 7.5 pS respectively. The noise spectra required the sum of two Lorentzian curves to fit them. 7. By whole-cell patch clamping cells in retinal slices, the synaptic transmitter released by photoreceptors was shown to close channels with an extrapolated reversal potential around -3 mV in depolarizing bipolar cells.(ABSTRACT TRUNCATED AT 400 WORDS)
Full text
PDF










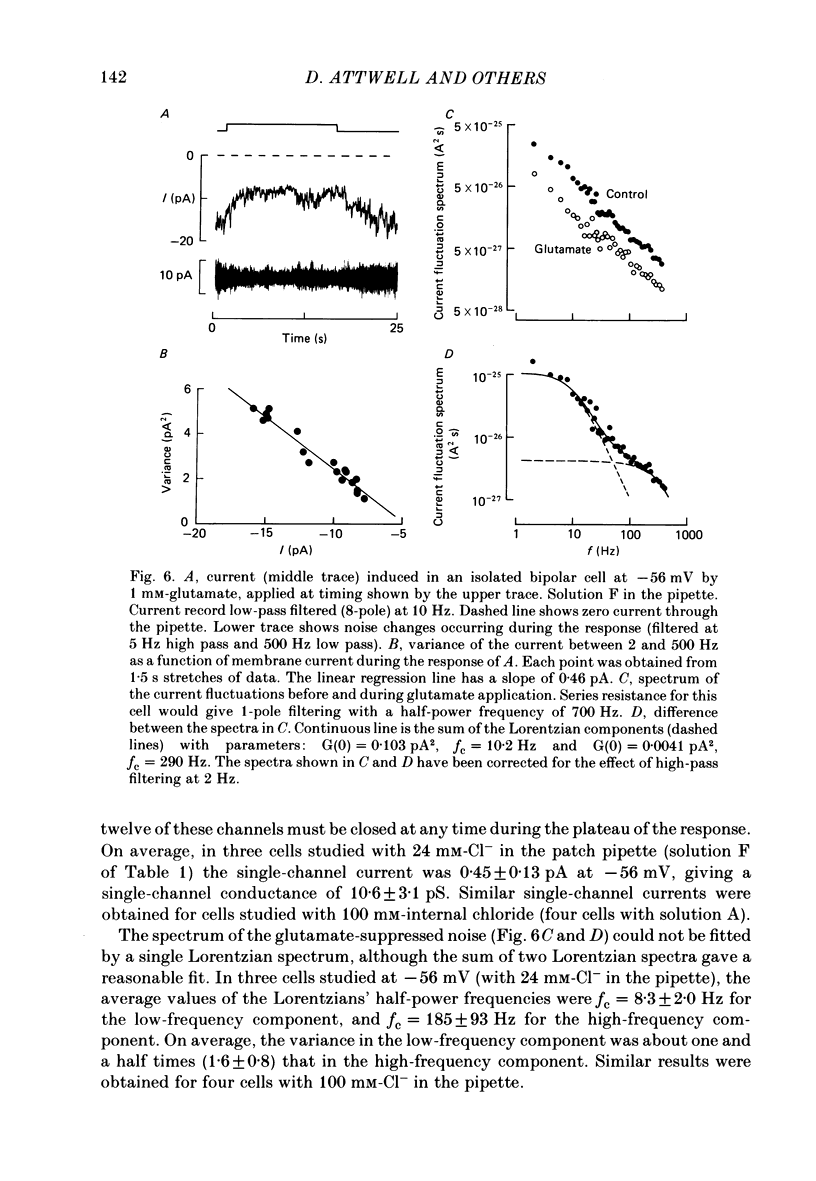
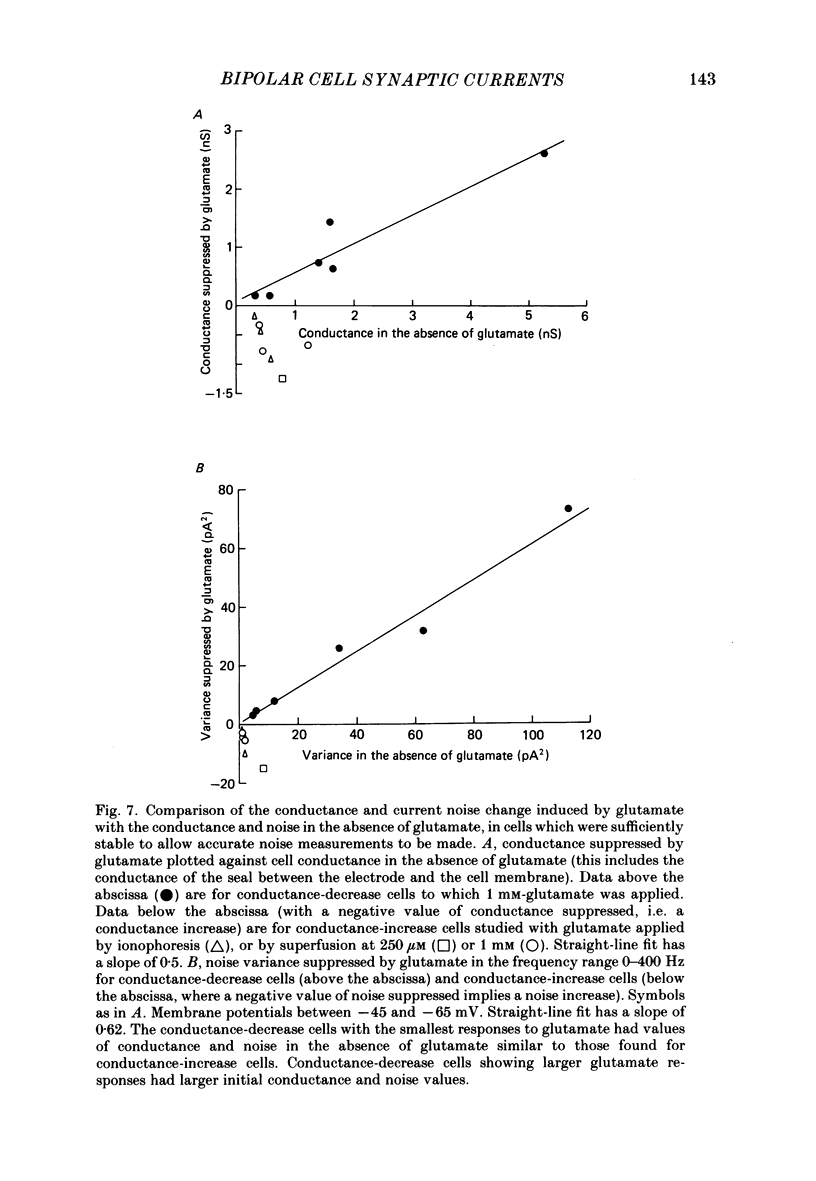



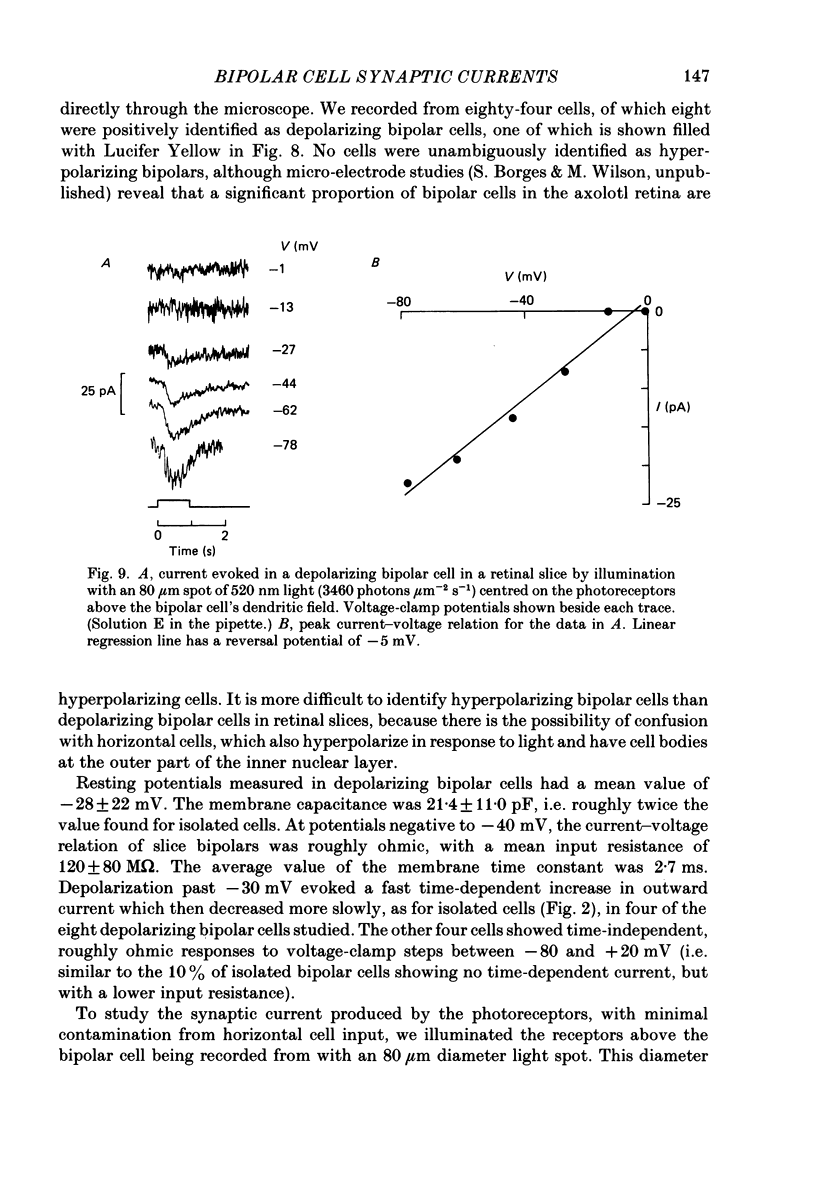
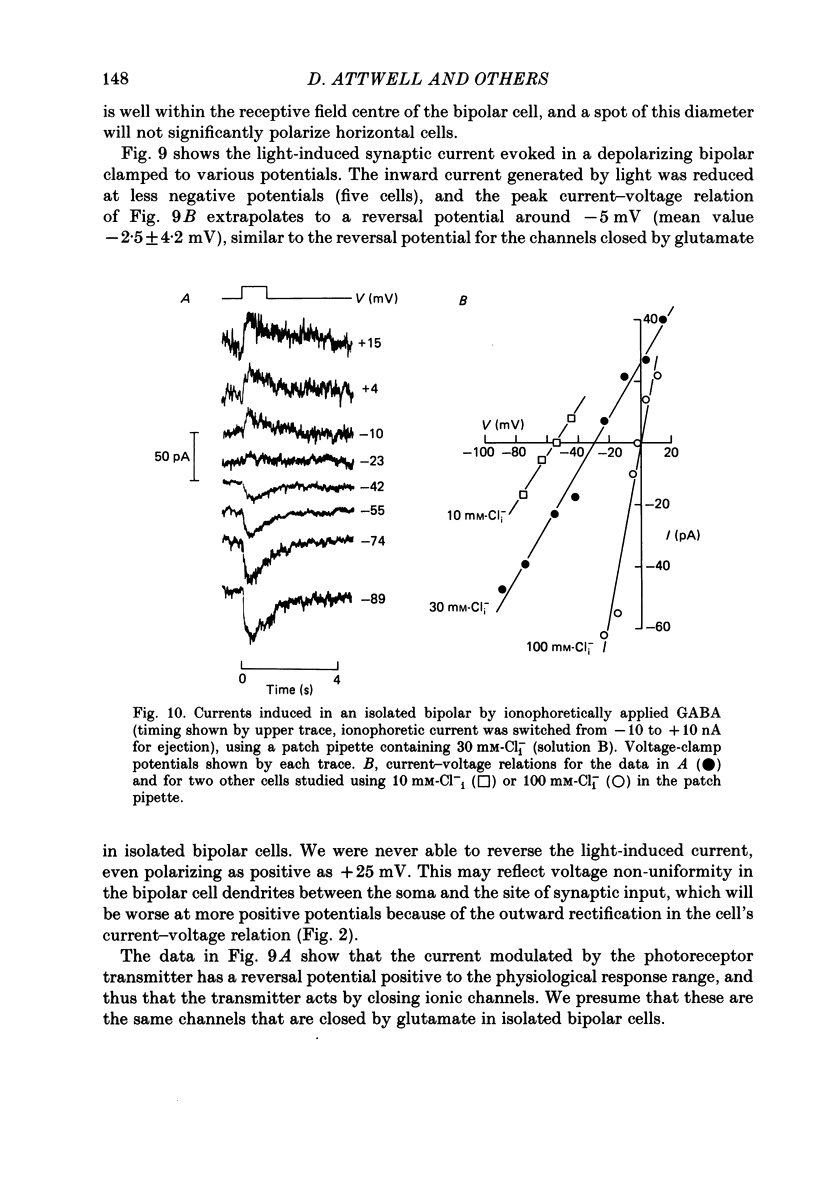









Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Anderson C. R., Cull-Candy S. G., Miledi R. Glutamate current noise: post-synaptic channel kinetics investigated under voltage clamp. J Physiol. 1978 Sep;282:219–242. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1978.sp012459. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Anderson C. R., Stevens C. F. Voltage clamp analysis of acetylcholine produced end-plate current fluctuations at frog neuromuscular junction. J Physiol. 1973 Dec;235(3):655–691. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1973.sp010410. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ashmore J. F., Copenhagen D. R. An analysis of transmission from cones to hyperpolarizing bipolar cells in the retina of the turtle. J Physiol. 1983 Jul;340:569–597. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1983.sp014781. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ashmore J. F., Copenhagen D. R. Different postsynaptic events in two types of retinal bipolar cell. Nature. 1980 Nov 6;288(5786):84–86. doi: 10.1038/288084a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ashmore J. F., Falk G. An analysis of voltage noise in rod bipolar cells of the dogfish retina. J Physiol. 1982 Nov;332:273–297. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1982.sp014413. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ashmore J. F., Falk G. Responses of rod bipolar cells in the dark-adapted retina of the dogfish, Scyliorhinus canicula. J Physiol. 1980 Mar;300:115–150. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1980.sp013155. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Attwell D. The Sharpey-Schafer lecture. Ion channels and signal processing in the outer retina. Q J Exp Physiol. 1986 Oct;71(4):497–536. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Attwell D., Werblin F. S., Wilson M. The properties of single cones isolated from the tiger salamander retina. J Physiol. 1982 Jul;328:259–283. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1982.sp014263. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Attwell D., Werblin F. S., Wilson M., Wu S. M. A sign-reversing pathway from rods to double and single cones in the retina of the tiger salamander. J Physiol. 1983 Mar;336:313–333. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1983.sp014583. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Attwell D., Wilson M. Behaviour of the rod network in the tiger salamander retina mediated by membrane properties of individual rods. J Physiol. 1980 Dec;309:287–315. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1980.sp013509. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bader C. R., Macleish P. R., Schwartz E. A. A voltage-clamp study of the light response in solitary rods of the tiger salamander. J Physiol. 1979 Nov;296:1–26. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1979.sp012988. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Baylor D. A., Fettiplace R. Kinetics of synaptic transfer from receptors to ganglion cells in turtle retina. J Physiol. 1977 Oct;271(2):425–448. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1977.sp012007. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Baylor D. A., Fuortes M. G., O'Bryan P. M. Receptive fields of cones in the retina of the turtle. J Physiol. 1971 Apr;214(2):265–294. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1971.sp009432. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cahalan M. D., Chandy K. G., DeCoursey T. E., Gupta S. A voltage-gated potassium channel in human T lymphocytes. J Physiol. 1985 Jan;358:197–237. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1985.sp015548. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cervetto L., MacNichol E. F., Jr Inactivation of horizontal cells in turtle retina by glutamate and aspartate. Science. 1972 Nov 17;178(4062):767–768. doi: 10.1126/science.178.4062.767. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chin C. A., Lam D. M. The uptake and release of [3H]glycine in the goldfish retina. J Physiol. 1980 Nov;308:185–195. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1980.sp013467. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Colquhoun D., Dreyer F., Sheridan R. E. The actions of tubocurarine at the frog neuromuscular junction. J Physiol. 1979 Aug;293:247–284. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1979.sp012888. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Colquhoun D., Hawkes A. G. Relaxation and fluctuations of membrane currents that flow through drug-operated channels. Proc R Soc Lond B Biol Sci. 1977 Nov 14;199(1135):231–262. doi: 10.1098/rspb.1977.0137. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Connor J. A., Stevens C. F. Inward and delayed outward membrane currents in isolated neural somata under voltage clamp. J Physiol. 1971 Feb;213(1):1–19. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1971.sp009364. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Connor J. A., Stevens C. F. Voltage clamp studies of a transient outward membrane current in gastropod neural somata. J Physiol. 1971 Feb;213(1):21–30. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1971.sp009365. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cull-Candy S. G., Ogden D. C. Ion channels activated by L-glutamate and GABA in cultured cerebellar neurons of the rat. Proc R Soc Lond B Biol Sci. 1985 May 22;224(1236):367–373. doi: 10.1098/rspb.1985.0038. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Detwiler P. B., Hodgkin A. L., McNaughton P. A. A surprising property of electrical spread in the network of rods in the turtle's retina. Nature. 1978 Aug 10;274(5671):562–565. doi: 10.1038/274562a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dionne V. E. Characterization of drug iontophoresis with a fast microassay technique. Biophys J. 1976 Jul;16(7):705–717. doi: 10.1016/S0006-3495(76)85723-2. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fenwick E. M., Marty A., Neher E. A patch-clamp study of bovine chromaffin cells and of their sensitivity to acetylcholine. J Physiol. 1982 Oct;331:577–597. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1982.sp014393. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fukushima Y., Hagiwara S., Henkart M. Potassium current in clonal cytotoxic T lymphocytes from the mouse. J Physiol. 1984 Jun;351:645–656. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1984.sp015268. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hamill O. P., Bormann J., Sakmann B. Activation of multiple-conductance state chloride channels in spinal neurones by glycine and GABA. 1983 Oct 27-Nov 2Nature. 305(5937):805–808. doi: 10.1038/305805a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hamill O. P., Marty A., Neher E., Sakmann B., Sigworth F. J. Improved patch-clamp techniques for high-resolution current recording from cells and cell-free membrane patches. Pflugers Arch. 1981 Aug;391(2):85–100. doi: 10.1007/BF00656997. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hollyfield J. G., Rayborn M. E., Sarthy P. V., Lam D. M. The emergence, localization and maturation of neurotransmitter systems during development of the retina in Xenopus laevis. I. Gamma aminobutyric acid. J Comp Neurol. 1979 Dec 15;188(4):587–598. doi: 10.1002/cne.901880406. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ishida A. T., Kaneko A., Tachibana M. Responses of solitary retinal horizontal cells from Carassius auratus to L-glutamate and related amino acids. J Physiol. 1984 Mar;348:255–270. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1984.sp015108. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ishida A. T., Neyton J. Quisqualate and L-glutamate inhibit retinal horizontal-cell responses to kainate. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1985 Mar;82(6):1837–1841. doi: 10.1073/pnas.82.6.1837. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kaneko A. Physiological studies of single retinal cells and their morphological identification. Vision Res. 1971;Suppl 3:17–26. doi: 10.1016/0042-6989(71)90027-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kaneko A., Tachibana M. A voltage-clamp analysis of membrane currents in solitary bipolar cells dissociated from Carassius auratus. J Physiol. 1985 Jan;358:131–152. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1985.sp015544. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lasansky A. Contacts between receptors and electrophysiologically identified neurones in the retina of the larval tiger salamander. J Physiol. 1978 Dec;285:531–542. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1978.sp012587. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lasansky A. Organization of the outer synaptic layer in the retina of the larval tiger salamander. Philos Trans R Soc Lond B Biol Sci. 1973;265(872):471–489. doi: 10.1098/rstb.1973.0033. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lasater E. M., Dowling J. E., Ripps H. Pharmacological properties of isolated horizontal and bipolar cells from the skate retina. J Neurosci. 1984 Aug;4(8):1966–1975. doi: 10.1523/JNEUROSCI.04-08-01966.1984. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Marc R. E., Stell W. K., Bok D., Lam D. M. GABA-ergic pathways in the goldfish retina. J Comp Neurol. 1978 Nov 15;182(2):221–244. doi: 10.1002/cne.901820204. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Marr D., Hildreth E. Theory of edge detection. Proc R Soc Lond B Biol Sci. 1980 Feb 29;207(1167):187–217. doi: 10.1098/rspb.1980.0020. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Marr D., Ullman S. Directional selectivity and its use in early visual processing. Proc R Soc Lond B Biol Sci. 1981 Mar 6;211(1183):151–180. doi: 10.1098/rspb.1981.0001. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Matthews-Bellinger J., Salpeter M. M. Distribution of acetylcholine receptors at frog neuromuscular junctions with a discussion of some physiological implications. J Physiol. 1978 Jun;279:197–213. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1978.sp012340. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Miller A. M., Schwartz E. A. Evidence for the identification of synaptic transmitters released by photoreceptors of the toad retina. J Physiol. 1983 Jan;334:325–349. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1983.sp014497. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Miller R. F., Dacheux R. F. Intracellular chloride in retinal neurons: measurement and meaning. Vision Res. 1983;23(4):399–411. doi: 10.1016/0042-6989(83)90087-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Miller R. F., Dacheux R. F. Synaptic organization and ionic basis of on and off channels in mudpuppy retina. III. A model of ganglion cell receptive field organization based on chloride-free experiments. J Gen Physiol. 1976 Jun;67(6):679–690. doi: 10.1085/jgp.67.6.679. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Miller R. F., Frumkes T. E., Slaughter M., Dacheux R. F. Physiological and pharmacological basis of GABA and glycine action on neurons of mudpuppy retina. I. Receptors, horizontal cells, bipolars, and G-cells. J Neurophysiol. 1981 Apr;45(4):743–763. doi: 10.1152/jn.1981.45.4.743. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Murakami M., Otsu K., Otsuka T. Effects of chemicals on receptors and horizontal cells in the retina. J Physiol. 1972 Dec;227(3):899–913. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1972.sp010065. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nowak L., Bregestovski P., Ascher P., Herbet A., Prochiantz A. Magnesium gates glutamate-activated channels in mouse central neurones. Nature. 1984 Feb 2;307(5950):462–465. doi: 10.1038/307462a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rayborn M. E., Sarthy P. V., Lam D. M., Hollyfield J. G. The emergence, localization, and maturation of neurotransmitter systems during development of the retina in Xenopus laevis: II. Glycine. J Comp Neurol. 1981 Feb 1;195(4):585–593. doi: 10.1002/cne.901950404. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Saito T., Kondo H., Toyoda J. Rod and cone signals in the on-center bipolar cell: their different ionic mechanisms. Vision Res. 1978;18(5):591–595. doi: 10.1016/0042-6989(78)90208-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schwartz E. A. Calcium-independent release of GABA from isolated horizontal cells of the toad retina. J Physiol. 1982 Feb;323:211–227. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1982.sp014069. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schwartz E. A. Responses of bipolar cells in the retina of the turtle. J Physiol. 1974 Jan;236(1):211–224. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1974.sp010431. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schwartz E. A. Voltage noise observed in rods of the turtle retina. J Physiol. 1977 Nov;272(2):217–246. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1977.sp012042. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shantz M., Naka K. The bipolar cell. Vision Res. 1976;16(12):1517–1519. doi: 10.1016/0042-6989(76)90175-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shiells R. A., Falk G., Naghshineh S. Action of glutamate and aspartate analogues on rod horizontal and bipolar cells. Nature. 1981 Dec 10;294(5841):592–594. doi: 10.1038/294592a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Simon E. J., Lamb T. D., Hodgkin A. L. Spontaneous voltage fluctuations in retinal cones and bipolar cells. Nature. 1975 Aug 21;256(5519):661–662. doi: 10.1038/256661a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Slaughter M. M., Miller R. F. 2-amino-4-phosphonobutyric acid: a new pharmacological tool for retina research. Science. 1981 Jan 9;211(4478):182–185. doi: 10.1126/science.6255566. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Slaughter M. M., Miller R. F. An excitatory amino acid antagonist blocks cone input to sign-conserving second-order retinal neurons. Science. 1983 Mar 11;219(4589):1230–1232. doi: 10.1126/science.6131536. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Slaughter M. M., Miller R. F. Characterization of an extended glutamate receptor of the on bipolar neuron in the vertebrate retina. J Neurosci. 1985 Jan;5(1):224–233. doi: 10.1523/JNEUROSCI.05-01-00224.1985. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Slaughter M. M., Miller R. F. The role of excitatory amino acid transmitters in the mudpuppy retina: an analysis with kainic acid and N-methyl aspartate. J Neurosci. 1983 Aug;3(8):1701–1711. doi: 10.1523/JNEUROSCI.03-08-01701.1983. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Srinivasan M. V., Laughlin S. B., Dubs A. Predictive coding: a fresh view of inhibition in the retina. Proc R Soc Lond B Biol Sci. 1982 Nov 22;216(1205):427–459. doi: 10.1098/rspb.1982.0085. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tachibana M., Kaneko A. gamma-Aminobutyric acid acts at axon terminals of turtle photoreceptors: difference in sensitivity among cell types. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1984 Dec;81(24):7961–7964. doi: 10.1073/pnas.81.24.7961. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tachibana M. Permeability changes induced by L-glutamate in solitary retinal horizontal cells isolated from Carassius auratus. J Physiol. 1985 Jan;358:153–167. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1985.sp015545. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Toyoda J. Membrane resistance changes underlying the bipolar cell response in the carp retina. Vision Res. 1973 Feb;13(2):283–294. doi: 10.1016/0042-6989(73)90107-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Werblin F. S., Dowling J. E. Organization of the retina of the mudpuppy, Necturus maculosus. II. Intracellular recording. J Neurophysiol. 1969 May;32(3):339–355. doi: 10.1152/jn.1969.32.3.339. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Werblin F. S. Transmission along and between rods in the tiger salamander retina. J Physiol. 1978 Jul;280:449–470. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1978.sp012394. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wong-Riley M. T. Synaptic orgnization of the inner plexiform layer in the retina of the tiger salamander. J Neurocytol. 1974 Mar;3(1):1–33. doi: 10.1007/BF01111929. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wu S. M. Effects of gamma-aminobutyric acid on cones and bipolar cells of the tiger salamander retina. Brain Res. 1986 Feb 12;365(1):70–77. doi: 10.1016/0006-8993(86)90723-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]