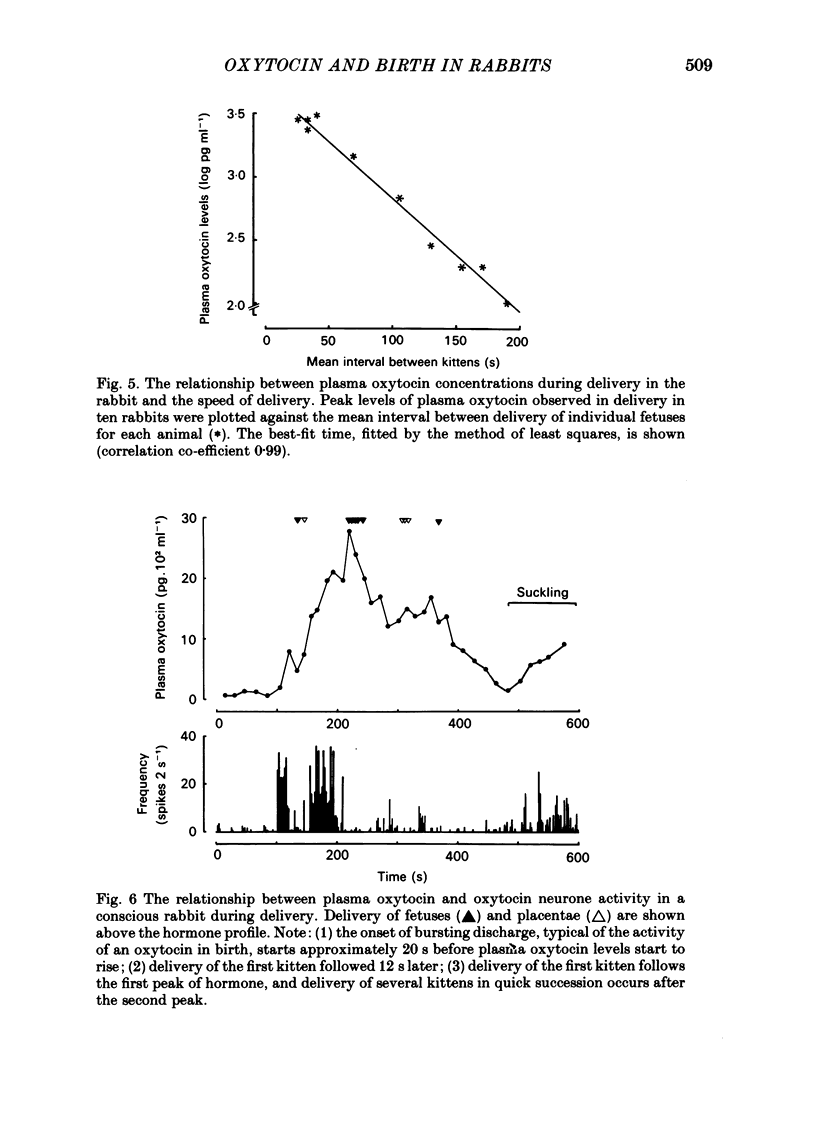
Abstract
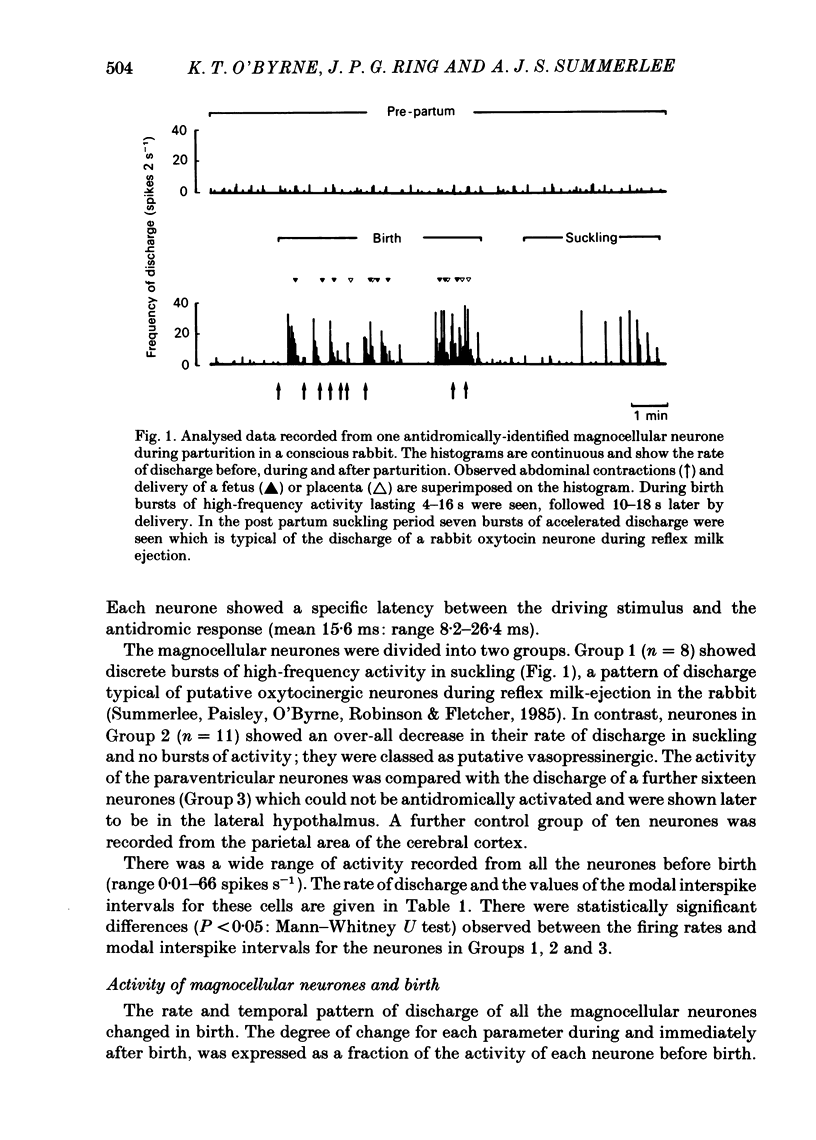
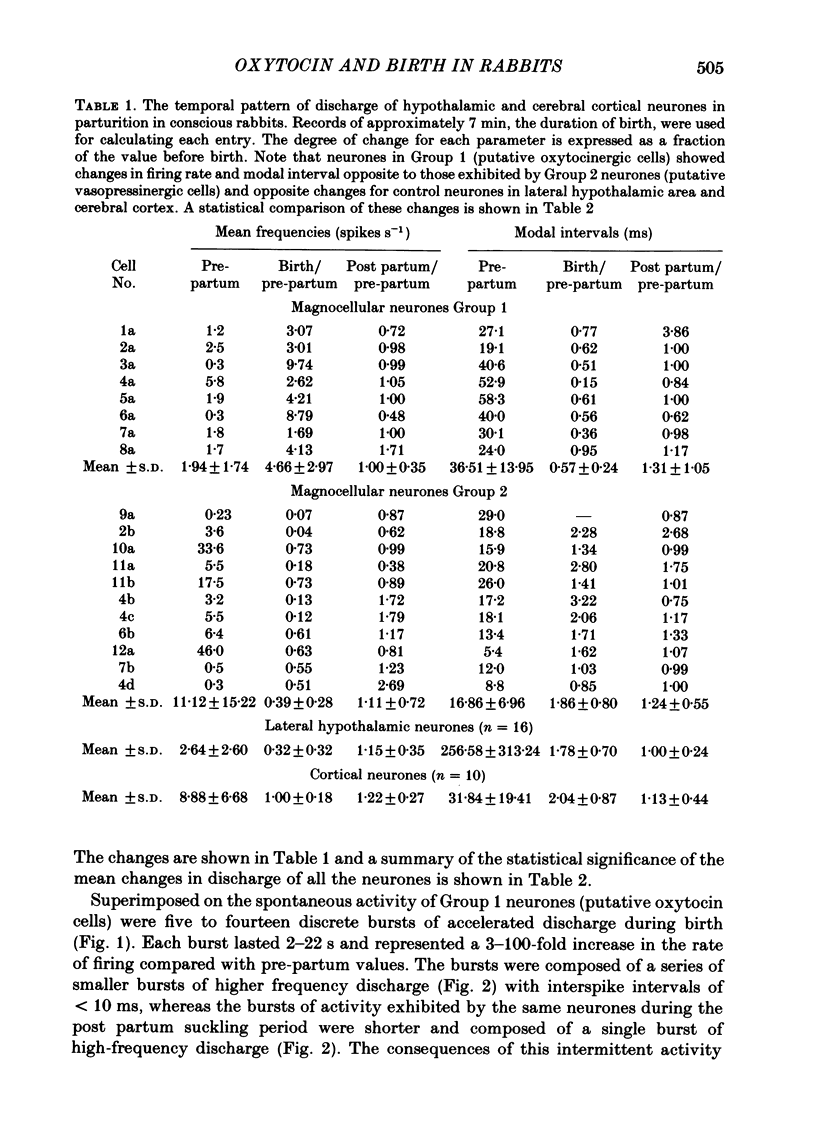
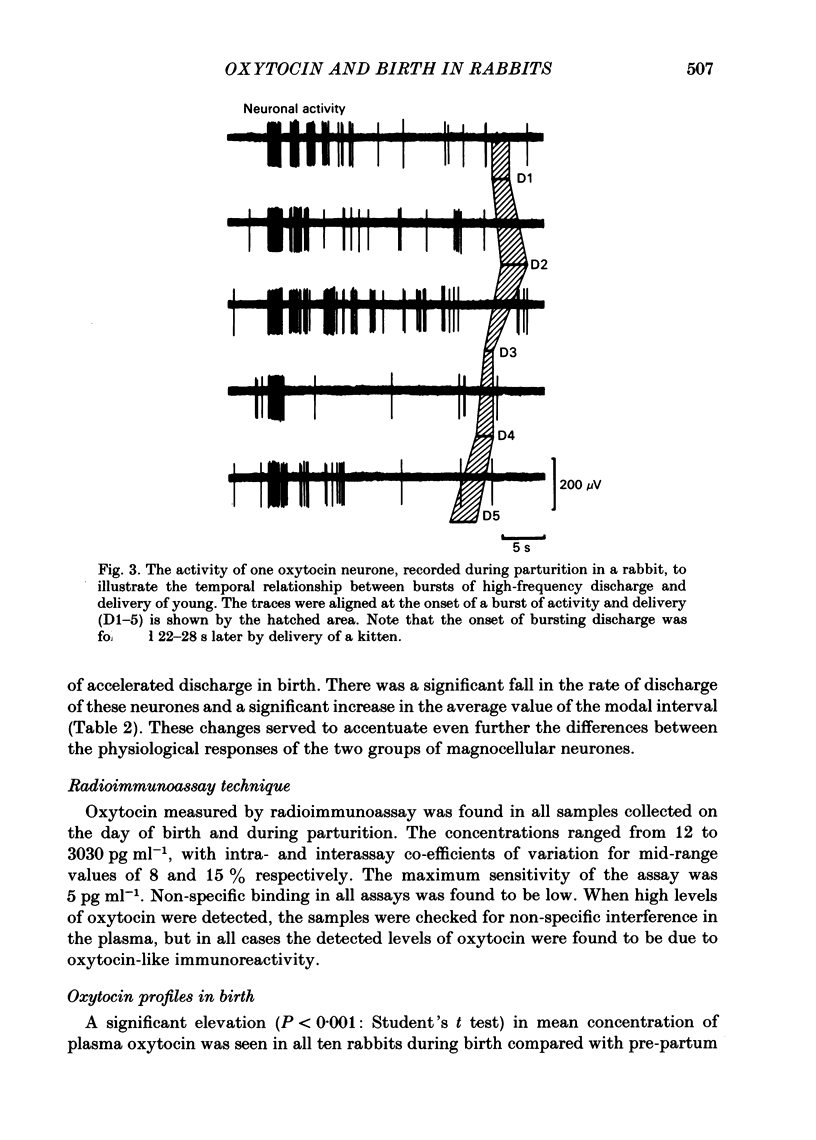
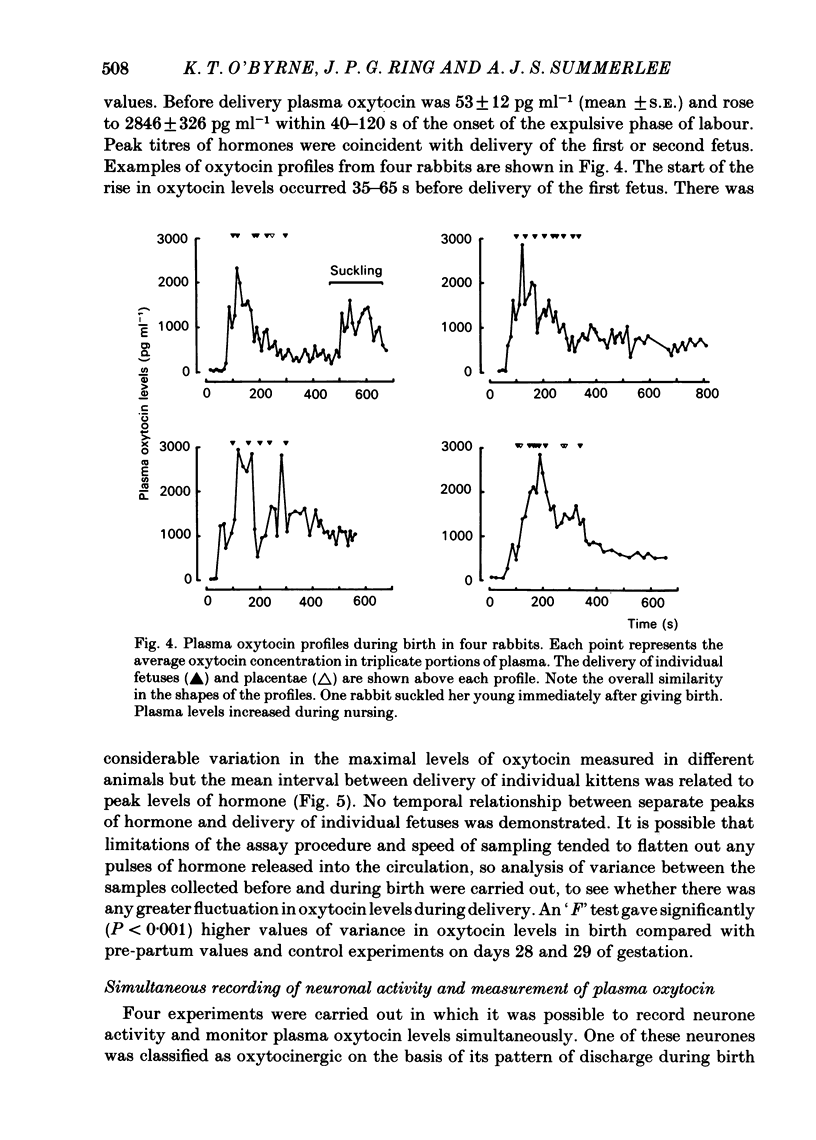
The extracellular electrical activity of magnocellular neurones was recorded from unanaesthetized, unrestrained rabbits in birth and the post partum suckling period. The activity of oxytocin neurones was differentiated from that of vasopressin cells on the basis of their stereotyped activity in suckling. Oxytocin neurones showed five to fourteen discrete bursts of accelerated discharge in parturition. Each burst lasted 2-22 s and represented a 3-100-fold increase in the rate of firing, compared with pre-partum values, and was followed 10-34 s later by delivery. After parturition, the spontaneous activity of these neurones returned to pre-partum rates of firing. Vasopressin neurones did not show any bursts of discharge in delivery. There was a significant fall in the discharge frequency compared with pre-partum levels (P less than 0.05: Student's t test) and a significant (P less than 0.01) lengthening of the modal interspike interval. Serial blood samples were obtained during parturition in ten rabbits. Simultaneous recordings of magnocellular neurones activity and plasma oxytocin measurements were made in four of these experiments. Plasma oxytocin profiles were related to the observed events of parturition. Frequent blood samples (0.2-0.3 ml every 10-15 s) were taken throughout delivery and plasma oxytocin measured by sensitive radioimmunoassay in unextracted plasma (lower limit sensitivity of assay 5 pg ml-1). Before birth, plasma oxytocin was 53 +/- 12 pg ml-1 (mean +/- S.E. of mean) and rose to 2846 +/- 326 pg ml-1 within 40-120 s of the onset of the expulsive phase of delivery. Peak concentrations of oxytocin were coincident with delivery of the first or second fetus. No sign of pulsatile release of oxytocin was demonstrated in the profiles but significantly (P less than 0.001) greater variance in oxytocin titres was found during birth compared with pre-partum values which is suggestive of pulsatile release. There was a straight line relationship between peak oxytocin concentrations in the plasma and the speed of delivery, implying that oxytocin facilitates as well as maintains labour in the rabbit.
Full text
PDF







Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Boer K., Nolten J. W. Hypothalamic paraventricular unit activity during labour in the rat. J Endocrinol. 1978 Jan;76(1):155–163. doi: 10.1677/joe.0.0760155. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Burns B. D., Webb A. C. The spontaneous activity of neurones in the cat's cerebral cortex. Proc R Soc Lond B Biol Sci. 1976 Oct 15;194(1115):211–223. doi: 10.1098/rspb.1976.0074. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dreifuss J. J., Tribollet E., Baertschi A. J. Excitation of supraoptic neurones by vaginal distention in lactating rats; correlation with neurohypophysial hormone release. Brain Res. 1976 Sep 3;113(3):600–605. doi: 10.1016/0006-8993(76)90062-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fabian M., Forsling M. L., Jones J. J., Lee J. The release, clearance and plasma protein binding of oxytocin in the anaesthetized rat. J Endocrinol. 1969 Feb;43(2):175–189. doi: 10.1677/joe.0.0430175. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Flint A. P., Forsling M. L., Mitchell M. D. Blockade of the Ferguson reflex by lumbar epidural anaesthesia in the parturient sheep: effects on oxytocin secretion and uterine venous prostaglandin F levels. Horm Metab Res. 1978 Nov;10(6):545–547. doi: 10.1055/s-0028-1093388. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fuchs A. R., Dawood M. Y. Oxytocin release and uterine activation during parturition iin rabbits. Endocrinology. 1980 Oct;107(4):1117–1126. doi: 10.1210/endo-107-4-1117. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fuchs A. R., Saito S. Pituitary oxytocin and vasopressin content of pregnant rats before, during and after parturition. Endocrinology. 1971 Mar;88(3):574–578. doi: 10.1210/endo-88-3-574. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gibbens G. L., Chard T. Observations on maternal oxytocin release during human labor and the effect of intravenous alcohol administration. Am J Obstet Gynecol. 1976 Sep 15;126(2):243–246. doi: 10.1016/0002-9378(76)90283-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Haldar J. Independent release of oxytocin and vasopressin during parturition in the rabbit. J Physiol. 1970 Mar;206(3):723–730. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1970.sp009040. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lincoln D. W. Labour in the rabbit: effect of electrical stimulation applied to the infundibulum and median eminence. J Endocrinol. 1971 Aug;50(4):607–618. doi: 10.1677/joe.0.0500607. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Otsuki Y., Yamaji K., Fujita M., Takagi T., Tanizawa O. Serial plasma oxytocin levels during pregnancy and labor. Acta Obstet Gynecol Scand. 1983;62(1):15–18. doi: 10.3109/00016348309155750. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Paisley A. C., Summerlee A. J. Activity of putative oxytocin neurones during reflex milk ejection in conscious rabbits. J Physiol. 1984 Feb;347:465–478. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1984.sp015076. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Robinson I. C. The development and evaluation of a sensitive and specific radioimmunoassay for oxytocin in unextracted plasma. J Immunoassay. 1980;1(3):323–347. doi: 10.1080/01971528008058475. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Summerlee A. J. Extracellular recordings from oxytocin neurones during the expulsive phase of birth in unanaesthetized rats. J Physiol. 1981 Dec;321:1–9. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1981.sp013967. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Summerlee A. J., Paisley A. C., Goodall C. L. A method for determining the position of chronically implanted platinum microwire electrodes. J Neurosci Methods. 1982 Jan;5(1-2):7–11. doi: 10.1016/0165-0270(82)90045-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


