Abstract
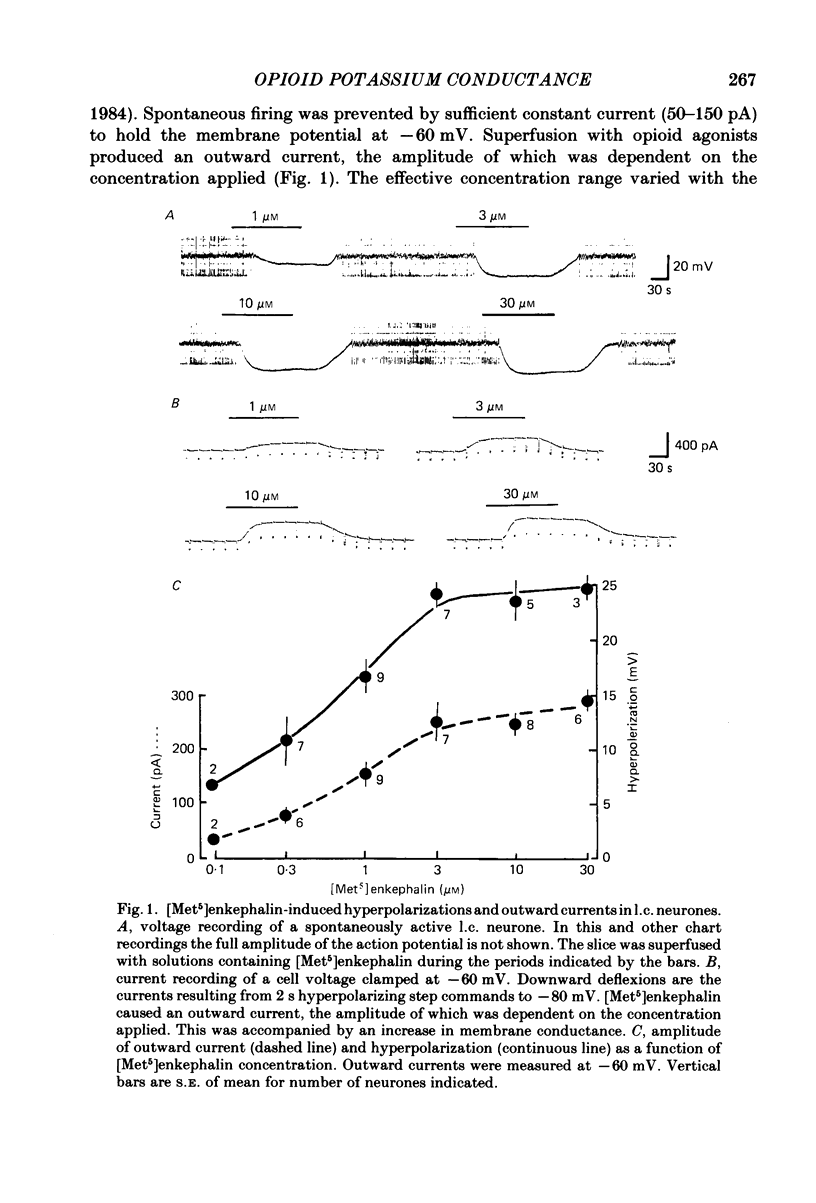
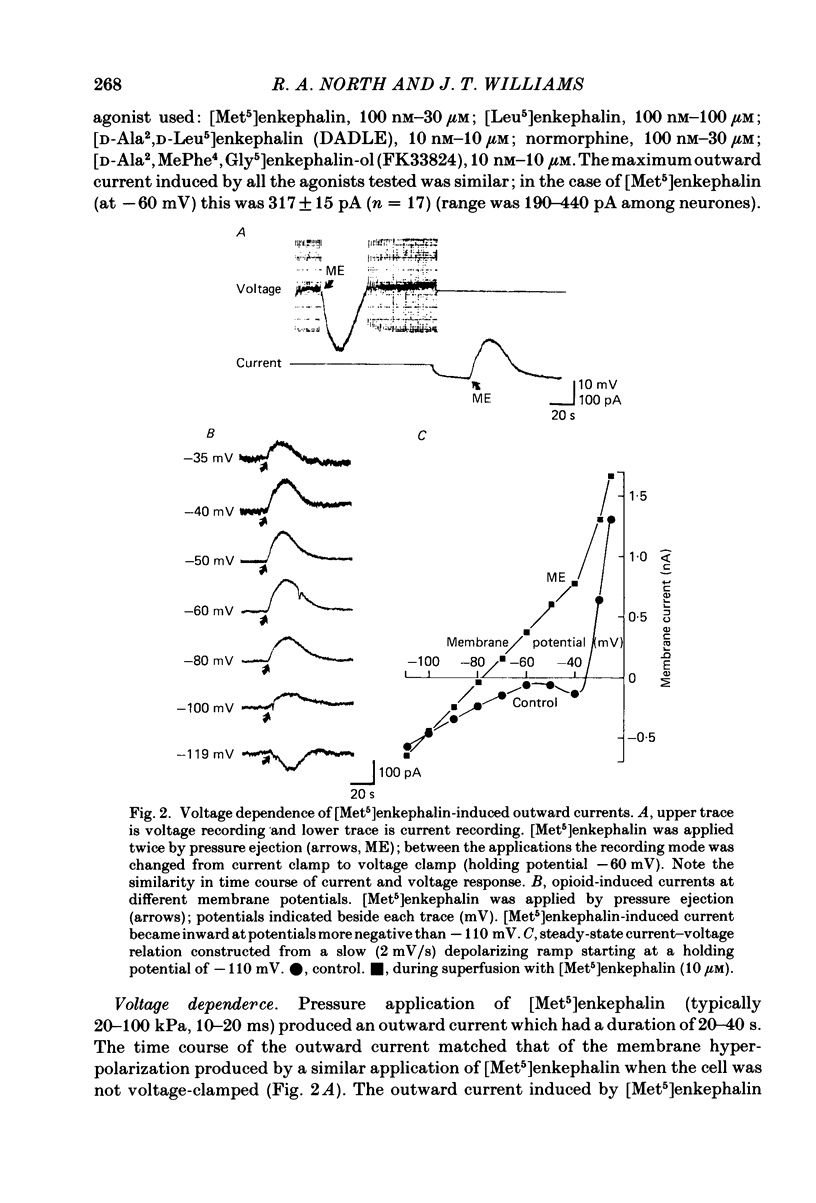
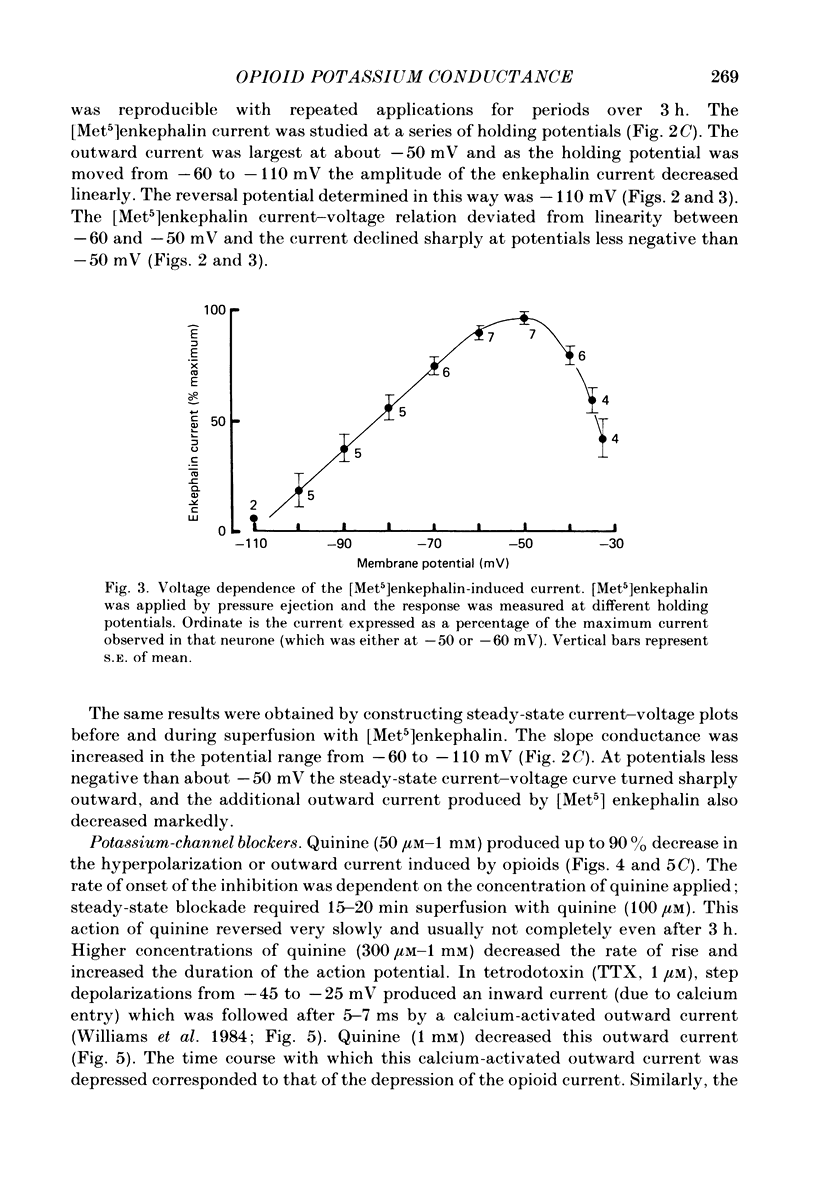
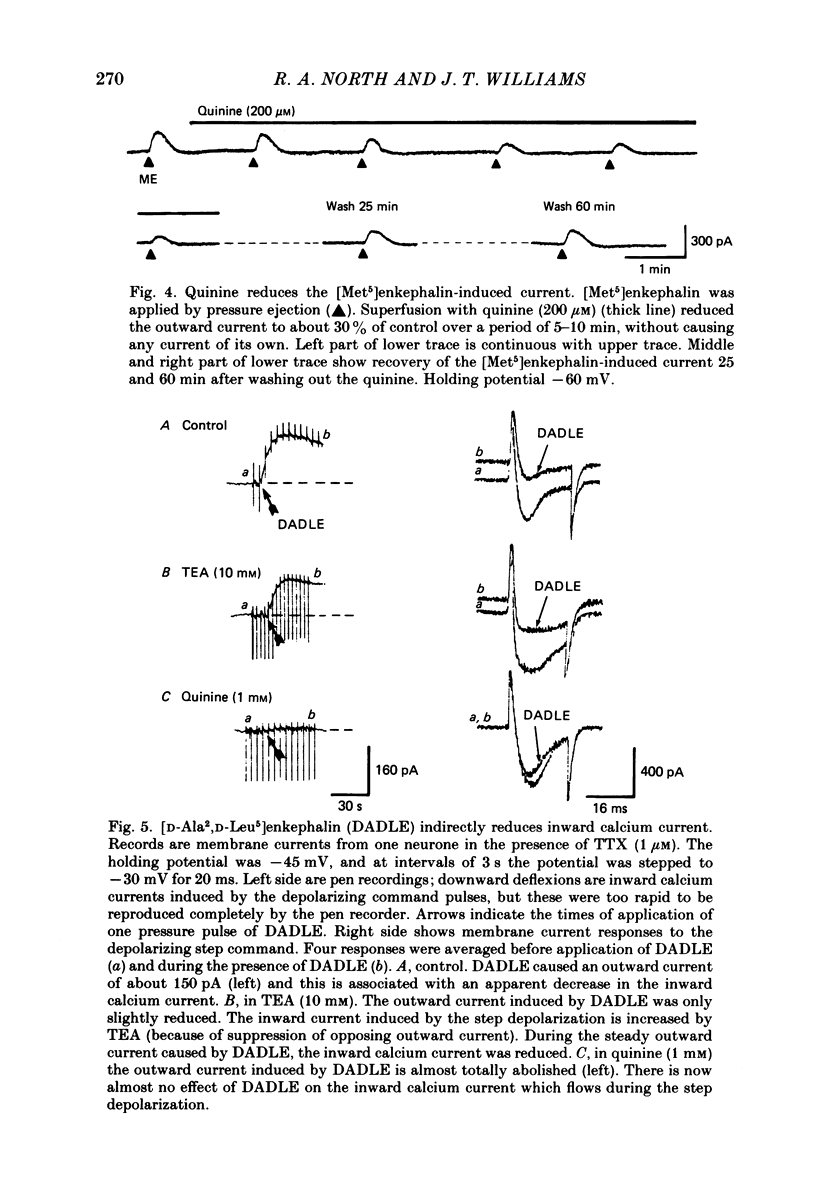
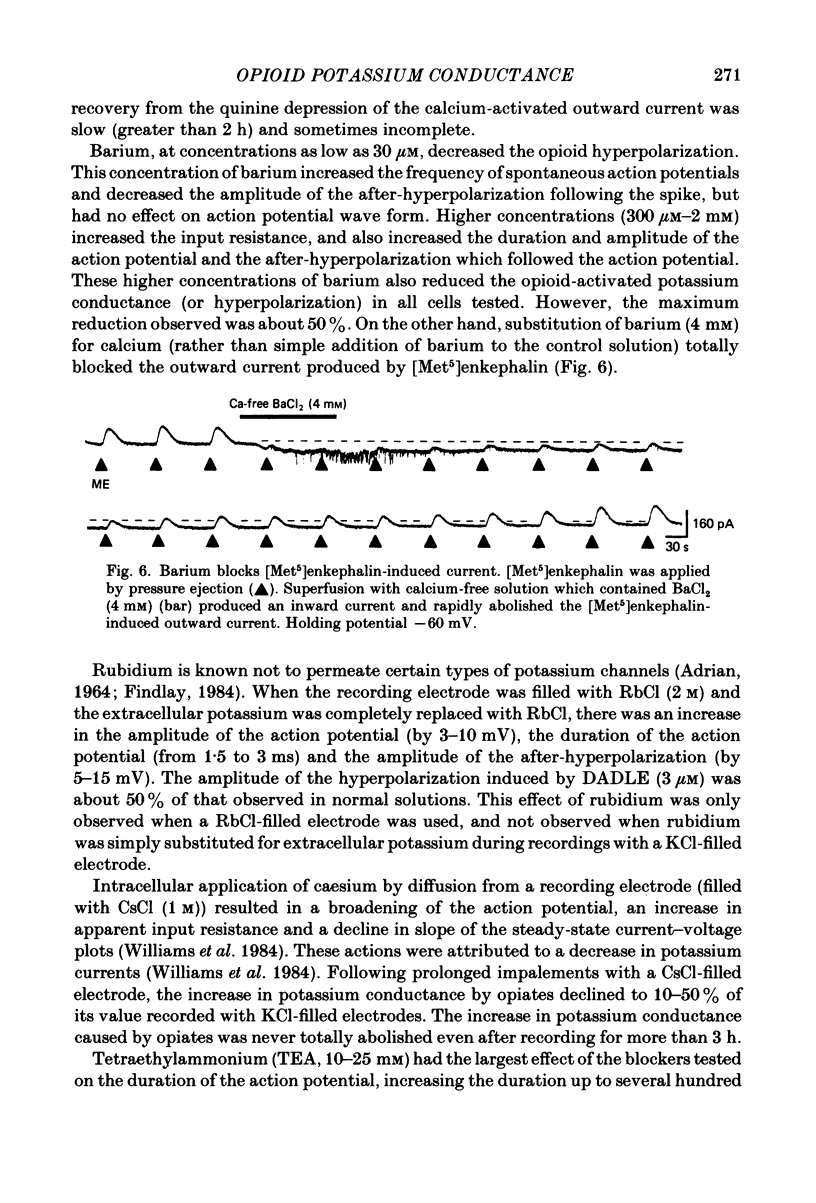
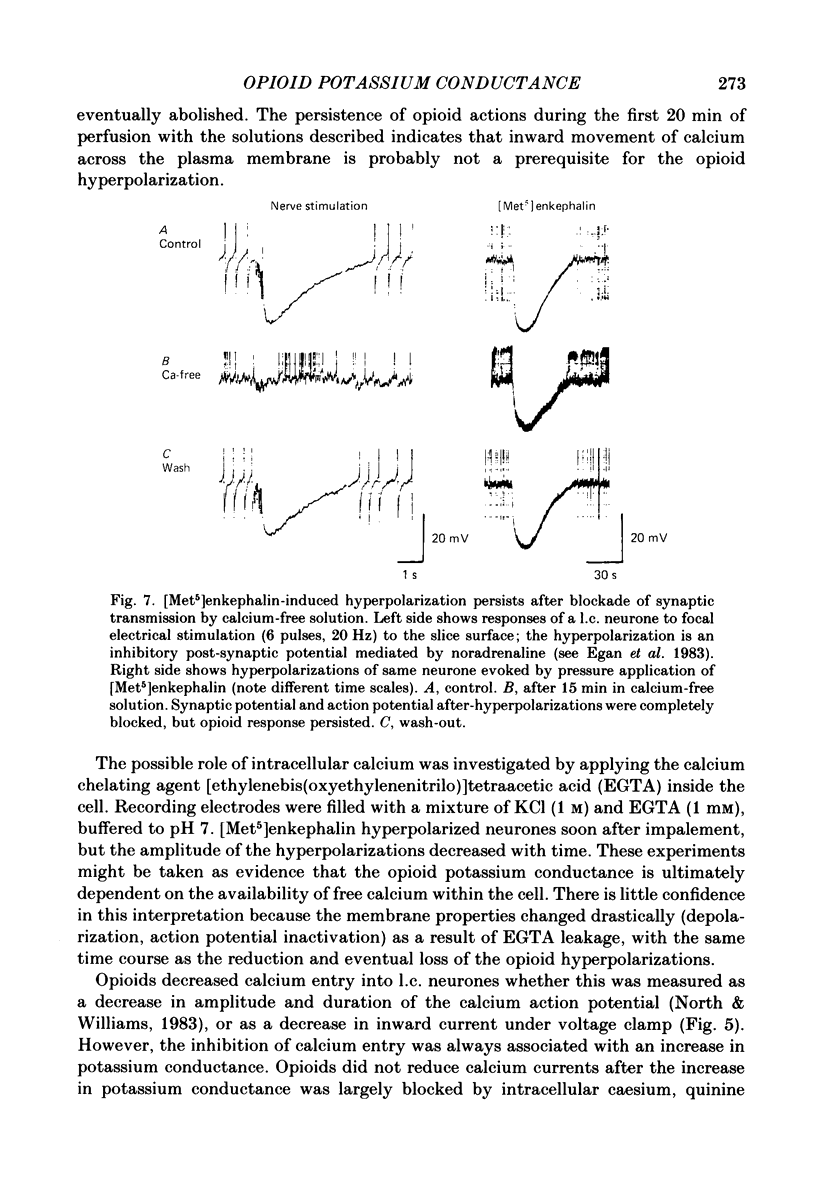
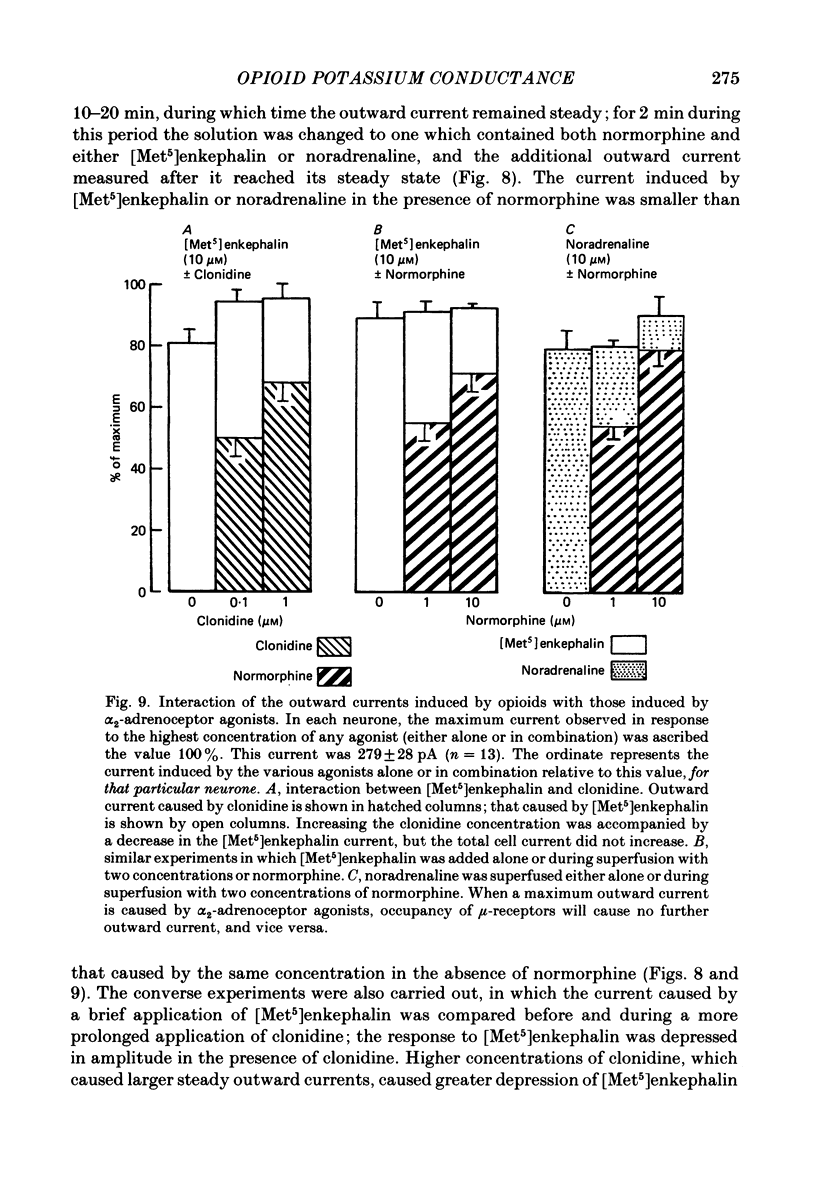
Intracellular recordings were made from locus coeruleus neurones in slices cut from rat pons and superfused in vitro. Membrane currents were recorded with a single-electrode switch-clamp amplifier. Opioids, enkephalin analogues or morphine, caused a concentration-dependent potassium current, which had a maximum value of about 300 pA at -60 mV. The opioid-sensitive potassium conductance was independent of membrane potential between -60 and -130 mV, but became less as the membrane potential was changed from -60 to -30 mV. The opioid outward current was reduced by quinine (100 microM-1 mM) and barium (30 microM-2 mM), but not by 4-aminopyridine (100 microM-1 mM) or tetraethylammonium (10 mM). A potassium current with similar properties flowed for several seconds after a burst of action potentials; this appeared to result from calcium entering the neurone during the action potentials. The alpha 2-adrenoceptor agonists noradrenaline and clonidine caused a concentration-dependent potassium conductance increase which had the same maximum value as that caused by opioids in the same neurones. Experiments in which an opioid and an alpha 2-adrenoceptor agonist were superfused together indicated that the same potassium conductance is increased by both agonists.
Full text
PDF








Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- ADRIAN R. H. THE RUBIDIUM AND POTASSIUM PERMEABILITY OF FROG MUSCLE MEMBRANE. J Physiol. 1964 Dec;175:134–159. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1964.sp007508. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Adams P. R., Constanti A., Brown D. A., Clark R. B. Intracellular Ca2+ activates a fast voltage-sensitive K+ current in vertebrate sympathetic neurones. Nature. 1982 Apr 22;296(5859):746–749. doi: 10.1038/296746a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Aghajanian G. K., VanderMaelen C. P. alpha 2-adrenoceptor-mediated hyperpolarization of locus coeruleus neurons: intracellular studies in vivo. Science. 1982 Mar 12;215(4538):1394–1396. doi: 10.1126/science.6278591. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Banks B. E., Brown C., Burgess G. M., Burnstock G., Claret M., Cocks T. M., Jenkinson D. H. Apamin blocks certain neurotransmitter-induced increases in potassium permeability. Nature. 1979 Nov 22;282(5737):415–417. doi: 10.1038/282415a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bird S. J., Kuhar M. J. Iontophoretic application of opiates to the locus coeruleus. Brain Res. 1977 Feb 25;122(3):523–533. doi: 10.1016/0006-8993(77)90462-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Burgess G. M., Claret M., Jenkinson D. H. Effects of quinine and apamin on the calcium-dependent potassium permeability of mammalian hepatocytes and red cells. J Physiol. 1981 Aug;317:67–90. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1981.sp013814. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cedarbaum J. M., Aghajanian G. K. Catecholamine receptors on locus coeruleus neurons: pharmacological characterization. Eur J Pharmacol. 1977 Aug 15;44(4):375–385. doi: 10.1016/0014-2999(77)90312-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cherubini E., North R. A., Surprenant A. Quinine blocks a calcium-activated potassium conductance in mammalian enteric neurones. Br J Pharmacol. 1984 Sep;83(1):3–5. doi: 10.1111/j.1476-5381.1984.tb10112.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Daut J. Modulation of the excitatory synaptic response by fast transient K+ current in snail neurones. Nat New Biol. 1973 Dec 19;246(155):193–196. doi: 10.1038/newbio246193a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Duggan A. W., North R. A. Electrophysiology of opioids. Pharmacol Rev. 1983 Dec;35(4):219–281. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Egan T. M., Henderson G., North R. A., Williams J. T. Noradrenaline-mediated synaptic inhibition in rat locus coeruleus neurones. J Physiol. 1983 Dec;345:477–488. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1983.sp014990. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Findlay I. A patch-clamp study of potassium channels and whole-cell currents in acinar cells of the mouse lacrimal gland. J Physiol. 1984 May;350:179–195. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1984.sp015195. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hanani M., Shaw C. A potassium contribution to the response of the barnacle photoreceptor. J Physiol. 1977 Aug;270(1):151–163. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1977.sp011943. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Higashi H., Morita K., North R. A. Calcium-dependent after-potentials in visceral afferent neurones of the rabbit. J Physiol. 1984 Oct;355:479–492. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1984.sp015433. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Korf J., Bunney B. S., Aghajanian G. K. Noradrenergic neurons: morphine inhibition of spontaneous activity. Eur J Pharmacol. 1974 Feb;25(2):165–169. doi: 10.1016/0014-2999(74)90045-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Latorre R., Miller C. Conduction and selectivity in potassium channels. J Membr Biol. 1983;71(1-2):11–30. doi: 10.1007/BF01870671. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Morita K., North R. A. Clonidine activates membrane potassium conductance in myenteric neurones. Br J Pharmacol. 1981 Oct;74(2):419–428. doi: 10.1111/j.1476-5381.1981.tb09987.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Morita K., North R. A. Opiate activation of potassium conductance in myenteric neurons: inhibition by calcium ion. Brain Res. 1982 Jun 17;242(1):145–150. doi: 10.1016/0006-8993(82)90504-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Morita K., North R. A., Tokimasa T. The calcium-activated potassium conductance in guinea-pig myenteric neurones. J Physiol. 1982 Aug;329:341–354. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1982.sp014306. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nemeth P. R., Zafirov D., Wood J. D. Forskolin mimics slow synaptic excitation in myenteric neurons. Eur J Pharmacol. 1984 Jun 1;101(3-4):303–304. doi: 10.1016/0014-2999(84)90176-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- North R. A., Surprenant A. Inhibitory synaptic potentials resulting from alpha 2-adrenoceptor activation in guinea-pig submucous plexus neurones. J Physiol. 1985 Jan;358:17–33. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1985.sp015537. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- North R. A., Tokimasa T. The time course of muscarinic depolarization of guinea-pig myenteric neurones. Br J Pharmacol. 1984 May;82(1):85–91. doi: 10.1111/j.1476-5381.1984.tb16444.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- North R. A., Williams J. T. Opiate activation of potassium conductance inhibits calcium action potentials in rat locus coeruleus neurones. Br J Pharmacol. 1983 Oct;80(2):225–228. doi: 10.1111/j.1476-5381.1983.tb10023.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- North R. A., Yoshimura M. The actions of noradrenaline on neurones of the rat substantia gelatinosa in vitro. J Physiol. 1984 Apr;349:43–55. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1984.sp015141. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pepper C. M., Henderson G. Opiates and opioid peptides hyperpolarize locus coeruleus neurons in vitro. Science. 1980 Jul 18;209(4454):394–395. doi: 10.1126/science.7384811. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Petersen O. H., Maruyama Y. Calcium-activated potassium channels and their role in secretion. Nature. 1984 Feb 23;307(5953):693–696. doi: 10.1038/307693a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Werz M. A., MacDonald R. L. Opioid peptides selective for mu- and delta-opiate receptors reduce calcium-dependent action potential duration by increasing potassium conductance. Neurosci Lett. 1983 Dec 2;42(2):173–178. doi: 10.1016/0304-3940(83)90402-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- West R. E., Jr, Miller R. J. Opiates, second messengers and cell response. Br Med Bull. 1983 Jan;39(1):53–58. doi: 10.1093/oxfordjournals.bmb.a071791. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Williams J. T., Egan T. M., North R. A. Enkephalin opens potassium channels on mammalian central neurones. Nature. 1982 Sep 2;299(5878):74–77. doi: 10.1038/299074a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Williams J. T., Henderson G., North R. A. Characterization of alpha 2-adrenoceptors which increase potassium conductance in rat locus coeruleus neurones. Neuroscience. 1985 Jan;14(1):95–101. doi: 10.1016/0306-4522(85)90166-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Williams J. T., North R. A. Opiate-receptor interactions on single locus coeruleus neurones. Mol Pharmacol. 1984 Nov;26(3):489–497. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Williams J. T., North R. A., Shefner S. A., Nishi S., Egan T. M. Membrane properties of rat locus coeruleus neurones. Neuroscience. 1984 Sep;13(1):137–156. doi: 10.1016/0306-4522(84)90265-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yoshimura M., North R. A. Substantia gelatinosa neurones hyperpolarized in vitro by enkephalin. Nature. 1983 Oct 6;305(5934):529–530. doi: 10.1038/305529a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


