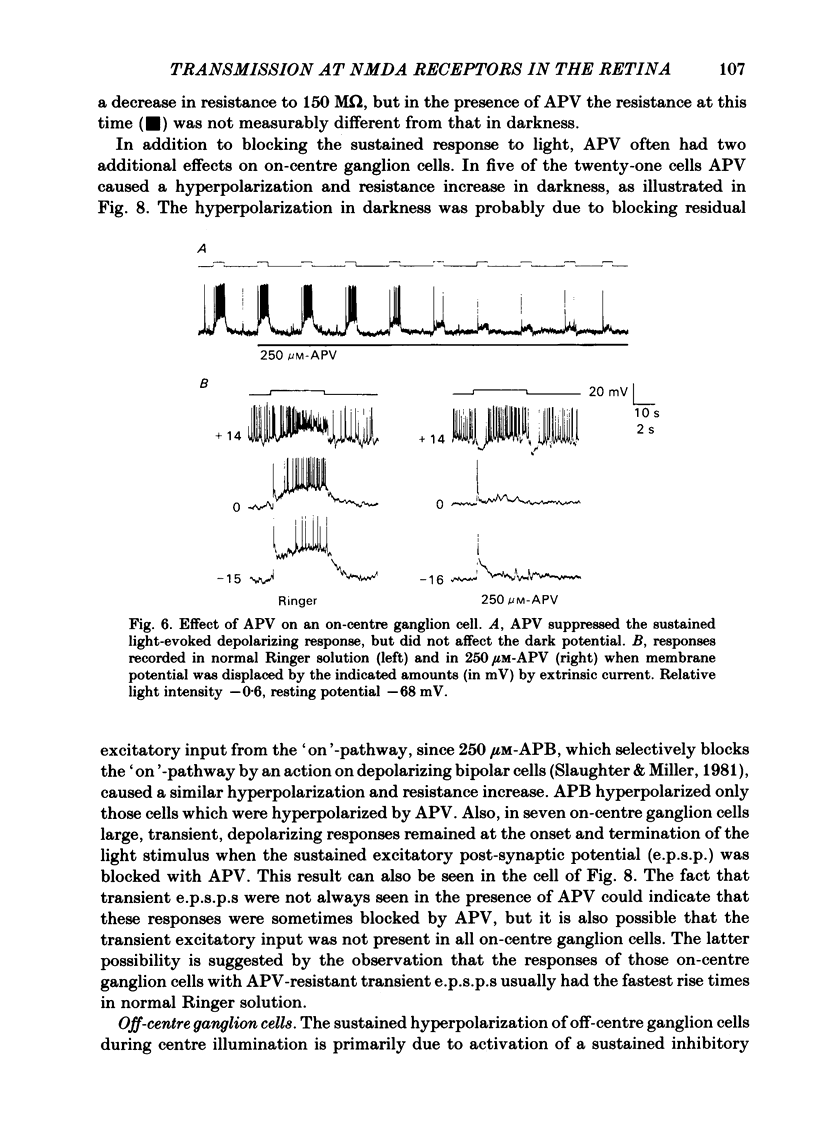
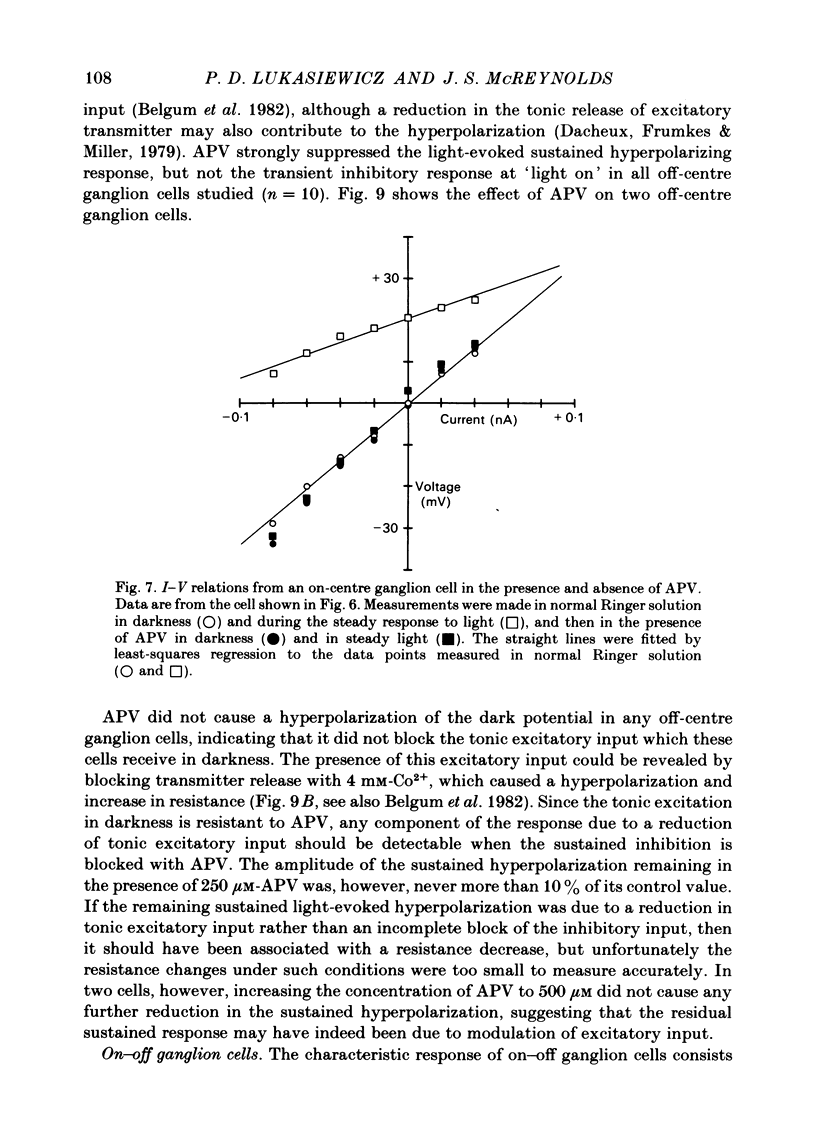
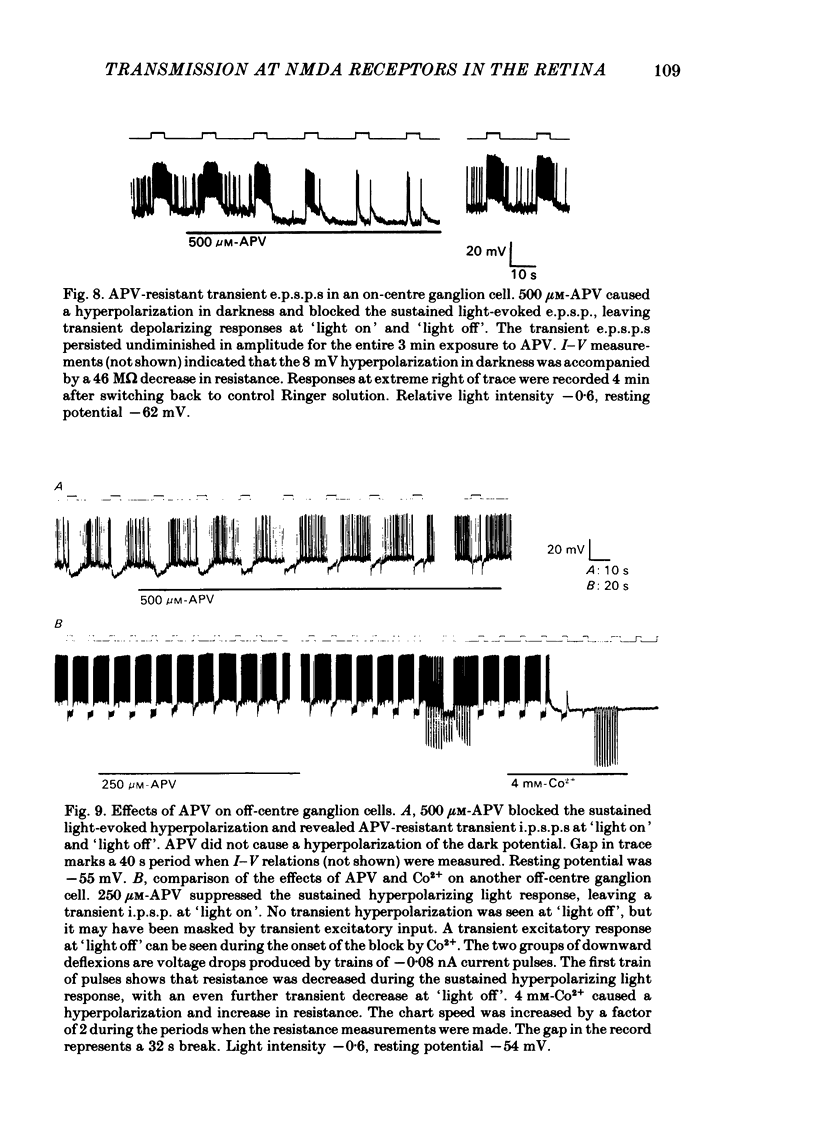
Abstract
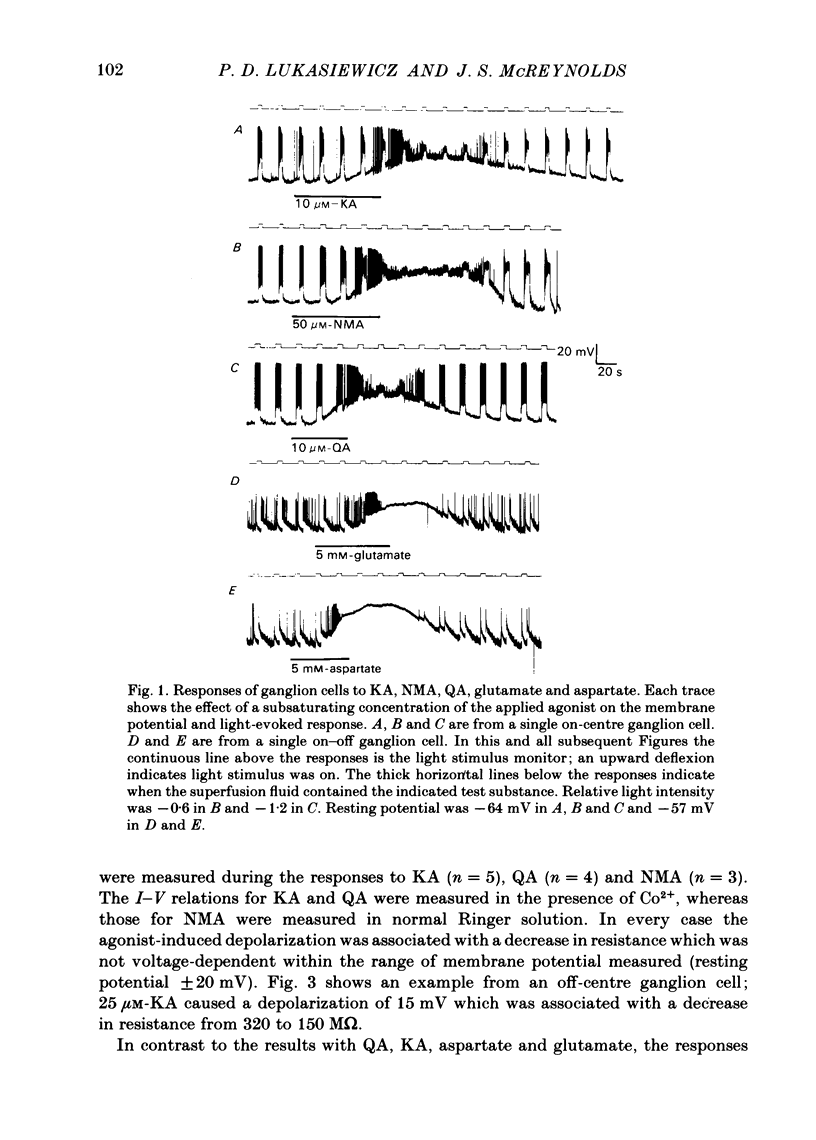
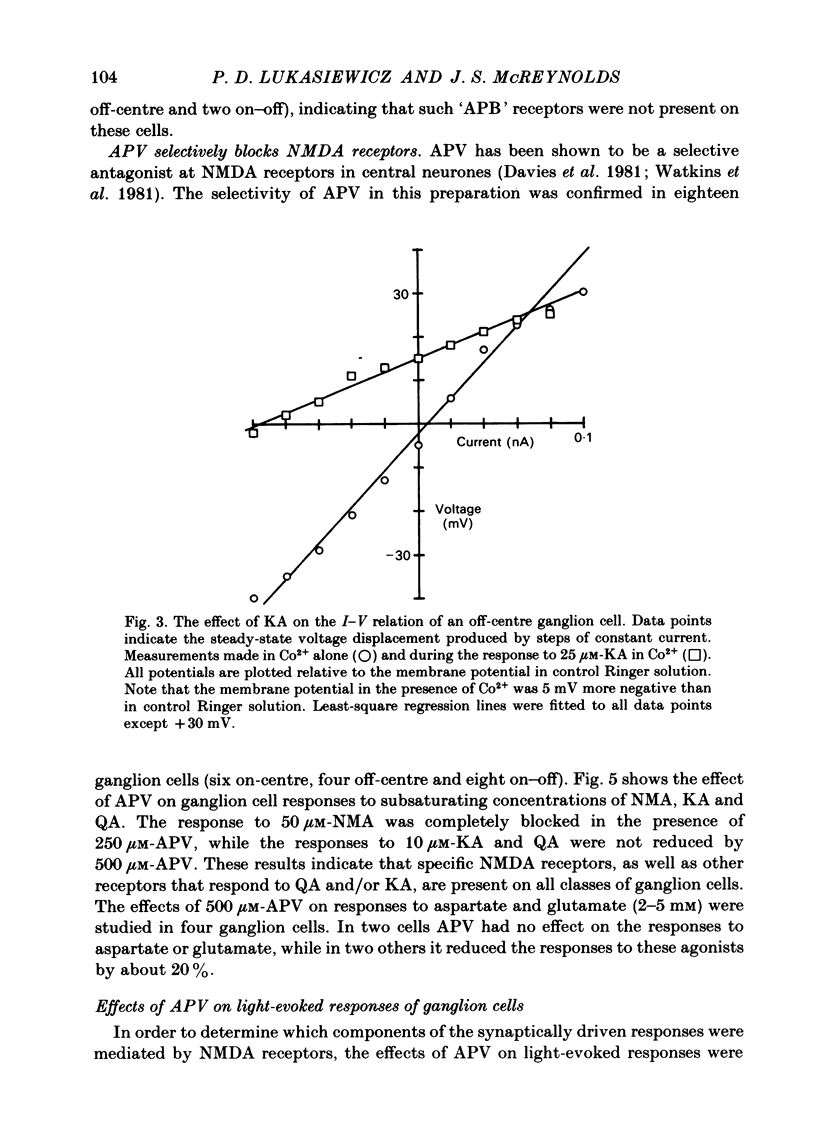
The effects of excitatory amino acid analogues and antagonists on retinal ganglion cells were studied using intracellular recording in the superfused mudpuppy eyecup preparation. Aspartate, glutamate, quisqualate (QA), kainate (KA) and N-methylaspartate (NMA) caused depolarization and decreased input resistance in all classes of ganglion cells. The order of sensitivity was QA greater than or equal to KA greater than NMA greater than aspartate greater than or equal to glutamate. All of these agonists were effective when transmitter release was blocked with 4 mM-Co2+ or Mn2+, indicating that they acted at receptor sites on the ganglion cells. At a concentration of 250 microM, 2-amino-5-phosphonovalerate (APV) blocked the responses of all ganglion cells to NMA, but not to QA or KA, indicating that NMA acts at different receptor sites from QA or KA. Responses to bath-applied aspartate and glutamate were reduced slightly or not at all in the presence of APV, indicating that they were acting mainly at non-NMDA (N-methyl-D-aspartate) receptors. In all ganglion cells 250 microM-APV strongly suppressed the sustained responses driven by the 'on'-pathway but not those driven by the 'off'-pathway. In most on-off ganglion cells the transient excitatory responses at 'light on' and 'light off' were not reduced by 500 microM-APV. APV-resistant transient excitatory responses were also present in some on-centre ganglion cells. APV did not block the transient inhibitory responses in any class of ganglion cells. At concentrations which blocked the sustained responses of ganglion cells, APV did not affect the sustained responses of bipolar cells, indicating that it acted at sites which were post-synaptic to bipolar cells. The simplest interpretation of these results is that the transmitter released by depolarizing bipolar cells acts at NMDA receptors on sustained depolarizing amacrine and ganglion cells. It may act at non-NMDA receptors at synapses which produce transient excitatory responses, but this could not be proved. The transmitter released by hyperpolarizing bipolar cells does not appear to act at NMDA receptors on any post-synaptic cells.
Full text
PDF









Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Ariel M., Daw N. W. Effects of cholinergic drugs on receptive field properties of rabbit retinal ganglion cells. J Physiol. 1982 Mar;324:135–160. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1982.sp014104. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
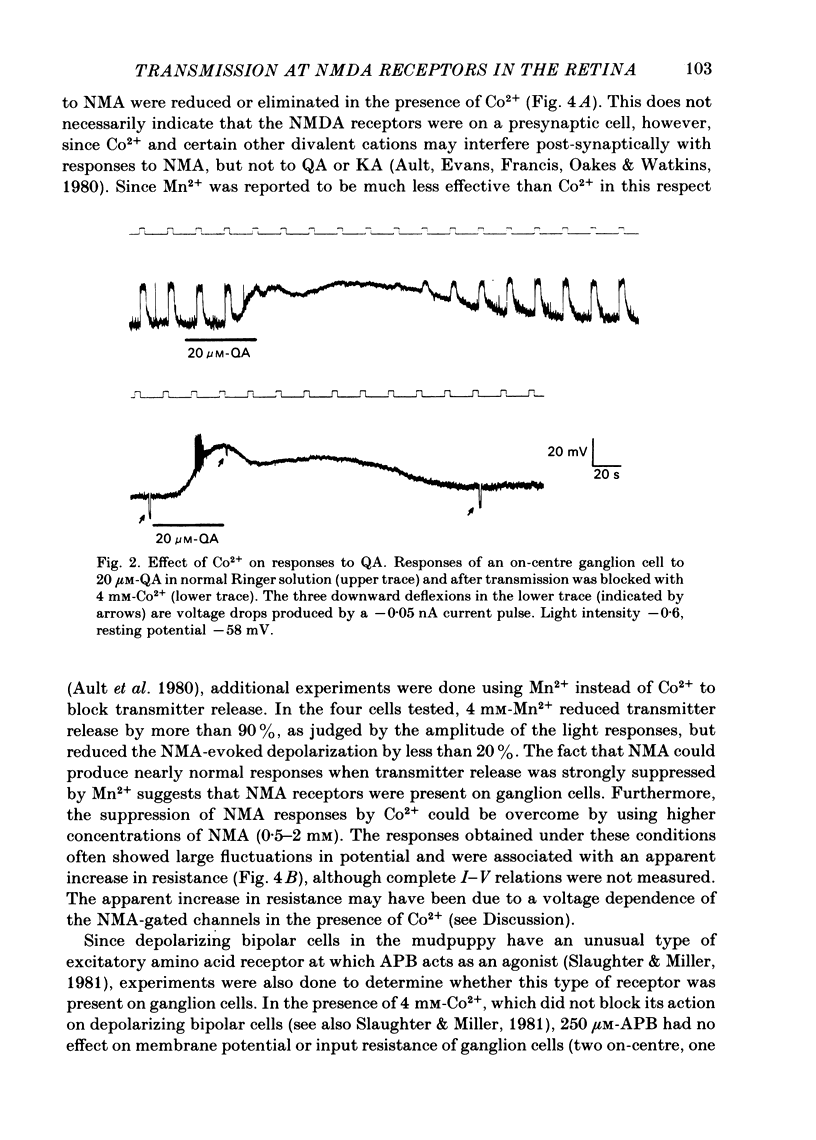
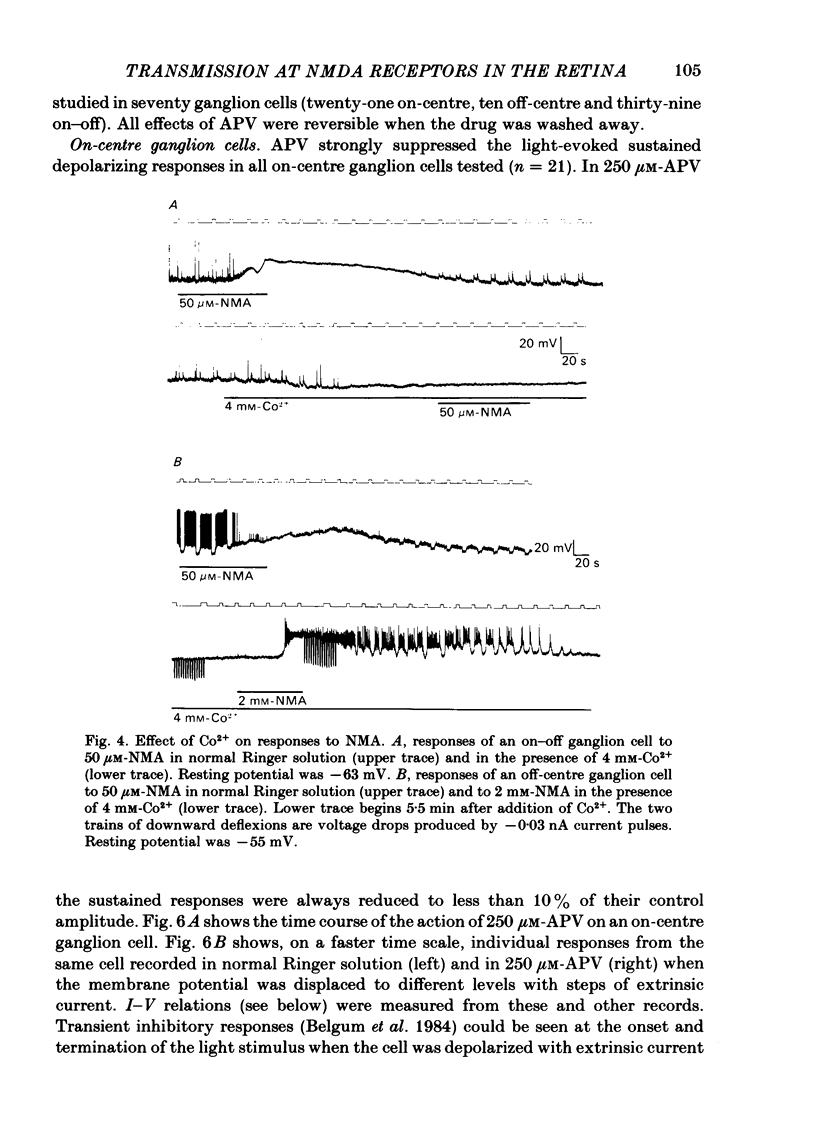
- Ault B., Evans R. H., Francis A. A., Oakes D. J., Watkins J. C. Selective depression of excitatory amino acid induced depolarizations by magnesium ions in isolated spinal cord preparations. J Physiol. 1980 Oct;307:413–428. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1980.sp013443. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Belgum J. H., Dvorak D. R., McReynolds J. S. Strychnine blocks transient but not sustained inhibition in mudpuppy retinal ganglion cells. J Physiol. 1984 Sep;354:273–286. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1984.sp015375. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Belgum J. H., Dvorak D. R., McReynolds J. S. Sustained and transient synaptic inputs to on-off ganglion cells in the mudpuppy retina. J Physiol. 1983 Jul;340:599–610. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1983.sp014782. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Belgum J. H., Dvorak D. R., McReynolds J. S. Sustained synaptic input to ganglion cells of mudpuppy retina. J Physiol. 1982 May;326:91–108. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1982.sp014179. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cervetto L., MacNichol E. F., Jr Inactivation of horizontal cells in turtle retina by glutamate and aspartate. Science. 1972 Nov 17;178(4062):767–768. doi: 10.1126/science.178.4062.767. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Colburn T. R., Schwartz E. A. Linear voltage control of current passed through a micropipette with variable resistance. Med Biol Eng. 1972 Jul;10(4):504–509. doi: 10.1007/BF02474198. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dacheux R. F., Frumkes T. E., Miller R. F. Pathways and polarities of synaptic interactions in the inner retina of the mudpuppy: I. Synaptic blocking studies. Brain Res. 1979 Jan 26;161(1):1–12. doi: 10.1016/0006-8993(79)90191-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Davies J., Francis A. A., Jones A. W., Watkins J. C. 2-Amino-5-phosphonovalerate (2APV), a potent and selective antagonist of amino acid-induced and synaptic excitation. Neurosci Lett. 1981 Jan 1;21(1):77–81. doi: 10.1016/0304-3940(81)90061-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dingledine R. N-methyl aspartate activates voltage-dependent calcium conductance in rat hippocampal pyramidal cells. J Physiol. 1983 Oct;343:385–405. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1983.sp014899. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fain G. L. Interactions of rod and cone signals in the mudpuppy retina. J Physiol. 1975 Nov;252(3):735–769. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1975.sp011168. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Frumkes T. E., Miller R. F., Slaughter M., Dacheux R. F. Physiological and pharmacological basis of GABA and glycine action on neurons of mudpuppy retina. III. Amacrine-mediated inhibitory influences on ganglion cell receptive-field organization: a model. J Neurophysiol. 1981 Apr;45(4):783–804. doi: 10.1152/jn.1981.45.4.783. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ikeda H., Sheardown M. J. Acetylcholine may be an excitatory transmitter mediating visual excitation of 'transient' cells with the periphery effect in the cat retina: iontophoretic studies in vivo. Neuroscience. 1982 May;7(5):1299–1308. doi: 10.1016/0306-4522(82)91135-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ikeda H., Sheardown M. J. Aspartate may be an excitatory transmitter mediating visual excitation of "sustained" but not "transient" cells in the cat retina: iontophoretic studies in vivo. Neuroscience. 1982 Jan;7(1):25–36. doi: 10.1016/0306-4522(82)90150-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lasater E. M., Dowling J. E. Carp horizontal cells in culture respond selectively to L-glutamate and its agonists. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1982 Feb;79(3):936–940. doi: 10.1073/pnas.79.3.936. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lasater E. M., Dowling J. E., Ripps H. Pharmacological properties of isolated horizontal and bipolar cells from the skate retina. J Neurosci. 1984 Aug;4(8):1966–1975. doi: 10.1523/JNEUROSCI.04-08-01966.1984. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- MacDonald J. F., Porietis A. V., Wojtowicz J. M. L-Aspartic acid induces a region of negative slope conductance in the current-voltage relationship of cultured spinal cord neurons. Brain Res. 1982 Apr 8;237(1):248–253. doi: 10.1016/0006-8993(82)90575-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Masland R. H., Ames A., 3rd Responses to acetylcholine of ganglion cells in an isolated mammalian retina. J Neurophysiol. 1976 Nov;39(6):1220–1235. doi: 10.1152/jn.1976.39.6.1220. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Masland R. H., Mills J. W., Cassidy C. The functions of acetylcholine in the rabbit retina. Proc R Soc Lond B Biol Sci. 1984 Nov 22;223(1230):121–139. doi: 10.1098/rspb.1984.0086. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mayer M. L., Westbrook G. L. Mixed-agonist action of excitatory amino acids on mouse spinal cord neurones under voltage clamp. J Physiol. 1984 Sep;354:29–53. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1984.sp015360. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- McLennan H. Receptors for the excitatory amino acids in the mammalian central nervous system. Prog Neurobiol. 1983;20(3-4):251–271. doi: 10.1016/0301-0082(83)90004-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Murakami M., Otsuka T., Shimazaki H. Effects of aspartate and glutamate on the bipolar cells in the carp retina. Vision Res. 1975 Mar;15(3):456–458. doi: 10.1016/0042-6989(75)90101-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nowak L., Bregestovski P., Ascher P., Herbet A., Prochiantz A. Magnesium gates glutamate-activated channels in mouse central neurones. Nature. 1984 Feb 2;307(5950):462–465. doi: 10.1038/307462a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Olverman H. J., Jones A. W., Watkins J. C. L-glutamate has higher affinity than other amino acids for [3H]-D-AP5 binding sites in rat brain membranes. Nature. 1984 Feb 2;307(5950):460–462. doi: 10.1038/307460a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shiells R. A., Falk G., Naghshineh S. Action of glutamate and aspartate analogues on rod horizontal and bipolar cells. Nature. 1981 Dec 10;294(5841):592–594. doi: 10.1038/294592a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Slaughter M. M., Miller R. F. 2-amino-4-phosphonobutyric acid: a new pharmacological tool for retina research. Science. 1981 Jan 9;211(4478):182–185. doi: 10.1126/science.6255566. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Slaughter M. M., Miller R. F. An excitatory amino acid antagonist blocks cone input to sign-conserving second-order retinal neurons. Science. 1983 Mar 11;219(4589):1230–1232. doi: 10.1126/science.6131536. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Slaughter M. M., Miller R. F. Bipolar cells in the mudpuppy retina use an excitatory amino acid neurotransmitter. Nature. 1983 Jun 9;303(5917):537–538. doi: 10.1038/303537a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Slaughter M. M., Miller R. F. The role of excitatory amino acid transmitters in the mudpuppy retina: an analysis with kainic acid and N-methyl aspartate. J Neurosci. 1983 Aug;3(8):1701–1711. doi: 10.1523/JNEUROSCI.03-08-01701.1983. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stone T. W., Perkins M. N. Quisqualic acid excitation of cortical neurones is selectively antagonized by streptomycin. Brain Res. 1983 Feb 7;260(2):347–349. doi: 10.1016/0006-8993(83)90695-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Watkins J. C., Davies J., Evans R. H., Francis A. A., Jones A. W. Pharmacology of receptors for excitatory amino acids. Adv Biochem Psychopharmacol. 1981;27:263–273. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Watkins J. C., Evans R. H. Excitatory amino acid transmitters. Annu Rev Pharmacol Toxicol. 1981;21:165–204. doi: 10.1146/annurev.pa.21.040181.001121. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Werblin F. S. Regenerative amacrine cell depolarization and formation of on-off ganglion cell response. J Physiol. 1977 Jan;264(3):767–785. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1977.sp011693. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wu S. M., Dowling J. E. L-aspartate: evidence for a role in cone photoreceptor synaptic transmission in the carp retina. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1978 Oct;75(10):5205–5209. doi: 10.1073/pnas.75.10.5205. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wunk D. F., Werblin F. S. Synaptic inputs to the ganglion cells in the tiger salamander retina. J Gen Physiol. 1979 Mar;73(3):265–286. doi: 10.1085/jgp.73.3.265. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


