Abstract
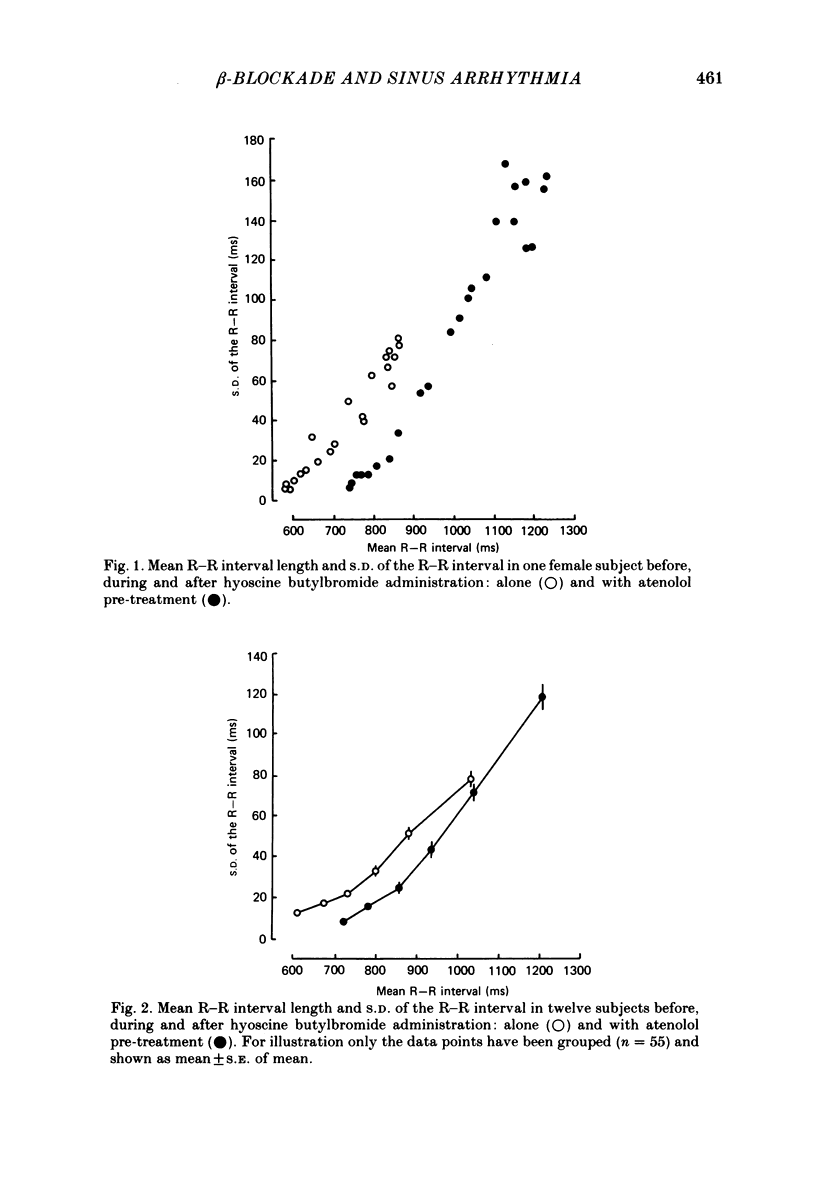
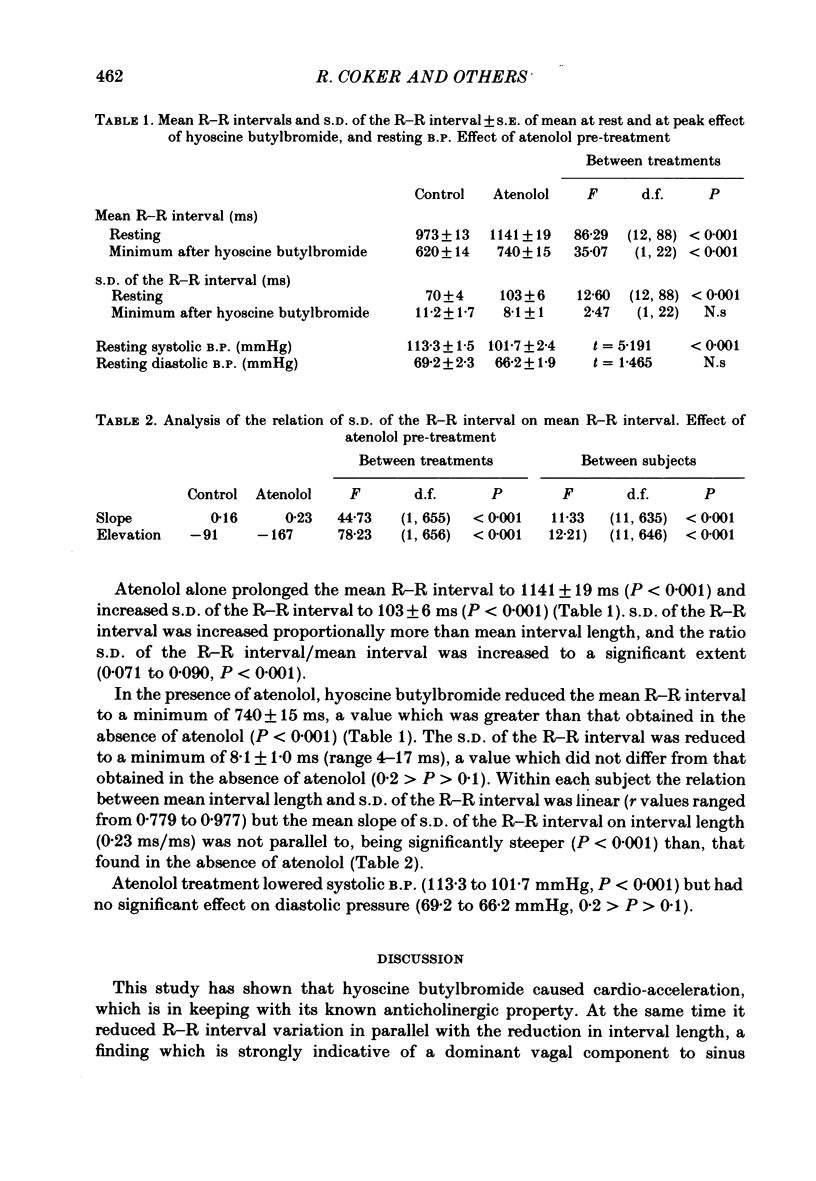
The influences of vagal and sympathetic efferent activity on sinus arrhythmia in man have been studied in healthy subjects by administration of hyoscine butylbromide and atenolol alone and combined using a microcomputer-linked electrocardiogram (e.c.g.) system. Sinus arrhythmia was quantitated as the S.D. of the R-R interval. Sinus arrhythmia was reduced by hyoscine butylbromide, in some subjects to near abolition, but this end-point was unchanged by pre-treatment with atenolol. Atenolol alone prolonged the mean R-R interval and increased sinus arrhythmia. It is suggested that sinus arrhythmia in man is mediated through vagal efferents alone but that atenolol increases the arrhythmia through a central vagotonic effect.
Full text
PDF



Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Adrian E. D., Bronk D. W., Phillips G. Discharges in mammalian sympathetic nerves. J Physiol. 1932 Feb 8;74(2):115–133. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1932.sp002832. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Baxter R. H., Lennox I. M. Increased exercise tolerance with nitrates in beta-blockaded patients with angina. Br Med J. 1977 Aug 27;2(6086):550–552. doi: 10.1136/bmj.2.6086.550. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cruickshank J. M., Neil-Dwyer G., Cameron M. M., McAinsh J. beta-Adrenoreceptor-blocking agents and the blood-brain barrier. Clin Sci (Lond) 1980 Dec;59 (Suppl 6):453s–455s. doi: 10.1042/cs059453s. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hamlin R. L., Smith C. R., Smetzer D. L. Sinus arrhythmia in the dog. Am J Physiol. 1966 Feb;210(2):321–328. doi: 10.1152/ajplegacy.1966.210.2.321. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- JOELS N., SAMUELOFF M. The activity of the medullary centres in diffusion respiration. J Physiol. 1956 Aug 28;133(2):360–372. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1956.sp005592. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Katona P. G., Jih F. Respiratory sinus arrhythmia: noninvasive measure of parasympathetic cardiac control. J Appl Physiol. 1975 Nov;39(5):801–805. doi: 10.1152/jappl.1975.39.5.801. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kunze D. L. Reflex discharge patterns of cardiac vagal efferent fibres. J Physiol. 1972 Apr;222(1):1–15. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1972.sp009784. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Levy M. N., Zieske H. Autonomic control of cardiac pacemaker activity and atrioventricular transmission. J Appl Physiol. 1969 Oct;27(4):465–470. doi: 10.1152/jappl.1969.27.4.465. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pomeroy A. R., Rand M. J. Anticholinergic effects and passage through the intestinal wall of N-butylhyoscine bromide. J Pharm Pharmacol. 1969 Mar;21(3):180–187. doi: 10.1111/j.2042-7158.1969.tb08224.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Samaan A. The antagonistic cardiac nerves and heart rate. J Physiol. 1935 Feb 9;83(3):332–340. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1935.sp003232. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Scott E. M. The effect of atenolol on the spontaneous and reflex activity of the sympathetic nerves in the cat: influence of cardiopulmonary receptors. Br J Pharmacol. 1983 Feb;78(2):425–431. doi: 10.1111/j.1476-5381.1983.tb09407.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Smith S. E., Smith S. A. Heart rate variability in healthy subjects measured with a bedside computer-based technique. Clin Sci (Lond) 1981 Oct;61(4):379–383. doi: 10.1042/cs0610379. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wheeler T., Watkins P. J. Cardiac denervation in diabetes. Br Med J. 1973 Dec 8;4(5892):584–586. doi: 10.1136/bmj.4.5892.584. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Woods P. B., Robinson M. L. An investigation of the comparative liposolubilities of beta-adrenoceptor blocking agents. J Pharm Pharmacol. 1981 Mar;33(3):172–173. doi: 10.1111/j.2042-7158.1981.tb13743.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


