Abstract
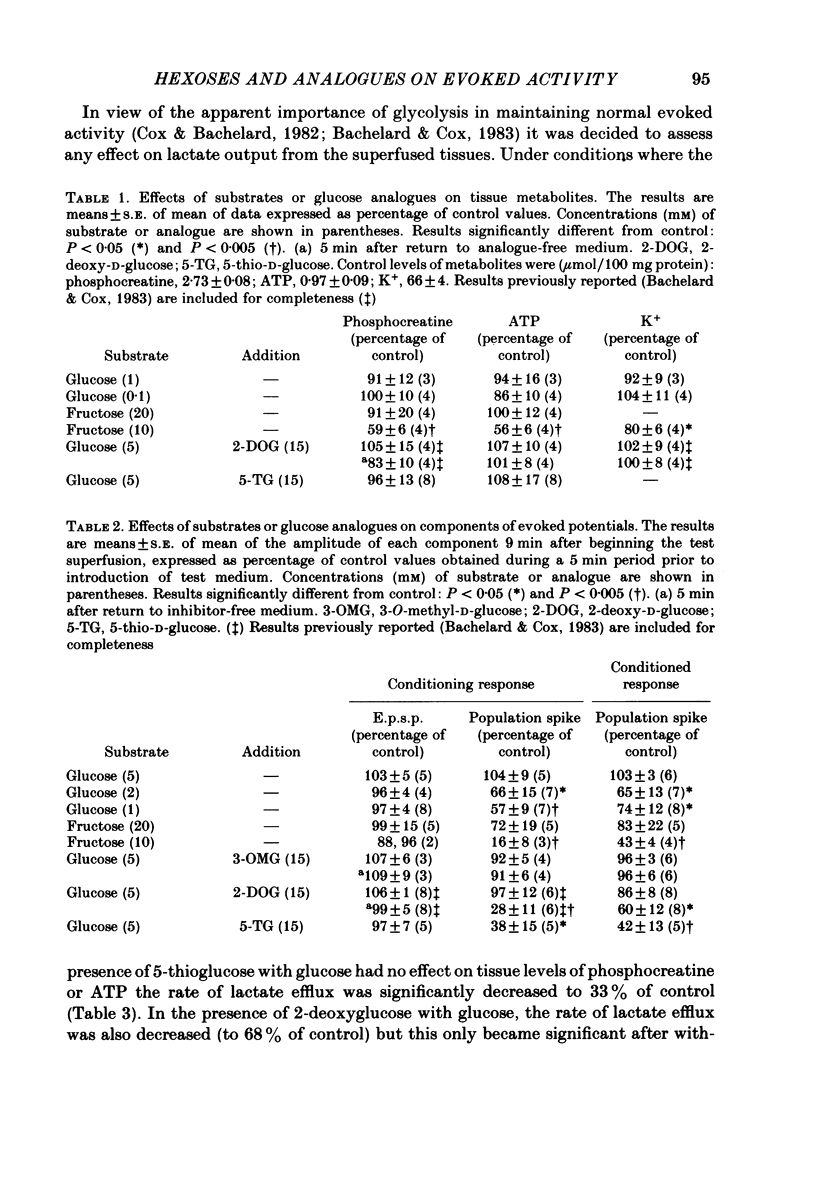
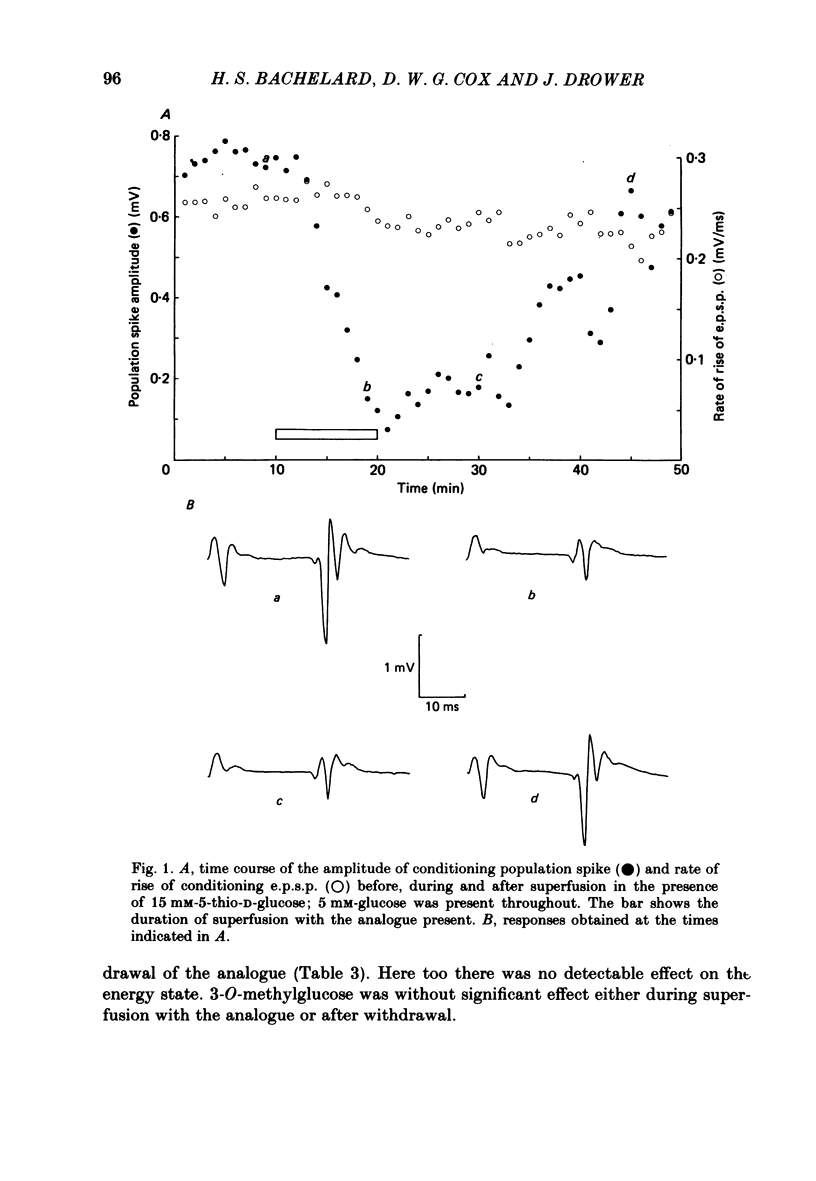
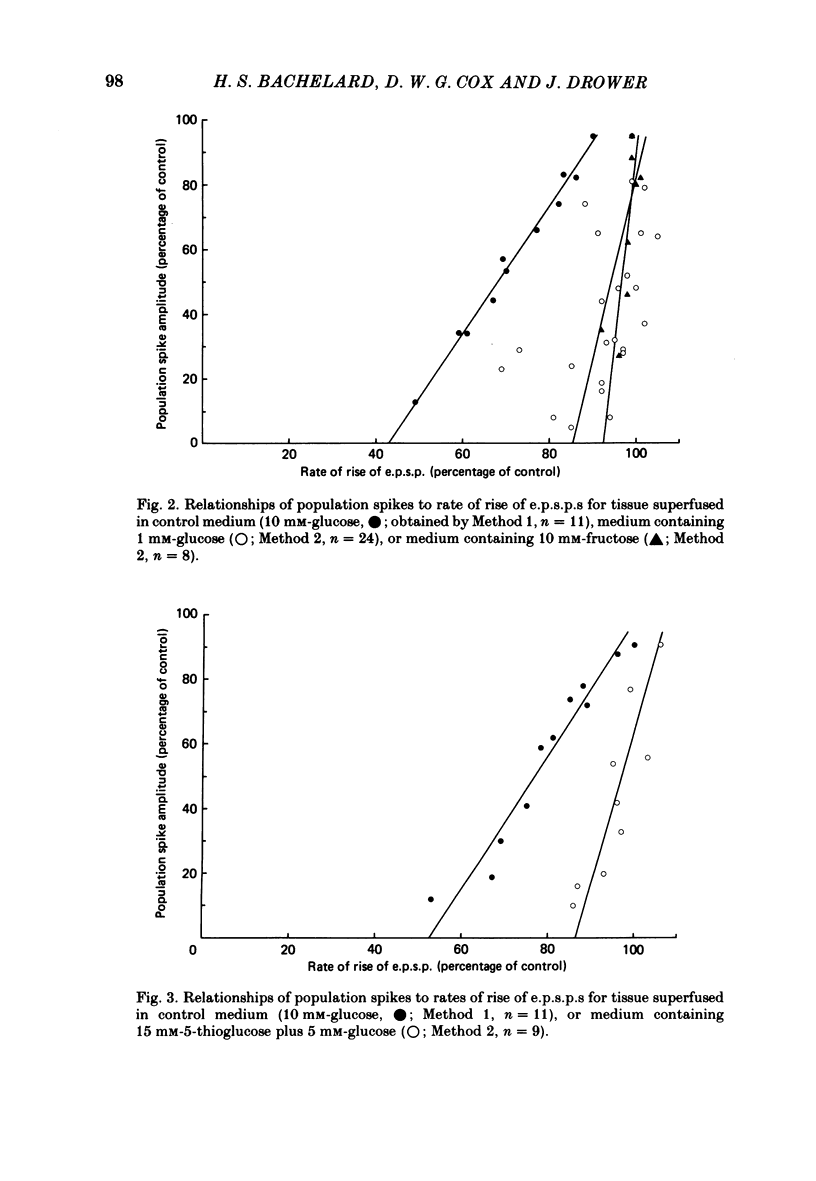
Evoked granule cell field potentials, and levels of tissue metabolites, in superfused guinea-pig hippocampal slices have been studied in the presence of low glucose and an alternative glycolytic substrate (D-fructose). The effects of glucose analogues (5-thio-D-glucose, 2-deoxy-D-glucose or 3-O-methyl-D-glucose) in the presence of glucose were also tested. Concentrations of glucose or fructose in excess of 2 mM and 10 mM respectively were required to maintain normal evoked activity. 5-Thioglucose (15 mM) in the presence of 5 mM-glucose decreased the amplitude of the population spike by 60% with little effect on population excitatory post-synaptic potential (e.p.s.p.). Tissue levels of phosphocreatine and ATP were essentially unchanged under all conditions tested, with the exception of 10 mM-fructose. The decrease in rates of lactate efflux from superfused tissue during and after superfusion with 3-O-methylglucose, 2-deoxyglucose or 5-thioglucose was found to be positively correlated with the extent of attenuation of field potentials. Analysis of the relationship between population spike amplitude and rates of rise of e.p.s.p., under conditions where field potentials were attenuated, showed that the population spike was always more sensitive to metabolic perturbation than was the e.p.s.p., thus indicating an effect on cell excitability. It is suggested that some aspect of non-oxidative glucose metabolism is important in maintaining this granule cell excitability.
Full text
PDF








Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Bachelard H. S., Clark A. G., Thompson M. F. Cerebral-cortex hexokinase. Elucidation of reaction mechanisms by substrate and dead-end inhibitor kinetic analysis. Biochem J. 1971 Aug;123(5):707–715. doi: 10.1042/bj1230707. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bachelard H. S. Specificity and kinetic properties of monosaccharide uptake into guinea pig cerebral cortex in vitro. J Neurochem. 1971 Feb;18(2):213–222. doi: 10.1111/j.1471-4159.1971.tb00559.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Betz A. L., Drewes L. R., Gilboe D. D. Inhibition of glucose transport into brain by phlorizin, phloretin and glucose analogues. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1975 Nov 3;406(4):505–515. doi: 10.1016/0005-2736(75)90028-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- CSAKY T. Z., WILSON J. E. The fate of 3-O-14CH3-glucose in the rat. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1956 Oct;22(1):185–186. doi: 10.1016/0006-3002(56)90237-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chen M., Whistler R. L. Action of 5-thio-D-glucose and its 1-phosphate with hexokinase and phosphoglucomutase. Arch Biochem Biophys. 1975 Aug;169(2):392–396. doi: 10.1016/0003-9861(75)90180-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cox D. W., Bachelard H. S. Attenuation of evoked field potentials from dentate granule cells by low glucose, pyruvate + malate, and sodium fluoride. Brain Res. 1982 May 13;239(2):527–534. doi: 10.1016/0006-8993(82)90527-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cox D. W., Morris P. G., Feeney J., Bachelard H. S. 31P-n.m.r. studies on cerebral energy metabolism under conditions of hypoglycaemia and hypoxia in vitro. Biochem J. 1983 May 15;212(2):365–370. doi: 10.1042/bj2120365. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ferrendelli J. A., Chang M. M. Brain metabolism during hypoglycemia. Effect of insulin on regional central nervous system glucose and energy reserves in mice. Arch Neurol. 1973 Mar;28(3):173–177. doi: 10.1001/archneur.1973.00490210053006. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fujii T., Yoshizaki K. Temperature influence on the development of electrical activities in mammalian brain slice during incubation. Jpn J Physiol. 1976;26(4):355–365. doi: 10.2170/jjphysiol.26.355. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hinzen D. H., Müller U. Energiestoffwechsel und Funktion des Kaninchengehirns während Insulinhypoglykämie. Pflugers Arch. 1971;322(1):47–59. doi: 10.1007/BF00586664. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Horton R. W., Meldrum B. S., Bachelard H. S. Enzymic and cerebral metabolic effects of 2-deoxy-D-glucose. J Neurochem. 1973 Sep;21(3):507–520. doi: 10.1111/j.1471-4159.1973.tb05996.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- LOWRY O. H., ROSEBROUGH N. J., FARR A. L., RANDALL R. J. Protein measurement with the Folin phenol reagent. J Biol Chem. 1951 Nov;193(1):265–275. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lewis L. D., Ljunggren B., Ratcheson R. A., Siesjö B. K. Cerebral energy state in insulin-induced hypoglycemia, related to blood glucose and to EEG. J Neurochem. 1974 Oct;23(4):673–679. doi: 10.1111/j.1471-4159.1974.tb04390.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- McILWAIN H. Glucose level, metabolism, and response to electrical impulses in cerebral tissues from man and laboratory animals. Biochem J. 1953 Nov;55(4):618–624. doi: 10.1042/bj0550618. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Meldrum B. S., Horton R. W. Cerebral functional effects of 2-deoxy-D-glucose and 3-O-methylglucose in rhesus monkeys. Electroencephalogr Clin Neurophysiol. 1973 Jul;35(1):59–66. doi: 10.1016/0013-4694(73)90131-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nicholls D. G., Akerman K. E. Biochemical approaches to the study of cytosolic calcium regulation in nerve endings. Philos Trans R Soc Lond B Biol Sci. 1981 Dec 18;296(1080):115–122. doi: 10.1098/rstb.1981.0176. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Richards C. D., White A. E. The actions of volatile anaesthetics on synaptic transmission in the dentate gyrus. J Physiol. 1975 Oct;252(1):241–257. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1975.sp011142. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- SOLS A., CRANE R. K. Substrate specificity of brain hexokinase. J Biol Chem. 1954 Oct;210(2):581–595. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Scott I. D., Nicholls D. G. Energy transduction in intact synaptosomes. Influence of plasma-membrane depolarization on the respiration and membrane potential of internal mitochondria determined in situ. Biochem J. 1980 Jan 15;186(1):21–33. doi: 10.1042/bj1860021. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- WOODMAN R. J., McILWAIN H. Glutamic acid, other amino acids and related compounds as substrates for cerebral tissues: their effects on tissue phosphates. Biochem J. 1961 Oct;81:83–93. doi: 10.1042/bj0810083. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


