Abstract
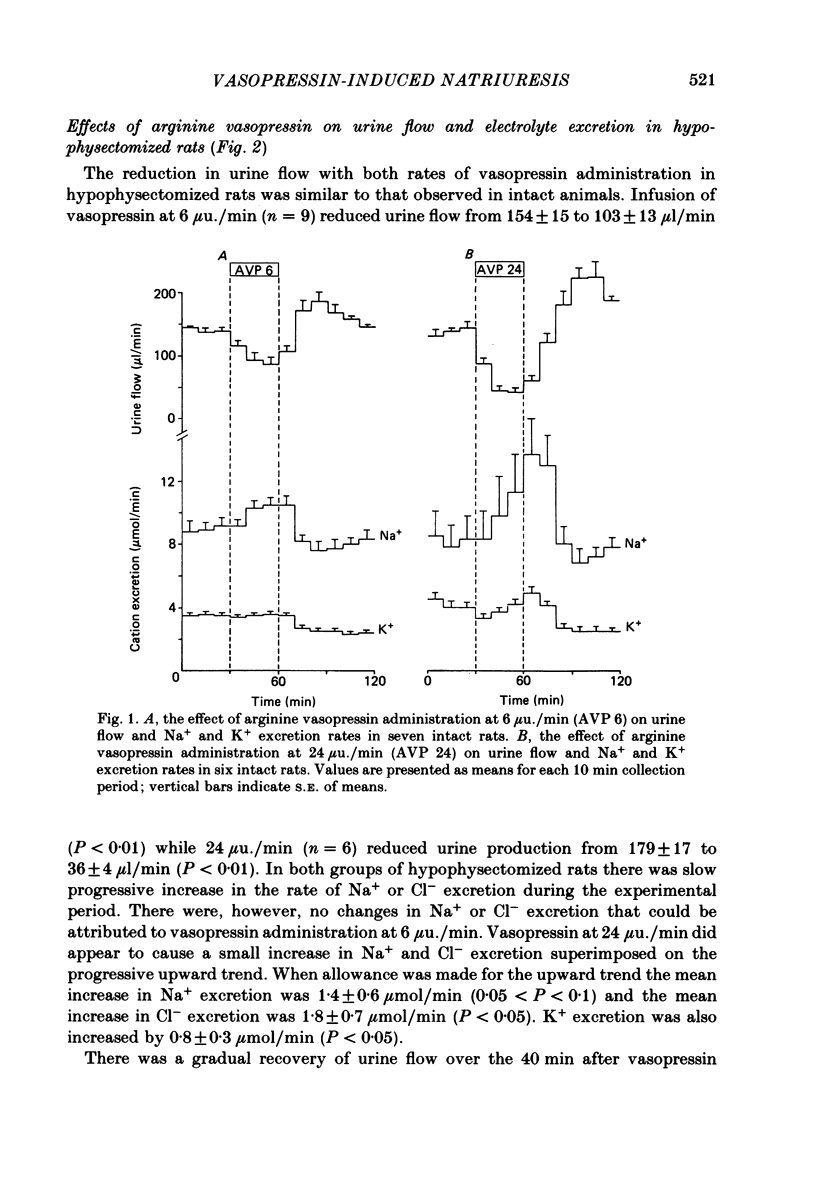
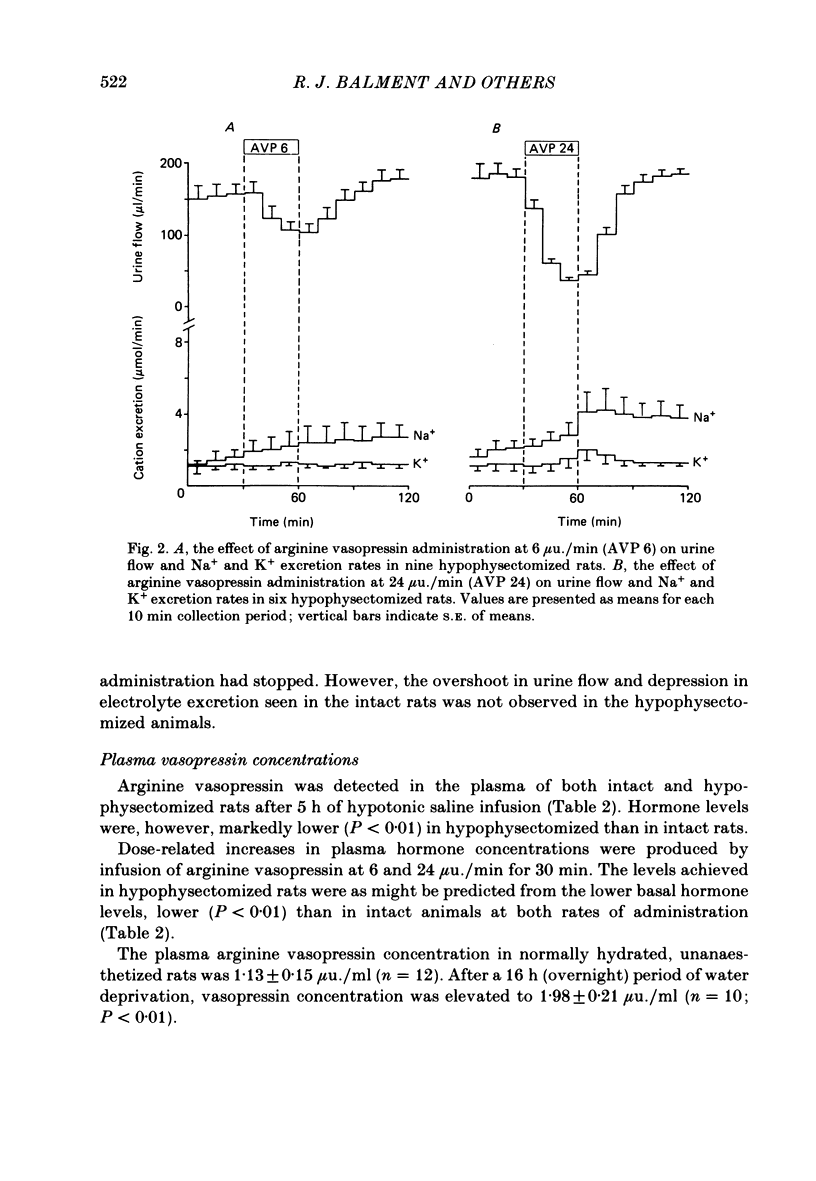
The relationship of plasma vasopressin concentrations in the physiological range to renal electrolyte excretion was investigated. Unanaesthetized rats, when normally hydrated, were found to have a plasma vasopressin concentration of 1.13 +/- 0.15 mu u./ml. 16 h water deprivation raised this to 1.98 +/- 0.21 mu u./ml. Inactin-anaesthetized rats infused with 0.45% NaCl had a plasma vasopressin concentration of 1.19 +/- 0.18 mu u./ml. Administration of synthetic arginine vasopressin at 6 and 24 mu u./min raised plasma vasopressin levels to 1.88 +/- 0.17 and 4.26 +/- 0.43 microunits./ml respectively. In addition to the expected antidiuresis, vasopressin at a rate of 6 microunits./min also produced a highly significant increase in Na+ excretion from 8.9 +/- 0.6 to 10.5 +/- 0.6 mumol/min and Cl- excretion from 9.1 +/- 0.7 to 10.5 +/- 0.7 mumol/min. At 24 microunits./min it produced larger increases in Na+ and Cl- excretion. Inactin-anaesthetized hypophysectomized rats infused with 0.45% NaCl had a plasma vasopressin concentration of only 0.17 +/- 0.04 microunits./ml. Administration of vasopressin at 6 and 24 microunits./ml raised plasma vasopressin levels in these animals to 0.63 +/- 0.17 and 2.20 +/- 0.11 microunits./ml respectively. Hypophysectomized rats failed to exhibit a natriuresis in response to the lower dose of vasopressin, despite exhibiting an undiminished antidiuresis. The failure of the natriuresis may be related to the lower plasma vasopressin concentration achieved. It is concluded that in the rat plasma vasopressin concentrations within the physiological range do influence Na+ and Cl- excretion by the kidney as well as controlling urine flow rate.
Full text
PDF







Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Atherton J. C., Green R., Thomas S. Influence of lysine-vasopressin dosage on the time course of changes in renal tissue and urinary composition in the conscious rat. J Physiol. 1971 Mar;213(2):291–309. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1971.sp009383. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Atherton J. C., Hai M. A., Thomas S. Acute effects of lysine vasopressin injection (single and continuous) on urinary composition in the conscious water diuretic rat. Pflugers Arch. 1969;310(4):281–296. doi: 10.1007/BF00587240. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Balment R. J., Brimble M. J., Forsling M. L. Release of oxytocin induced by salt loading and its influence on renal excretion in the male rat. J Physiol. 1980 Nov;308:439–449. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1980.sp013481. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Buckalew V. M., Dimond K. A. Effect of vasopressin on sodium excretion and plasma antinatriferic activity in the dog. Am J Physiol. 1976 Jul;231(1):28–33. doi: 10.1152/ajplegacy.1976.231.1.28. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chan W. Y. An investigation of the natriuretic, antidiuretic and oxytocic actions of neurohypophysial hormones and related peptides: delineation of separate mechanisms of action and assessment of molecular requirements. J Pharmacol Exp Ther. 1976 Mar;196(3):746–757. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chan W. Y., Du Vigneaud V. Natriuretic, diuretic and anti-arginine-vasopressin (ADH) effects of two analogs of oxytocin: [4-leucine]-oxytocin and [2,4-diisoleucine]-oxytocin. J Pharmacol Exp Ther. 1970 Sep;174(3):541–549. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- DICKER S. E. Urine concentration in the rat during acute and prolonged dehydration. J Physiol. 1957 Nov 14;139(1):108–122. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1957.sp005879. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dogterom J., van Wimersma Greidanus T. B., De Wied D. Vasopressin in cerebrospinal fluid and plasma of man, dog, and rat. Am J Physiol. 1978 May;234(5):E463–E467. doi: 10.1152/ajpendo.1978.234.5.E463. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dunn F. L., Brennan T. J., Nelson A. E., Robertson G. L. The role of blood osmolality and volume in regulating vasopressin secretion in the rat. J Clin Invest. 1973 Dec;52(12):3212–3219. doi: 10.1172/JCI107521. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Forsling M. L., Brimble M. J., Balment R. J. The influence of vasopressin on oxytocin-induced changes in urine flow in the male rat. Acta Endocrinol (Copenh) 1982 Jun;100(2):216–220. doi: 10.1530/acta.0.1000216. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fyhrquist F., Tikkanen I., Linkola J. Plasma vasopressin concentration and renin in the rat: effect of hydration and hemorrhage. Acta Physiol Scand. 1981 Dec;113(4):507–510. doi: 10.1111/j.1748-1716.1981.tb06929.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Garland H. O., Balment R. J., Brimble M. J. Oxytocin and renal function in the rat; an investigation of a possible proximal site of action. Acta Endocrinol (Copenh) 1983 Apr;102(4):517–520. doi: 10.1530/acta.0.1020517. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hall D. A., Varney D. M. Effect of vasopressin on electrical potential difference and chloride transport in mouse medullary thick ascending limb of Henle's loop. J Clin Invest. 1980 Oct;66(4):792–802. doi: 10.1172/JCI109917. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Husain M. K., Manger W. M., Rock T. W., Weiss R. J., Frantz A. G. Vasopressin release due to manual restraint in the rat: role of body compression and comparison with other stressful stimuli. Endocrinology. 1979 Mar;104(3):641–644. doi: 10.1210/endo-104-3-641. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- JACOBSON H. N., KELLOGG R. H. Isotonic NaCl diuresis in rats: antidiuresis and chloruresis produced by posterior pituitary extracts. Am J Physiol. 1956 Feb;184(2):376–389. doi: 10.1152/ajplegacy.1956.184.2.376. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Keil L. C., Severs W. B. Reduction in plasma vasopressin levels of dehydrated rats following acute stress. Endocrinology. 1977 Jan;100(1):30–38. doi: 10.1210/endo-100-1-30. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kurtzman N. A., Rogers P. W., Boonjarern S., Arruda J. A. Effect of infusion of pharmacologic amounts of vasopressin on renal electrolyte excretion. Am J Physiol. 1975 Mar;228(3):890–894. doi: 10.1152/ajplegacy.1975.228.3.890. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lichardus B., Ponec J. Effect of hypophysectomy on sodium excretion in rats without blood dilution during blood volume expansion. Experientia. 1972 Apr 15;28(4):471–472. doi: 10.1007/BF02008348. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lichardus B., Ponec J. On the role of the hypophysis in the renal mechanism of body fluid volumes regulation. Endokrinologie. 1973 Jun;61(3):403–412. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Luke R. G. Natriuresis and chloruresis during hydropenia in the rat. Am J Physiol. 1973 Jan;224(1):13–20. doi: 10.1152/ajplegacy.1973.224.1.13. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sasaki S., Imai M. Effects of vasopressin on water and NaCl transport across the in vitro perfused medullary thick ascending limb of Henle's loop of mouse, rat, and rabbit kidneys. Pflugers Arch. 1980 Feb;383(3):215–221. doi: 10.1007/BF00587521. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Scott D., Morton J. J. Changes in urinary water and electrolyte excretion in sodium-loaded sheep in response to intravenous infusion of arginine vasopressin. Q J Exp Physiol Cogn Med Sci. 1976 Jan;61(1):57–70. doi: 10.1113/expphysiol.1976.sp002334. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Skowsky W. R., Rosenbloom A. A., Fisher D. A. Radioimmunoassay measurement of arginine vasopressin in serum: development and application. J Clin Endocrinol Metab. 1974 Feb;38(2):278–287. doi: 10.1210/jcem-38-2-278. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Strömberg P., Forsling M. L., Akerlund M. Effects of prostaglandin inhibition on vasopressin levels in women with primary dysmenorrhea. Obstet Gynecol. 1981 Aug;58(2):206–208. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


