Abstract
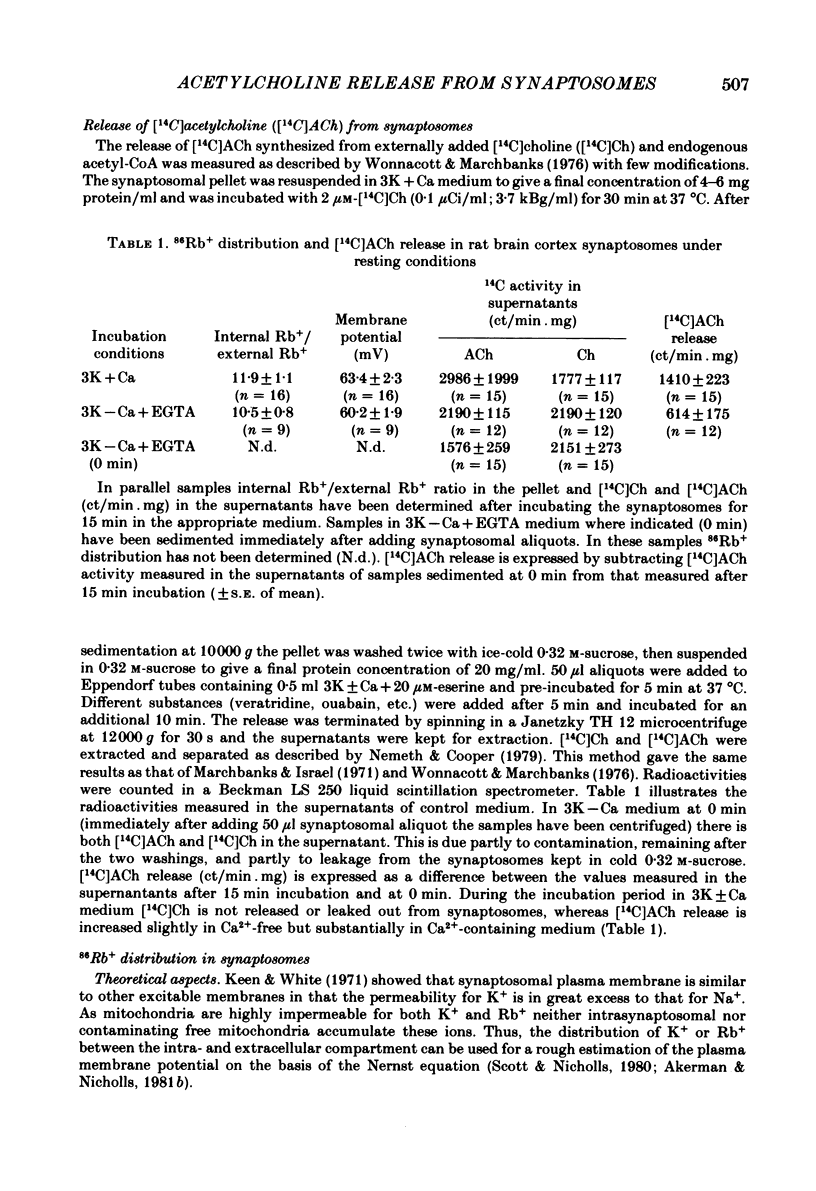
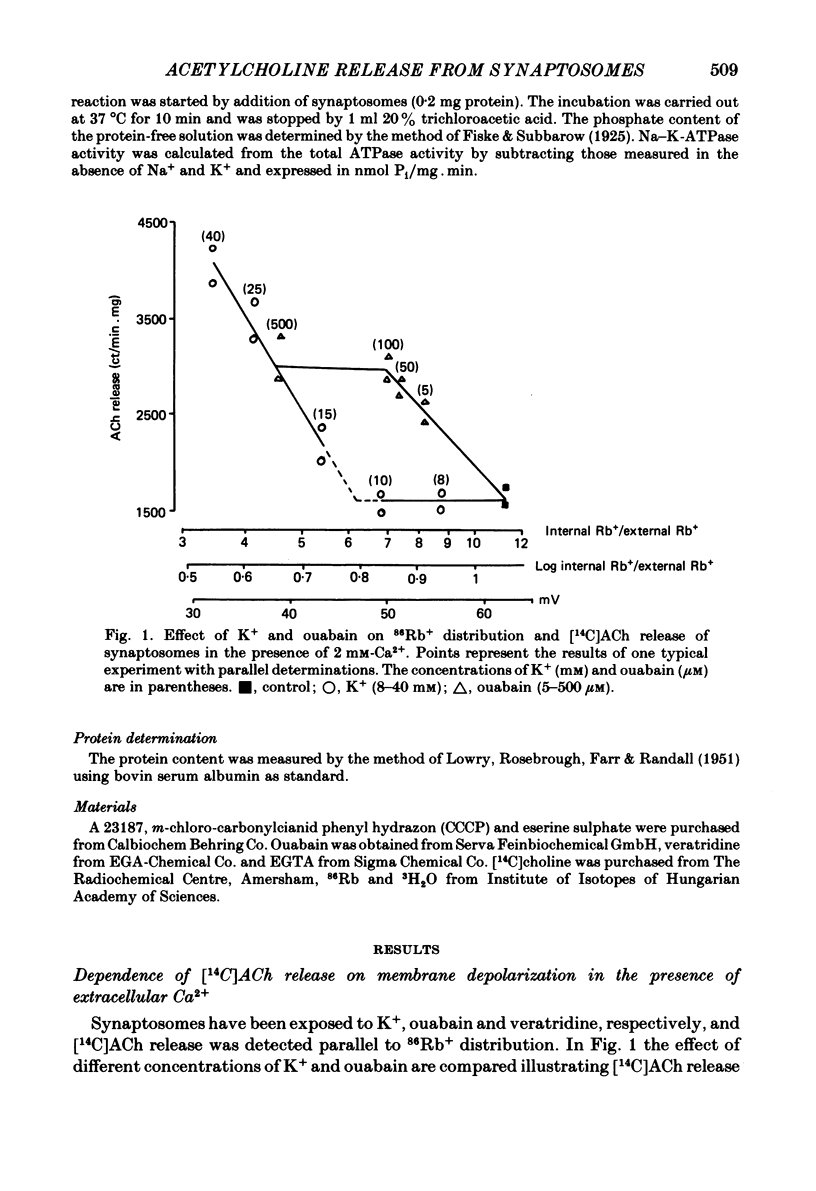
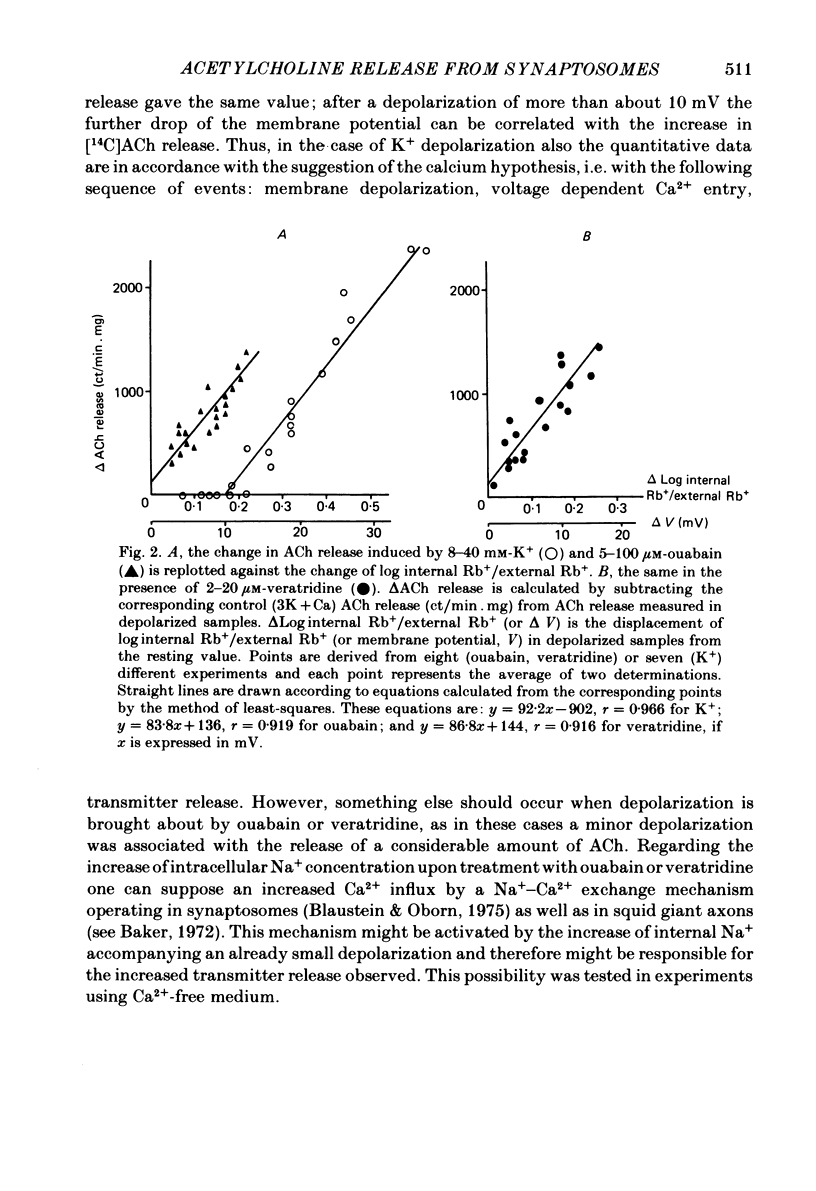
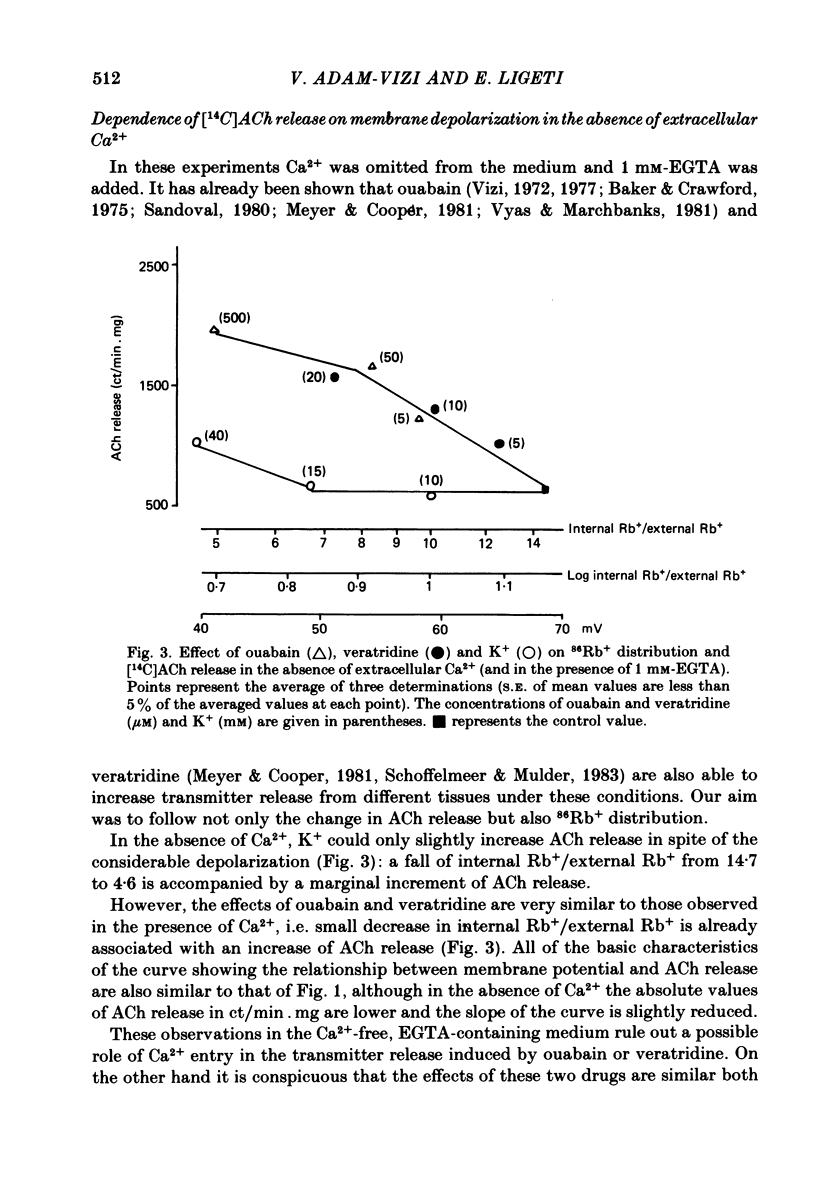
The relationship between 86Rb+ distribution across synaptosomal membrane and [14C]acetylcholine (ACh) release have been studied in a rat brain cortex synaptosomal preparation using K+, ouabain and veratridine depolarization. Decrease in membrane potential, approximated from the 86Rb+ distribution, is accompanied by an increase in [14C]ACh release, but the extent of the increase at a certain depolarization is dependent on how the depolarization is induced. A substantial depolarization by K+ is necessary to enhance ACh release, as compared to ouabain and veratridine where only a slight depolarization is accompanied by an increase in ACh release. In Ca2+-free, EGTA-containing medium ouabain and veratridine can also increase [14C]ACh release. The relationship between membrane potential and ACh release is very similar in the presence of ouabain and veratridine both in Ca2+-containing and Ca2+-free medium. The effect of ouabain and veratridine on the Na-K exchange pump is different; ouabain can completely abolish Na-K-ATPase activity and 86Rb+ uptake of synaptosomes, whereas veratridine does not seem to influence the activity of the pump. m-Chloro-carbonylcianid phenyl hydrazon (50-500 nM) increases [14C]ACh release in a concentration-dependent manner without a considerable change of membrane potential or Na-K pump activity. The Ca2+ ionophore A 23187 induces a substantial increase in [14C]ACh release in the absence of external Ca2+. In this case neither Na-K pump activity nor membrane potential of synaptosomes is changed. A possible role of intracellular Ca2+ mobilization as a consequence of increased intracellular Na+ concentration in some depolarization-induced transmitter release is discussed.
Full text
PDF



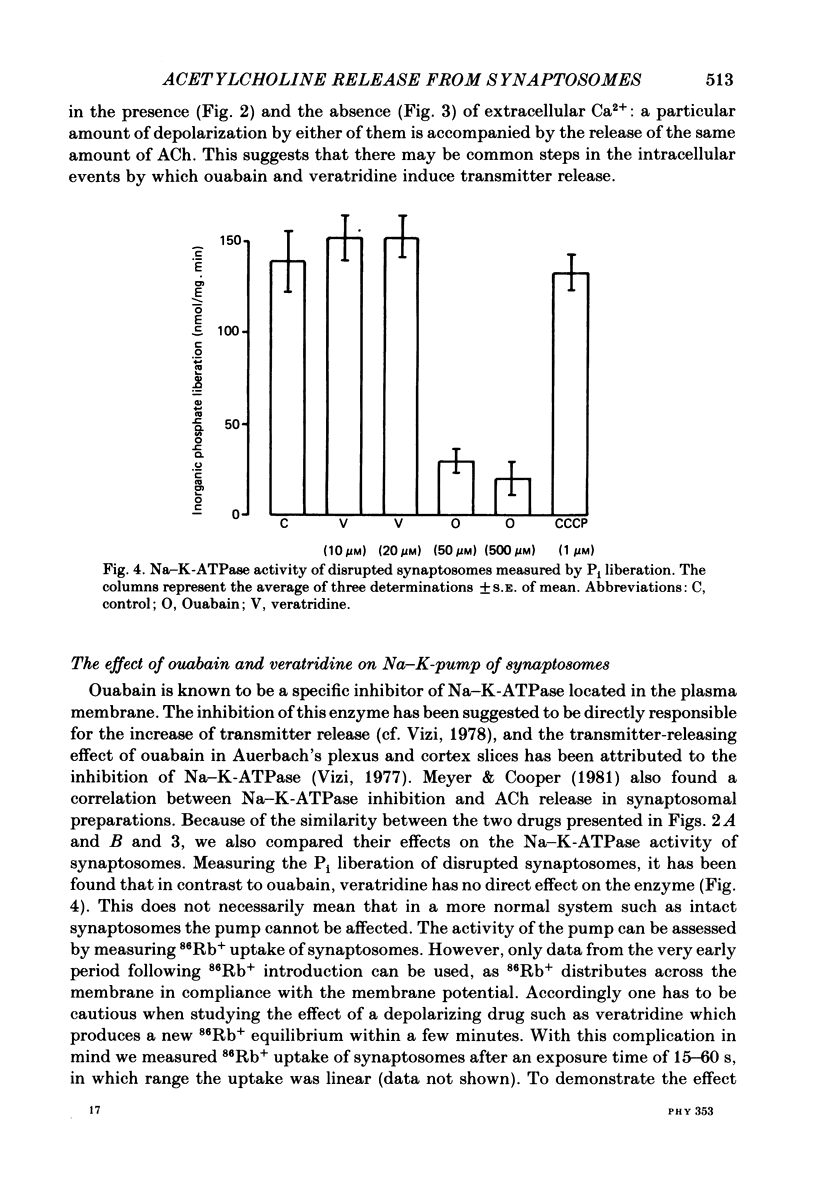
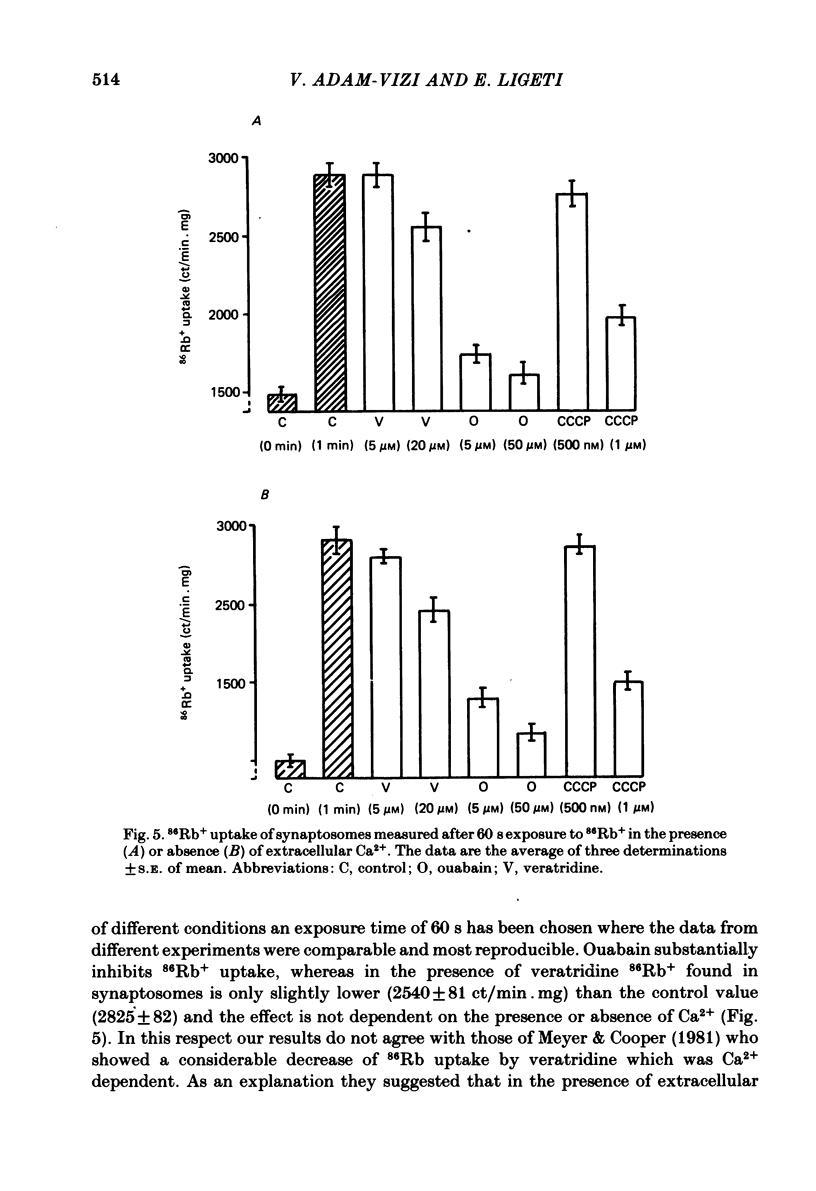
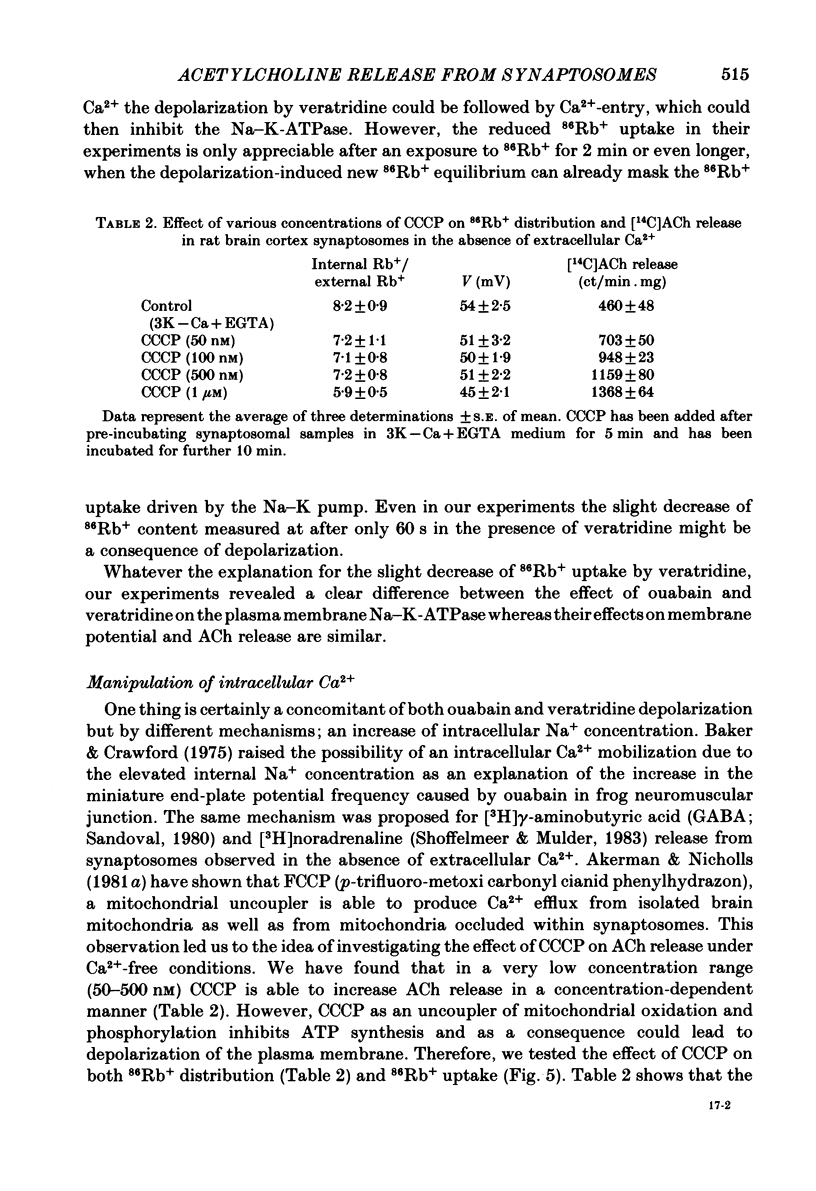
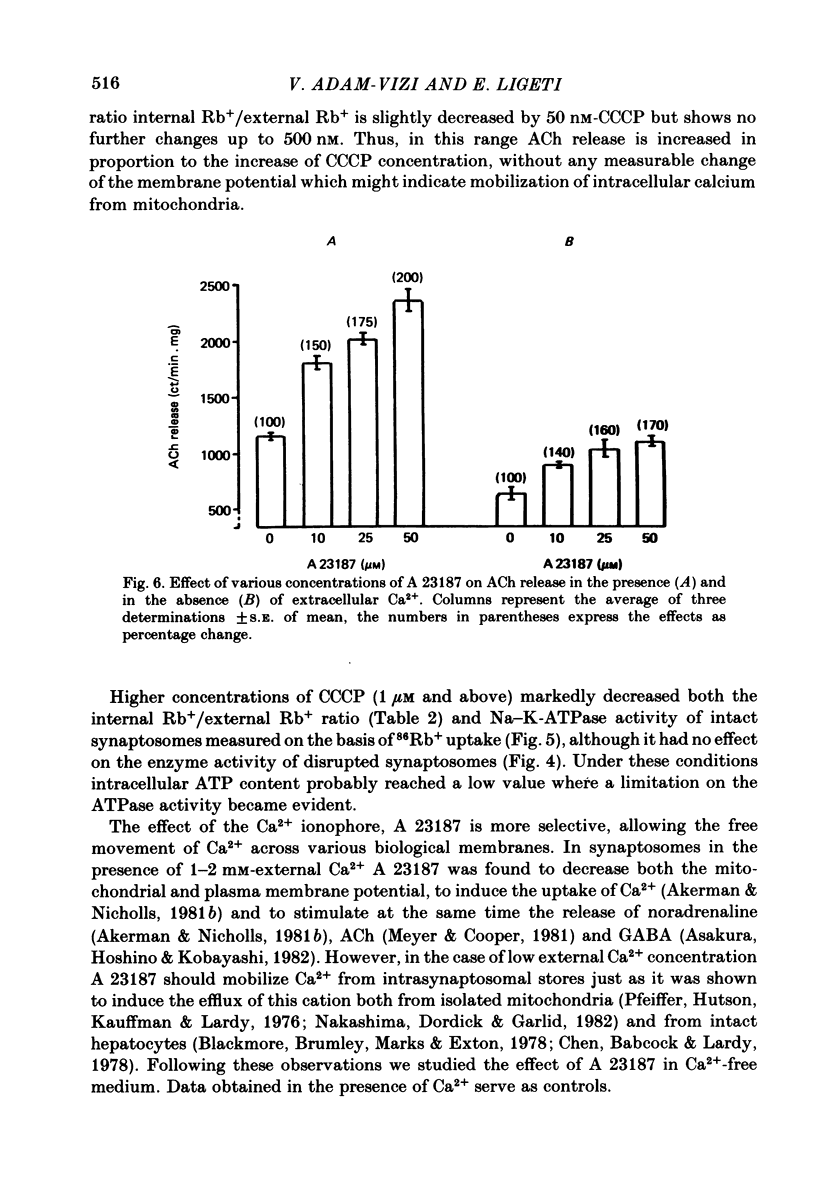





Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Akerman K. E., Nicholls D. G. Calcium transport by intact synaptosomes. Influence of ionophore A23187 on plasma-membrane potential, plasma-membrane calcium transport, mitochondrial membrane potential, respiration, cytosolic free-calcium concentration and noradrenaline release. Eur J Biochem. 1981 Mar 16;115(1):67–73. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Akerman K. E., Nicholls D. G. Intrasynaptosomal compartmentation of calcium during depolarization-induced calcium uptake across the plasma membrane. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1981 Jul 6;645(1):41–48. doi: 10.1016/0005-2736(81)90509-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Asakura T., Hoshino M., Kobayashi T. Effect of calcium ion on the release of gamma-aminobutyric acid from synaptosomal fraction. J Biochem. 1982 Dec;92(6):1919–1923. doi: 10.1093/oxfordjournals.jbchem.a134122. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Baker P. F., Crawford A. C. A note of the mechanism by which inhibitors of the sodium pump accelerate spontaneous release of transmitter from motor nerve terminals. J Physiol. 1975 May;247(1):209–226. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1975.sp010928. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Baker P. F. Transport and metabolism of calcium ions in nerve. Prog Biophys Mol Biol. 1972;24:177–223. doi: 10.1016/0079-6107(72)90007-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Blackmore P. F., Brumley F. T., Marks J. L., Exton J. H. Studies on alpha-adrenergic activation of hepatic glucose output. Relationship between alpha-adrenergic stimulation of calcium efflux and activation of phosphorylase in isolated rat liver parenchymal cells. J Biol Chem. 1978 Jul 25;253(14):4851–4858. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Blaustein M. P. Effects of potassium, veratridine, and scorpion venom on calcium accumulation and transmitter release by nerve terminals in vitro. J Physiol. 1975 Jun;247(3):617–655. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1975.sp010950. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Blaustein M. P., Goldring J. M. Membrane potentials in pinched-off presynaptic nerve ternimals monitored with a fluorescent probe: evidence that synaptosomes have potassium diffusion potentials. J Physiol. 1975 Jun;247(3):589–615. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1975.sp010949. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Blaustein M. P., Oborn C. J. The influence of sodium on calcium fluxes in pinched-off nerve terminals in vitro. J Physiol. 1975 Jun;247(3):657–686. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1975.sp010951. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Carafoli E., Crompton M. The regulation of intracellular calcium by mitochondria. Ann N Y Acad Sci. 1978 Apr 28;307:269–284. doi: 10.1111/j.1749-6632.1978.tb41957.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chen J. L., Babcock D. F., Lardy H. A. Norepinephrine, vasopressin, glucagon, and A23187 induce efflux of calcium from an exchangeable pool in isolated rat hepatocytes. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1978 May;75(5):2234–2238. doi: 10.1073/pnas.75.5.2234. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Creveling C. R., McNeal E. T., McCulloh D. H., Daly J. W. Membrane potentials in cell-free preparations from guinea pig cerebral cortex: effect of depolarizing agents and cyclic nucleotides. J Neurochem. 1980 Oct;35(4):922–932. doi: 10.1111/j.1471-4159.1980.tb07091.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Crompton M., Moser R., Lüdi H., Carafoli E. The interrelations between the transport of sodium and calcium in mitochondria of various mammalian tissues. Eur J Biochem. 1978 Jan 2;82(1):25–31. doi: 10.1111/j.1432-1033.1978.tb11993.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Katz B., Miledi R. A study of synaptic transmission in the absence of nerve impulses. J Physiol. 1967 Sep;192(2):407–436. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1967.sp008307. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Katz B., Miledi R. The release of acetylcholine from nerve endings by graded electric pulses. Proc R Soc Lond B Biol Sci. 1967 Jan 31;167(1006):23–38. doi: 10.1098/rspb.1967.0011. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Katz B., Miledi R. The timing of calcium action during neuromuscular transmission. J Physiol. 1967 Apr;189(3):535–544. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1967.sp008183. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Keen P., White T. D. The permeability of pinched-off nerve endings to sodium, potassium and chloride and the effects of gramicidin. J Neurochem. 1971 Jun;18(6):1097–1103. doi: 10.1111/j.1471-4159.1971.tb12038.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kostyuk P. G. Calcium ionic channels in electrically excitable membrane. Neuroscience. 1980;5(6):945–959. doi: 10.1016/0306-4522(80)90178-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- LI C. L. Cortical intracellular potentials and their responses to strychnine. J Neurophysiol. 1959 Jul;22(4):436–450. doi: 10.1152/jn.1959.22.4.436. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- LOWRY O. H., ROSEBROUGH N. J., FARR A. L., RANDALL R. J. Protein measurement with the Folin phenol reagent. J Biol Chem. 1951 Nov;193(1):265–275. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Llinás R., Steinberg I. Z., Walton K. Presynaptic calcium currents and their relation to synaptic transmission: voltage clamp study in squid giant synapse and theoretical model for the calcium gate. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1976 Aug;73(8):2918–2922. doi: 10.1073/pnas.73.8.2918. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Marchbanks R. M., Israël M. Aspects of acetylcholine metabolism in the electric organ of Torpedo marmorata. J Neurochem. 1971 Mar;18(3):439–448. doi: 10.1111/j.1471-4159.1971.tb11971.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Marchbanks R. M. The osmotically sensitive potassium and sodium compartments of synaptosomes. Biochem J. 1967 Jul;104(1):148–157. doi: 10.1042/bj1040148. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Meyer E. M., Cooper J. R. Correlations between Na+-K+ ATPase activity and acetylcholine release in rat cortical synaptosomes. J Neurochem. 1981 Feb;36(2):467–475. doi: 10.1111/j.1471-4159.1981.tb01616.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Miledi R., Thies R. Tetanic and post-tetanic rise in frequency of miniature end-plate potentials in low-calcium solutions. J Physiol. 1971 Jan;212(1):245–257. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1971.sp009320. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Miledi R. Transmitter release induced by injection of calcium ions into nerve terminals. Proc R Soc Lond B Biol Sci. 1973 Jul 3;183(1073):421–425. doi: 10.1098/rspb.1973.0026. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nakashima R. A., Dordick R. S., Garlid K. D. On the relative roles of Ca2+ and Mg2+ in regulating the endogenous K+/H+ exchanger of rat liver mitochondria. J Biol Chem. 1982 Nov 10;257(21):12540–12545. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nemeth E. F., Cooper J. R. Effect of somatostatin on acetylcholine release from rat hippocampal synaptosomes. Brain Res. 1979 Apr 6;165(1):166–170. doi: 10.1016/0006-8993(79)90057-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pfeiffer D. R., Hutson S. M., Kauffman R. F., Lardy H. A. Some effects of ionophore A23187 on energy utilization and the distribution of cations and anions in mitochondria. Biochemistry. 1976 Jun 15;15(12):2690–2697. doi: 10.1021/bi00657a032. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sandoval M. E. Sodium-dependent efflux of [3H]GABA from synaptosomes probably related to mitochondrial calcium mobilization. J Neurochem. 1980 Oct;35(4):915–921. doi: 10.1111/j.1471-4159.1980.tb07090.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schoffelmeer A. N., Mulder A. H. [3H]noradrenaline release from brain slices induced by an increase in the intracellular sodium concentration: role of intracellular calcium stores. J Neurochem. 1983 Mar;40(3):615–621. doi: 10.1111/j.1471-4159.1983.tb08025.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Scott I. D., Nicholls D. G. Energy transduction in intact synaptosomes. Influence of plasma-membrane depolarization on the respiration and membrane potential of internal mitochondria determined in situ. Biochem J. 1980 Jan 15;186(1):21–33. doi: 10.1042/bj1860021. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Silbergeld E. K. Na+ regulates release of Ca++ sequestered in synaptosomal mitochondria. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1977 Jul 25;77(2):464–469. doi: 10.1016/s0006-291x(77)80003-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Vizi E. S. Na+-K+-activated adenosinetriphosphatase as a trigger in transmitter release. Neuroscience. 1978;3(4-5):367–384. doi: 10.1016/0306-4522(78)90040-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Vizi E. S. Stimulation, by inhibition of (Na + -K + -Mg 2+ )-activated ATP-ase, of acetylcholine release in cortical slices from rat brain. J Physiol. 1972 Oct;226(1):95–117. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1972.sp009975. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Vizi E. S. Termination of transmitter release by stimulation of sodium-potassium activated ATPase. J Physiol. 1977 May;267(2):261–280. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1977.sp011812. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Vyas S., Marchbanks R. M. The effect of ouabain on the release of [14C]acetylcholine and other substances from synaptosomes. J Neurochem. 1981 Dec;37(6):1467–1474. doi: 10.1111/j.1471-4159.1981.tb06316.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wonnacott S., Marchbanks R. M. Inhibition by botulinum toxin of depolarization-evoked release of (14C)acetylcholine from synaptosomes in vitro. Biochem J. 1976 Jun 15;156(3):701–712. doi: 10.1042/bj1560701. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


