Abstract
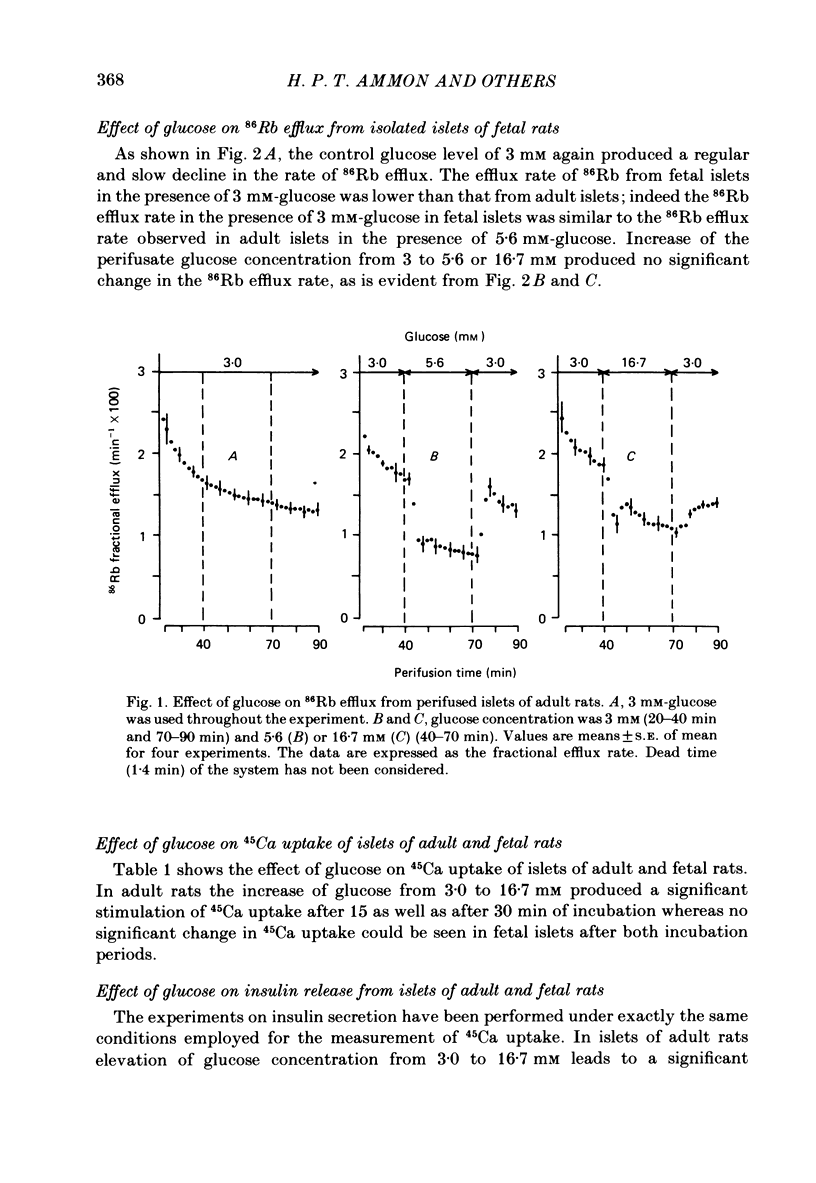
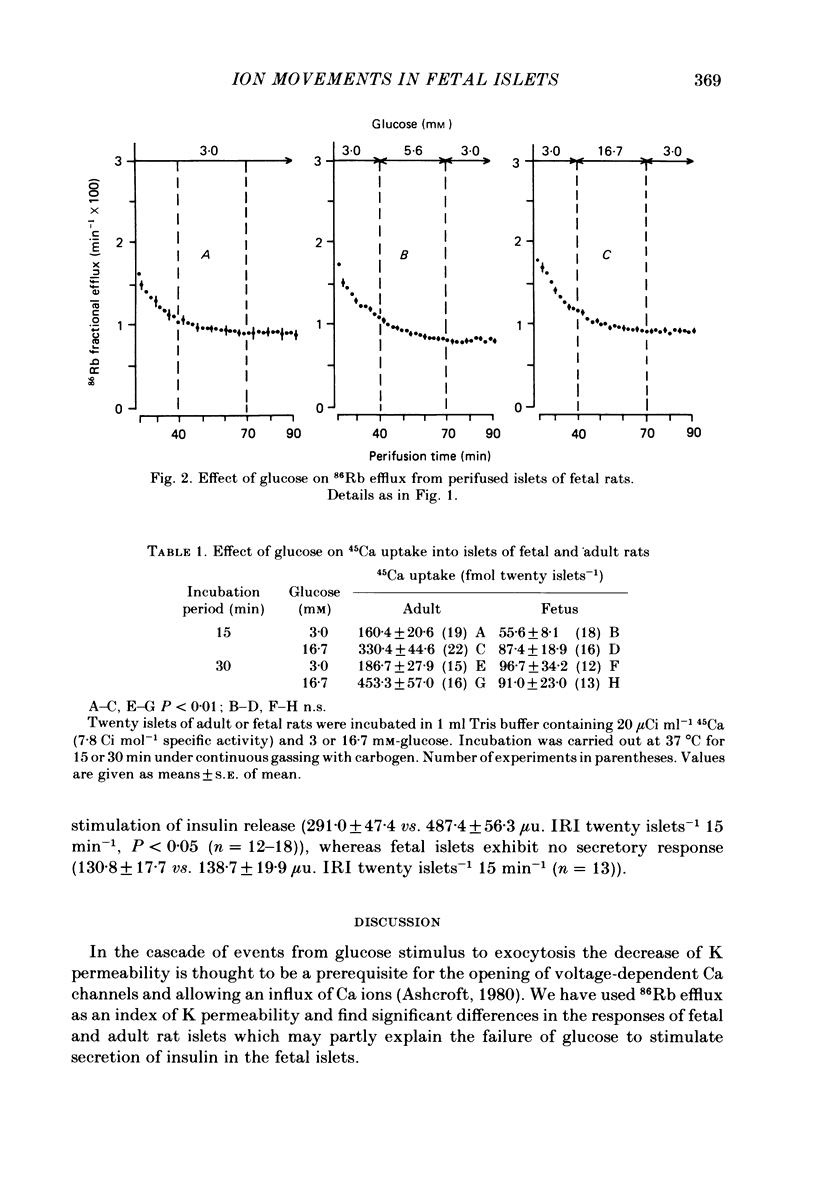
Ion movements and insulin secretion of pancreatic islets of adult and fetal rats have been studied at three glucose concentrations. In islets of adult rats, 86Rb efflux is maximally decreased by 5.6 mM-glucose. 16.7 mM-glucose caused a biphasic efflux pattern which may be due to glucose-stimulated Ca uptake. In islets of fetal rats elevation of the glucose concentration from 3 to 5.6 or 16.7 mM does not cause a change of 86Rb efflux, and the fractional efflux from fetal islets in the presence of 3 mM-glucose is similar to that from adult rat islets in the presence of 5.6 mM-glucose. Elevation of the glucose concentration from 3 to 16.7 mM is not associated with an increase in 45Ca uptake into fetal islets, although this change in glucose concentration doubles 45Ca uptake into adult islets. When challenged with 16.7 mM-glucose, fetal islets exhibit no insulin secretory response; however, they do respond to theophylline. It is concluded that the failure of fetal islets to exhibit an insulin-secretory response when challenged with glucose might be related to the inability of glucose to affect 86Rb efflux and Ca uptake. The present data are discussed in light of differences between pancreatic islets of fetal and adult rats with respect to the redox state of pyridine nucleotides, thiols and glucose metabolism.
Full text
PDF





Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Ammon H. P., Abdel-Hamid M., Rao P. G., Enz G. Thiol-dependent and non-thiol-dependent stimulations of insulin release. Diabetes. 1984 Mar;33(3):251–257. doi: 10.2337/diab.33.3.251. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ammon H. P., Bumiller G., Düppenbecker H., Heinze E., Lutz S., Verspohl E. J. Pentose phosphate shunt, pyridine nucleotides, glutathione, and insulin secretion of fetal islets. Am J Physiol. 1983 Apr;244(4):E354–E360. doi: 10.1152/ajpendo.1983.244.4.E354. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ammon H. P., Grimm A., Lutz S., Wagner-Teschner D., Händel M., Hagenloh I. Islet glutathione and insulin release. Diabetes. 1980 Oct;29(10):830–834. doi: 10.2337/diacare.20.10.830. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ammon H. P., Hägele R., Youssif N., Eujen R., El-Amri N. A possible role of intracellular and membrane thiols of rat pancreatic islets in calcium uptake and insulin release. Endocrinology. 1983 Feb;112(2):720–726. doi: 10.1210/endo-112-2-720. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ashcroft S. J. Glucoreceptor mechanisms and the control of insulin release and biosynthesis. Diabetologia. 1980 Jan;18(1):5–15. doi: 10.1007/BF01228295. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Asplund K. Dynamics of insulin release from the foetal and neonatal rat pancreas. Eur J Clin Invest. 1973 Jul;3(4):338–344. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-2362.1973.tb00360.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Asplund K., Westman S., Hellerström C. Glucose stimulation of insulin secretion from the isolated pancreas of foetal and newborn rats. Diabetologia. 1969 Aug;5(4):260–262. doi: 10.1007/BF01212095. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Boschero A. C., Malaisse W. J. Stimulus-secretion coupling of glucose-induced insulin release. XXIX. Regulation of 86Rb+ efflux from perfused islets. Am J Physiol. 1979 Feb;236(2):E139–E146. doi: 10.1152/ajpendo.1979.236.2.E139. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Heinze E., Steinke J. Glucose metabolism of isolated pancreatic islets: difference between fetal, newborn and adult rats. Endocrinology. 1971 May;88(5):1259–1263. doi: 10.1210/endo-88-5-1259. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Heinze E., Steinke J. Insulin secretion during development: response of isolated pancreatic islets of fetal, newborn and adult rats to theophylline and arginine. Horm Metab Res. 1972 Jul;4(4):234–236. doi: 10.1055/s-0028-1094056. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hellman B., Sehlin J., Söderberg M., Täljedal I. B. The mechanisms of action of chloromercuribenzene-p-sulphonic acid as insulin secretagogue: fluxes of calcium, sodium and rubidium in islets exposed to mercurial and a membrane-active antagonist. J Physiol. 1975 Nov;252(3):701–712. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1975.sp011166. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hellman B., Sehlin J., Täljedal I. B. Effects of glucose on 45Ca2+ uptake by pancreatic islets as studied with the lanthanum method. J Physiol. 1976 Jan;254(3):639–656. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1976.sp011250. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Henquin J. C., Meissner H. P., Schmeer W. Cyclic variations of glucose-induced electrical activity in pancreatic B cells. Pflugers Arch. 1982 Jun;393(4):322–327. doi: 10.1007/BF00581418. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Henquin J. C. Metabolic control of potassium permeability in pancreatic islet cells. Biochem J. 1980 Feb 15;186(2):541–550. doi: 10.1042/bj1860541. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Henquin J. C. Tetraethylammonium potentiation of insulin release and inhibition of rubidium efflux in pancreatic islets. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1977 Jul 25;77(2):551–556. doi: 10.1016/s0006-291x(77)80014-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kervran A., Randon J. Development of insulin release by fetal rat pancreas in vitro: effects of glucose, amino acids, and theophylline. Diabetes. 1980 Sep;29(9):673–678. doi: 10.2337/diab.29.9.673. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lacy P. E., Kostianovsky M. Method for the isolation of intact islets of Langerhans from the rat pancreas. Diabetes. 1967 Jan;16(1):35–39. doi: 10.2337/diab.16.1.35. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lebrun P., Malaisse W. J., Herchuelz A. Paradoxical activation by glucose of quinine-sensitive potassium channels in the pancreatic B-cell. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1982 Jul 16;107(1):350–356. doi: 10.1016/0006-291x(82)91711-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Malaisse W. J., Hutton J. C., Sener A., Levy J., Herchuelz A., Devis G., Somers G. Calcium antagonists and islet function: VII. Effect of calcium deprivation. J Membr Biol. 1978 Jan 18;38(3):193–208. doi: 10.1007/BF01871922. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sodoyez-Goffaux F. R., Sodoyez J. C., De Vos C. J. Insulin secretion and metabolism during the perinatal period in the rat. Evidence for a placental role in fetal hyperinsulinemia. J Clin Invest. 1979 Jun;63(6):1095–1102. doi: 10.1172/JCI109401. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sodoyez-Goffaux F., Sodoyez J. C., De Vos C. J., Foà P. P. Insulin and glucagon secretion by islets isolated from fetal and neonatal rats. Diabetologia. 1979 Feb;16(2):121–123. doi: 10.1007/BF01225461. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Soeldner J. S., Slone D. Critical variables in the radioimmunoassay of serum insulin using the double antibody technic. Diabetes. 1965 Dec;14(12):771–779. doi: 10.2337/diab.14.12.771. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


