Abstract
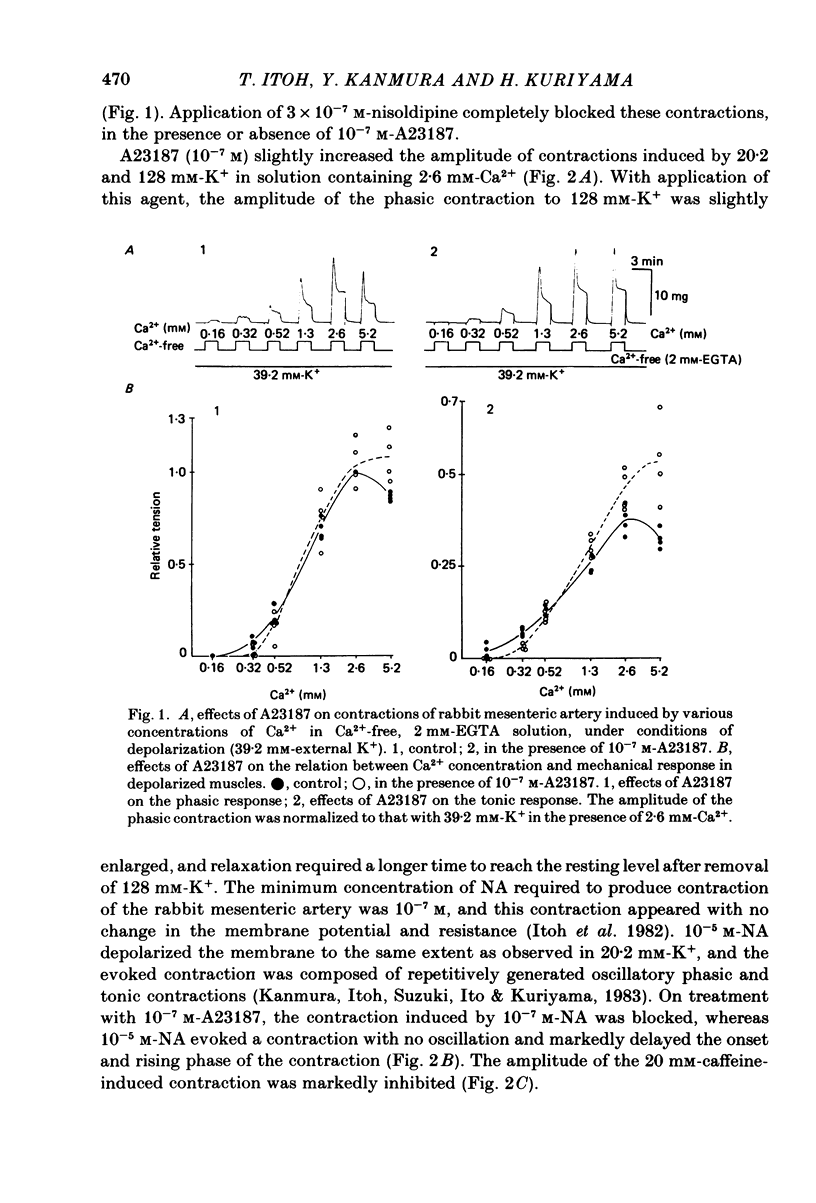
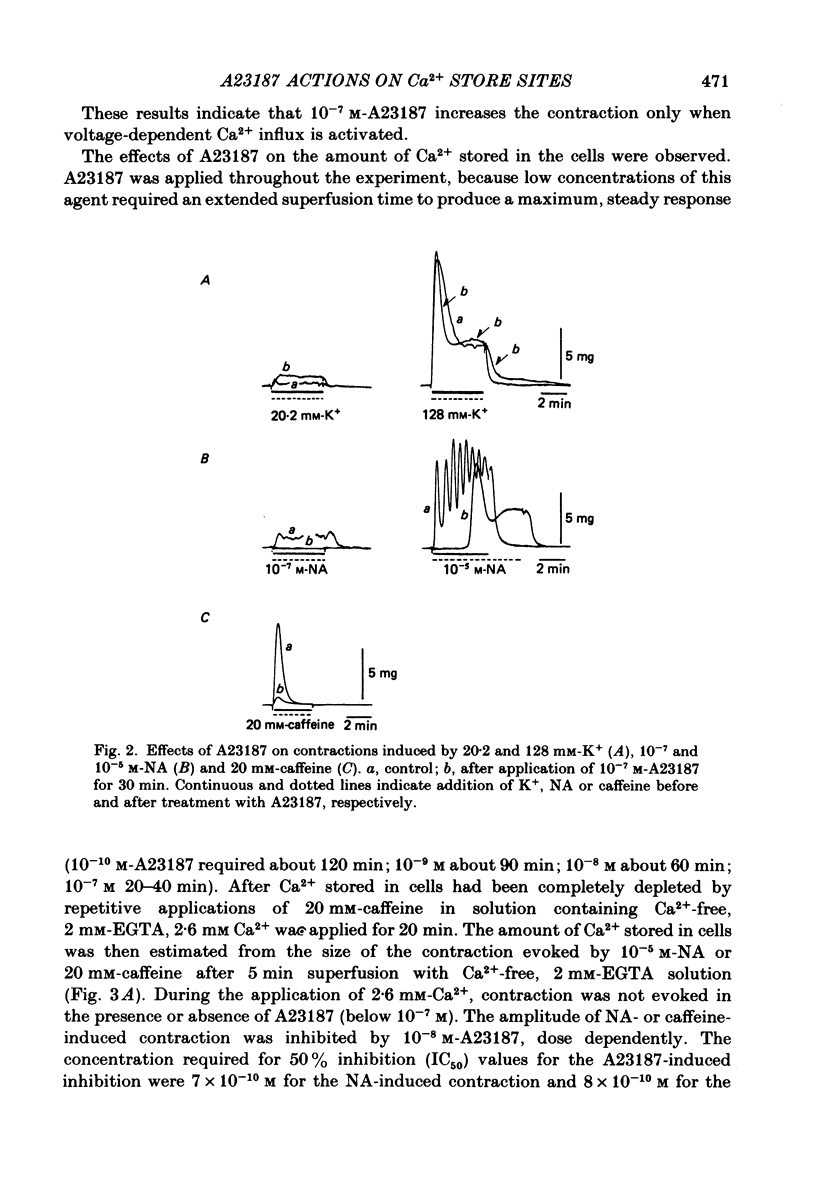
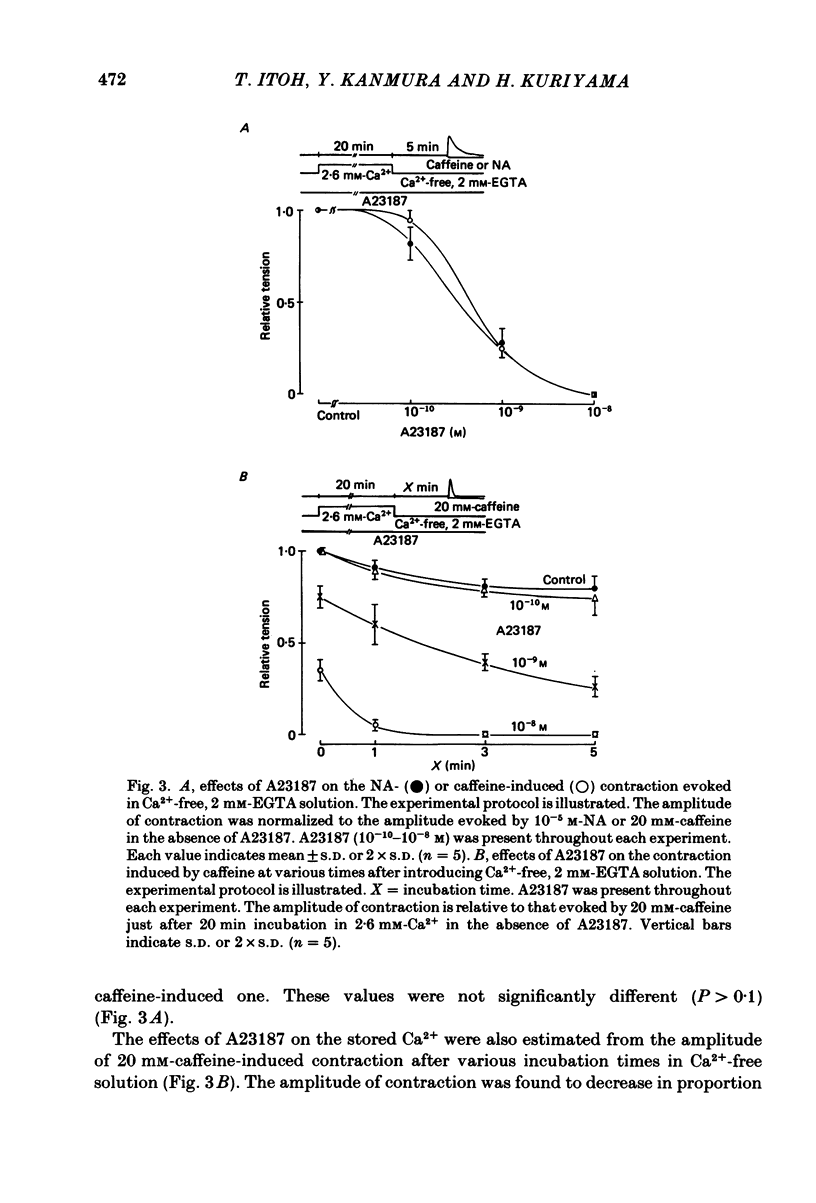
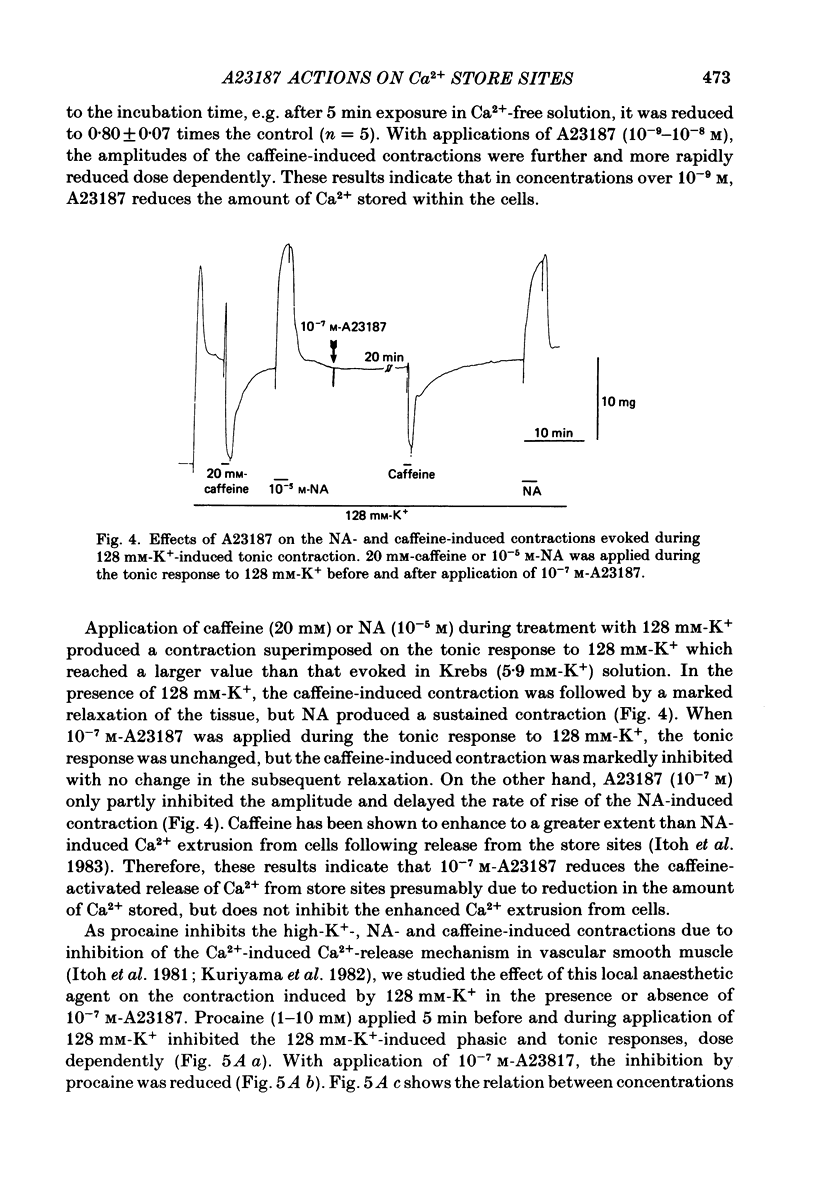
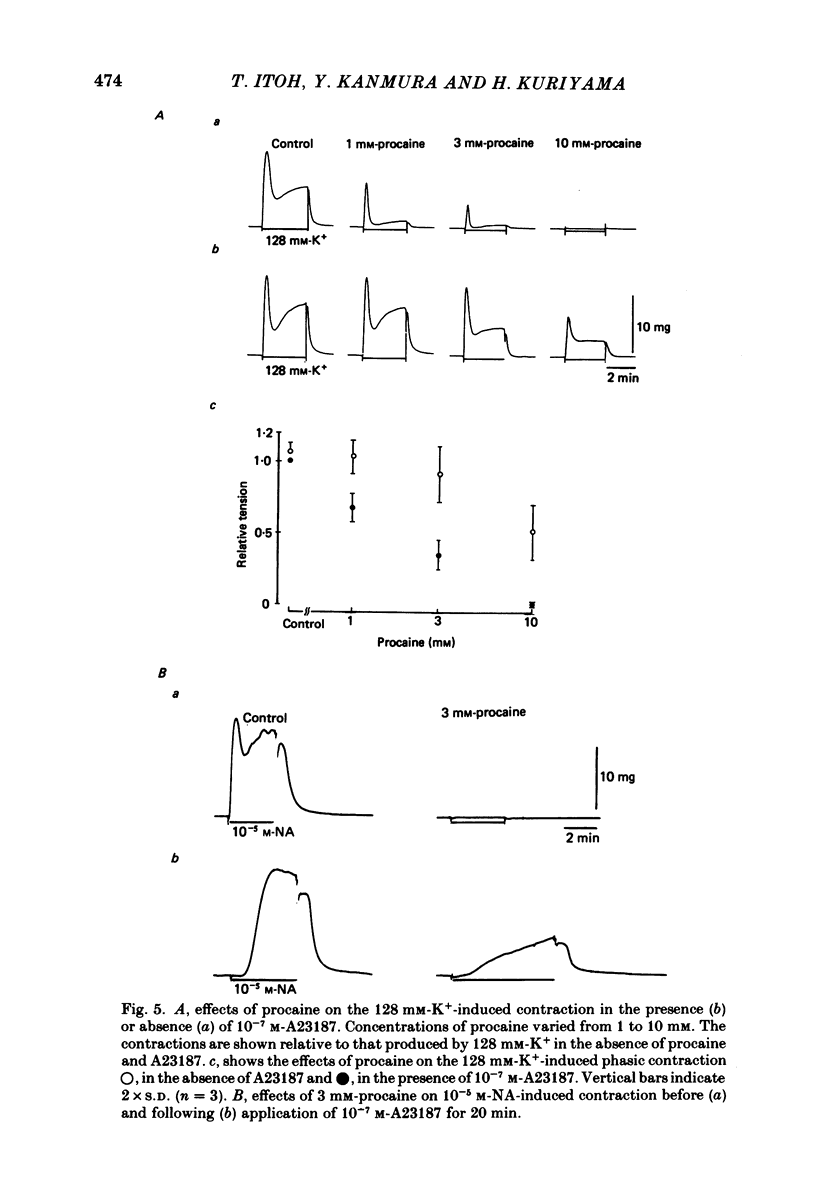
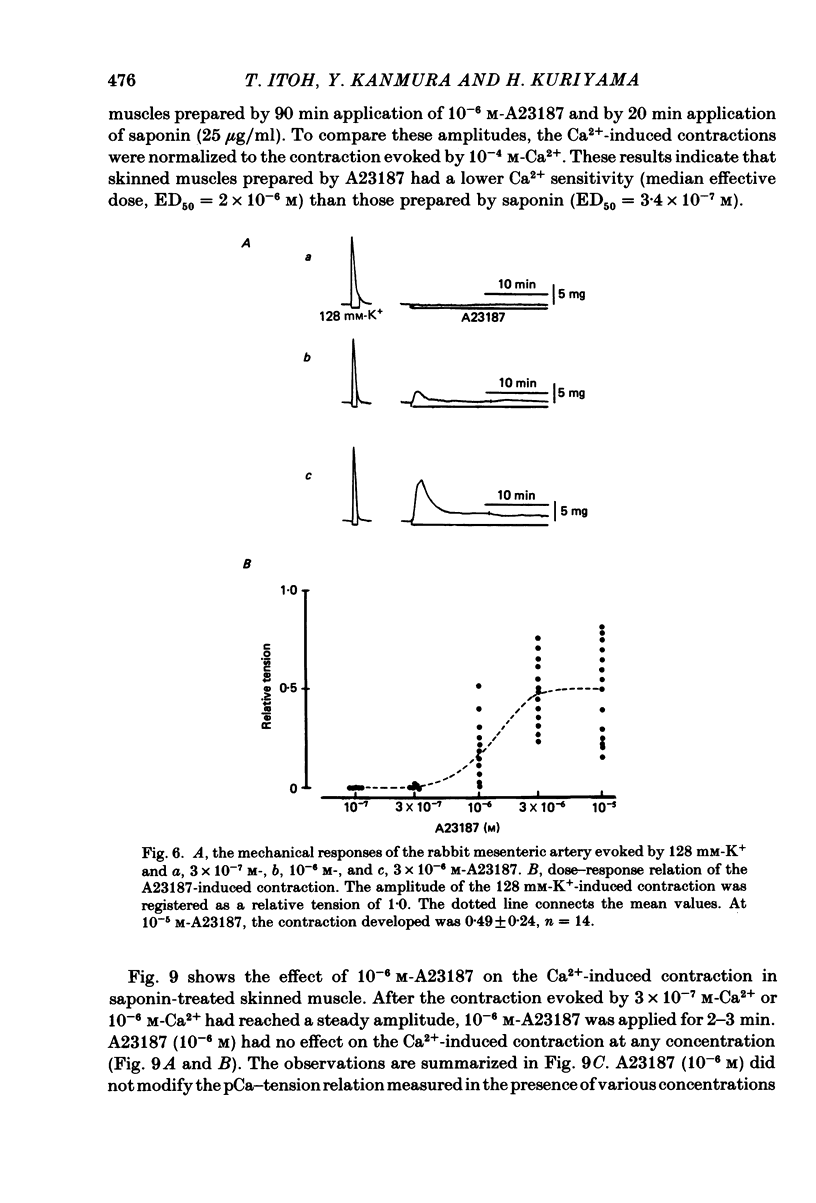
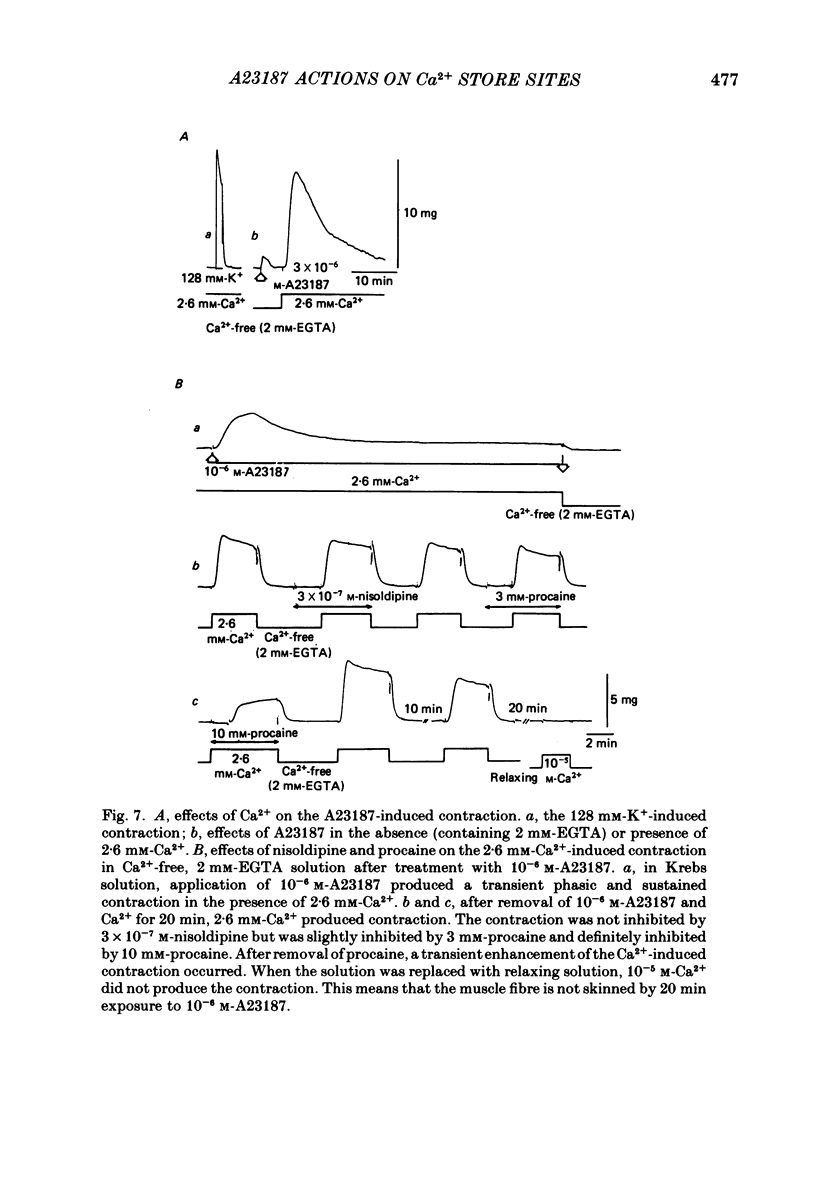
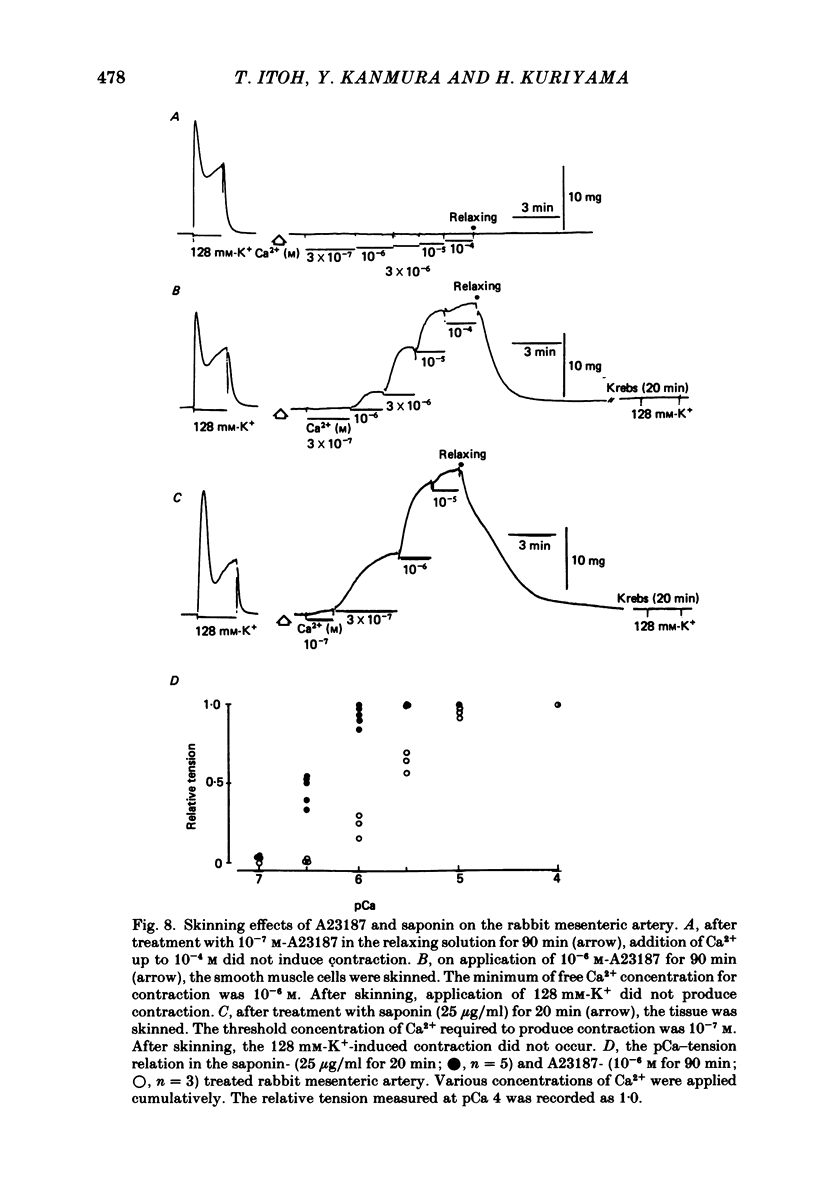
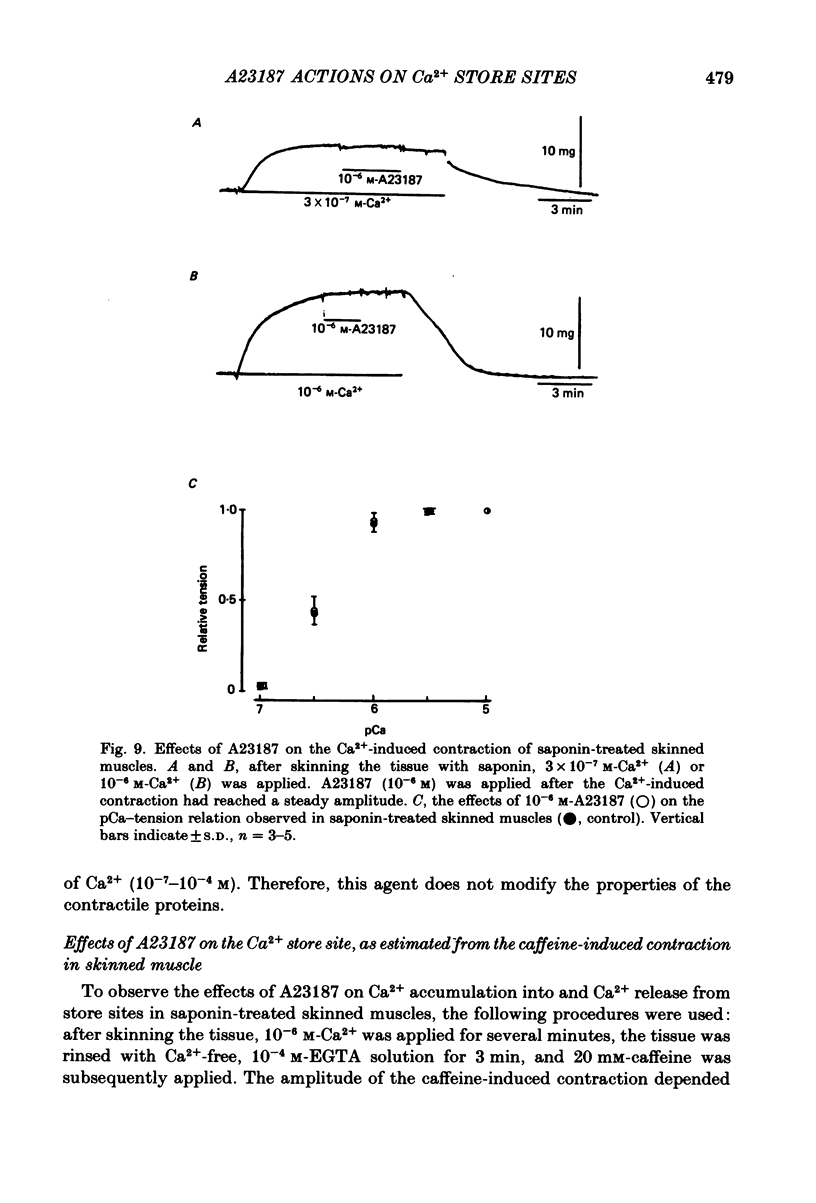
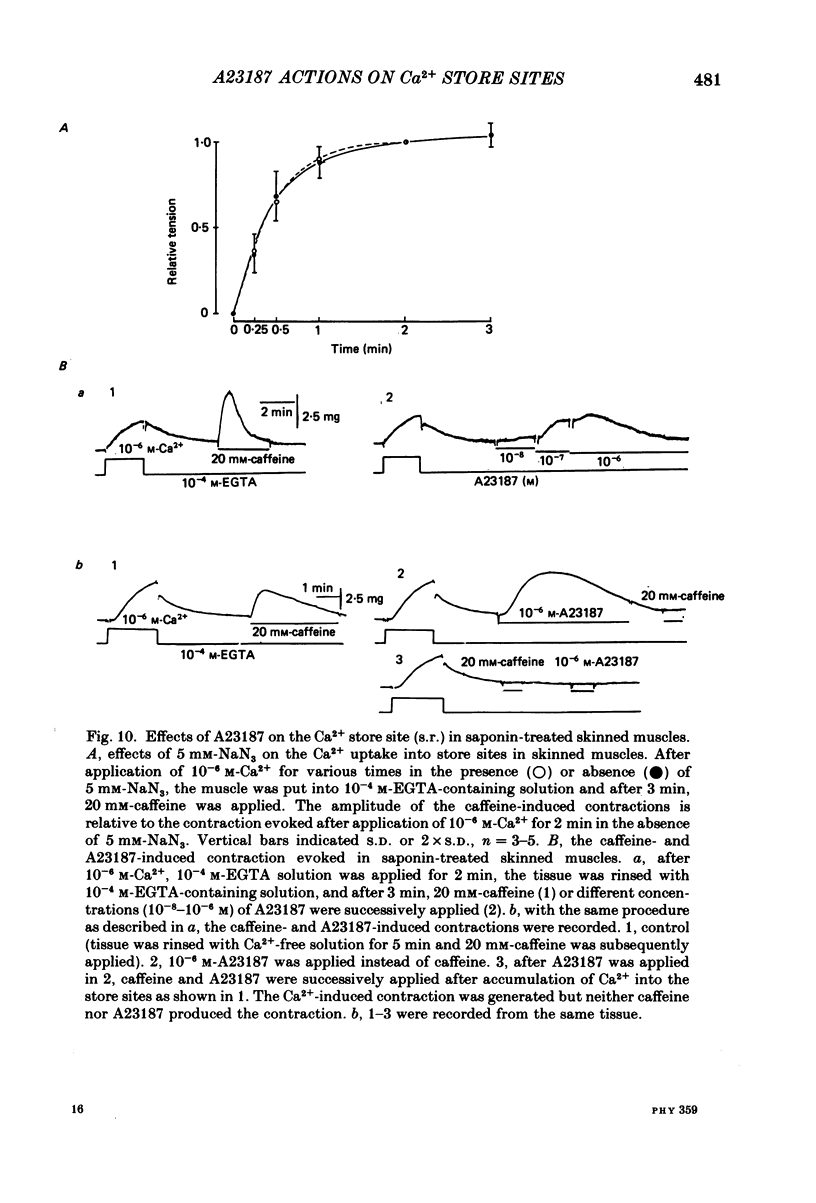
The effects of a Ca ionophore, A23187, were investigated on intact and skinned smooth muscle tissues of the rabbit mesenteric artery. A23187 (over 10(-9) M) inhibited, dose dependently, contractions induced by 10(-5) M-noradrenaline (NA) or 10 mM-caffeine in Ca2+-free solution containing 2 mM-EGTA. Procaine (3 mM) led to cessation of the caffeine- or NA-induced contractions in the presence or absence of Ca2+. When A23187 (10(-7) M) was applied, the contractions in the presence of procaine were to some extent restored in Krebs solution. A23187 at a concentration of 10(-7) M did not modify the resting muscle tone, but this concentration did increase the amplitude of the contraction evoked by 20.2 or 128 mM-K+ and markedly inhibited the 10(-7) M-NA or 10 mM-caffeine-induced contraction in Krebs solution. A23187 (10(-7) M) delayed the onset and rising phase of the 10(-5) M-NA-induced contraction with inhibition of the oscillatory contractions. High concentrations of A23187 (over 10(-6) M) produced a large contraction in the presence and a small contraction in the absence of 2.6 mM-Ca2+. These A23187-induced contractions were not inhibited by 10(-7) M-nisoldipine, a Ca2+ antagonist. A23187 (over 10(-6) M) applied for a long period functionally skinned the muscle tissues. However, the Ca2+ sensitivity of the A23187-treated skinned muscles was lower than that of saponin-treated muscles. In saponin-treated skinned muscles, A23187 (below 10(-6) M) had no effect on the pCa-tension relation. After filling the store, A23187 (over 10(-7) M) generated a larger contraction than did caffeine in Ca2+-free solution, in the presence or absence of 5 mM-NaN3. When 10(-7) M-A23187 was applied once for 5 min, subsequently applied caffeine (20 mM), following application of Ca2+, no longer produced contraction of skinned muscle tissues. The present results indicate that low concentrations of A23187 show a selective Ca2+-releasing action on Ca2+ store sites in muscle cells and that high concentrations increase the Ca2+ leakage (influx) and the cell membrane is skinned.
Full text
PDF







Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Caswell A. H., Pressman B. C. Kinetics of transport of divalent cations across sarcoplasmic reticulum vesicles induced by ionophores. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1972 Oct 6;49(1):292–298. doi: 10.1016/0006-291x(72)90043-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Deth R., Casteels R. A study of releasable Ca fractions in smooth muscle cells of the rabbit aorta. J Gen Physiol. 1977 Apr;69(4):401–416. doi: 10.1085/jgp.69.4.401. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Deth R., van Breemen C. Relative contributions of Ca2+ influx and cellular Ca2+ release during drug induced activation of the rabbit aorta. Pflugers Arch. 1974 Apr 4;348(1):13–22. doi: 10.1007/BF00587735. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Endo M. Calcium release from the sarcoplasmic reticulum. Physiol Rev. 1977 Jan;57(1):71–108. doi: 10.1152/physrev.1977.57.1.71. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fabiato A., Fabiato F. Calcium release from the sarcoplasmic reticulum. Circ Res. 1977 Feb;40(2):119–129. doi: 10.1161/01.res.40.2.119. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Furchgott R. F. Role of endothelium in responses of vascular smooth muscle. Circ Res. 1983 Nov;53(5):557–573. doi: 10.1161/01.res.53.5.557. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Haeusler G., Richards J. G., Thorens S. Noradrenaline contractions in rabbit mesenteric arteries skinned with saponin. J Physiol. 1981 Dec;321:537–556. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1981.sp014001. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Harafuji H., Ogawa Y. Re-examination of the apparent binding constant of ethylene glycol bis(beta-aminoethyl ether)-N,N,N',N'-tetraacetic acid with calcium around neutral pH. J Biochem. 1980 May;87(5):1305–1312. doi: 10.1093/oxfordjournals.jbchem.a132868. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Iino M. Tension responses of chemically skinned fibre bundles of the guinea-pig taenia caeci under varied ionic environments. J Physiol. 1981 Nov;320:449–467. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1981.sp013961. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ishida Y., Shibata S. Characteristics contractile response to the calcium ionophore, A23187, in guinea-pig vas deferens. Br J Pharmacol. 1980;71(2):581–583. doi: 10.1111/j.1476-5381.1980.tb10976.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ishida Y., Shibata S. Relaxing and metabolic inhibitory action of X537A (Lasalocid) on the taenia of the guinea-pig caecum. J Physiol. 1982 Dec;333:293–304. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1982.sp014454. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Itoh T., Kajiwara M., Kitamura K., Kuriyama H. Roles of stored calcium on the mechanical response evoked in smooth muscle cells of the porcine coronary artery. J Physiol. 1982 Jan;322:107–125. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1982.sp014026. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Itoh T., Kuriyama H., Suzuki H. Differences and similarities in the noradrenaline- and caffeine-induced mechanical responses in the rabbit mesenteric artery. J Physiol. 1983 Apr;337:609–629. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1983.sp014645. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Itoh T., Kuriyama H., Suzuki H. Excitation--contraction coupling in smooth muscle cells of the guinea-pig mesenteric artery. J Physiol. 1981 Dec;321:513–535. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1981.sp014000. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kanmura Y., Itoh T., Suzuki H., Ito Y., Kuriyama H. Effects of nifedipine on smooth muscle cells of the rabbit mesenteric artery. J Pharmacol Exp Ther. 1983 Jul;226(1):238–248. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kuriyama H., Ito Y., Suzuki H., Kitamura K., Itoh T. Factors modifying contraction-relaxation cycle in vascular smooth muscles. Am J Physiol. 1982 Nov;243(5):H641–H662. doi: 10.1152/ajpheart.1982.243.5.H641. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mandrek K., Golenhofen K. Activation of gastro-intestinal smooth muscle induced by the calcium ionophore A23187. Pflugers Arch. 1977 Oct 19;371(1-2):119–124. doi: 10.1007/BF00580779. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mobley B. A. Calcium ionophores and tension production in skinned frog muscle fibers. Eur J Pharmacol. 1977 Sep 15;45(2):101–104. doi: 10.1016/0014-2999(77)90079-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Murray J. J., Reed P. W., Fay F. S. Contraction of isolated smooth muscle cells by inophore A23187. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1975 Nov;72(11):4459–4463. doi: 10.1073/pnas.72.11.4459. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pressman B. C. Properties of ionophores with broad range cation selectivity. Fed Proc. 1973 Jun;32(6):1698–1703. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Reed P. W., Lardy H. A. A23187: a divalent cation ionophore. J Biol Chem. 1972 Nov 10;247(21):6970–6977. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Saida K., van Breemen C. Characteristics of the norepinephrine-sensitive Ca2+ store in vascular smooth muscle. Blood Vessels. 1984;21(1):43–52. doi: 10.1159/000158493. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Somlyo A. V., Somlyo A. P. Electromechanical and pharmacomechanical coupling in vascular smooth muscle. J Pharmacol Exp Ther. 1968 Jan;159(1):129–145. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Swamy V. C., Ticku M., Triggle C. R., Triggle D. J. The action of the ionophores, X-537A and A-23187, on smooth muscle. Can J Physiol Pharmacol. 1975 Dec;53(6):1108–1114. doi: 10.1139/y75-154. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Vághy P. L., Johnson J. D., Matlib M. A., Wang T., Schwartz A. Selective inhibition of Na+-induced Ca2+ release from heart mitochondria by diltiazem and certain other Ca2+ antagonist drugs. J Biol Chem. 1982 Jun 10;257(11):6000–6002. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Watson E. L. Effects of ionophores A23187 and X537A on vascular smooth muscle activity. Eur J Pharmacol. 1978 Nov 15;52(2):171–178. doi: 10.1016/0014-2999(78)90203-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


