Abstract
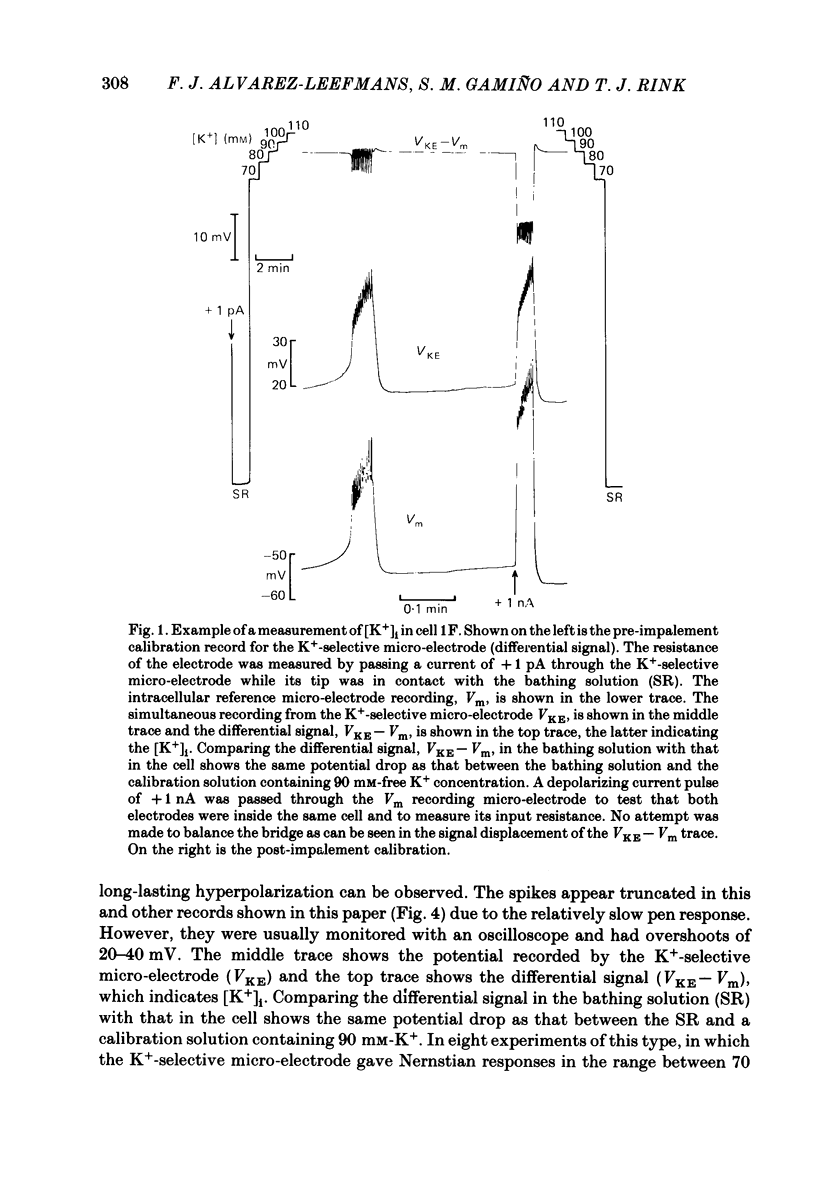
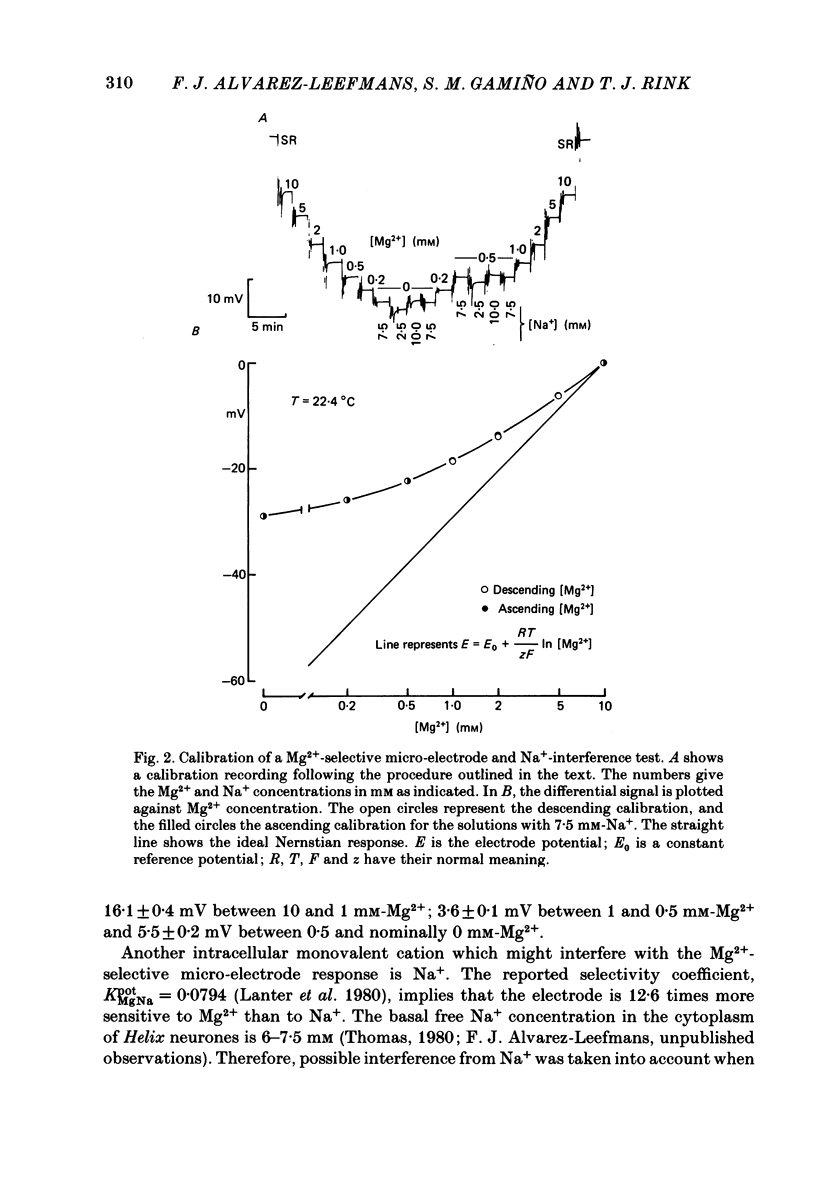
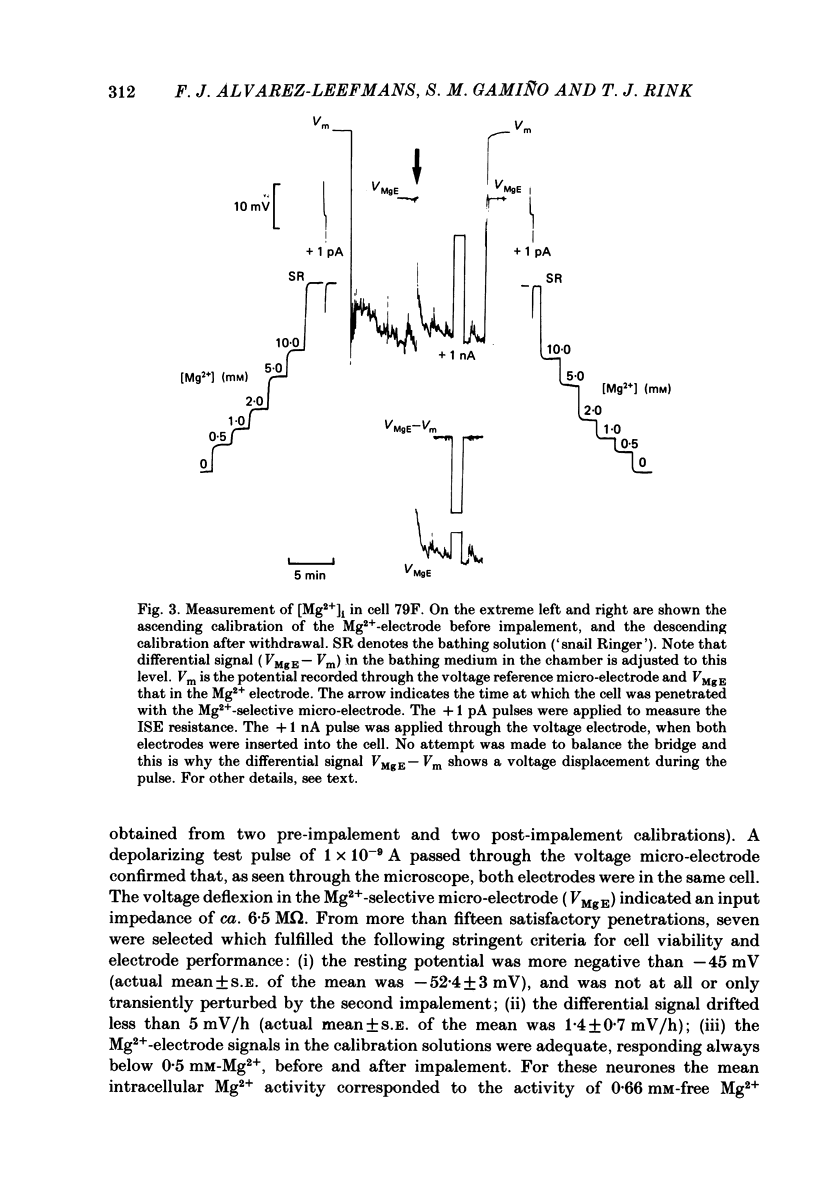
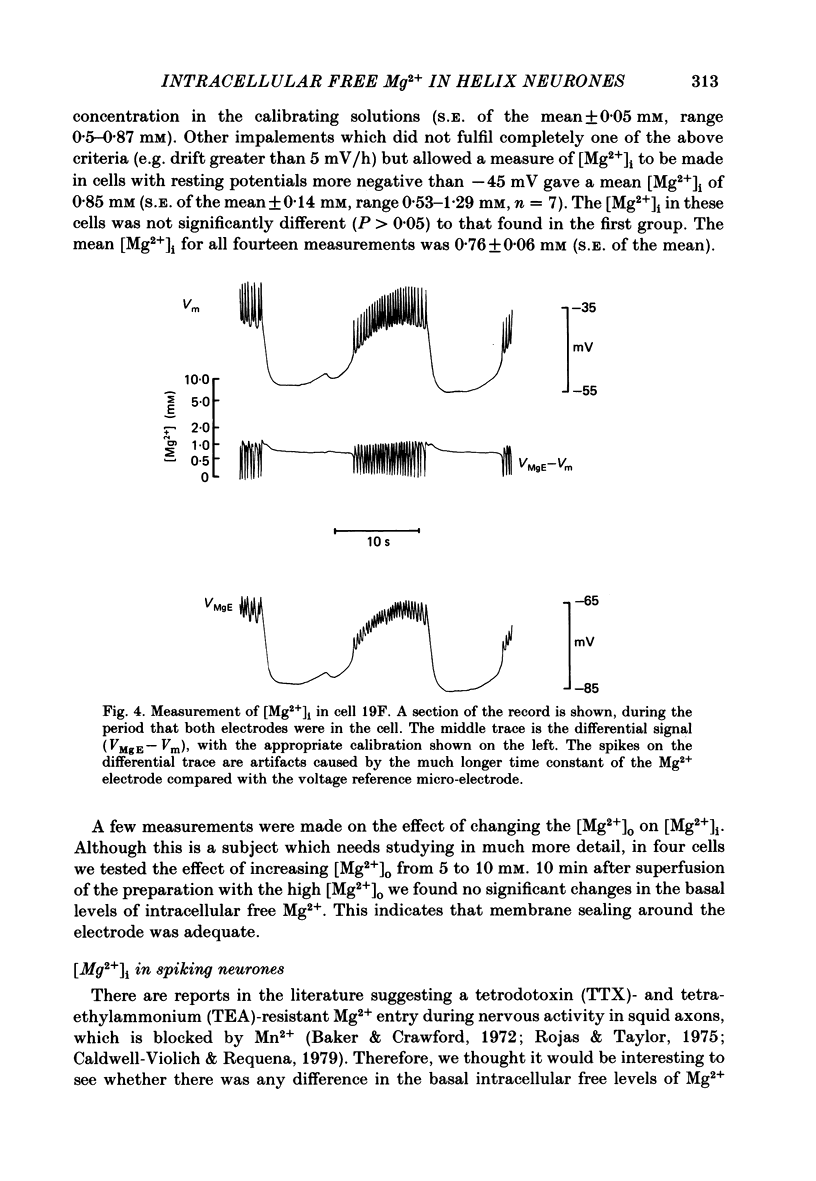
Cytoplasmic free Mg2+ concentration, [Mg2+]i, was measured in identified neuronal cell bodies of the suboesophageal ganglia of Helix aspersa, using Mg2+-selective micro-electrodes. In calibration solutions, the electrodes showed significant interference from K+, but not from Na+, or Ca2+, at concentrations found intracellularly. Therefore, in order to calibrate the electrodes properly, it was necessary first to obtain an accurate value for intracellular free K+ concentration [( K+]i). The mean value for [K+]i was 91 mM (S.E. of the mean +/- 2.2 mM, n = 8), measured with K+-sensitive 'liquid ion exchanger micro-electrodes'. In seven experiments, which met stringent criteria for satisfactory impalement and electrode calibration, the mean [Mg2+]i was 0.66 mM (S.E. of the mean +/- 0.05 mM). The mean [Mg2+]i in cells that had spontaneous spike activity was not significantly different from that in quiescent cells. If Mg2+ was in electrochemical equilibrium, the ratio [Mg2+]i/[Mg2+]o would be about 55. Mg2+ is therefore not passively distributed across the neuronal membrane and an outwardly directed extrusion mechanism must exist to keep [Mg2+]i low and constant, even in cells undergoing spike activity.
Full text
PDF










Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Adams D. J., Smith S. J., Thompson S. H. Ionic currents in molluscan soma. Annu Rev Neurosci. 1980;3:141–167. doi: 10.1146/annurev.ne.03.030180.001041. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Alvarez-Leefmans F. J., Rink T. J., Tsien R. Y. Free calcium ions in neurones of Helix aspersa measured with ion-selective micro-electrodes. J Physiol. 1981 Jun;315:531–548. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1981.sp013762. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Baker P. F., Crawford A. C. Mobility and transport of magnesium in squid giant axons. J Physiol. 1972 Dec;227(3):855–874. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1972.sp010062. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Brinley F. J., Jr, Scarpa A. Ionized magnesium concentration in axoplasm of dialyzed squid axons. FEBS Lett. 1975 Jan 15;50(1):82–85. doi: 10.1016/0014-5793(75)81046-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Caldwell-Violich M., Requena J. Magnesium content and net fluxes in squid giant axons. J Gen Physiol. 1979 Dec;74(6):739–752. doi: 10.1085/jgp.74.6.739. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cohen S. M., Burt C. T. 31P nuclear magnetic relaxation studies of phosphocreatine in intact muscle: determination of intracellular free magnesium. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1977 Oct;74(10):4271–4275. doi: 10.1073/pnas.74.10.4271. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- De Weer P. Axoplasmic free magnesium levels and magnesium extrusion from squid giant axons. J Gen Physiol. 1976 Aug;68(2):159–178. doi: 10.1085/jgp.68.2.159. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Edzes H. T., Berendsen H. J. The physical state of diffusible ions in cells. Annu Rev Biophys Bioeng. 1975;4(00):265–285. doi: 10.1146/annurev.bb.04.060175.001405. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Flatman P. W., Lew V. L. The magnesium dependence of sodium-pump-mediated sodium-potassium and sodium-sodium exchange in intact human red cells. J Physiol. 1981 Jun;315:421–446. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1981.sp013756. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Flatman P. W. The effect of buffer composition and deoxygenation on the concentration of ionized magnesium inside human red blood cells. J Physiol. 1980 Mar;300:19–30. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1980.sp013148. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Flatman P., Lew V. L. Use of ionophore A23187 to measure and to control free and bound cytoplasmic Mg in intact red cells. Nature. 1977 May 26;267(5609):360–362. doi: 10.1038/267360a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gupta R. K., Moore R. D. 31P NMR studies of intracellular free Mg2+ in intact frog skeletal muscle. J Biol Chem. 1980 May 10;255(9):3987–3993. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hess P., Metzger P., Weingart R. Free magnesium in sheep, ferret and frog striated muscle at rest measured with ion-selective micro-electrodes. J Physiol. 1982 Dec;333:173–188. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1982.sp014447. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- KERKUT G. A., THOMAS R. C. AN ELECTROGENIC SODIUM PUMP IN SNAIL NERVE CELLS. Comp Biochem Physiol. 1965 Jan;14:167–183. doi: 10.1016/0010-406x(65)90017-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kerkut G. A., Lambert J. D., Gayton R. J., Loker J. E., Walker R. J. Mapping of nerve cells in the suboesophageal ganglia of Helix aspersa. Comp Biochem Physiol A Comp Physiol. 1975 Jan 1;50(1A):1–25. doi: 10.1016/s0010-406x(75)80194-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kushmerick M. J., Podolsky R. J. Ionic mobility in muscle cells. Science. 1969 Dec 5;166(3910):1297–1298. doi: 10.1126/science.166.3910.1297. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Maughan D. Diffusible magnesium in frog skeletal muscle cells. Biophys J. 1983 Jul;43(1):75–80. doi: 10.1016/S0006-3495(83)84325-2. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Moreton R. B. An application of the constant-field theory to the behaviour of giant neurones of the snail, Helix aspersa. J Exp Biol. 1968 Jun;48(3):611–623. doi: 10.1242/jeb.48.3.611. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Moreton R. B. Electrophysiology and ionic movements in the central nervous system of the snail, Helix aspersa. J Exp Biol. 1972 Oct;57(2):513–541. doi: 10.1242/jeb.57.2.513. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mullins L. J., Brinley F. J. Magnesium influx in dialyzed squid axons. J Membr Biol. 1978 Oct 19;43(2-3):243–250. doi: 10.1007/BF01933481. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rink T. J., Tsien R. Y., Pozzan T. Cytoplasmic pH and free Mg2+ in lymphocytes. J Cell Biol. 1982 Oct;95(1):189–196. doi: 10.1083/jcb.95.1.189. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rojas E., Taylor R. E. Simultaneous measurements of magnesium, calcium and sodium influxes in perfused squid giant axons under membrane potential control. J Physiol. 1975 Oct;252(1):1–27. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1975.sp011131. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tsien R. Y. Intracellular measurements of ion activities. Annu Rev Biophys Bioeng. 1983;12:91–116. doi: 10.1146/annurev.bb.12.060183.000515. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tsien R. Y., Rink T. J. Neutral carrier ion-selective microelectrodes for measurement of intracellular free calcium. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1980 Jul;599(2):623–638. doi: 10.1016/0005-2736(80)90205-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Veloso D., Guynn R. W., Oskarsson M., Veech R. L. The concentrations of free and bound magnesium in rat tissues. Relative constancy of free Mg 2+ concentrations. J Biol Chem. 1973 Jul 10;248(13):4811–4819. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wacker W. E. The biochemistry of magnesium. Ann N Y Acad Sci. 1969 Aug 15;162(2):717–726. doi: 10.1111/j.1749-6632.1969.tb13003.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Walker J. L., Brown H. M. Intracellular ionic activity measurements in nerve and muscle. Physiol Rev. 1977 Oct;57(4):729–778. doi: 10.1152/physrev.1977.57.4.729. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Walser M. Magnesium metabolism. Ergeb Physiol. 1967;59:185–296. doi: 10.1007/BF02269144. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


