Abstract
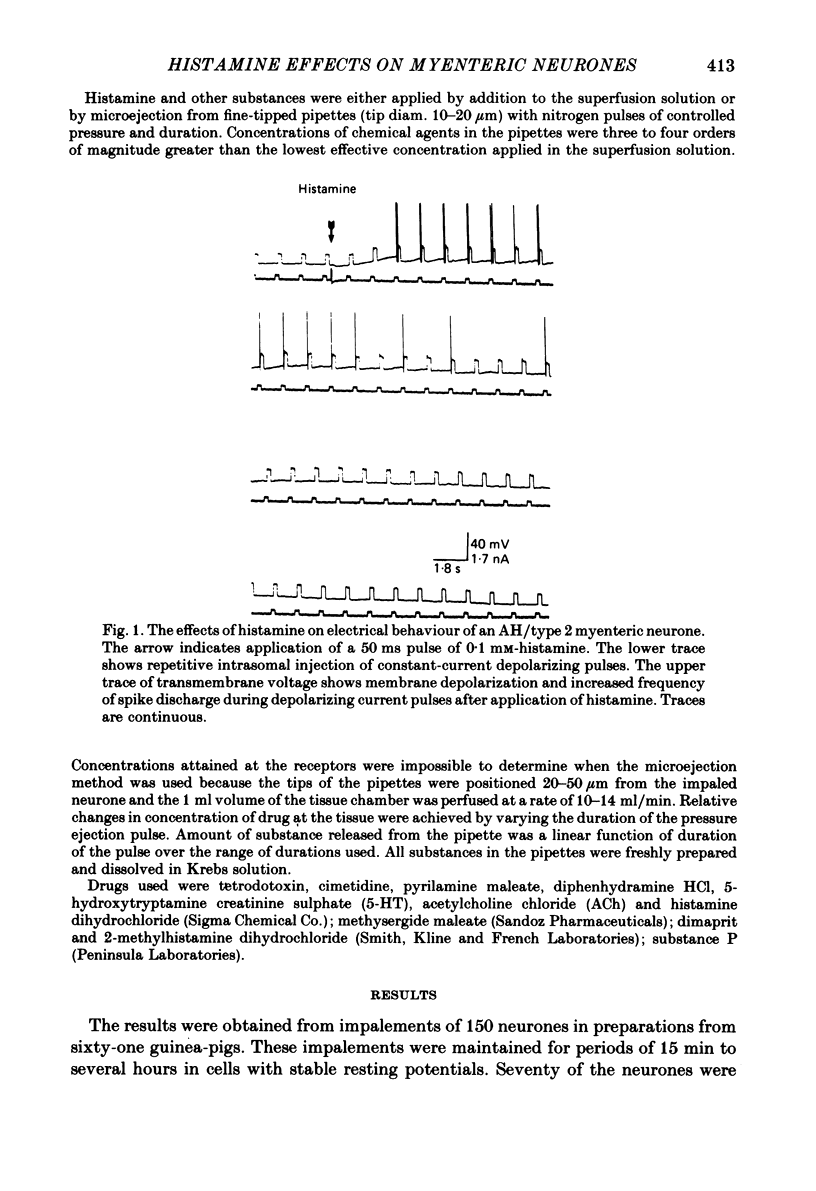
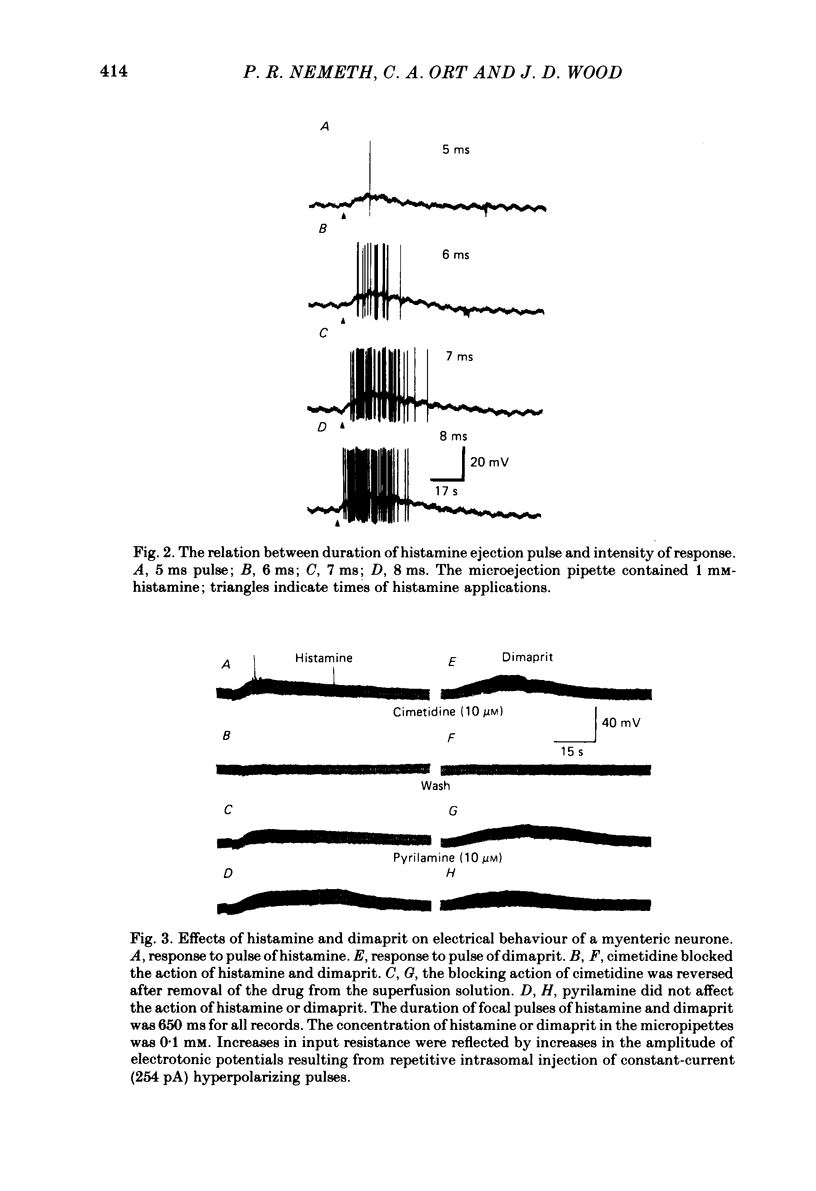
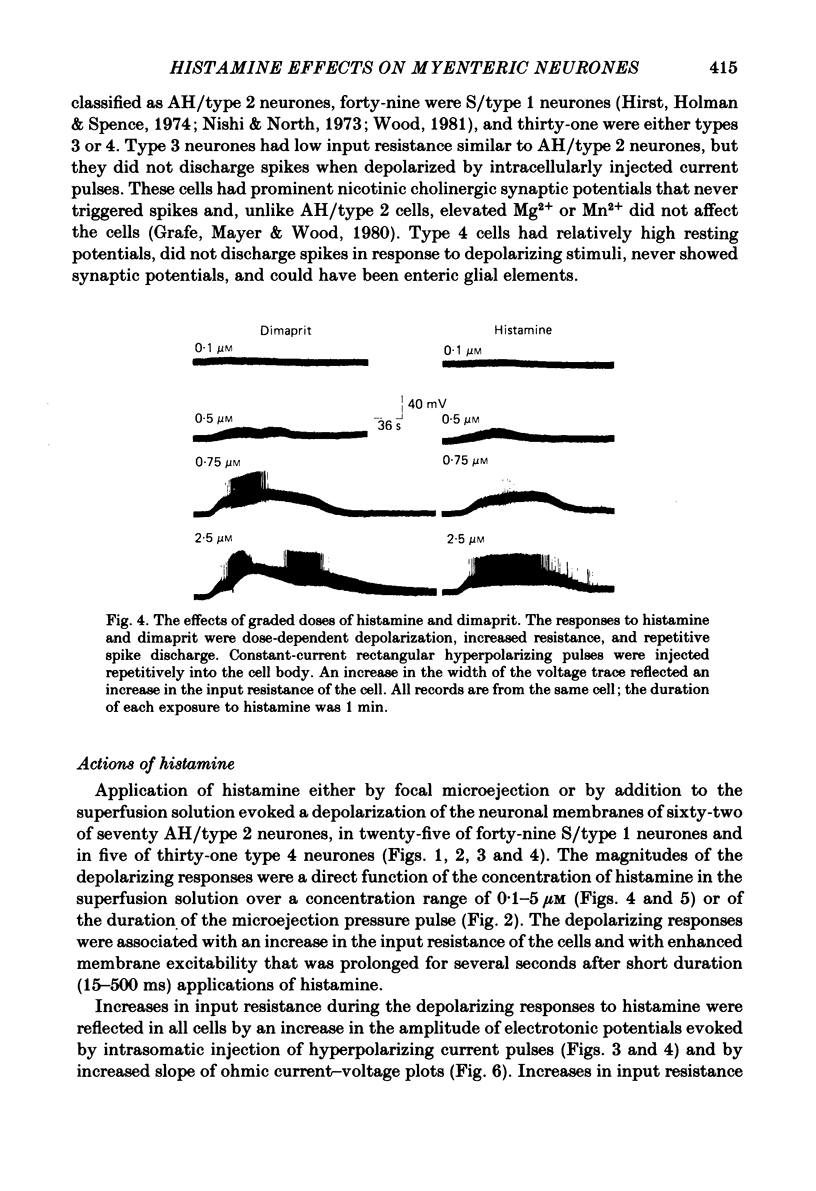
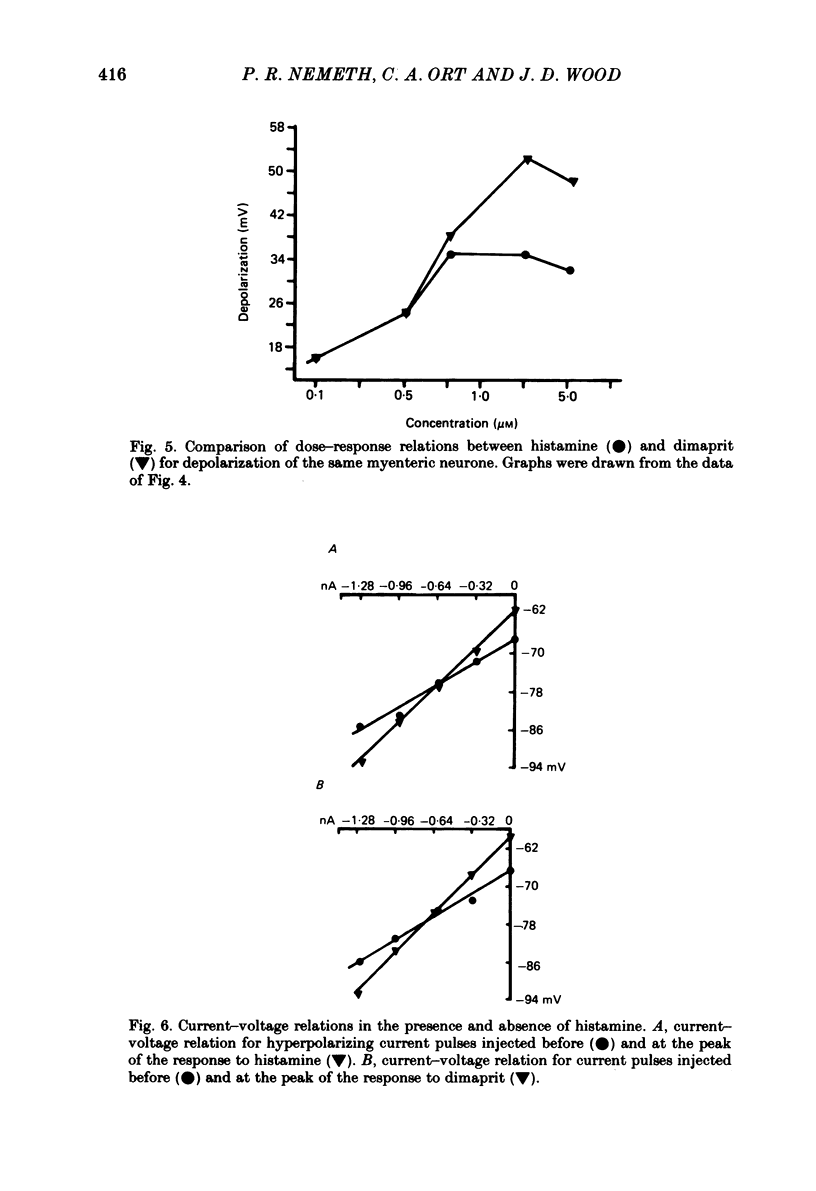
The actions of histamine on myenteric neurones were investigated with intracellular recording methods in guinea-pig small intestine. The actions of histamine at the ganglion cell soma were: membrane depolarization, increased input resistance, suppression of post-spike hyperpolarizing potentials, augmented excitability and repetitive spike discharge. Excitability was enhanced also at spike initiation sites remote from the cell body. Both H1, and H2, receptors were involved in the response to histamine. Dimaprit mimicked the responses to histamine in 80% and 2-methylhistamine in 50% of the trials. Cimetidine was an antagonist for histamine in 82% and for dimaprit in all of the trials. Pyrilamine blocked the actions of histamine in 59% of the cells and always blocked the action of 2-methylhistamine. Histamine mimicked slow synaptic excitation in the neurones, but was ruled out as a neurotransmitter for the slow excitatory post-synaptic potential (e.p.s.p.). Histamine either did not affect the responses to 5-hydroxytryptamine, substance P and acetylcholine or it potentiated the responses to these putative neurotransmitters for slow synaptic excitation. The results support the possibility that histamine released from mast cells by circulating peptidergic messengers, by neurotransmitters or during anaphylaxis could influence enteric nervous function.
Full text
PDF






Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Barker L. A., Ebersole B. J. Histamine H2-receptors on guinea-pig ileum myenteric plexus neurons mediate the release of contractile agents. J Pharmacol Exp Ther. 1982 Apr;221(1):69–75. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Beaven M. A. Histamine: its role in physiological and pathological processes. Monogr Allergy. 1978;13:1–113. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Black J. W., Duncan W. A., Durant C. J., Ganellin C. R., Parsons E. M. Definition and antagonism of histamine H 2 -receptors. Nature. 1972 Apr 21;236(5347):385–390. doi: 10.1038/236385a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Brezenoff H. E., Gertner S. B. The actions of polymyxin B and histamine on ganglionic transmission. Can J Physiol Pharmacol. 1972 Aug;50(8):824–831. doi: 10.1139/y72-119. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Brimble M. J., Wallis D. I. Histamine H1 and H2-receptors at a ganglionic synapse. Nature. 1973 Nov 16;246(5429):156–158. doi: 10.1038/246156a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cooke H. J., Nemeth P. R., Wood J. D. Histamine action on guinea pig ileal mucosa. Am J Physiol. 1984 Apr;246(4 Pt 1):G372–G377. doi: 10.1152/ajpgi.1984.246.4.G372. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dale M. M., Zilletti L. The Schultz-Dale response of the longitudinal muscle strip preparation of guinea-pig ileum. Br J Pharmacol. 1970 Jul;39(3):542–545. doi: 10.1111/j.1476-5381.1970.tb10362.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- GERTNER S. B., KOHN R. Effect of histamine on ganglionic transmission. Br J Pharmacol Chemother. 1959 Jun;14(2):179–182. doi: 10.1111/j.1476-5381.1959.tb01380.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gershon M. D., Erde S. M. The nervous system of the gut. Gastroenterology. 1981 Jun;80(6):1571–1594. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Grafe P., Mayer C. J., Wood J. D. Synaptic modulation of calcium-dependent potassium conductance in myenteric neurones in the guinea-pig. J Physiol. 1980 Aug;305:235–248. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1980.sp013360. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Haas H. L., Konnerth A. Histamine and noradrenaline decrease calcium-activated potassium conductance in hippocampal pyramidal cells. 1983 Mar 31-Apr 6Nature. 302(5907):432–434. doi: 10.1038/302432a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hirst G. D., Holman M. E., Spence I. Two types of neurones in the myenteric plexus of duodenum in the guinea-pig. J Physiol. 1974 Jan;236(2):303–326. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1974.sp010436. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Håkanson R., Wahlestedt C., Westlin L., Vallgren S., Sundler F. Neuronal histamine in the gut wall releasable by gastrin and cholecystokinin. Neurosci Lett. 1983 Dec 11;42(3):305–310. doi: 10.1016/0304-3940(83)90279-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Johnson A. R., Erdös E. G. Release of histamine from mast cells by vasoactive peptides. Proc Soc Exp Biol Med. 1973 Apr;142(4):1252–1256. doi: 10.3181/00379727-142-37219. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Katayama Y., North R. A. Does substance P mediate slow synaptic excitation within the myenteric plexus? Nature. 1978 Jul 27;274(5669):387–388. doi: 10.1038/274387a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kiernan J. A. The involvement of mast cells in vasodilatation due to axon reflexes in injured skin. Q J Exp Physiol Cogn Med Sci. 1972 Jul;57(3):311–317. doi: 10.1113/expphysiol.1972.sp002164. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lindl T. Effects of histamine agonists and antagonists (H1 and H2) on ganglionic transmission and on accumulation of cyclic nucleotides (cAMP and cGMP) in rat superior cervical ganglion in vitro. Neuropharmacology. 1983 Feb;22(2):203–211. doi: 10.1016/0028-3908(83)90010-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- McCaman R. E., Weinreich D. On the nature of histamine-mediated slow hyperpolarizing synaptic potentials in identified molluscan neurones. J Physiol. 1982 Jul;328:485–506. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1982.sp014279. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Morita K., North R. A., Tokimasa T. Muscarinic agonists inactivate potassium conductance of guinea-pig myenteric neurones. J Physiol. 1982 Dec;333:125–139. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1982.sp014443. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nandiwada P. A., Lokhandwala M. F., Jandhyala B. S. Modulation by histamine of peripheral vagal transmission in anesthetized mongrel dogs. Eur J Pharmacol. 1980 May 16;63(4):281–286. doi: 10.1016/0014-2999(80)90256-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Newson B., Dahlström A., Enerbäck L., Ahlman H. Suggestive evidence for a direct innervation of mucosal mast cells. Neuroscience. 1983 Oct;10(2):565–570. doi: 10.1016/0306-4522(83)90153-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nishi S., North R. A. Intracellular recording from the myenteric plexus of the guinea-pig ileum. J Physiol. 1973 Jun;231(3):471–491. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1973.sp010244. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Oishi M., Ishiko J., Inagaki C., Takaori S. Release of histamine and adrenaline in vivo following intravenous administration of neurotensin. Life Sci. 1983 May 9;32(19):2231–2239. doi: 10.1016/0024-3205(83)90421-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Reite O. B. Comparative physiology of histamine. Physiol Rev. 1972 Jul;52(3):778–819. doi: 10.1152/physrev.1972.52.3.778. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schwartz J. C., Pollard H., Quach T. T. Histamine as a neurotransmitter in mammalian brain: neurochemical evidence. J Neurochem. 1980 Jul;35(1):26–33. doi: 10.1111/j.1471-4159.1980.tb12485.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Skofitsch G., Donnerer J., Petronijevic S., Saria A., Lembeck F. Release of histamine by neuropeptides from the perfused rat hindquarter. Naunyn Schmiedebergs Arch Pharmacol. 1983 Mar;322(2):153–157. doi: 10.1007/BF00512389. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- TORP A. Histamine and mast cells in nerves. Med Exp Int J Exp Med. 1961;4:180–182. doi: 10.1159/000135010. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- TRENDELENBURG U. The action of histamine and pilocarpine on the superior cervical ganglion and the adrenal glands of the cat. Br J Pharmacol Chemother. 1954 Dec;9(4):481–487. doi: 10.1111/j.1476-5381.1954.tb00865.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Theoharides T. C., Douglas W. W. Mast cell histamine secretion in response to somatostatin analogues: structural considerations. Eur J Pharmacol. 1981 Jul 17;73(2-3):131–136. doi: 10.1016/0014-2999(81)90084-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Weinreich D. Synaptic responses mediated by identified histamine-containing neurones. Nature. 1977 Jun 30;267(5614):854–856. doi: 10.1038/267854a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wood J. D. Intrinsic neural control of intestinal motility. Annu Rev Physiol. 1981;43:33–51. doi: 10.1146/annurev.ph.43.030181.000341. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wood J. D., Mayer C. J. Adrenergic inhibition of serotonin release from neurons in guinea pig Auerback's plexus. J Neurophysiol. 1979 Mar;42(2):594–603. doi: 10.1152/jn.1979.42.2.594. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wood J. D., Mayer C. J. Intracellular study of electrical activity of Auerbach's plexus in guinea-pig small intestine. Pflugers Arch. 1978 May 31;374(3):265–275. doi: 10.1007/BF00585604. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wood J. D., Mayer C. J. Intracellular study of tonic-type enteric neurons in guinea pig small intestine. J Neurophysiol. 1979 Mar;42(2):569–581. doi: 10.1152/jn.1979.42.2.569. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wood J. D., Mayer C. J. Serotonergic activation of tonic-type enteric neurons in guinea pig small bowel. J Neurophysiol. 1979 Mar;42(2):582–593. doi: 10.1152/jn.1979.42.2.582. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wood J. D., Mayer C. J. Slow synaptic excitation mediated by serotonin in Auerbach's plexus. Nature. 1978 Dec 21;276(5690):836–837. doi: 10.1038/276836a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yamada M., Tokimasa T., Koketsu K. Effects of histamine on acetylcholine release in bullfrog sympathetic ganglia. Eur J Pharmacol. 1982 Aug 13;82(1-2):15–20. doi: 10.1016/0014-2999(82)90547-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zavecz J. H., Yellin T. O. Histamine receptors in the myenteric plexus-longitudinal muscle of the guinea-pig ileum: H1- and H2-receptor-mediated potentiation of the contractile response to electrical stimulation. J Pharmacol Exp Ther. 1982 Oct;223(1):177–182. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


