Abstract
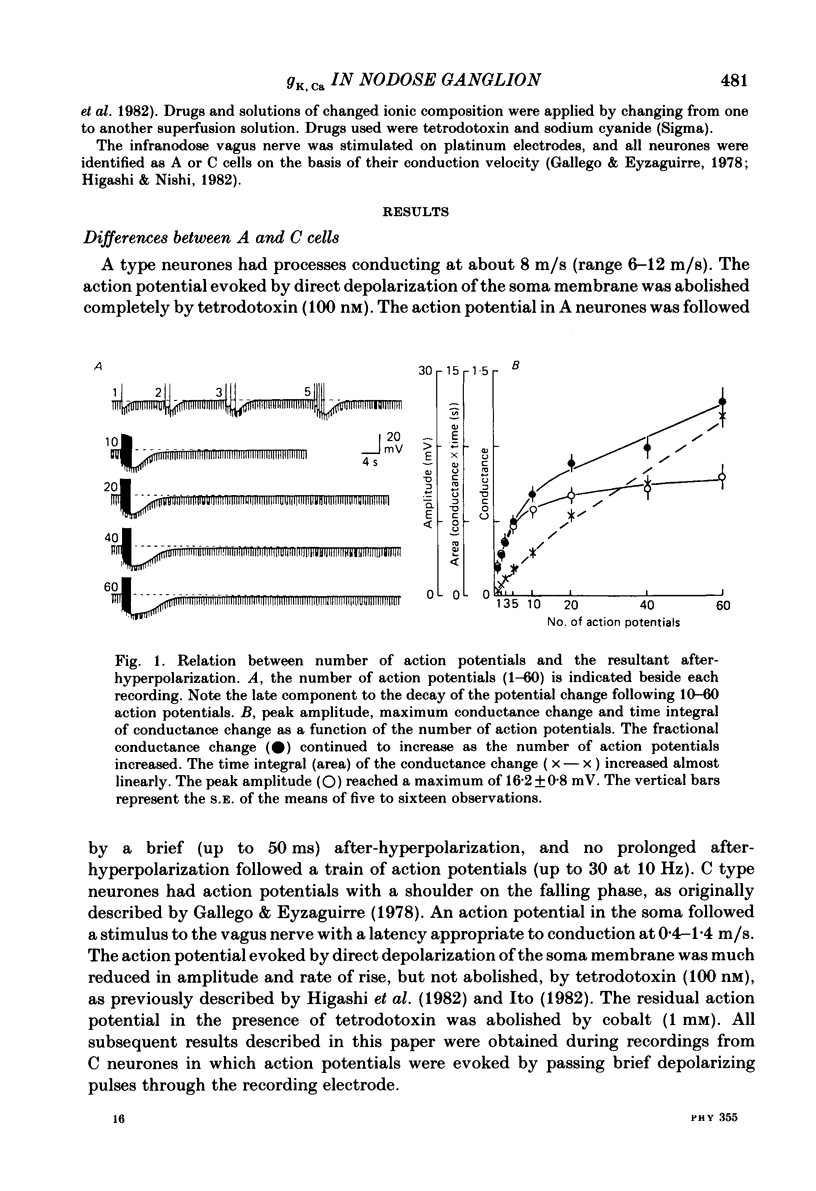
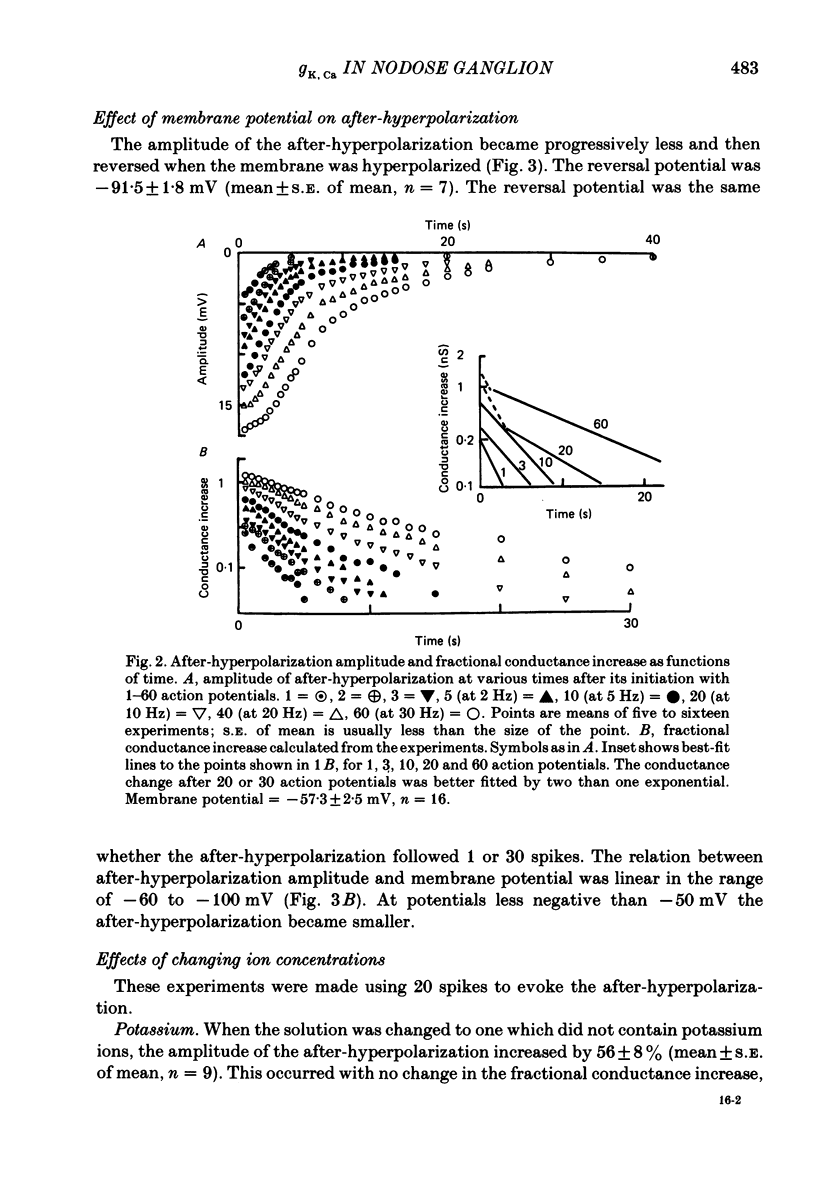
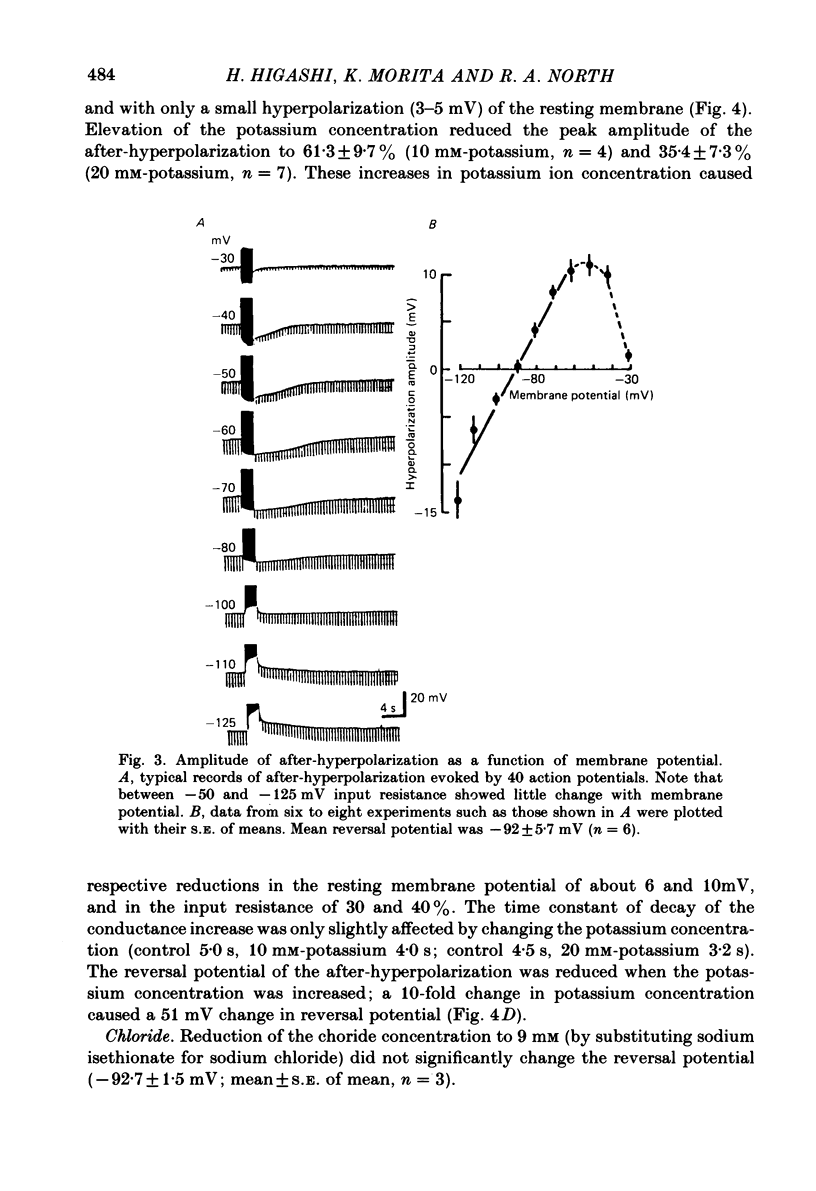
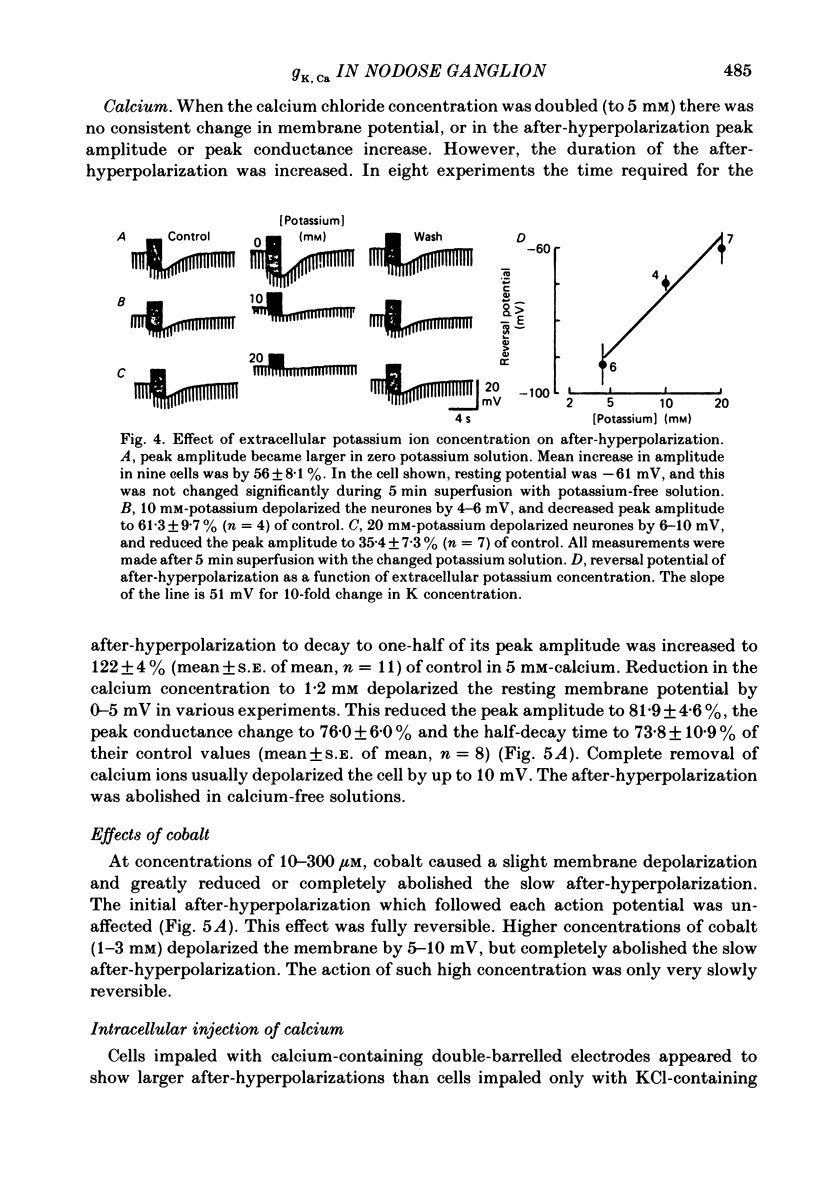
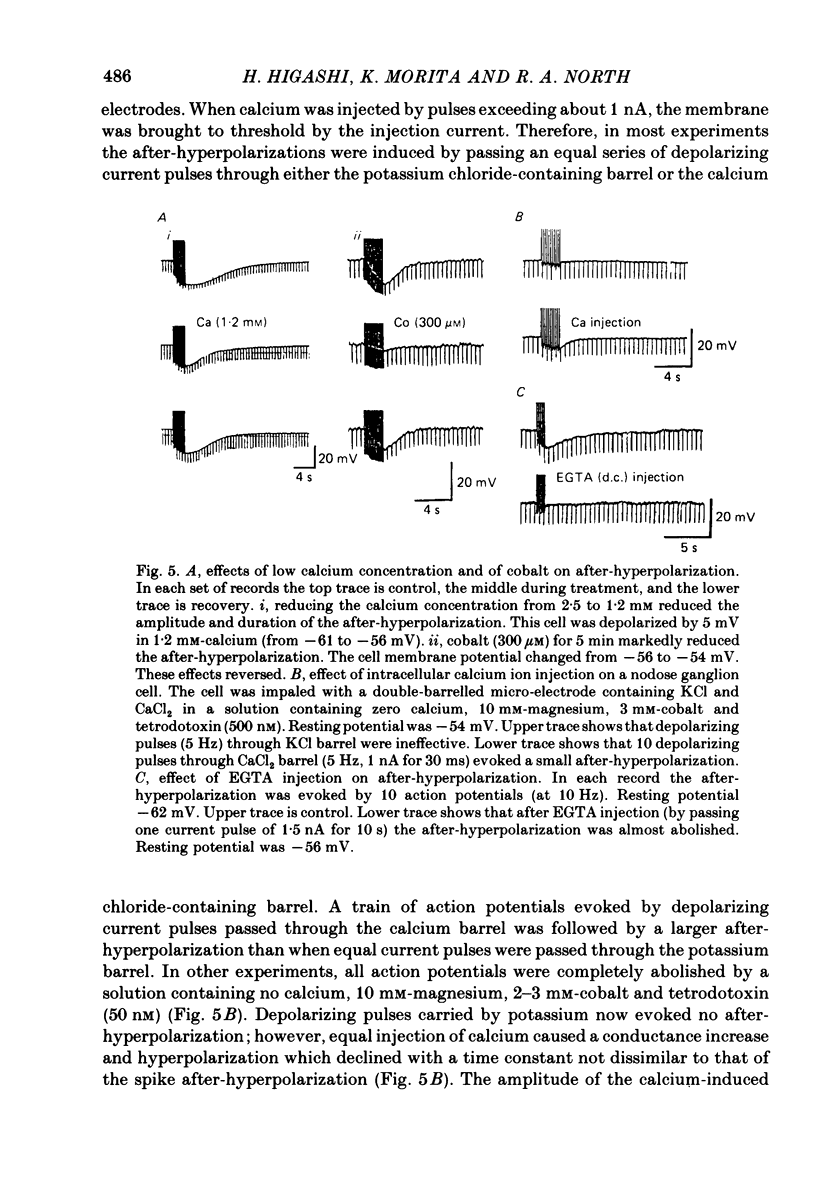
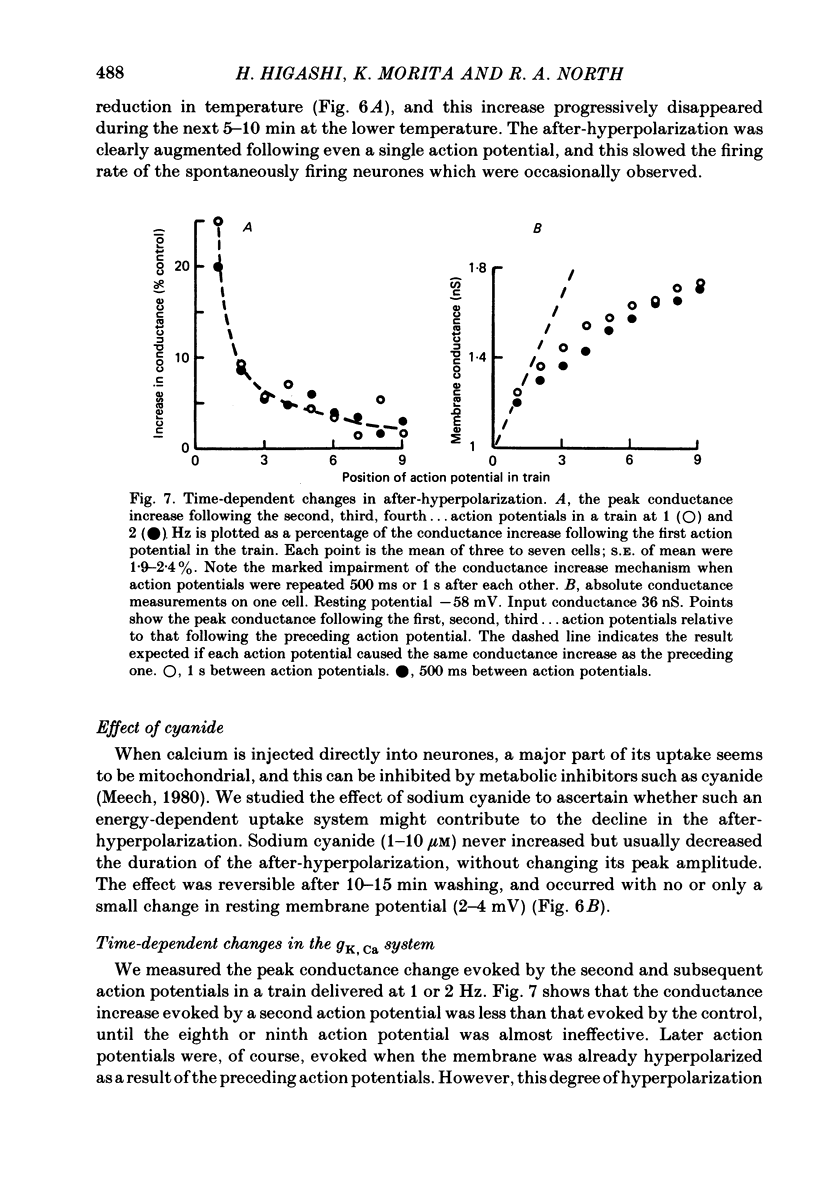
Intracellular recordings were made from neurones in nodose ganglia excised from rabbits. In C neurones, 1-60 action potentials were followed by an after-hyperpolarization with a peak amplitude of 16 mV and a time constant of decay ranging from 3 to 10 s. In A neurones, the action potentials were followed only by a brief (up to 50 ms) after-hyperpolarization. The after-hyperpolarization was associated with an increase in the membrane conductance to potassium ions; it reversed polarity at the potassium equilibrium potential. The increase in conductance following the action potentials was blocked by removal of calcium ions, or addition of cobalt to the extracellular solution. Intracellular injection of ethyleneglycol-bis(beta-aminoethylether)-N,N'-tetraacetic acid (EGTA) abolished the after-hyperpolarization; intracellular injection of calcium mimicked the after-hyperpolarization. It is concluded that calcium entry during the action potential leads to a long-lasting increase in potassium conductance in visceral afferent C neurones.
Full text
PDF







Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Adams P. R., Constanti A., Brown D. A., Clark R. B. Intracellular Ca2+ activates a fast voltage-sensitive K+ current in vertebrate sympathetic neurones. Nature. 1982 Apr 22;296(5859):746–749. doi: 10.1038/296746a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Akaike N., Brown A. M., Dahl G., Higashi H., Isenberg G., Tsuda Y., Yatani A. Voltage-dependent activation of potassium current in Helix neurones by endogenous cellular calcium. J Physiol. 1983 Jan;334:309–324. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1983.sp014496. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Baccaglini P. I., Cooper E. Electrophysiological studies of new-born rat nodose neurones in cell culture. J Physiol. 1982 Mar;324:429–439. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1982.sp014122. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Barrett J. N., Magleby K. L., Pallotta B. S. Properties of single calcium-activated potassium channels in cultured rat muscle. J Physiol. 1982 Oct;331:211–230. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1982.sp014370. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Baylor D. A., Nicholls J. G. After-effects of nerve impulses on signalling in the central nervous system of the leech. J Physiol. 1969 Aug;203(3):571–589. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1969.sp008880. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Belmonte C., Gallego R. Membrane properties of cat sensory neurones with chemoreceptor and baroreceptor endings. J Physiol. 1983 Sep;342:603–614. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1983.sp014871. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fujimoto S., Yamamoto K., Kuba K., Morita K., Kato E. Calcium localization in the sympathetic ganglion of the bullfrog and effects of caffeine. Brain Res. 1980 Nov 24;202(1):21–32. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gallego R., Eyzaguirre C. Membrane and action potential characteristics of A and C nodose ganglion cells studied in whole ganglia and in tissue slices. J Neurophysiol. 1978 Sep;41(5):1217–1232. doi: 10.1152/jn.1978.41.5.1217. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gallego R. The ionic basis of action potentials in petrosal ganglion cells of the cat. J Physiol. 1983 Sep;342:591–602. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1983.sp014870. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gorman A. L., Thomas M. V. Intracellular calcium accumulation during depolarization in a molluscan neurone. J Physiol. 1980 Nov;308:259–285. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1980.sp013471. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hagiwara S., Byerly L. Calcium channel. Annu Rev Neurosci. 1981;4:69–125. doi: 10.1146/annurev.ne.04.030181.000441. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Heyer C. B., Lux H. D. Control of the delayed outward potassium currents in bursting pace-maker neurones of the snail, Helix pomatia. J Physiol. 1976 Nov;262(2):349–382. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1976.sp011599. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Heyer C. B., Lux H. D. Properties of a facilitating calcium current in pace-maker neurones of the snail, Helix pomatia. J Physiol. 1976 Nov;262(2):319–348. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1976.sp011598. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Higashi H., Nishi S. 5-Hydroxytryptamine receptors of visceral primary afferent neurones on rabbit nodose ganglia. J Physiol. 1982 Feb;323:543–567. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1982.sp014091. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Higashi H., Shinnick-Gallagher P., Gallagher J. P. Morphine enhances and depresses Ca2+-dependent responses in visceral primary afferent neurons. Brain Res. 1982 Nov 11;251(1):186–191. doi: 10.1016/0006-8993(82)91291-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ito H. Evidence for initiation of calcium spikes in C-cells of the rabbit nodose ganglion. Pflugers Arch. 1982 Aug;394(2):106–112. doi: 10.1007/BF00582910. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jaffe R. A., Sampson S. R. Analysis of passive and active electrophysiologic properties of neurons in mammalian nodose ganglia maintained in vitro. J Neurophysiol. 1976 Jul;39(4):802–815. doi: 10.1152/jn.1976.39.4.802. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kuba K., Morita K., Nohmi M. Origin of calcium ions involved in the generation of a slow afterhyperpolarization in bullfrog sympathetic neurones. Pflugers Arch. 1983 Nov;399(3):194–202. doi: 10.1007/BF00656714. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kuba K. Release of calcium ions linked to the activation of potassium conductance in a caffeine-treated sympathetic neurone. J Physiol. 1980 Jan;298:251–269. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1980.sp013079. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kuno M., Miyahara J. T., Weakly J. N. Post-tetanic hyperpolarization produced by an electrogenic pump in dorsal spinocerebellar tract neurones of the cat. J Physiol. 1970 Nov;210(4):839–855. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1970.sp009245. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Latorre R., Miller C. Conduction and selectivity in potassium channels. J Membr Biol. 1983;71(1-2):11–30. doi: 10.1007/BF01870671. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Magaribuchi T., Ito Y., Kuriyama H. Effects of rapid cooling on the mechanical and electrical activities of smooth muscles of guinea pig stomach and taenia coli. J Gen Physiol. 1973 Mar;61(3):323–341. doi: 10.1085/jgp.61.3.323. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Marty A. Ca-dependent K channels with large unitary conductance in chromaffin cell membranes. Nature. 1981 Jun 11;291(5815):497–500. doi: 10.1038/291497a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Meech R. W. Calcium-dependent potassium activation in nervous tissues. Annu Rev Biophys Bioeng. 1978;7:1–18. doi: 10.1146/annurev.bb.07.060178.000245. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Meech R. W. Intracellular calcium injection causes increased potassium conductance in Aplysia nerve cells. Comp Biochem Physiol A Comp Physiol. 1972 Jun 1;42(2):493–499. doi: 10.1016/0300-9629(72)90128-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Meech R. W. The sensitivity of Helix aspersa neurones to injected calcium ions. J Physiol. 1974 Mar;237(2):259–277. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1974.sp010481. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Meech R. W., Thomas R. C. The effect of calcium injection on the intracellular sodium and pH of snail neurones. J Physiol. 1977 Mar;265(3):867–879. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1977.sp011749. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Morita K., North R. A., Tokimasa T. The calcium-activated potassium conductance in guinea-pig myenteric neurones. J Physiol. 1982 Aug;329:341–354. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1982.sp014306. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nakajima S., Takahashi K. Post-tetanic hyperpolarization and electrogenic Na pump in stretch receptor neurone of crayfish. J Physiol. 1966 Nov;187(1):105–127. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1966.sp008078. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nohmi M., Kuba K., Morita K. Does intracellular release of Ca2+ participate in the afterhyperpolarization of a sympathetic neurone? Brain Res. 1983 May 23;268(1):158–161. doi: 10.1016/0006-8993(83)90401-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rang H. P., Ritchie J. M. On the electrogenic sodium pump in mammalian non-myelinated nerve fibres and its activation by various external cations. J Physiol. 1968 May;196(1):183–221. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1968.sp008502. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


