Abstract
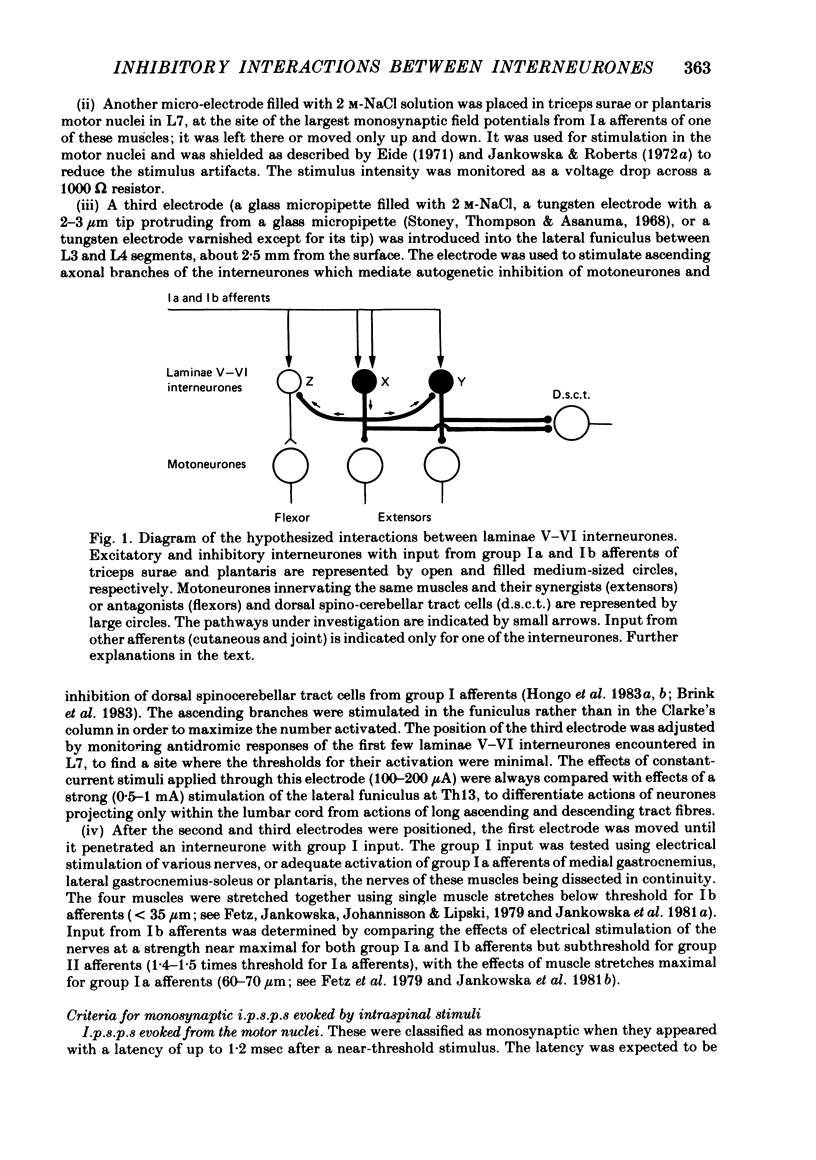
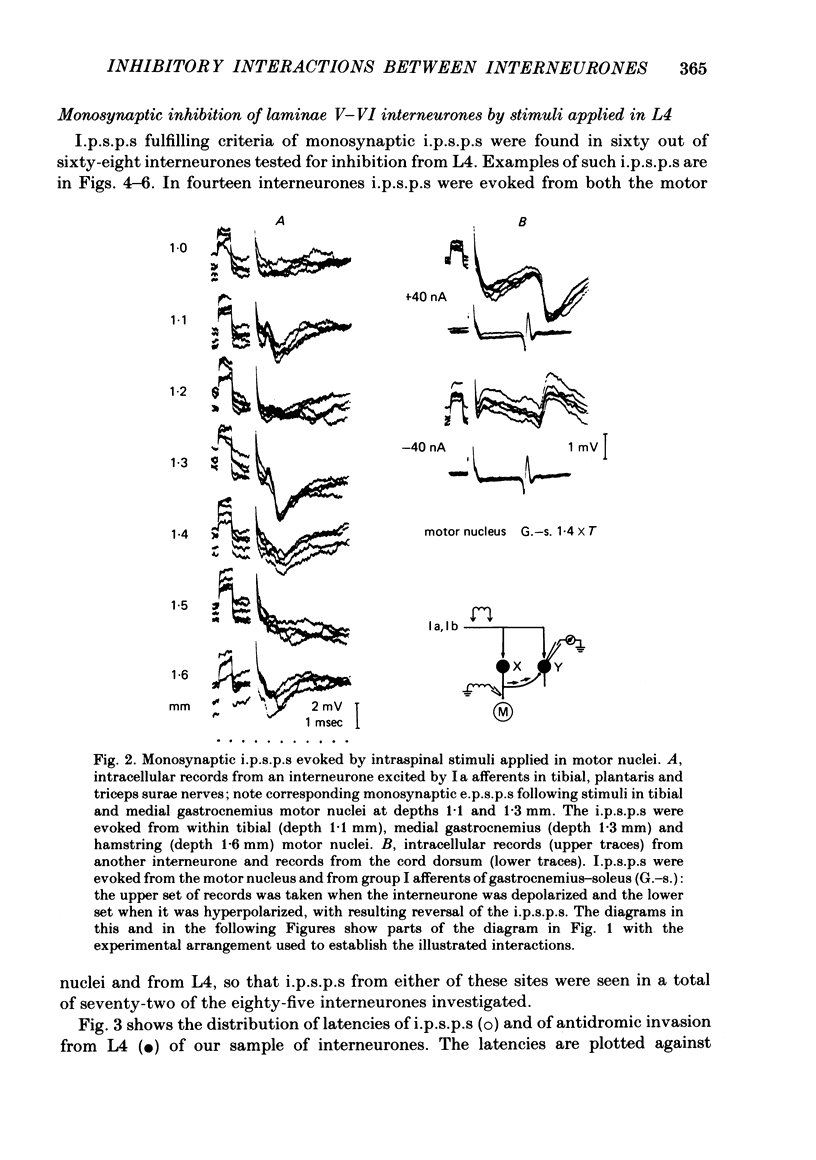
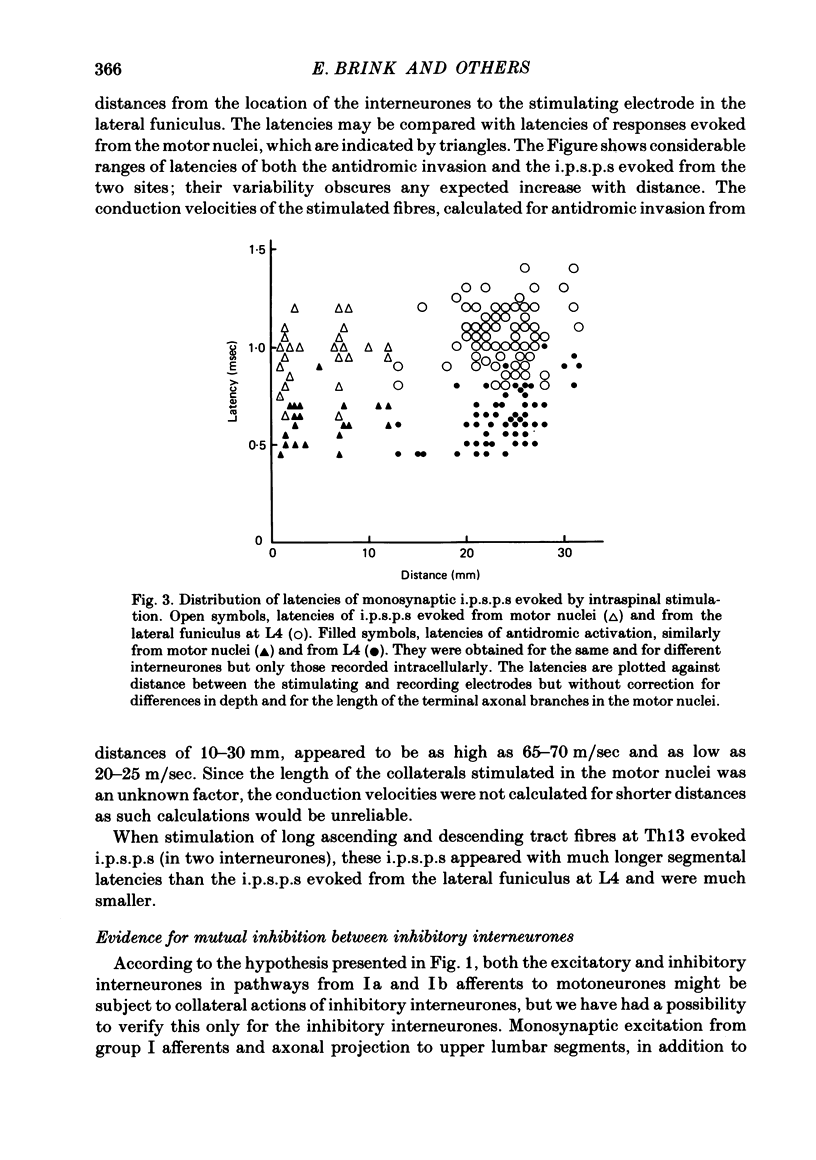
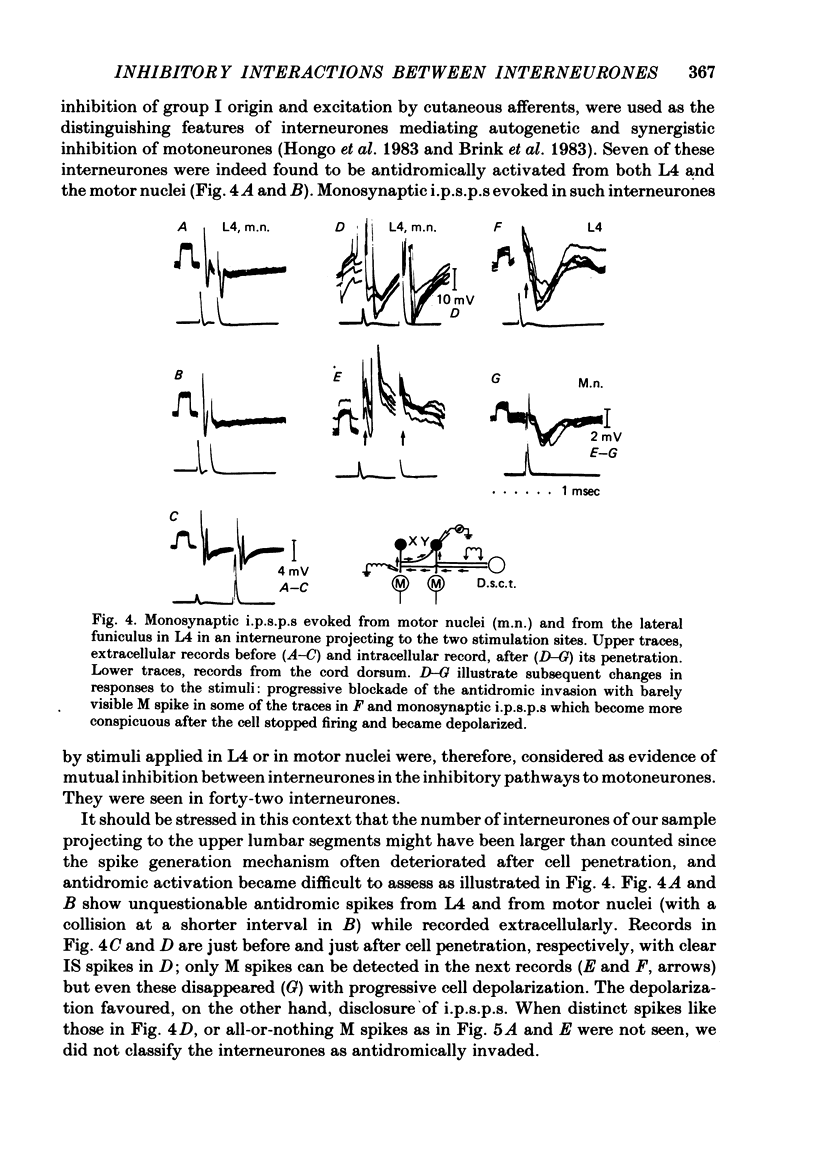
A hypothesis has been verified that laminae V-VI interneurones which mediate non-reciprocal inhibition of motoneurones from group I muscle afferents have collateral actions on other laminae V-VI interneurones. Stimulation within the areas of projection of these inhibitory interneurones in motor nuclei and in Clarke's column would be expected to give rise to monosynaptic i.p.s.p.s in interneurones with disynaptic i.p.s.p.s from group I afferents if the hypothesis were correct. Intracellular records were made from eighty-five laminae V-VI interneurones with input from group Ia muscle spindle and/or group Ib tendon organ afferents. Weak intraspinal stimuli applied in motor nuclei in L7 and S1 segments, or in the lateral funiculus just caudal to Clarke's column in L4, were found to evoke monosynaptic i.p.s.p.s in seventy-two interneurones. These i.p.s.p.s were systematically correlated with disynaptic inhibition from group Ia or Ib afferents but not from other fibres. Such monosynaptic i.p.s.p.s evoked by intraspinal stimuli were seen in forty-two interneurones which themselves projected to the level of Clarke's column and therefore (on the basis of previous evidence) should mediate inhibition of motoneurones. For seven of these interneurones it was also shown directly that they projected to motor nuclei. The inhibition of such interneurones demonstrates mutual interactions between those interneurones which are interposed in inhibitory pathways from group I afferents. Only indirect indications have been obtained for inhibition of interneurones in the excitatory pathways.
Full text
PDF








Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Brink E., Harrison P. J., Jankowska E., McCrea D. A., Skoog B. Post-synaptic potentials in a population of motoneurones following activity of single interneurones in the cat. J Physiol. 1983 Oct;343:341–359. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1983.sp014896. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Burke R. E., Strick P. L., Kanda K., Kim C. C., Walmsley B. Anatomy of medial gastrocnemius and soleus motor nuclei in cat spinal cord. J Neurophysiol. 1977 May;40(3):667–680. doi: 10.1152/jn.1977.40.3.667. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Czarkowska J., Jankowska E., Sybirska E. Common interneurones in reflex pathways from group 1a and 1b afferents of knee flexors and extensors in the cat. J Physiol. 1981 Jan;310:367–380. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1981.sp013555. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Czarkowska J., Jankowska E., Sybirska E. Diameter and internodal length of axons of spinal interneurones excited by group I afferents in the cat. Brain Res. 1976 Dec 10;118(1):119–122. doi: 10.1016/0006-8993(76)90845-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- ECCLES J. C., ECCLES R. M., LUNDBERG A. Synaptic actions on motoneurones caused by impulses in Golgi tendon organ afferents. J Physiol. 1957 Sep 30;138(2):227–252. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1957.sp005849. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- ECCLES J. C., ECCLES R. M., LUNDBERG A. Synaptic actions on motoneurones in relation to the two components of the group I muscle afferent volley. J Physiol. 1957 May 23;136(3):527–546. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1957.sp005778. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- ECCLES J. C., FATT P., LANDGREN S. Central pathway for direct inhibitory action of impulses in largest afferent nerve fibres to muscle. J Neurophysiol. 1956 Jan;19(1):75–98. doi: 10.1152/jn.1956.19.1.75. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fetz E. E., Jankowska E., Johannisson T., Lipski J. Autogenetic inhibition of motoneurones by impulses in group Ia muscle spindle afferents. J Physiol. 1979 Aug;293:173–195. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1979.sp012884. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- GRANIT R. Reflex self-regulation of muscle contraction and autogenetic inhibition. J Neurophysiol. 1950 Sep;13(5):351–372. doi: 10.1152/jn.1950.13.5.351. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gustafsson B., Jankowska E. Direct and indirect activation of nerve cells by electrical pulses applied extracellularly. J Physiol. 1976 Jun;258(1):33–61. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1976.sp011405. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hikosaka O., Igusa Y., Nakao S., Shimazu H. Direct inhibitory synaptic linkage of pontomedullary reticular burst neurons with abducens motoneurons in the cat. Exp Brain Res. 1978 Nov 15;33(3-4):337–352. doi: 10.1007/BF00235558. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hongo T., Jankowska E., Lundberg A. Convergence of excitatory and inhibitory action on interneurones in the lumbosacral cord. Exp Brain Res. 1966;1(4):338–358. doi: 10.1007/BF00237706. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hongo T., Jankowska E., Lundberg A. The rubrospinal tract. II. Facilitation of interneuronal transmission in reflex paths to motoneurones. Exp Brain Res. 1969;7(4):365–391. doi: 10.1007/BF00237321. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hongo T., Jankowska E., Lundberg A. The rubrospinal tract. IV. Effects on interneurones. Exp Brain Res. 1972;15(1):54–78. doi: 10.1007/BF00234958. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hongo T., Jankowska E., Ohno T., Sasaki S., Yamashita M., Yoshida K. Inhibition of dorsal spinocerebellar tract cells by interneurones in upper and lower lumbar segments in the cat. J Physiol. 1983 Sep;342:145–159. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1983.sp014844. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hongo T., Jankowska E., Ohno T., Sasaki S., Yamashita M., Yoshida K. The same interneurones mediate inhibition of dorsal spinocerebellar tract cells and lumbar motoneurones in the cat. J Physiol. 1983 Sep;342:161–180. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1983.sp014845. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hultborn H., Illert M., Santini M. Convergence on interneurones mediating the reciprocal Ia inhibition of motoneurones. I. Disynaptic Ia inhibition of Ia inhibitory interneurones. Acta Physiol Scand. 1976 Feb;96(2):193–201. doi: 10.1111/j.1748-1716.1976.tb10188.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Illert M., Lundberg A., Tanaka R. Integration in descending motor pathways controlling the forelimb in the cat. 2. Convergence on neurones mediating disynaptic cortico-motoneuronal excitation. Exp Brain Res. 1976 Dec 22;26(5):521–540. doi: 10.1007/BF00238825. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jankowska E., Johannisson T., Lipski J. Common interneurones in reflex pathways from group 1a and 1b afferents of ankle extensors in the cat. J Physiol. 1981 Jan;310:381–402. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1981.sp013556. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jankowska E., Lundberg A., Stuart D. Propriospinal control of interneurons in spinal reflex pathways from tendon organs in the cat. Brain Res. 1983 Feb 21;261(2):317–320. doi: 10.1016/0006-8993(83)90636-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jankowska E., McCrea D. A. Shared reflex pathways from Ib tendon organ afferents and Ia muscle spindle afferents in the cat. J Physiol. 1983 May;338:99–111. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1983.sp014663. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jankowska E., McCrea D., Mackel R. Oligosynaptic excitation of motoneurones by impulses in group Ia muscle spindle afferents in the cat. J Physiol. 1981 Jul;316:411–425. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1981.sp013797. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jankowska E., McCrea D., Mackel R. Pattern of 'non-reciprocal' inhibition of motoneurones by impulses in group Ia muscle spindle afferents in the cat. J Physiol. 1981 Jul;316:393–409. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1981.sp013796. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jankowska E., Roberts W. J. An electrophysiological demonstration of the axonal projections of single spinal interneurones in the cat. J Physiol. 1972 May;222(3):597–622. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1972.sp009817. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jankowska E., Roberts W. J. Synaptic actions of single interneurones mediating reciprocal Ia inhibition of motoneurones. J Physiol. 1972 May;222(3):623–642. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1972.sp009818. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- LAPORTE Y., LLOYD D. P. C. Nature and significance of the reflex connections established by large afferent fibers of muscular origin. Am J Physiol. 1952 Jun;169(3):609–621. doi: 10.1152/ajplegacy.1952.169.3.609. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- LUNDBERG A., VOORHOEVE P. Effects from the pyramidal tract on spinal reflex arcs. Acta Physiol Scand. 1962 Nov-Dec;56:201–219. doi: 10.1111/j.1748-1716.1962.tb02498.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lundberg A., Malmgren K., Schomburg E. D. Cutaneous facilitation of transmission in reflex pathways from Ib afferents to motoneurones. J Physiol. 1977 Mar;265(3):763–780. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1977.sp011742. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lundberg A., Malmgren K., Schomburg E. D. Role of joint afferents in motor control exemplified by effects on reflex pathways from Ib afferents. J Physiol. 1978 Nov;284:327–343. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1978.sp012543. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Munson J. B., Sypert G. W. Latency-rise time relationship in unitary postsynaptic potentials. Brain Res. 1978 Aug 4;151(2):404–408. doi: 10.1016/0006-8993(78)90897-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Munson J. B., Sypert G. W. Properties of single central Ia afferent fibres projecting to motoneurones. J Physiol. 1979 Nov;296:315–327. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1979.sp013007. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pierrot-Deseilligny E., Bergego C., Katz R., Morin C. Cutaneous depression of Ib reflex pathways to motoneurones in man. Exp Brain Res. 1981;42(3-4):351–361. doi: 10.1007/BF00237500. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pierrot-Deseilligny E., Bergego C., Katz R. Reversal in cutaneous of Ib pathways during human voluntary contraction. Brain Res. 1982 Feb 11;233(2):400–403. doi: 10.1016/0006-8993(82)91213-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rapoport S., Susswein A., Uchino Y., Wilson V. J. Synaptic actions of individual vestibular neurones on cat neck motoneurones. J Physiol. 1977 Nov;272(2):367–382. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1977.sp012049. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ryall R. W. Renshaw cell mediated inhibition of Renshaw cells: patterns of excitation and inhibition from impulses in motor axon collaterals. J Neurophysiol. 1970 Mar;33(2):257–270. doi: 10.1152/jn.1970.33.2.257. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stoney S. D., Jr, Thompson W. D., Asanuma H. Excitation of pyramidal tract cells by intracortical microstimulation: effective extent of stimulating current. J Neurophysiol. 1968 Sep;31(5):659–669. doi: 10.1152/jn.1968.31.5.659. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wall P. D., Werman R. The physiology and anatomy of long ranging afferent fibres within the spinal cord. J Physiol. 1976 Feb;255(2):321–334. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1976.sp011282. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


