Abstract
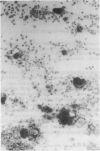
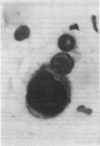
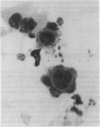
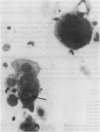
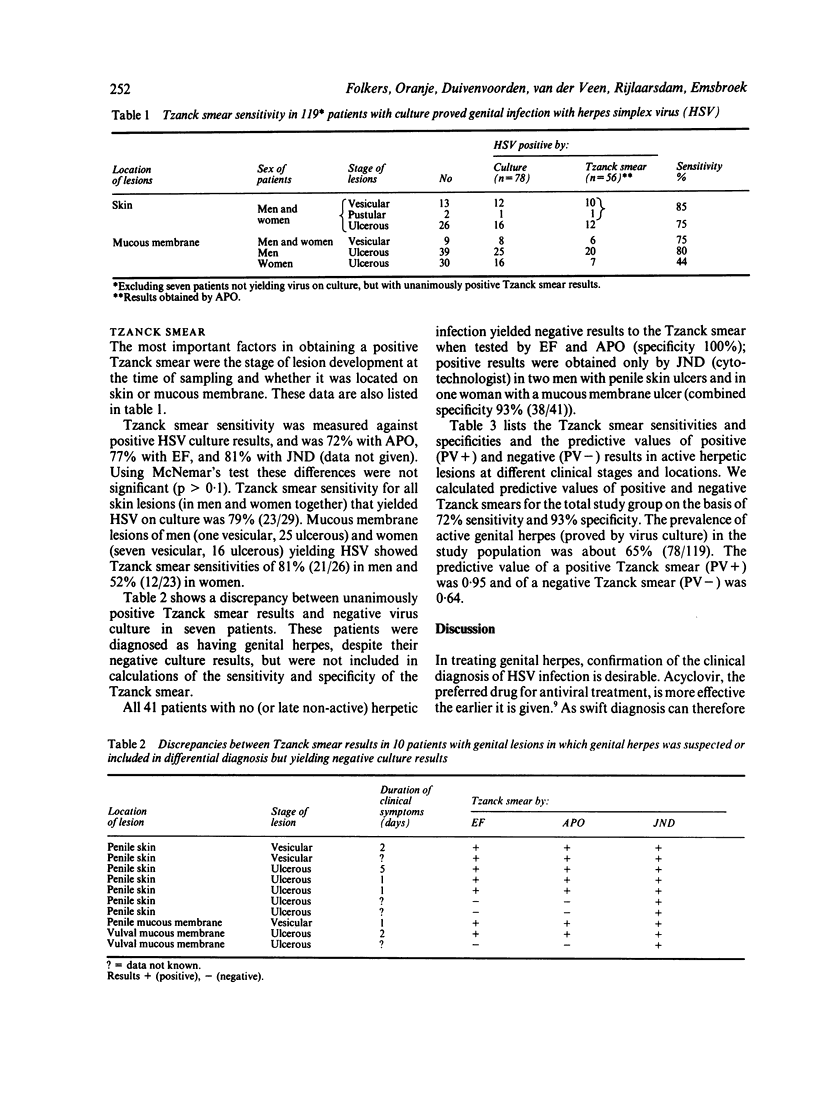
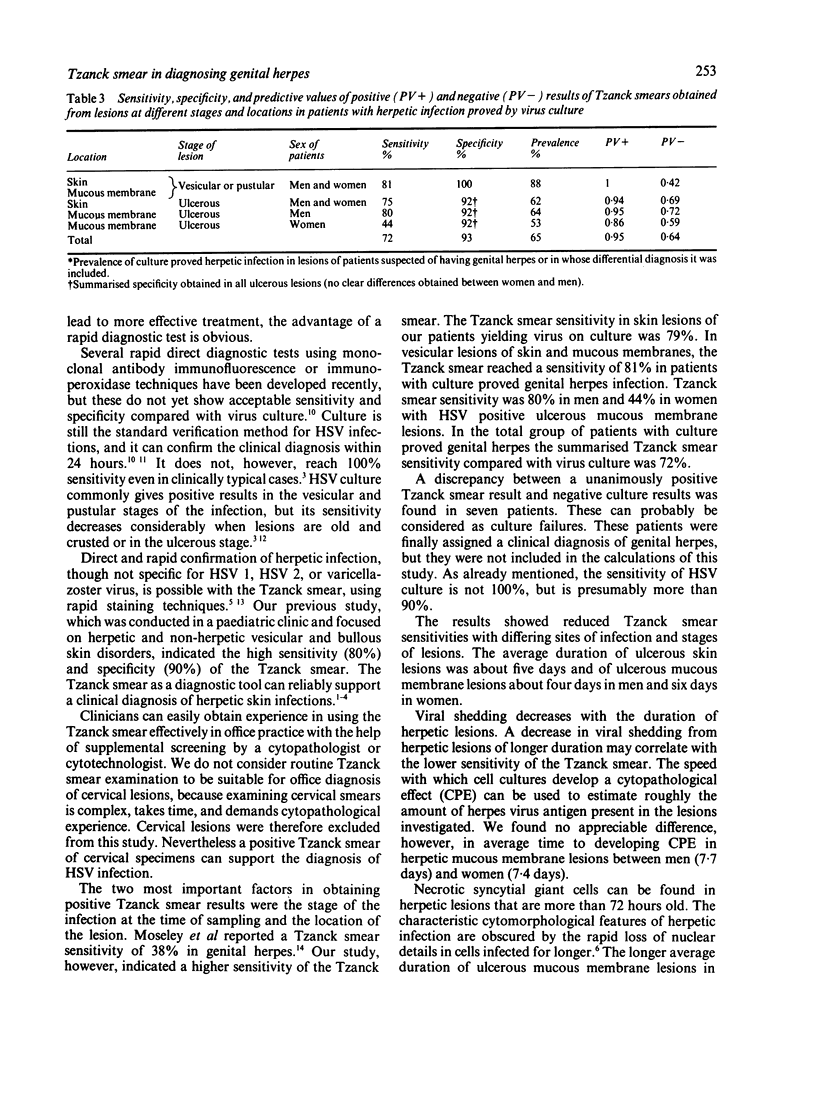
In 126 patients with anogenital lesions, in which herpes simplex virus (HSV) infection was suspected or included in the differential diagnosis, the results of cytodiagnosis of herpetic infection (Tzanck smear) were compared with virus culture. Cervical lesions were excluded from this study. HSV infection was proved by culture in 78 patients and was absent or non-active in 41 patients. Excluded from this study were seven patients who did not yield the virus on culture but had positive Tzanck smear results from three investigators. The characteristic cytopathic effect of herpetic infection was found in 78 patients who yielded HSV on culture. Tzanck smear sensitivity for skin lesions was 79% and for mucous membrane lesions was 81% in men and 52% in women. Tzanck smear specificity for the 41 patients without herpetic infection proved by virus culture was 93%. Differences in sensitivity and specificity between the results found by three investigators (double blind screening) were not significant. The Tzanck smear is reliable, inexpensive, and easy and quick to perform; it is suitable for office diagnosis because it does not require a specialised laboratory.
Full text
PDF



Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Folkers E., Oranje A. P. Een snelle diagnostische test (Tzanck-test) ter uitsluiting van herpesvirusinfecties bij blaasjes, blaren en pustels. Ned Tijdschr Geneeskd. 1985 Feb 9;129(6):241–243. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gleaves C. A., Wilson D. J., Wold A. D., Smith T. F. Detection and serotyping of herpes simplex virus in MRC-5 cells by use of centrifugation and monoclonal antibodies 16 h postinoculation. J Clin Microbiol. 1985 Jan;21(1):29–32. doi: 10.1128/jcm.21.1.29-32.1985. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Moseley R. C., Corey L., Benjamin D., Winter C., Remington M. L. Comparison of viral isolation, direct immunofluorescence, and indirect immunoperoxidase techniques for detection of genital herpes simplex virus infection. J Clin Microbiol. 1981 May;13(5):913–918. doi: 10.1128/jcm.13.5.913-918.1981. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- O'Keefe E. J., Burke W. A., Steinbaugh J. R. Diff-Quik stain for Tzanck smears. J Am Acad Dermatol. 1985 Jul;13(1):148–149. doi: 10.1016/s0190-9622(85)80326-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Oranje A. P., Folkers E., Choufoer-Habova J., Duivenvoorden J. N. Diagnostic value of Tzanck smear in herpetic and non-herpetic vesicular and bullous skin disorders in pediatric practice. Acta Derm Venereol. 1986;66(2):127–133. doi: 10.2340/0001555566127133. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Salmon V. C., Turner R. B., Speranza M. J., Overall J. C., Jr Rapid detection of herpes simplex virus in clinical specimens by centrifugation and immunoperoxidase staining. J Clin Microbiol. 1986 Apr;23(4):683–686. doi: 10.1128/jcm.23.4.683-686.1986. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Solomon A. R., Rasmussen J. E., Varani J., Pierson C. L. The Tzanck smear in the diagnosis of cutaneous herpes simplex. JAMA. 1984 Feb 3;251(5):633–635. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Solomon A. R., Rasmussen J. E., Weiss J. S. A comparison of the Tzanck smear and viral isolation in varicella and herpes zoster. Arch Dermatol. 1986 Mar;122(3):282–285. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Solomon A. R. The Tzanck smear. Viable and valuable in the diagnosis of herpes simplex, zoster, and varicella. Int J Dermatol. 1986 Apr;25(3):169–170. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-4362.1986.tb02209.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Veien N. K., Vestergaard B. F. Rapid diagnostic tests for cutaneous eruptions of herpes simplex. Acta Derm Venereol. 1978;58(1):83–85. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]