Abstract
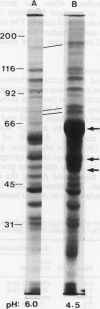
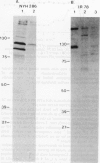
Trichomonas vaginalis isolates NYH 286 and IR 78 were grown in continuous flow culture conditions in a complex trypticase-yeast extract-maltose medium supplemented with heat-inactivated horse serum. Parasites could be stably maintained in the chemostat at high densities ranging from 1 x 10(6) to 1 x 10(7) organisms ml-1. Growth densities, acid production, and profiles of total versus secreted trichomonad proteins were characterised at different rates of growth and pH. Growth rate influenced the extent of parasite production of acid and the shedding of proteins into the medium but had no effect on overall parasite density. Lowering the pH from 6.0 to 5.0 resulted both in a decrease of cell density and acid production. At pH 4.5 isolate IR 78 but not NYH 286 was capable of growth and multiplication, showing the ability of some isolates to survive at the vaginal pH of healthy individuals. At this lower pH, however, isolate NYH 286 but not IR 78 synthesised new proteins which were detectable in stained gels. Also, inoculation of the chemostat with isolate NYH 286 comprising a mixture of fluorescent (positive, pos) and non-fluorescent (negative, neg) trichomonads as defined by monoclonal antibody reactivity to a surface immunogen resulted in a change in the parasite population to an almost homogeneous neg phenotype. These neg phenotype organisms switched back to pos phenotype after transfer to test tubes.
Full text
PDF




Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Alderete J. F. Antigen analysis of several pathogenic strains of Trichomonas vaginalis. Infect Immun. 1983 Mar;39(3):1041–1047. doi: 10.1128/iai.39.3.1041-1047.1983. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Alderete J. F., Demes P., Gombosová A., Valent M., Yánoska A., Fabusová H., Kasmala L., Garza G. E., Metcalfe E. C. Phenotypes and protein-epitope phenotypic variation among fresh isolates of Trichomonas vaginalis. Infect Immun. 1987 May;55(5):1037–1041. doi: 10.1128/iai.55.5.1037-1041.1987. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Alderete J. F., Garza G. E. Soluble Trichomonas vaginalis antigens in cell-free culture supernatants. Mol Biochem Parasitol. 1984 Oct;13(2):147–158. doi: 10.1016/0166-6851(84)90109-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Alderete J. F., Garza G. E. Specific nature of Trichomonas vaginalis parasitism of host cell surfaces. Infect Immun. 1985 Dec;50(3):701–708. doi: 10.1128/iai.50.3.701-708.1985. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Alderete J. F. Identification of immunogenic and antibody-binding membrane proteins of pathogenic Trichomonas vaginalis. Infect Immun. 1983 Apr;40(1):284–291. doi: 10.1128/iai.40.1.284-291.1983. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Alderete J. F., Kasmala L., Metcalfe E., Garza G. E. Phenotypic variation and diversity among Trichomonas vaginalis isolates and correlation of phenotype with trichomonal virulence determinants. Infect Immun. 1986 Aug;53(2):285–293. doi: 10.1128/iai.53.2.285-293.1986. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Alderete J. F., Pearlman E. Pathogenic Trichomonas vaginalis cytotoxicity to cell culture monolayers. Br J Vener Dis. 1984 Apr;60(2):99–105. doi: 10.1136/sti.60.2.99. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Alderete J. F., Suprun-Brown L., Kasmala L. Monoclonal antibody to a major surface glycoprotein immunogen differentiates isolates and subpopulations of Trichomonas vaginalis. Infect Immun. 1986 Apr;52(1):70–75. doi: 10.1128/iai.52.1.70-75.1986. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Alderete J. F. Trichomonas vaginalis NYH286 phenotypic variation may be coordinated for a repertoire of trichomonad surface immunogens. Infect Immun. 1987 Sep;55(9):1957–1962. doi: 10.1128/iai.55.9.1957-1962.1987. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cove J. H., Holland K. T., Cunliffe W. J. Effects of oxygen concentration on biomass production, maximum specific growth rate and extracellular enzyme production by three species of cutaneous propionibacteria grown in continuous culture. J Gen Microbiol. 1983 Nov;129(11):3327–3334. doi: 10.1099/00221287-129-11-3327. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- DIAMOND L. S. The establishment of various trichomonads of animals and man in axenic cultures. J Parasitol. 1957 Aug;43(4):488–490. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Demes P., Gombosová A., Valent M., Jánoska A., Fabusová H., Petrenko M. Differential susceptibility of fresh Trichomonas vaginalis isolates to complement in menstrual blood and cervical mucus. Genitourin Med. 1988 Jun;64(3):176–179. doi: 10.1136/sti.64.3.176. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Epps H. M., Gale E. F. The influence of the presence of glucose during growth on the enzymic activities of Escherichia coli: comparison of the effect with that produced by fermentation acids. Biochem J. 1942 Sep;36(7-9):619–623. doi: 10.1042/bj0360619. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gillin F. D., Sher A. Activation of the alternative complement pathway by Trichomonas vaginalis. Infect Immun. 1981 Oct;34(1):268–273. doi: 10.1128/iai.34.1.268-273.1981. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gorrell T. E. Effect of culture medium iron content on the biochemical composition and metabolism of Trichomonas vaginalis. J Bacteriol. 1985 Mar;161(3):1228–1230. doi: 10.1128/jb.161.3.1228-1230.1985. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hernandez E., Johnson M. J. Anaerobic growth yields of Aerobacter cloacae and Escherichia coli. J Bacteriol. 1967 Oct;94(4):991–995. doi: 10.1128/jb.94.4.991-995.1967. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jacques N. J., Morrey-Jones J. G., Walker G. J. Inducible and constitutive formation of fructanase in batch and continuous cultures of Streptococcus mutans. J Gen Microbiol. 1985 Jul;131(7):1625–1633. doi: 10.1099/00221287-131-7-1625. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Keevil C. W., Major N. C., Davies D. B., Robinson A. Physiology and virulence determinants of Neisseria gonorrhoeae grown in glucose-, oxygen- or cystine-limited continuous culture. J Gen Microbiol. 1986 Dec;132(12):3289–3302. doi: 10.1099/00221287-132-12-3289. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Krieger J. N., Poisson M. A., Rein M. F. Beta-hemolytic activity of Trichomonas vaginalis correlates with virulence. Infect Immun. 1983 Sep;41(3):1291–1295. doi: 10.1128/iai.41.3.1291-1295.1983. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Krieger J. N., Ravdin J. I., Rein M. F. Contact-dependent cytopathogenic mechanisms of Trichomonas vaginalis. Infect Immun. 1985 Dec;50(3):778–786. doi: 10.1128/iai.50.3.778-786.1985. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kulda J., Honigberg B. M. Behavior and pathogenicity of Tritrichomonas foetus in chick liver cell cultures. J Protozool. 1969 Aug;16(3):479–495. doi: 10.1111/j.1550-7408.1969.tb02304.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lockwood B. C., North M. J., Scott K. I., Bremner A. F., Coombs G. H. The use of a highly sensitive electrophoretic method to compare the proteinases of trichomonads. Mol Biochem Parasitol. 1987 May;24(1):89–95. doi: 10.1016/0166-6851(87)90119-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Müller M. Energy metabolism of protozoa without mitochondria. Annu Rev Microbiol. 1988;42:465–488. doi: 10.1146/annurev.mi.42.100188.002341. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Peterson K. M., Alderete J. F. Host plasma proteins on the surface of pathogenic Trichomonas vaginalis. Infect Immun. 1982 Aug;37(2):755–762. doi: 10.1128/iai.37.2.755-762.1982. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Peterson K. M., Alderete J. F. Iron uptake and increased intracellular enzyme activity follow host lactoferrin binding by Trichomonas vaginalis receptors. J Exp Med. 1984 Aug 1;160(2):398–410. doi: 10.1084/jem.160.2.398. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Peterson K. M., Alderete J. F. Trichomonas vaginalis is dependent on uptake and degradation of human low density lipoproteins. J Exp Med. 1984 Nov 1;160(5):1261–1272. doi: 10.1084/jem.160.5.1261. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rein M. F., Sullivan J. A., Mandell G. L. Trichomonacidal activity of human polymorphonuclear neutrophils: killing by disruption and fragmentation. J Infect Dis. 1980 Oct;142(4):575–585. doi: 10.1093/infdis/142.4.575. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Roth M., Noack D. Genetic stability of differentiated functions in Streptomyces hygroscopicus in relation to conditions of continuous culture. J Gen Microbiol. 1982 Jan;128(1):107–114. doi: 10.1099/00221287-128-1-107. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sugarman B., Mummaw N. The effect of hormones on Trichomonas vaginalis. J Gen Microbiol. 1988 Jun;134(6):1623–1628. doi: 10.1099/00221287-134-6-1623. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yarlett N. Polyamine biosynthesis and inhibition in Trichomonas vaginalis. Parasitol Today. 1988 Dec;4(12):357–360. doi: 10.1016/0169-4758(88)90007-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yarlett N., Yarlett N. C., Lloyd D. Metronidazole-resistant clinical isolates of Trichomonas vaginalis have lowered oxygen affinities. Mol Biochem Parasitol. 1986 May;19(2):111–116. doi: 10.1016/0166-6851(86)90115-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]