Abstract
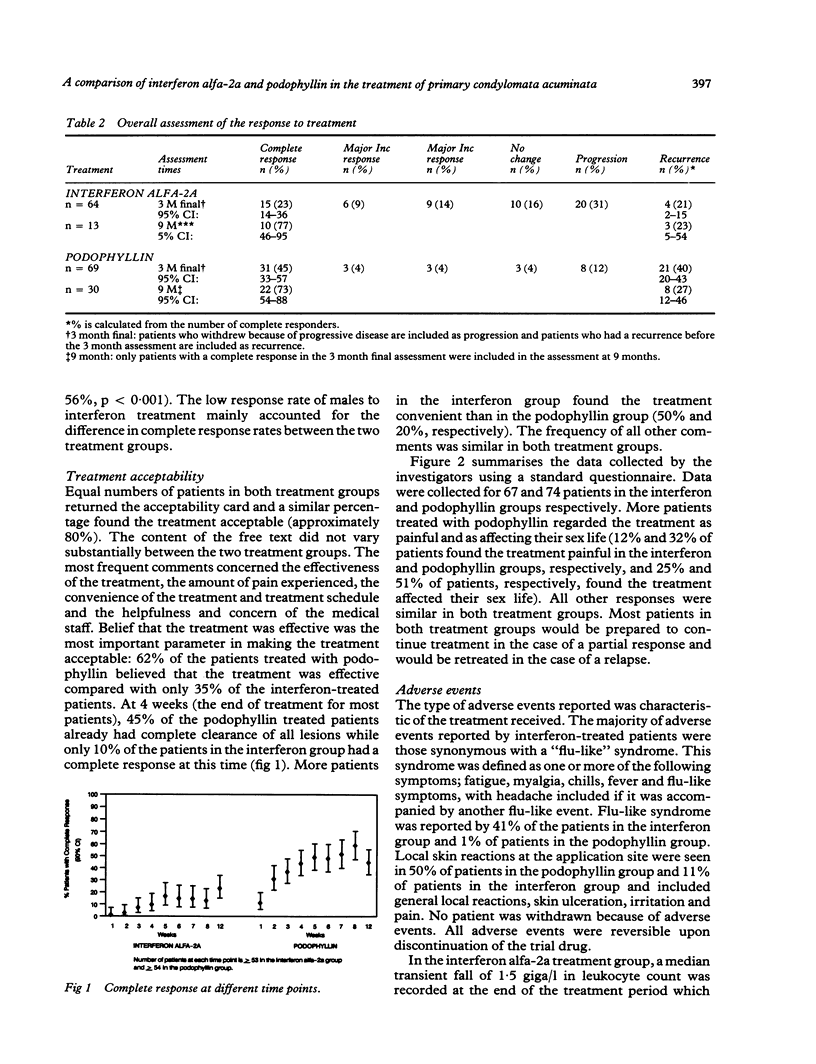
OBJECTIVES--to compare the response to treatment and recurrence rate of condylomata accuminata using subcutaneous injection of interferon alfa 2a 1.5 million units three times weekly for four weeks, or podophyllin resin 25% applied to lesions twice weekly for up to six weeks. DESIGN--Randomised open study. SETTING--Multicentre European study in genitourinary medicine, dermatovenereology, and gynaecology departments. PATIENTS--87 males and 67 females with condylomata acuminata for less than six months and no history of previous treatment. MAIN OUTCOME MEASURES--Complete clearance of lesions and evidence of recurrence at three months and nine months after treatment commenced. RESULTS--A complete response was achieved at three months in 15 of 64 (23%) in the interferon treated group, and 31 of 69 (45%) in the podophyllin treated group (p = 0.003). At nine months 10 of 13 patients in the interferon group and 22 of 30 patients in the podophyllin group remained completely clear of lesions.
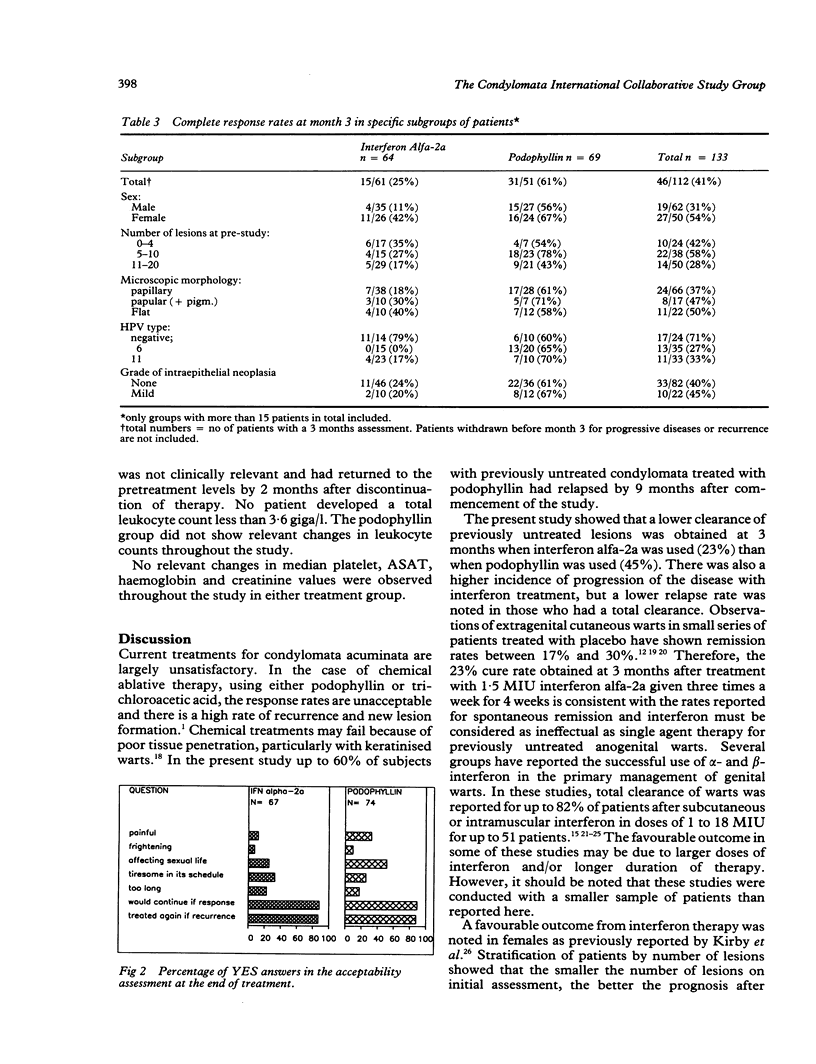
Full text
PDF



Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Dinsmore W. W. The therapy of genital warts. J Clin Hosp Pharm. 1986 Dec;11(6):381–388. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-2710.1986.tb00867.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Eron L. J., Judson F., Tucker S., Prawer S., Mills J., Murphy K., Hickey M., Rogers M., Flannigan S., Hien N. Interferon therapy for condylomata acuminata. N Engl J Med. 1986 Oct 23;315(17):1059–1064. doi: 10.1056/NEJM198610233151704. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Friedman-Kien A. E., Eron L. J., Conant M., Growdon W., Badiak H., Bradstreet P. W., Fedorczyk D., Trout J. R., Plasse T. F. Natural interferon alfa for treatment of condylomata acuminata. JAMA. 1988 Jan 22;259(4):533–538. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gabriel G., Thin R. N. Treatment of anogenital warts. Comparison of trichloracetic acid and podophyllin versus podophyllin alone. Br J Vener Dis. 1983 Apr;59(2):124–126. doi: 10.1136/sti.59.2.124. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gall S. A., Hughes C. E., Mounts P., Segriti A., Weck P. K., Whisnant J. K. Efficacy of human lymphoblastoid interferon in the therapy of resistant condyloma acuminata. Obstet Gynecol. 1986 May;67(5):643–651. doi: 10.1097/00006250-198605000-00008. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gall S. A., Hughes C. E., Trofatter K. Interferon for the therapy of condyloma acuminatum. Am J Obstet Gynecol. 1985 Sep 15;153(2):157–163. doi: 10.1016/0002-9378(85)90103-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Geffen J. R., Klein R. J., Friedman-Kien A. E. Intralesional administration of large doses of human leukocyte interferon for the treatment of condylomata acuminata. J Infect Dis. 1984 Oct;150(4):612–615. doi: 10.1093/infdis/150.4.612. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gross G., Ikenberg H., Roussaki A., Drees N., Schöpf E. Systemic treatment of condylomata acuminata with recombinant interferon-alpha-2a: low-dose superior to the high-dose regimen. Chemotherapy. 1986;32(6):537–541. doi: 10.1159/000238464. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gross G., Roussaki A., Schöpf E., De Villiers E. M., Papendick U. Successful treatment of condylomata acuminata and bowenoid papulosis with subcutaneous injections of low-dose recombinant interferon-alpha. Arch Dermatol. 1986 Jul;122(7):749–750. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kimchi A. Increased levels of interferon-induced (2'--5') oligo-isoadenylate synthetase in mature T-lymphocytes and in differentiated Friend-erythroleukemic cells. J Interferon Res. 1981;1(4):559–569. doi: 10.1089/jir.1981.1.559. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kirby P. K., Kiviat N., Beckman A., Wells D., Sherwin S., Corey L. Tolerance and efficacy of recombinant human interferon gamma in the treatment of refractory genital warts. Am J Med. 1988 Aug;85(2):183–188. doi: 10.1016/s0002-9343(88)80339-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Reichman R. C., Oakes D., Bonnez W., Greisberger C., Tyring S., Miller L., Whitley R., Carveth H., Weidner M., Krueger G. Treatment of condyloma acuminatum with three different interferons administered intralesionally. A double-blind, placebo-controlled trial. Ann Intern Med. 1988 May;108(5):675–679. doi: 10.7326/0003-4819-108-5-675. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rubinstein M., Orchansky P. The interferon receptors. CRC Crit Rev Biochem. 1986;21(3):249–275. doi: 10.3109/10409238609113613. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schneider A., Papendick U., Gissmann L., De Villiers E. M. Interferon treatment of human genital papillomavirus infection: importance of viral type. Int J Cancer. 1987 Nov 15;40(5):610–614. doi: 10.1002/ijc.2910400506. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schonfeld A., Nitke S., Schattner A., Wallach D., Crespi M., Hahn T., Levavi H., Yarden O., Shoham J., Doerner T. Intramuscular human interferon-beta injections in treatment of condylomata acuminata. Lancet. 1984 May 12;1(8385):1038–1042. doi: 10.1016/s0140-6736(84)91450-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Scott G. M., Csonka G. W. Effect of injections of small doses of human fibroblast interferon into genital warts. A pilot study. Br J Vener Dis. 1979 Dec;55(6):442–445. doi: 10.1136/sti.55.6.442. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Syrjänen S., Syrjänen K. An improved in situ DNA hybridization protocol for detection of human papillomavirus (HPV) DNA sequences in paraffin-embedded biopsies. J Virol Methods. 1986 Nov;14(3-4):293–304. doi: 10.1016/0166-0934(86)90031-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- WARD J. W., CLIFFORD W. S., MONACO A. R., BICKERSTAFF H. J. Fatal systemic poisoning following podophyllin treatment of condyloma acuminatum. South Med J. 1954 Dec;47(12):1204–1206. doi: 10.1097/00007611-195412000-00021. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


