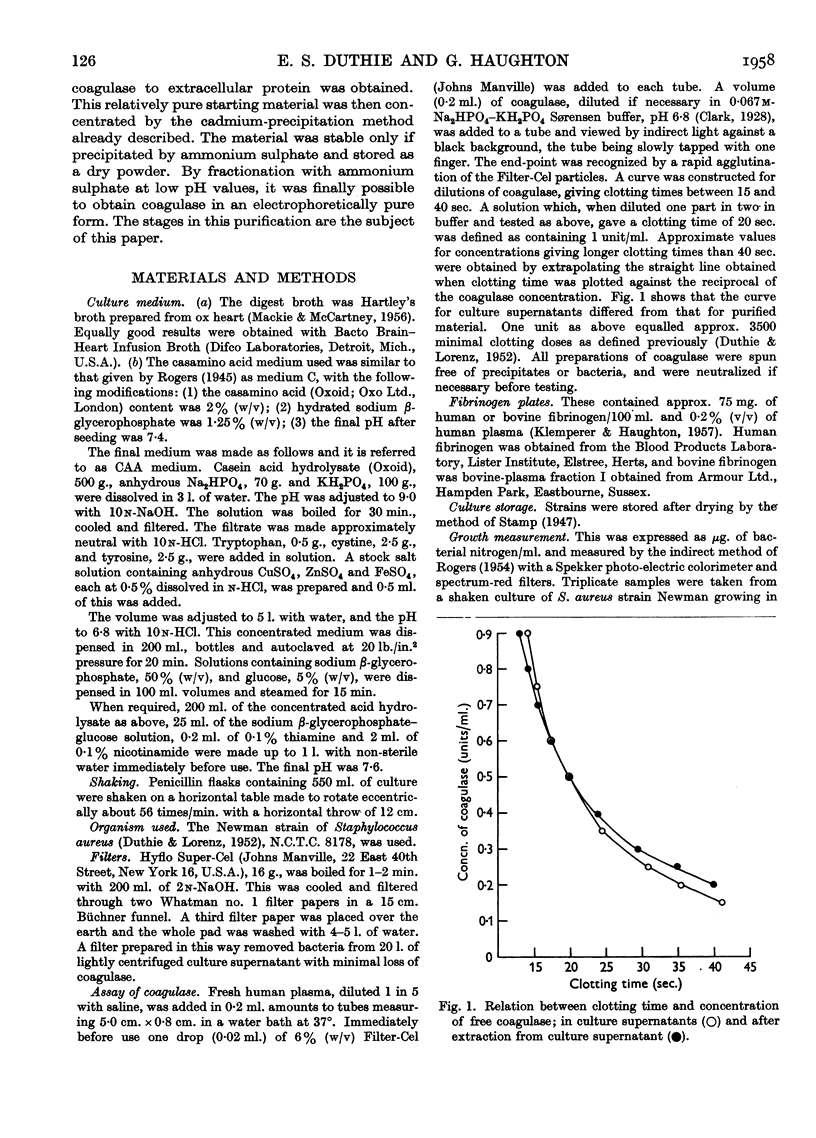
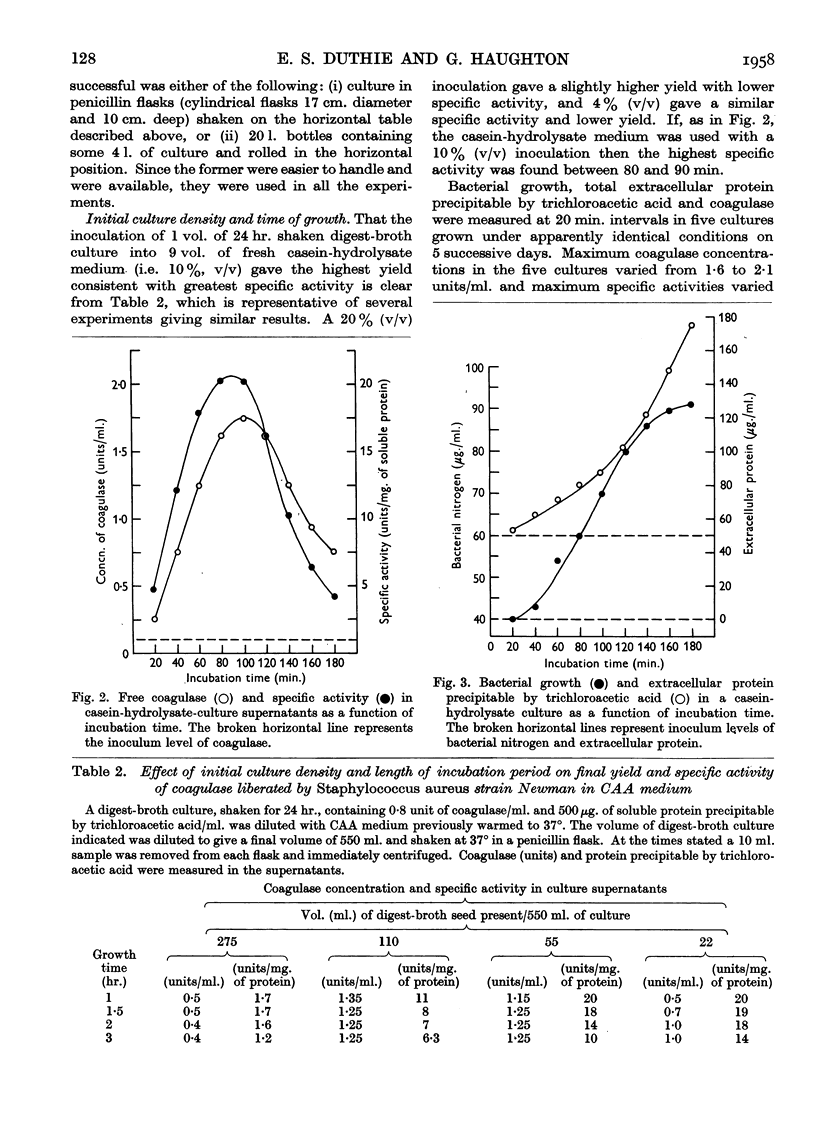
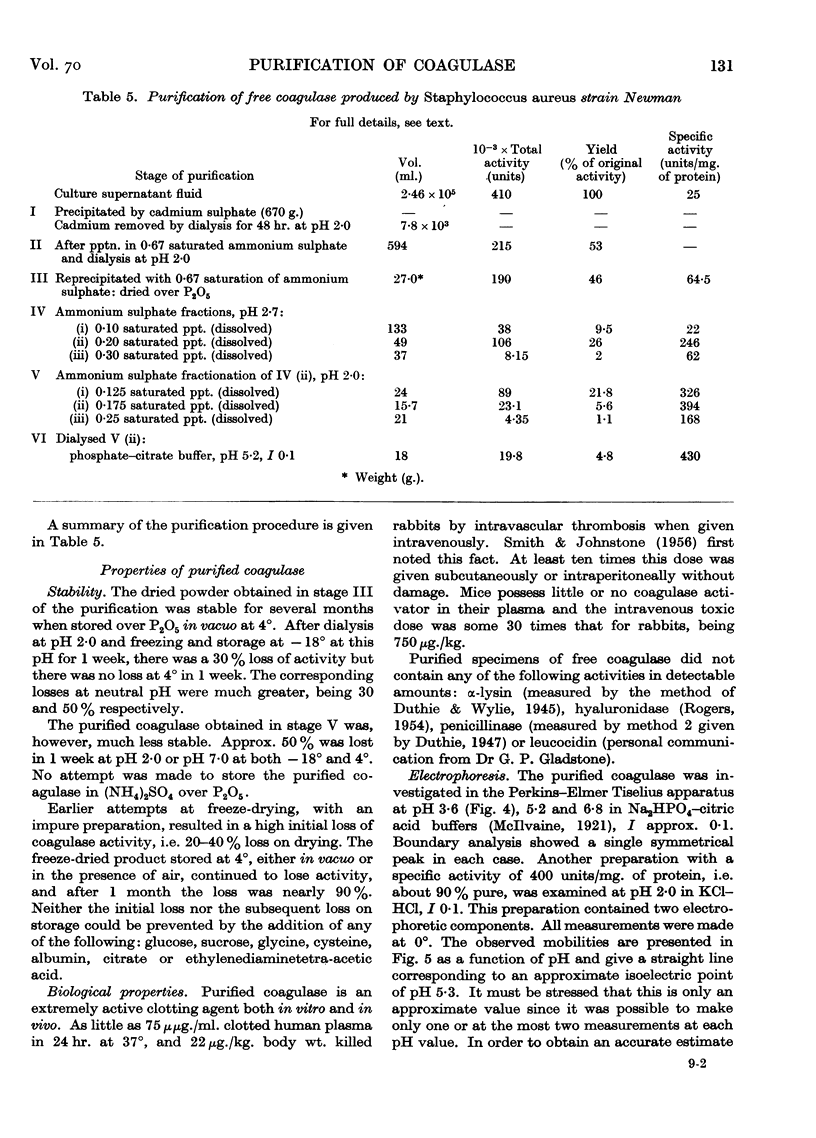
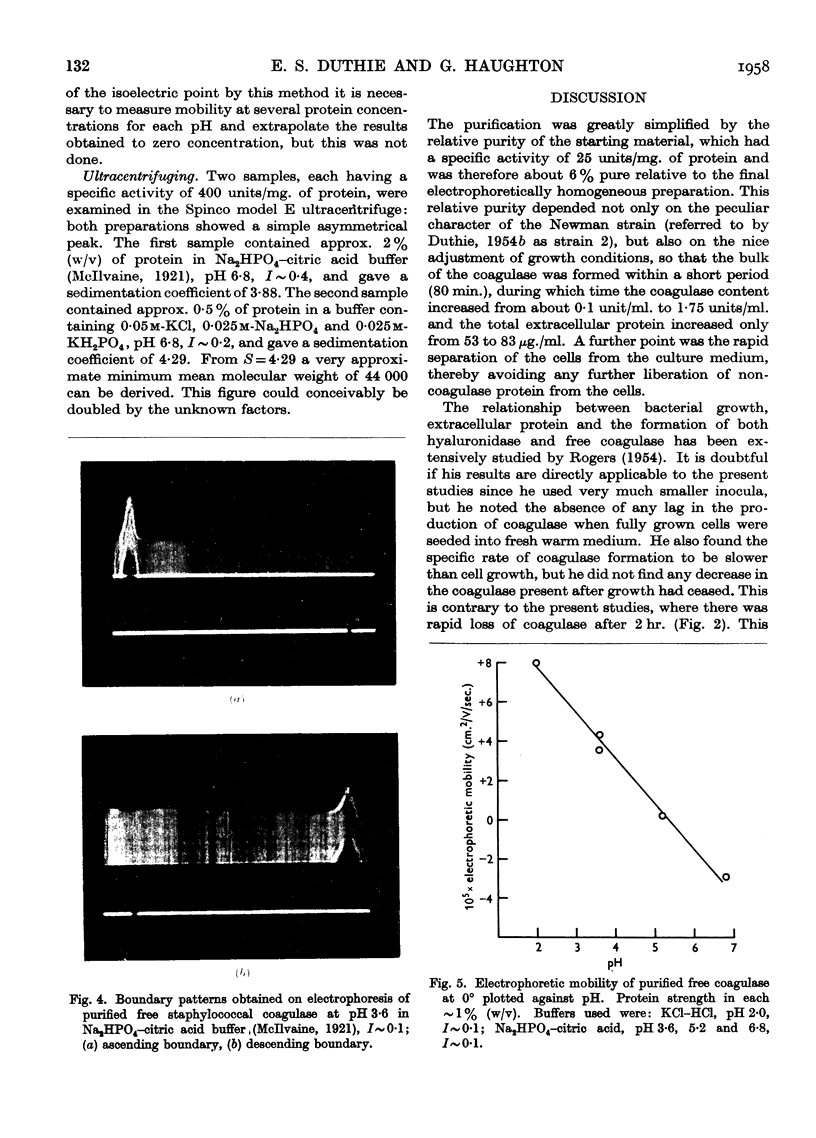
Full text
PDF





Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- CHAIN F. B., PALADINO S., CALLOW D. S., UGOLINI F., VAN DER SLUIS J. Studies on aeration. I. Bull World Health Organ. 1952;6(1-2):73–97. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Casman E. P. The Production of Staphylococcal Alpha-Hemolysin: The Rôle of Agar. J Bacteriol. 1940 Nov;40(5):601–617. doi: 10.1128/jb.40.5.601-617.1940. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- DUTHIE E. S. Evidence for two forms of staphylococcal coagulase. J Gen Microbiol. 1954 Jun;10(3):427–436. doi: 10.1099/00221287-10-3-427. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- DUTHIE E. S., LORENZ L. L. Staphylococcal coagulase; mode of action and antigenicity. J Gen Microbiol. 1952 Feb;6(1-2):95–107. doi: 10.1099/00221287-6-1-2-95. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- DUTHIE E. S. The action of fibrinogen on certain pathogenic cocci. J Gen Microbiol. 1955 Oct;13(2):383–393. doi: 10.1099/00221287-13-2-383. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- DUTHIE E. S. The production of free staphylococcal coagulase. J Gen Microbiol. 1954 Jun;10(3):437–444. doi: 10.1099/00221287-10-3-437. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- JOHNSTONE J. M., SMITH D. D. Coagulase activity in vivo. Nature. 1956 Nov 3;178(4540):982–983. doi: 10.1038/178982a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- KLEMPERER R., HAUGHTON G. A medium for the rapid recognition of penicillin-resistant coagulase-positive staphylococci. J Clin Pathol. 1957 Feb;10(1):96–99. doi: 10.1136/jcp.10.1.96. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- LOWRY O. H., ROSEBROUGH N. J., FARR A. L., RANDALL R. J. Protein measurement with the Folin phenol reagent. J Biol Chem. 1951 Nov;193(1):265–275. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- ROGERS H. J. The rate of formation of hyaluronidase, coagulase and total extracellular protein by strains of Staphylococcus aureus. J Gen Microbiol. 1954 Apr;10(2):209–220. doi: 10.1099/00221287-10-2-209. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- ROGERS H. J. Variant populations within a hyaluronidase-producing culture of Staphylococcus aureus. J Pathol Bacteriol. 1953 Oct;66(2):545–551. doi: 10.1002/path.1700660226. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rogers H. J. The conditions controlling the production of hyaluronidase by micro-organisms grown in simplified media. Biochem J. 1945;39(5):435–443. doi: 10.1042/bj0390435. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- TAGER M. Studies on the nature and the purification of the coagulase-reacting factor and its relation to prothrombin. J Exp Med. 1956 Nov 1;104(5):675–686. doi: 10.1084/jem.104.5.675. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]



