Full text
PDF


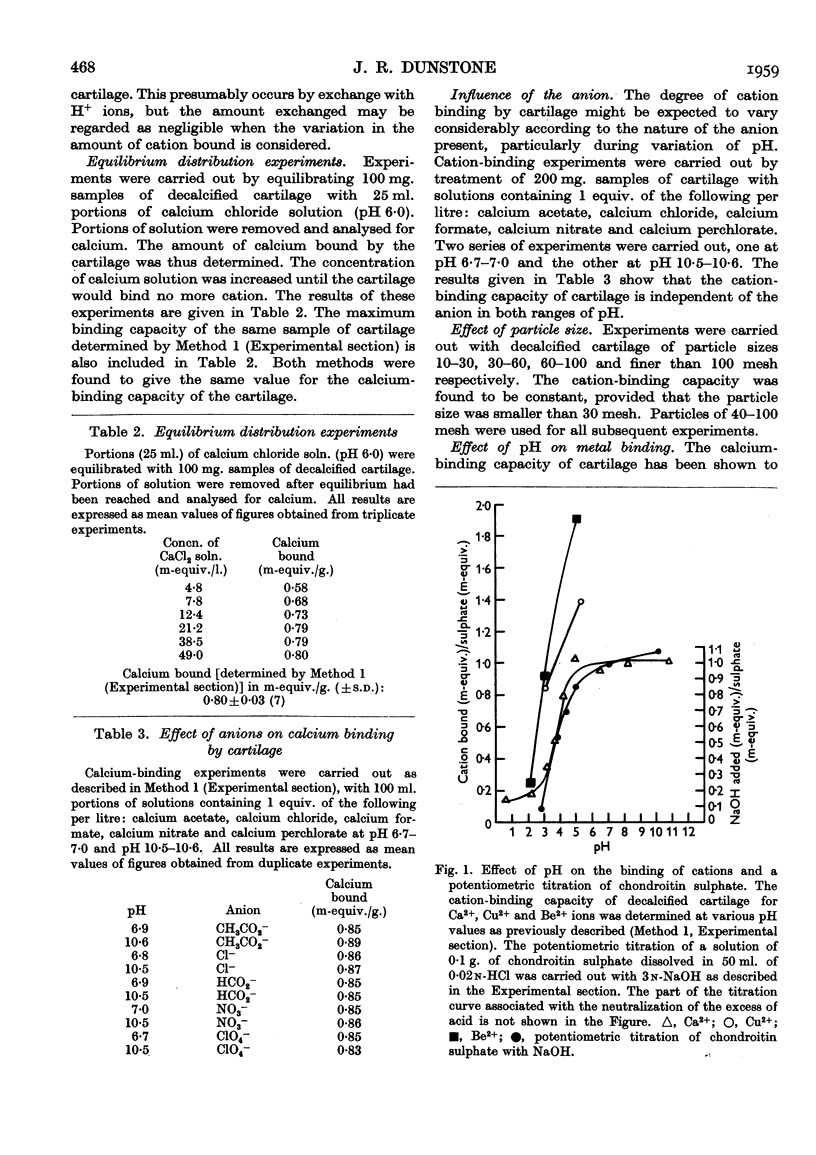
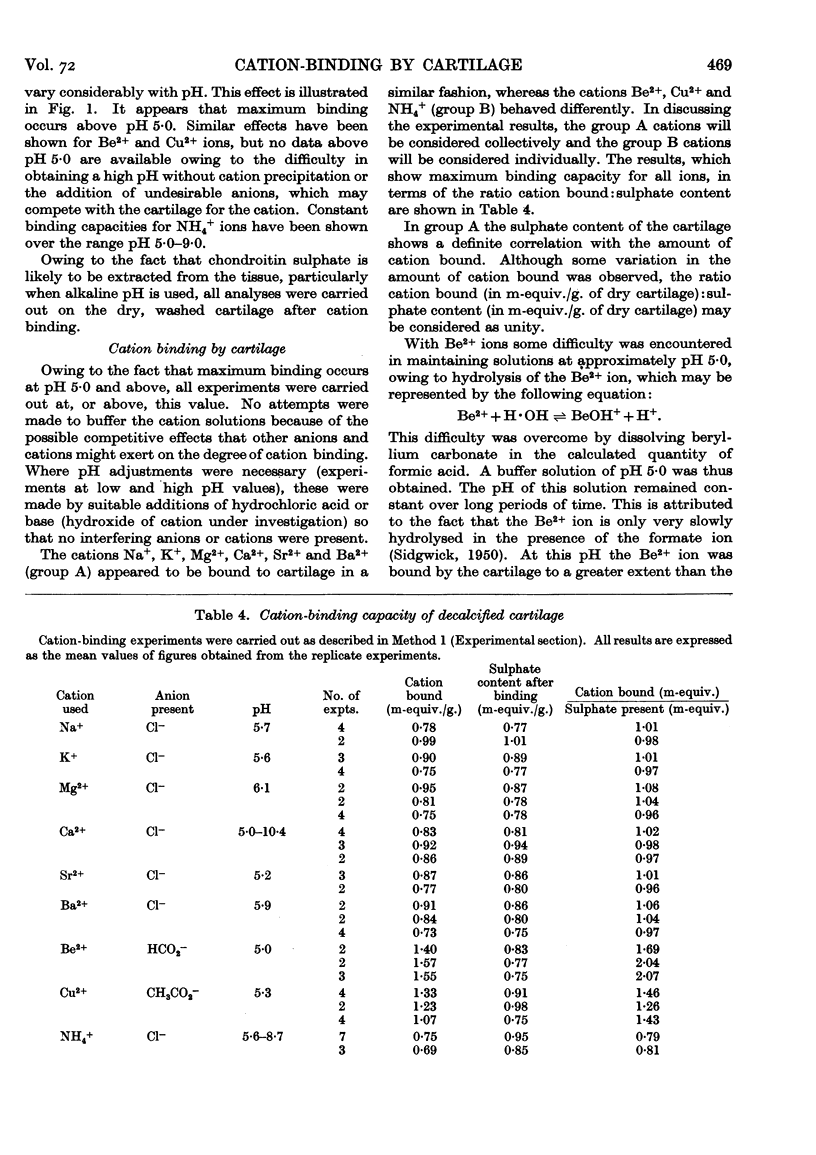
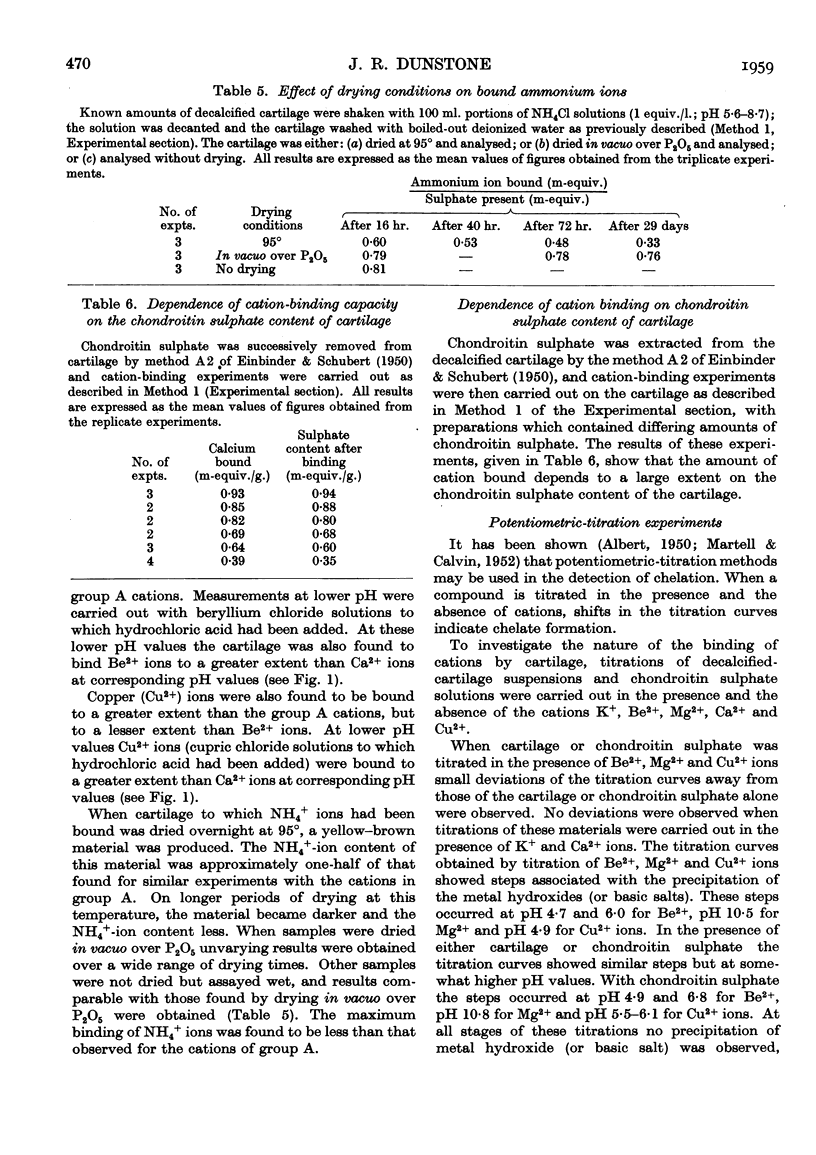
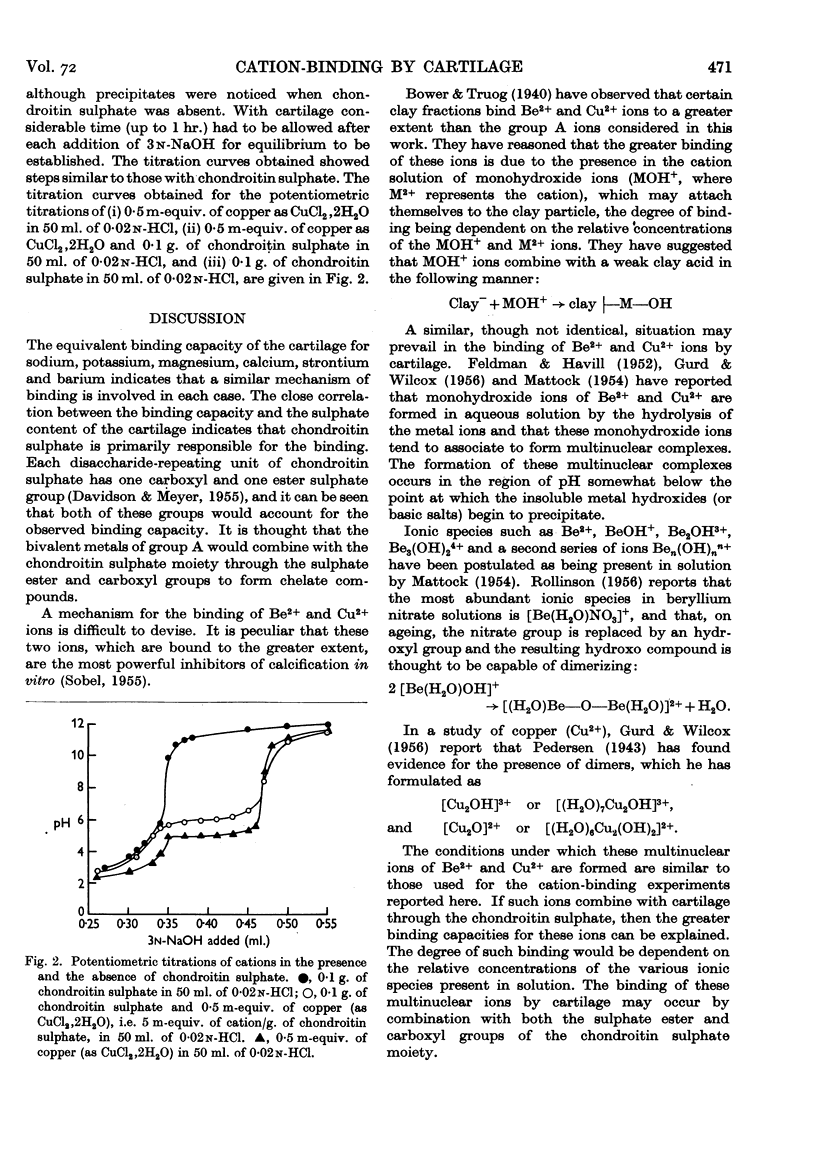


Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- ALBERT A. Quantitative studies of the avidity of naturally occurring substances for trace metals; amino-acids having only two ionizing groups. Biochem J. 1950 Nov-Dec;47(5):531–538. doi: 10.1042/bj0470531. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- BOYD E. S., NEUMAN W. F. The surface chemistry of bone. V. The ion-binding properties of cartilage. J Biol Chem. 1951 Nov;193(1):243–251. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- DUNSTONE J. R. The direct determination of calcium in biological material. Med J Aust. 1957 Oct 19;44(16):571–572. doi: 10.5694/j.1326-5377.1957.tb60083.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- EINBINDER J., SCHUBERT M. Separation of chondroitin sulfate from cartilage. J Biol Chem. 1950 Aug;185(2):725–730. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- FARBER S. J., SCHUBERT M., SCHUSTER N. The binding of cations by chondroitin sulfate. J Clin Invest. 1957 Dec;36(12):1715–1722. doi: 10.1172/JCI103573. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- GURD F. R., WILCOX P. E. Complex formation between metallic cations and proteins, peptides and amino acids. Adv Protein Chem. 1956;11:311–427. doi: 10.1016/s0065-3233(08)60424-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


