Abstract
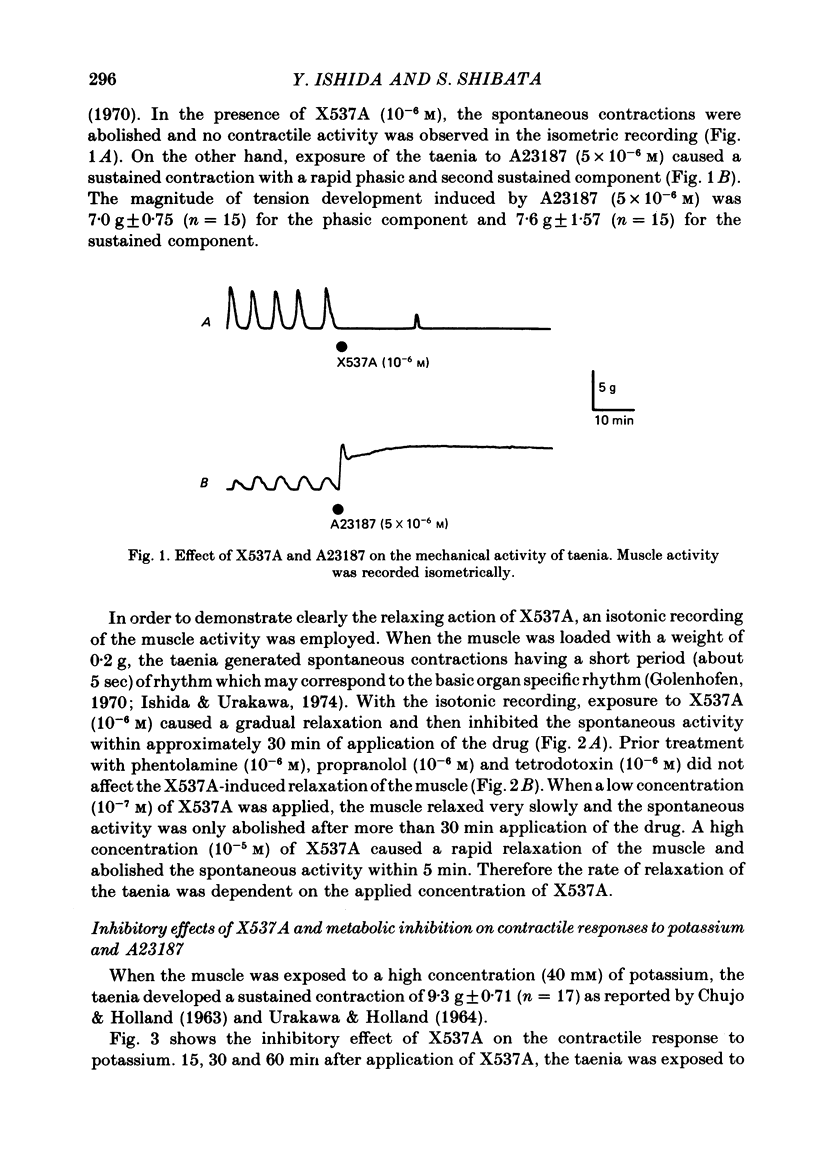
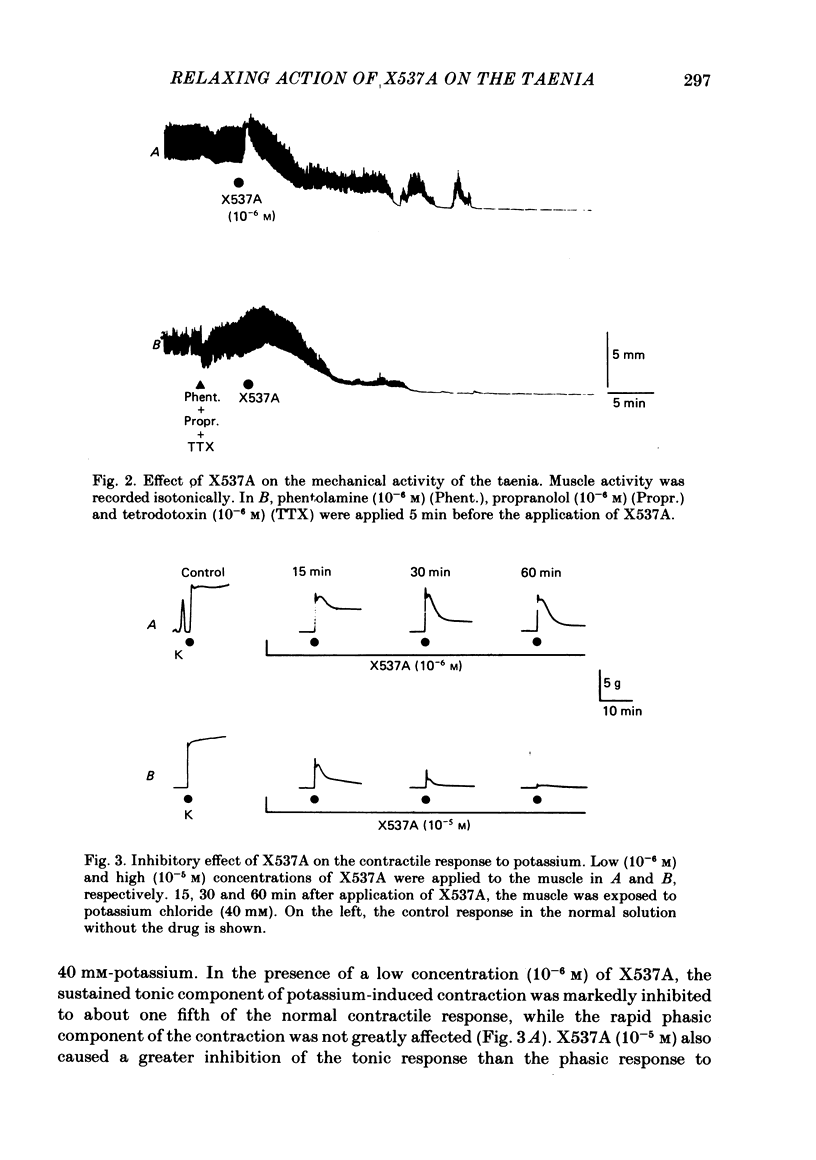
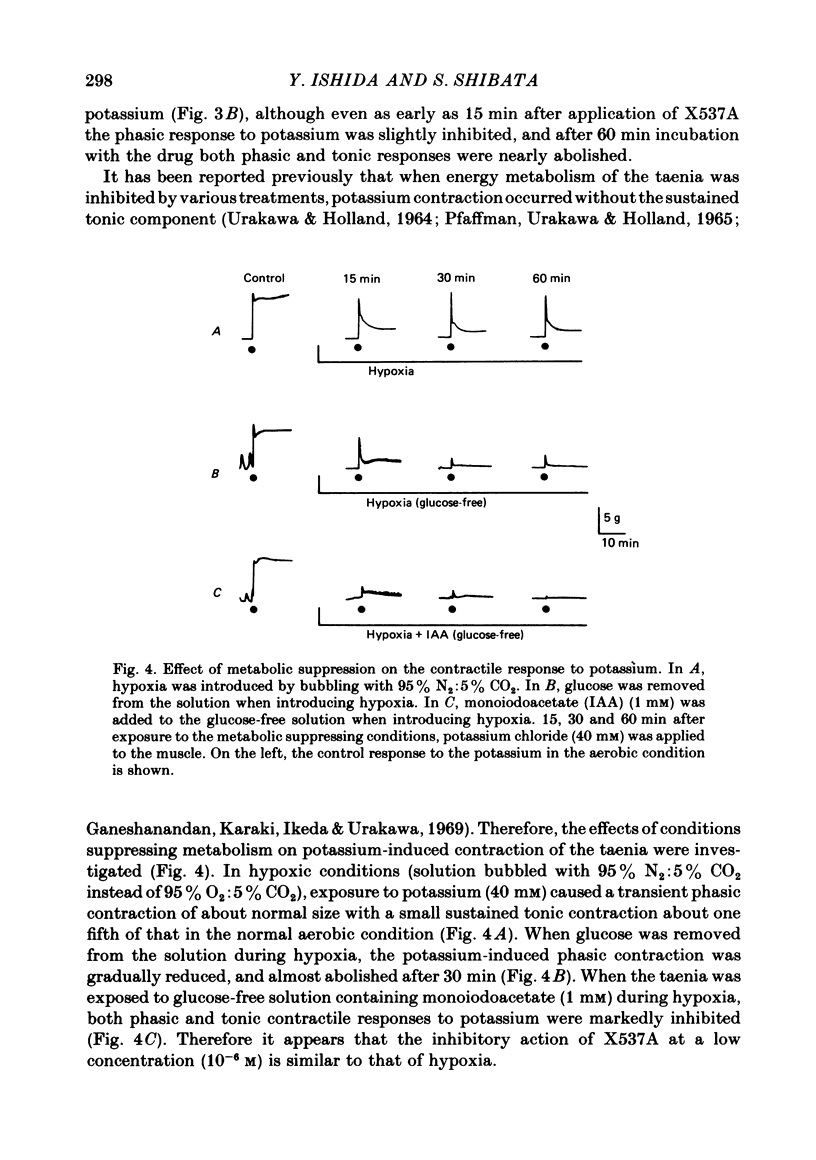
1. In the isolated guinea-pig taenia, application of X537A to the muscle caused a relaxation, while A23187 caused a sustained contraction. 2. Treatment with adrenergic blocking agents and tetrodotoxin had no effect on the relaxing response to X537A. 3. In the presence of a low concentration (10(-6) M) of X537A or under hypoxic conditions (bubbled with 95% N2: 5% CO2), the taenia lost the ability to respond to a high concentration (40 mM) of potassium with a sustained tonic contraction, although the rapid phasic contraction was still present. 4. When a low concentration of X537A was applied the shape of the contractile response to A23187 was changed from a sustained development of tension to an oscillatory tension which was also observed under hypoxia. 5. In tissues treated with glycerol for 3 weeks, neither X537A nor A23187 had any effect on the contractile response induced by elevation of calcium concentration (pCa = 4) in the presence of magnesium and ATP. 6. Exposure to a low concentration (10(-6) M) of X537A, or hypoxia, slightly yet significantly decreased the ATP content of the muscle. A high concentration (10(-5) M) of X537A markedly decreased the ATP content to about half normal. A23187 did not alter the ATP content. 7. Application of X537A did not alter the calcium content of the muscle and inhibited the A23187-induced increase in content. Under hypoxia, A23187 failed to increase the calcium content of the muscle. 8. The results indicate that, in contrast to A23187, X537A has a relaxing and metabolic inhibitory action on the guinea-pig taenia. The action of low concentrations of X537A resembled that of the hypoxia, indicating that X537A might exert its relaxing action, at least in part, by inhibition of aerobic energy metabolism of the muscle.
Full text
PDF


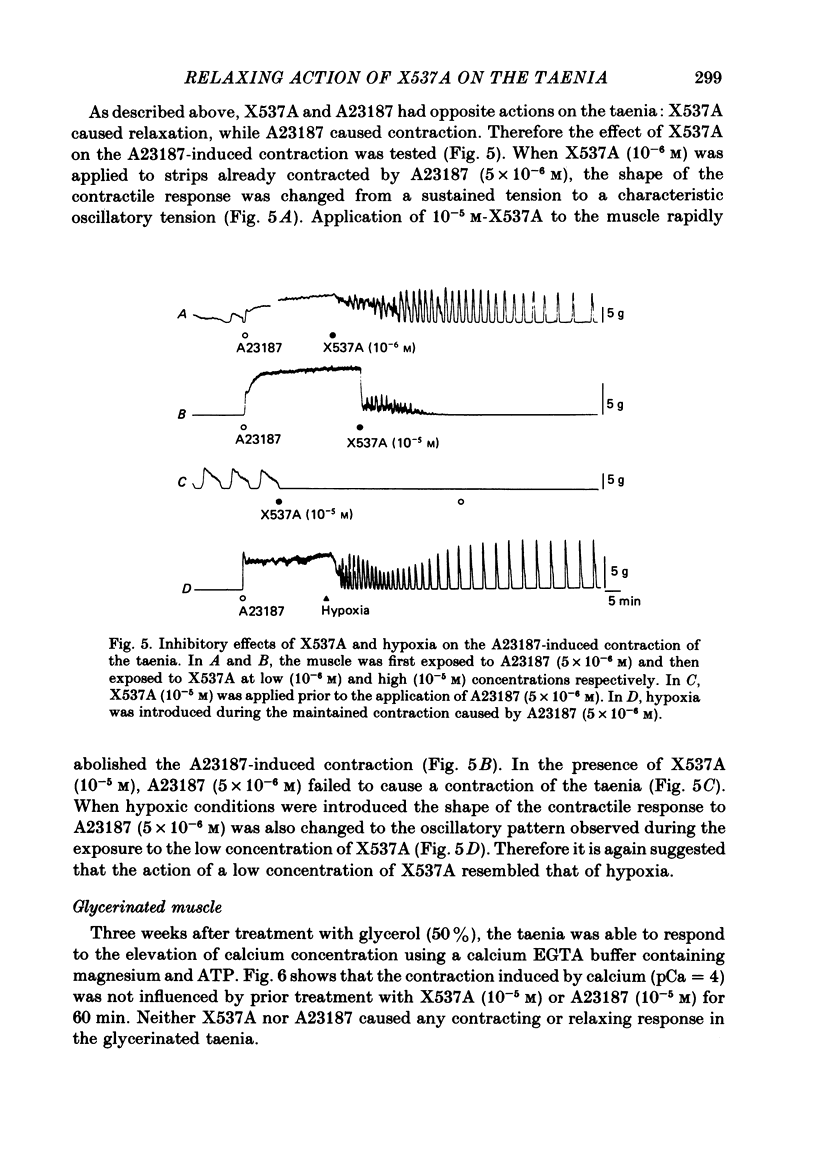





Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- AXELSSON J., BULBRING E. Metabolic factors affecting the electrical activity of intestinal smooth muscle. J Physiol. 1961 Apr;156:344–356. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1961.sp006680. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- BORN G. V., BULBRING E. The effect of 2:4-dinitrophenol (DNP) on the smooth muscle of the guinea-pig's taenia coli. J Physiol. 1955 Mar 28;127(3):626–635. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1955.sp005283. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- BULBRING E., LULLMANN H. The effect of metabolic inhibitors on the electrical and mechanical activity of the smooth muscle of the guinea-pig's taenia coli. J Physiol. 1957 Apr 30;136(2):310–323. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1957.sp005762. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Berner P. F., Disalvo J., Schwartz A. Differential inhibitory effects of the ionophore RO2-2985 (X537A) on contractile responses to potassium and histamine in coronary artery smooth muscle. J Pharmacol Exp Ther. 1980 Apr;213(1):59–63. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bukoski R. D., Seidel C. L., Allen J. C. Effect of ionophore RO 2-2985 on the contractile response of canine coronary, renal and femoral arteries. Blood Vessels. 1979;16(6):281–294. doi: 10.1159/000158218. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- CHUJYO N., HOLLAND W. C. Potassium-induced contracture and calcium exchange in the guinea pig's taenia coli. Am J Physiol. 1963 Jul;205:94–100. doi: 10.1152/ajplegacy.1963.205.1.94. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- CROSS R. J., TAGGART J. V. Studies on the cyclophorase system; the coupling of oxidation and phosphorylation. J Biol Chem. 1949 Feb;177(2):655–678. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Estrada S., Célis H., Calderón E., Gallo G., Montal M. Model translocators for divalent and monovalent ion transport in phospholipid membranes. II. The effects of ion translocator X-537A on the energy-conserving properties of mitochondrial membranes. J Membr Biol. 1974;18(3-4):201–218. doi: 10.1007/BF01870112. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ganeshanandan S. S., Karaki H., Ikeda M., Urakawa N. Mechanical response of guinea pig taenia coli in high-K-Na-deficient medium under anoxia. Jpn J Pharmacol. 1969 Jun;19(2):329–330. doi: 10.1254/jjp.19.329. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ishida Y., Shibata S. Characteristics contractile response to the calcium ionophore, A23187, in guinea-pig vas deferens. Br J Pharmacol. 1980;71(2):581–583. doi: 10.1111/j.1476-5381.1980.tb10976.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ishida Y., Urakawa N. Isometric and isotonic spontaneous contractions of guinea-pig taenia coli. Jpn J Pharmacol. 1974 Dec;24(6):925–927. doi: 10.1254/jjp.24.925. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ito S., Nakazato Y., Ohga A. The effect of the ionophores X-537A and A23187 on the noradrenaline output from peripheral adrenergic neurones in the presence of various divalent cations. Br J Pharmacol. 1978 Jan;62(1):91–98. doi: 10.1111/j.1476-5381.1978.tb07010.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- LOOMIS W. F., LIPMANN F. Reversible inhibition of the coupling between phosphorylation and oxidation. J Biol Chem. 1948 Apr;173(2):807–807. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Levy J. V., Cohen J. A., Inesi G. Contractile effects of a calcium ionophore. Nature. 1973 Apr 13;242(5398):461–463. doi: 10.1038/242461a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mandrek K., Golenhofen K. Activation of gastro-intestinal smooth muscle induced by the calcium ionophore A23187. Pflugers Arch. 1977 Oct 19;371(1-2):119–124. doi: 10.1007/BF00580779. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Murray J. J., Reed P. W., Fay F. S. Contraction of isolated smooth muscle cells by inophore A23187. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1975 Nov;72(11):4459–4463. doi: 10.1073/pnas.72.11.4459. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nasu T., Ishida Y. Interaction of Ca, Mg and ATP in glycerinated taenia coli of guinea pig. Jpn J Pharmacol. 1975 Oct;25(5):535–540. doi: 10.1254/jjp.25.535. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- PFAFFMAN M., URAKAWA N., HOLLAND W. C. ROLE OF METABOLISM IN K-INDUCED TENSION CHANGES IN GUINEA PIG TAENIA COLI. Am J Physiol. 1965 Jun;208:1203–1205. doi: 10.1152/ajplegacy.1965.208.6.1203. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pressman B. C. Biological applications of ionophores. Annu Rev Biochem. 1976;45:501–530. doi: 10.1146/annurev.bi.45.070176.002441. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pressman B. C. Properties of ionophores with broad range cation selectivity. Fed Proc. 1973 Jun;32(6):1698–1703. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Reed P. W., Lardy H. A. A23187: a divalent cation ionophore. J Biol Chem. 1972 Nov 10;247(21):6970–6977. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rosenberger L. B., Triggle D. J. The mechanism of action of ionophore A 23187 on guinea pig intestinal smooth muscle. Can J Physiol Pharmacol. 1979 Apr;57(4):348–358. doi: 10.1139/y79-053. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Saida K., Nonomura Y. Characteristics of Ca2+- and Mg2+-induced tension development in chemically skinned smooth muscle fibers. J Gen Physiol. 1978 Jul;72(1):1–14. doi: 10.1085/jgp.72.1.1. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Swamy V. C., Ticku M., Triggle C. R., Triggle D. J. The action of the ionophores, X-537A and A-23187, on smooth muscle. Can J Physiol Pharmacol. 1975 Dec;53(6):1108–1114. doi: 10.1139/y75-154. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Thoa N. B., Costa J. L., Moss J., Kopin I. J. Mechanism of release of norepinephrine from peripheral adrenergic neurones by the calcium ionophores X 537A and A 23187. Life Sci. 1974 May 1;14(9):1705–1719. doi: 10.1016/0024-3205(74)90272-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- URAKAWA N., HOLLAND W. C. CA45 UPTAKE AND TISSUE CALCIUM IN K-INDUCED PHASIC AND TONIC CONTRACTION IN TAENIA COLI. Am J Physiol. 1964 Oct;207:873–876. doi: 10.1152/ajplegacy.1964.207.4.873. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- WEST T. C., HADDEN G., FARAH A. Effect of anoxia on response of the isolated intestine to various drugs and enzyme inhibitors. Am J Physiol. 1951 Feb;164(2):565–572. doi: 10.1152/ajplegacy.1951.164.2.565. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Watson E. L. Effects of ionophores A23187 and X537A on vascular smooth muscle activity. Eur J Pharmacol. 1978 Nov 15;52(2):171–178. doi: 10.1016/0014-2999(78)90203-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


